Introduction into Financial Economics Lecturer: Letyukhin Ivan Dmitrievich,























finekonomika_lekciya_1_htl.ppt
- Размер: 947.0 Кб
- Автор:
- Количество слайдов: 28
Описание презентации Introduction into Financial Economics Lecturer: Letyukhin Ivan Dmitrievich, по слайдам
 Introduction into Financial Economics Lecturer: Letyukhin Ivan Dmitrievich, Senior lecturer of finance department
Introduction into Financial Economics Lecturer: Letyukhin Ivan Dmitrievich, Senior lecturer of finance department
 Plan of the course • Conception and content of financial economics • The basic foundation of budget system • The basic foundation of tax system • The banking system • The bond market • Conception and content of corporate finance
Plan of the course • Conception and content of financial economics • The basic foundation of budget system • The basic foundation of tax system • The banking system • The bond market • Conception and content of corporate finance
 Current marks M current= M test * 0, 3+ M hometask * 0, 3 +M seminar * 0,
Current marks M current= M test * 0, 3+ M hometask * 0, 3 +M seminar * 0,
 The test • an essay for one of the topics of the course • Example of topic: “Flat rate of personal income tax is better than progressive” • During the test you can use any material
The test • an essay for one of the topics of the course • Example of topic: “Flat rate of personal income tax is better than progressive” • During the test you can use any material
 Hometask • Business plan of the small entreprise • P r epa r e d in the small groups (2 -3 students)
Hometask • Business plan of the small entreprise • P r epa r e d in the small groups (2 -3 students)
 Final marks M final=M c u rrent * 0, 5+M exam * 0,
Final marks M final=M c u rrent * 0, 5+M exam * 0,
 If current mark is 8 or more:
If current mark is 8 or more:
 Main terms
Main terms
 Finance • the science that describes the management, creation and study of money, banking, credit, investments, assets and liabilities.
Finance • the science that describes the management, creation and study of money, banking, credit, investments, assets and liabilities.
 Financial economics • the branch of economics characterized by a «concentration on monetary activities», in which «money of one type or another is likely to appear on both sides of a trade».
Financial economics • the branch of economics characterized by a «concentration on monetary activities», in which «money of one type or another is likely to appear on both sides of a trade».
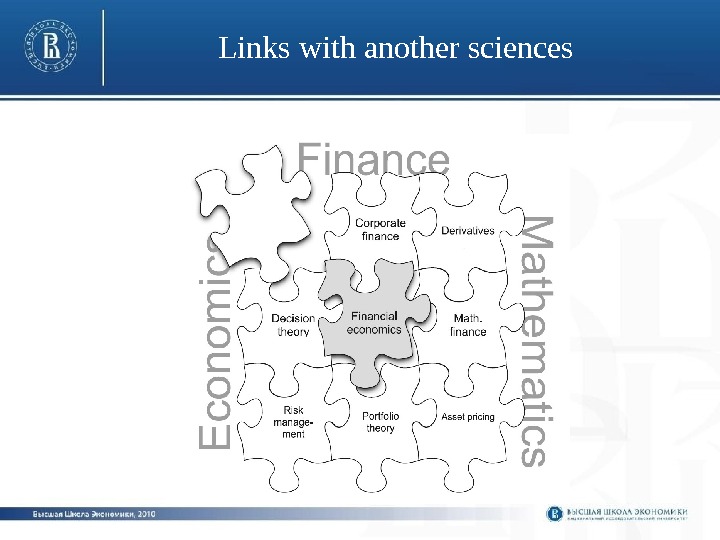
 L in k s with another sciences
L in k s with another sciences
 Financial Institution • an establishment that focuses on dealing with financial transactions, such as investments, loans and deposits
Financial Institution • an establishment that focuses on dealing with financial transactions, such as investments, loans and deposits
 Financial Instrument • a real or virtual document representing a legal agreement involving some sort of monetary value
Financial Instrument • a real or virtual document representing a legal agreement involving some sort of monetary value
 Classification of finances
Classification of finances
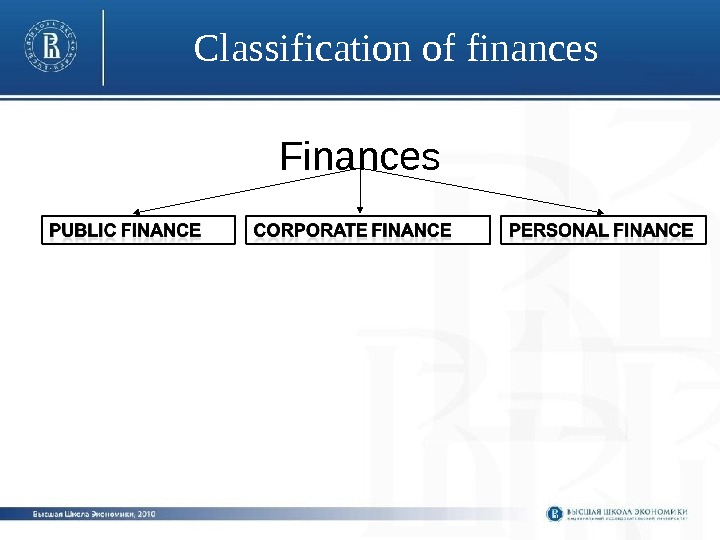
 Classification of finances Finances
Classification of finances Finances
 Public finance the branch of economics which assesses the government revenue and government expenditure of the public authorities, explains governmental effects on efficient allocation of resources, distribution of income, and macroeconomic stabilization.
Public finance the branch of economics which assesses the government revenue and government expenditure of the public authorities, explains governmental effects on efficient allocation of resources, distribution of income, and macroeconomic stabilization.
 Corporate finance the area of finance dealing with the sources of funding and the capital structure of corporations and the actions that managers take to increase the value of the firm to the shareholders, as well as the tools and analysis used to allocate financial resources.
Corporate finance the area of finance dealing with the sources of funding and the capital structure of corporations and the actions that managers take to increase the value of the firm to the shareholders, as well as the tools and analysis used to allocate financial resources.
 Personal finance the financial management which an individual or a family unit performs to budget, save, and spend monetary resources over time, taking into account various financial risks and future life events.
Personal finance the financial management which an individual or a family unit performs to budget, save, and spend monetary resources over time, taking into account various financial risks and future life events.
 Financial market
Financial market
 Financial market • a market in which people trade financial securities, co mmodities, and other fungible items of value at low transaction costs and at prices that reflect supply and demand.
Financial market • a market in which people trade financial securities, co mmodities, and other fungible items of value at low transaction costs and at prices that reflect supply and demand.
 Types of financial markets • Capital markets • Stock Markets • Bond Markets • Money Markets • Cash or Spot Market • Derivatives Markets • Forex and the Interbank Market
Types of financial markets • Capital markets • Stock Markets • Bond Markets • Money Markets • Cash or Spot Market • Derivatives Markets • Forex and the Interbank Market
 Types of financial markets • Primary Markets • Secondary Markets • The OTC Market • Third and Fourth Markets
Types of financial markets • Primary Markets • Secondary Markets • The OTC Market • Third and Fourth Markets
 Role of financial markets • Saving mobilization • Investment • National Growth • Entrepreneurship growth • Industrial development
Role of financial markets • Saving mobilization • Investment • National Growth • Entrepreneurship growth • Industrial development
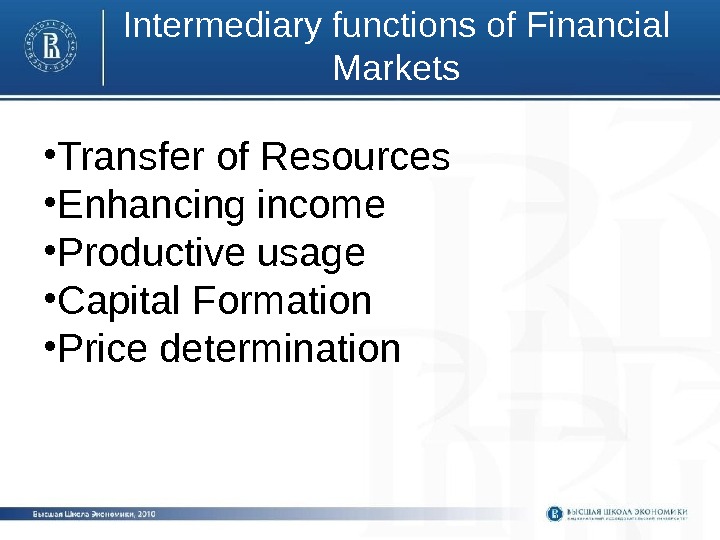
 Intermediary functions of Financial Markets • Transfer of Resources • Enhancing income • Productive usage • Capital Formation • Price determination
Intermediary functions of Financial Markets • Transfer of Resources • Enhancing income • Productive usage • Capital Formation • Price determination
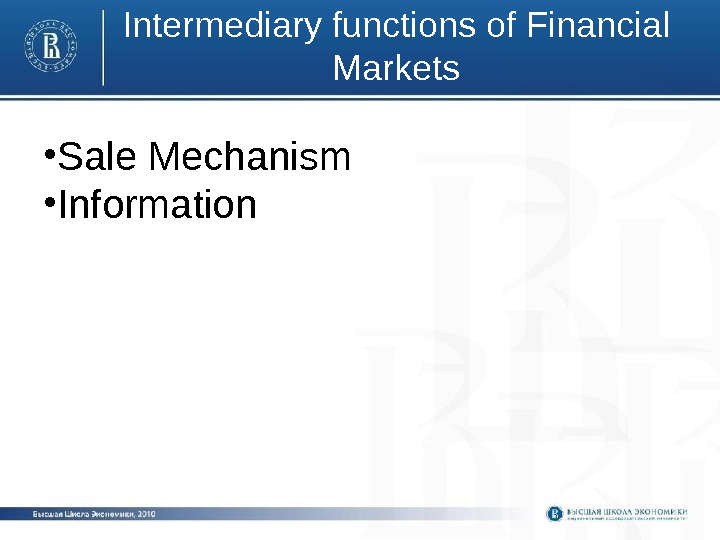
 Intermediary functions of Financial Markets • Sale Mechanism • Information
Intermediary functions of Financial Markets • Sale Mechanism • Information
 Financial Functions • Providing the borrower with funds so as to enable them to carry out their investment plans. • Providing the lenders with earning assets so as to enable them to earn wealth by deploying the assets in production debentures.
Financial Functions • Providing the borrower with funds so as to enable them to carry out their investment plans. • Providing the lenders with earning assets so as to enable them to earn wealth by deploying the assets in production debentures.
 Financial Functions • Providing liquidity in the market so as to facilitate trading of funds. • Providing liquidity to commercial bank • Facilitating credit creation • Promoting savings • Promoting investment • Facilitating balanced economic growth • Improving trading floors
Financial Functions • Providing liquidity in the market so as to facilitate trading of funds. • Providing liquidity to commercial bank • Facilitating credit creation • Promoting savings • Promoting investment • Facilitating balanced economic growth • Improving trading floors
 Thank you for attention!
Thank you for attention!

