234070e36715d91d617d47dba395827e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Introduction

Evolutions Business executives viewed the ICT function as the province of the technocrats primarily interested in new features with little relevance to real-world business problems; Technology executives have often considered business managers to be shortsighted, lacking vision to exploit all that technology has to offer. Ø Struggle as they attempt to implement increasingly complex systems in the face of rapid change in business and technology
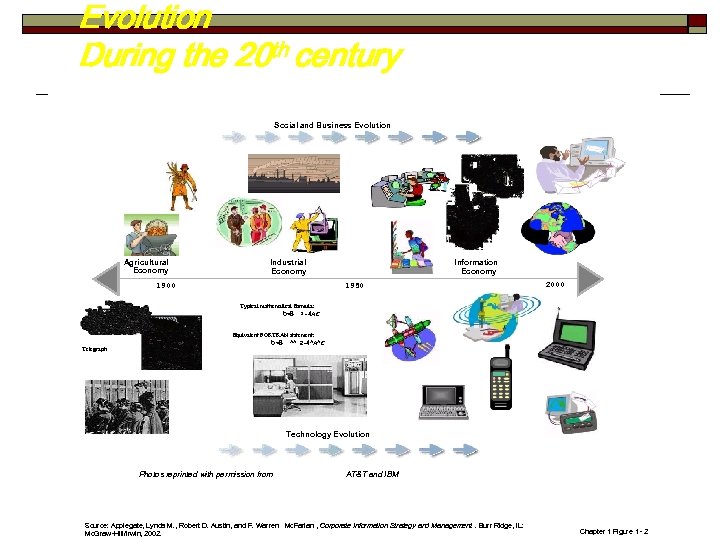
Evolution During the 20 th century Social and Business Evolution Agricultural Economy Information Economy Industrial Economy 1950 1900 2000 Typical mathematical formula: D=B 2 -4 AC Telegraph Equivalent FORTRAN statement: D=B ** 2 -4*A*C Technology Evolution Photos reprinted with permission from AT&T and IBM Source: Applegate, Lynda M. , Robert D. Austin, and F. Warren Mc. Farlan , Corporate Information Strategy and Management. Burr Ridge, IL: Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin, 2002. Chapter 1 Figure 1 - 2
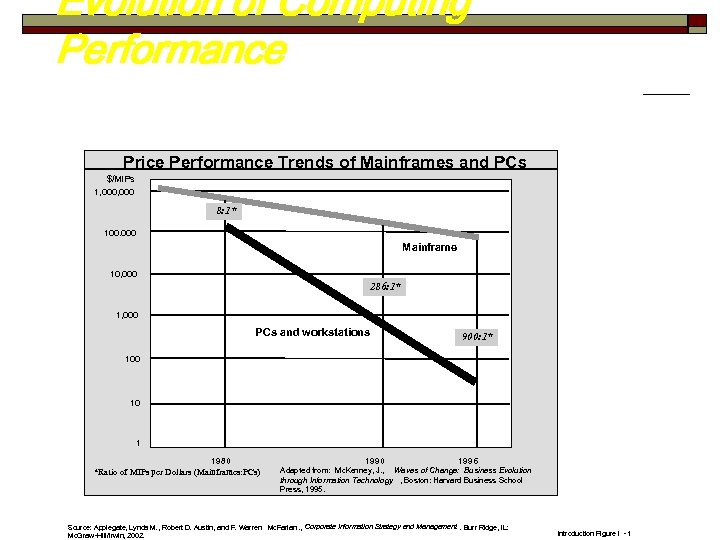
Evolution of Computing Performance Price Performance Trends of Mainframes and PCs $/MIPs 1, 000 8: 1* 100. 000 Mainframe 10, 000 286: 1* 1, 000 PCs and workstations 900: 1* 100 10 1 1980 *Ratio of MIPs per Dollars (Mainframes: PCs) 1990 1996 Adapted from: Mc. Kenney, J. , Waves of Change: Business Evolution through Information Technology , Boston: Harvard Business School Press, 1995. Source: Applegate, Lynda M. , Robert D. Austin, and F. Warren Mc. Farlan. , Corporate Information Strategy and Management. Burr Ridge, IL: Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin, 2002. Introduction Figure I -1

Examples American airlines Baxter Mrs. Field Coockies Open Market

Facts Business executives have begun to wrest control from IT executives who have failed to step up to the challenge of entering the boardroom We see IT-enabled “virtual organizations” in which many small independent agents (or firms) band together as nodes on an information network to achieve dramatic increases in scope and scale. Independency of time and physical location.

21 st Century insights: Themes Expanded processing capacity enables convergence of voice, video and data; encourages real-time transactions and interactivity; dramatically increases connectivity and access. The business models that dominated the industrial economy are evolving to take advantage of of the capabilities of new technologies. ICT infrastructure becomes more standardized, modular and scalable Ø From cost avoidance to asset-based, strategic approach Organizations “buy” rather than “make” IT-applications Cooperation amongst 4 constituencies Ø Business executives, IT-executives, users, technology providers Need to ensure high levels of security, privacy, reliability, and availability.
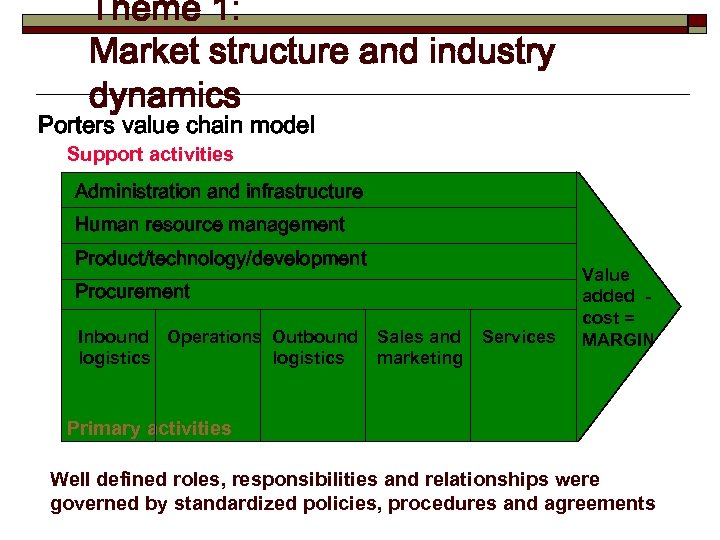
Theme 1: Market structure and industry dynamics Porters value chain model Support activities Administration and infrastructure Human resource management Product/technology/development Procurement Inbound Operations Outbound logistics Sales and marketing Services Value added cost = MARGIN Primary activities Well defined roles, responsibilities and relationships were governed by standardized policies, procedures and agreements
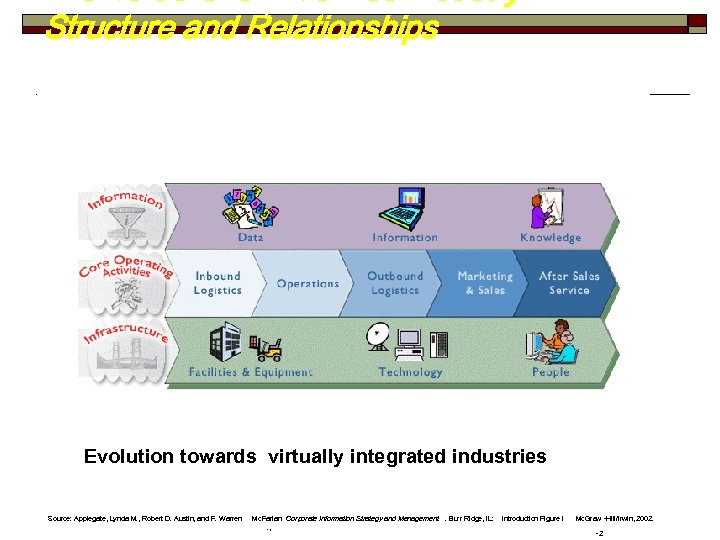
The Value Chain Defines Industry Structure and Relationships Evolution towards virtually integrated industries Source: Applegate, Lynda M. , Robert D. Austin, and F. Warren Mc. Farlan Corporate Information Strategy and Management. Burr Ridge, IL: . , Introduction Figure I Mc. Graw -Hill/Irwin, 2002. -2
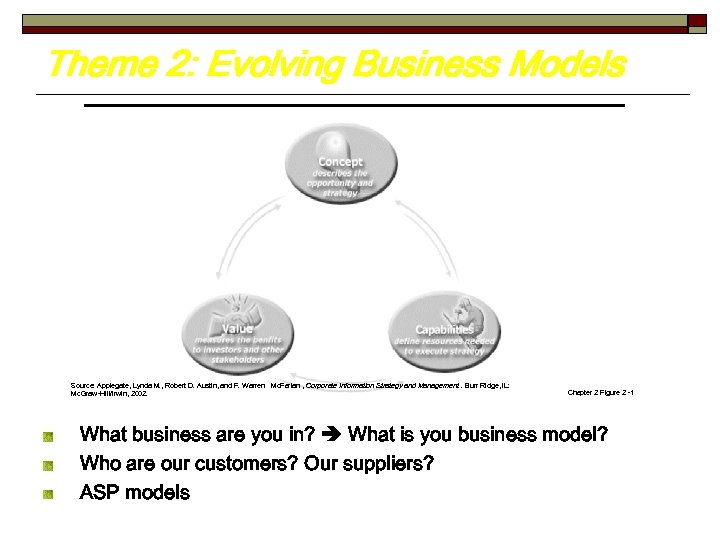
Theme 2: Evolving Business Models Source: Applegate, Lynda M. , Robert D. Austin, and F. Warren Mc. Farlan , Corporate Information Strategy and Management. Burr Ridge, IL: Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin, 2002. Chapter 2 Figure 2 -1 What business are you in? What is you business model? Who are our customers? Our suppliers? ASP models
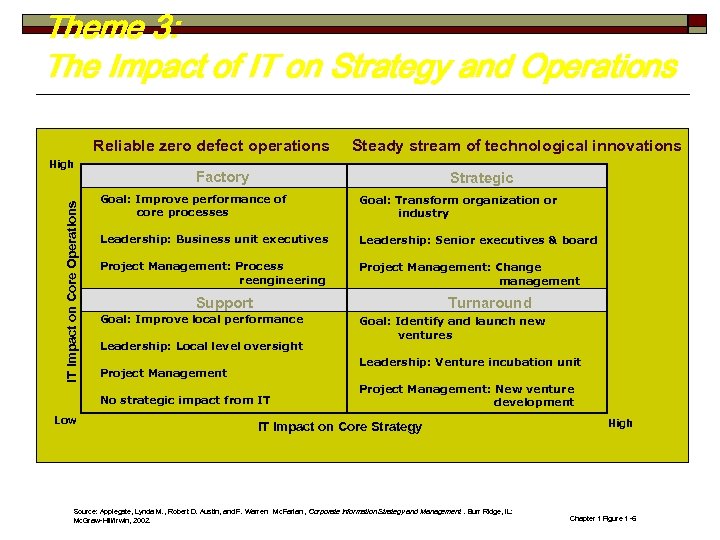
Theme 3: The Impact of IT on Strategy and Operations Reliable zero defect operations IT Impact on Core Operations High Factory Strategic Goal: Improve performance of core processes Goal: Transform organization or industry Leadership: Business unit executives Leadership: Senior executives & board Project Management: Process reengineering Project Management: Change management Support Turnaround Goal: Improve local performance Leadership: Local level oversight Goal: Identify and launch new ventures Leadership: Venture incubation unit Project Management No strategic impact from IT Low Steady stream of technological innovations Project Management: New venture development IT Impact on Core Strategy Source: Applegate, Lynda M. , Robert D. Austin, and F. Warren Mc. Farlan , Corporate Information Strategy and Management. Burr Ridge, IL: Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin, 2002. High Chapter 1 Figure 1 -6

Theme 4: Prioritizing IT investments Benefits from investments in Networked IT Infrastructure Ø Functionality and flexibility Benefits from doing business on a Networked IT Infrastructure Ø Ø Ø Commerce: operating efficiency, process performance Content/knowledge community
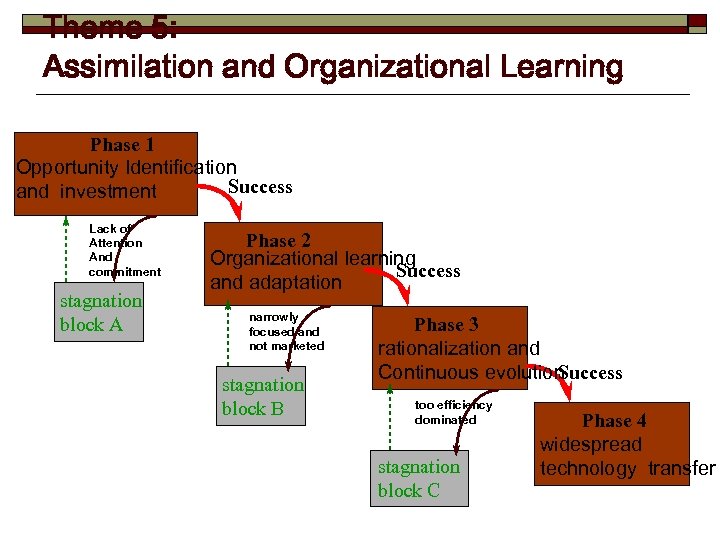
Theme 5: Assimilation and Organizational Learning Phase 1 Opportunity Identification Success and investment Lack of Attention And commitment stagnation block A Phase 2 Organizational learning Success and adaptation narrowly focused and not marketed stagnation block B Phase 3 rationalization and Success Continuous evolution too efficiency dominated stagnation block C Phase 4 widespread technology transfer

Theme 6: Buy versus Make User friendly personal software packages Can I outsource data centers, networks, help desks, PC support Allignment of short term and long term goals and incentives Provisions for death and divorce
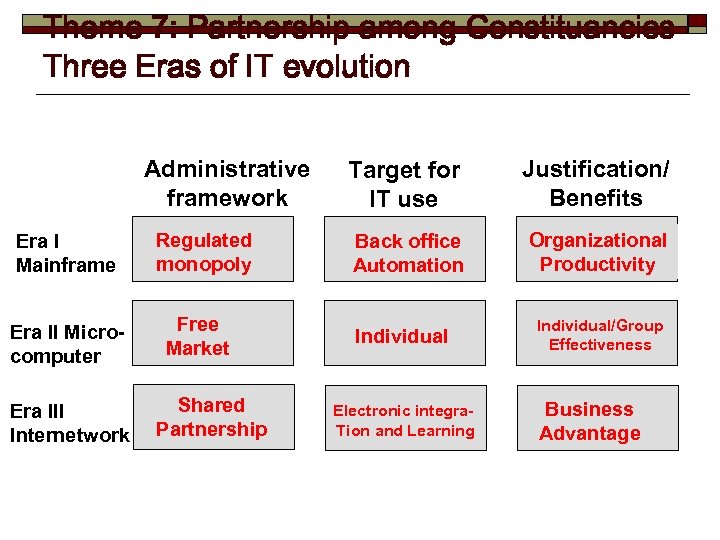
Theme 7: Partnership among Constituancies Three Eras of IT evolution Administrative framework Era I Mainframe Era II Microcomputer Era III Internetwork Regulated monopoly Free Market Shared Partnership Target for IT use Justification/ Benefits Back office Automation Organizational Productivity Individual Electronic integra. Tion and Learning Individual/Group Effectiveness Business Advantage

Five Questions to the Manager to be answered every six months or so. 1. Do the perspectives and skills of the IT and general management team fit the firm’s changing applications trust, operations challenges, user environment, and often shift in strategic relevance ? 2. Is the firm organized to identify , evaluate , and assimilate new IT-opportunities? In this fast moving field an internally focused, low-quality staff can generate severe problems. Unprofitable, unwitting obsolescence (from which it is hard to recover) is terribly easy here. There is no need for a firm to adopt leading-edge technology (indeed, many are ill equipped to do so), but it is inexcusable not to be aware of what the possibilities are. 3. Are three main management systems for integrating the environment to the firm as a whole in place and implemented? These are the strategic planning system, the management control system and the project management system. 4. Are the security , priority setting, manufacturing procedure , and change control systems in the IT operations function appropriate for the role it now plays in the firm? 5. Are organization structures and linking mechanisms in place that will ensure informed senior management on IT-evolutions such that IT is aligned with the needs of the company?

Investing in ICT If you think good information systems are expensive, try without them !

Company company not the same anymore Ø information Ø quality system became strategic requirements finally stated Ø management Ø Global at all levels involved knowledge management

IT - departments Not the same anymore Ø much larger action radius Ø role of the central system has changed Ø hardware within the budget of a department Ø required knowledge not pure technical anymore

User Not the same anymore either Ø not doing his first IT-project Ø got some computer training has his own preferred packages wants to build his own little system Ø doesn’t want to be forced into a system Ø wants to be involved in the development
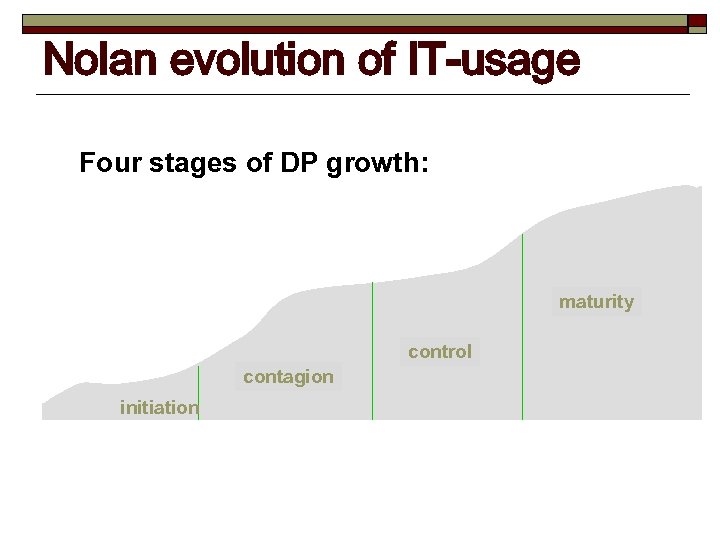
Nolan evolution of IT-usage Four stages of DP growth: maturity control contagion initiation
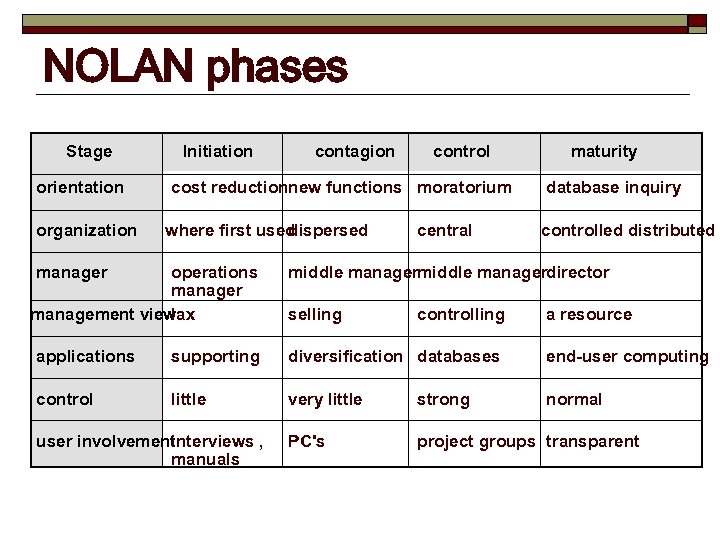
NOLAN phases Stage orientation organization Initiation contagion control cost reductionnew functions moratorium where first used dispersed manager operations manager management view lax central maturity database inquiry controlled distributed middle managerdirector selling controlling a resource applications supporting diversification databases end-user computing control little very little strong normal PC's project groups transparent user involvementnterviews , i manuals

Success of 21 st Century Company Depends on: Immediate availability of the right information on the right moment in time Ø Continuous scan of environment Learning company Ø Knowledge base Immediate reaction Ø Zero Latency Company Flexible organizational structure of independent cells virtual company Corporate Information Manager
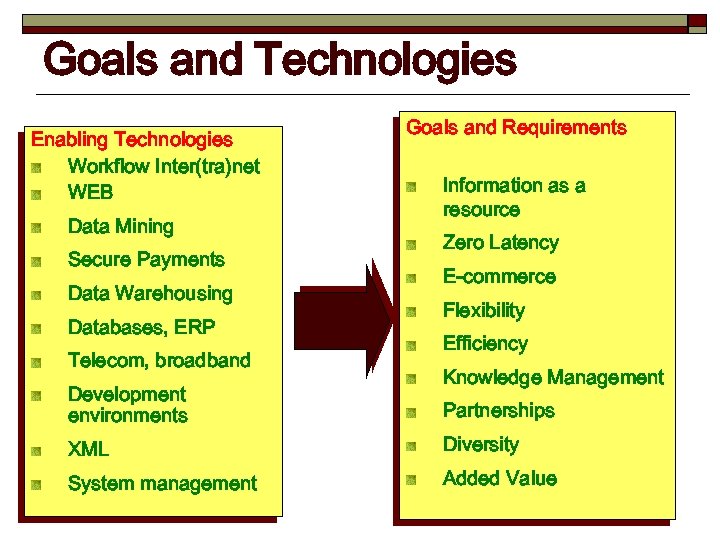
Goals and Technologies Enabling Technologies Workflow Inter(tra)net WEB Data Mining Secure Payments Data Warehousing Databases, ERP Telecom, broadband Development environments Goals and Requirements Information as a resource Zero Latency E-commerce Flexibility Efficiency Knowledge Management Partnerships XML Diversity System management Added Value

Citation There is nothing more difficult to plan , more doubtful of success, nor more dangerous to manage than the creation of a new system. For the initiator has the enmity of all who would profit by the preservation of the old system and merely lukewarm defenders in those who would gain by the new one. Machiavelli, 1513
234070e36715d91d617d47dba395827e.ppt