d31ab803195981c2e0daaec6acc912cb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69

Introduction E-cert Application of Business Rules to an XML Schema NAPPO Documentation of Use Cases

Introduction E-cert Craig Southwick United States Department of Agriculture Sheryn Kirkpatrick Canadian Food Inspection Agency

Introduction E-cert Presentation Outline 1) Brief overview of XML, and XML Schema 2) The need to apply of business rules to exchanged certificates 3) A proposed solution (ISO Schematron) 4) Overview of identified Use Cases 5) Miscellaneous issues to be considered

Building Blocks E-cert Developing a Standard Message • Universally accepted message format (XML) • Organisation of the information (XML Schema) • Common dictionary (data elements)

XML E-cert e. Xtensible Markup Language XML is a standard format for organizing and describing data. In XML, information is organized into ‘Elements’, similar to the boxes on a Certificate. Extract from Jason Dittrich presentation done at the Ottawa EPCW May 2009.

XML E-cert Paper Certificate verses XML
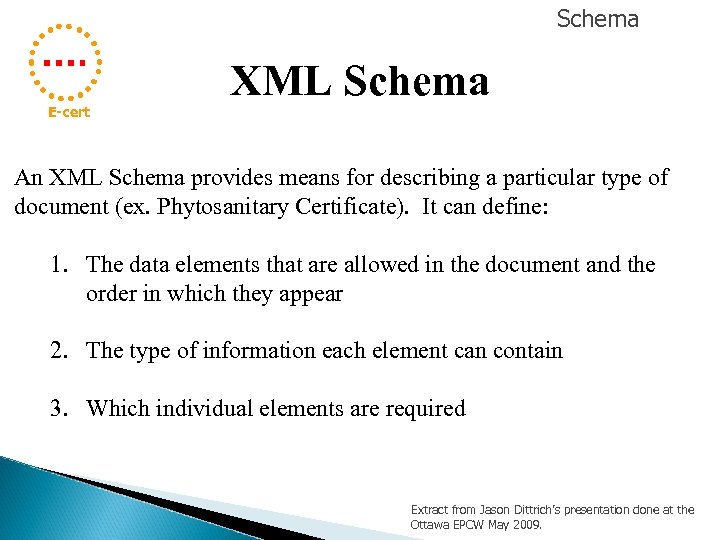
Schema E-cert XML Schema An XML Schema provides means for describing a particular type of document (ex. Phytosanitary Certificate). It can define: 1. The data elements that are allowed in the document and the order in which they appear 2. The type of information each element can contain 3. Which individual elements are required Extract from Jason Dittrich’s presentation done at the Ottawa EPCW May 2009.
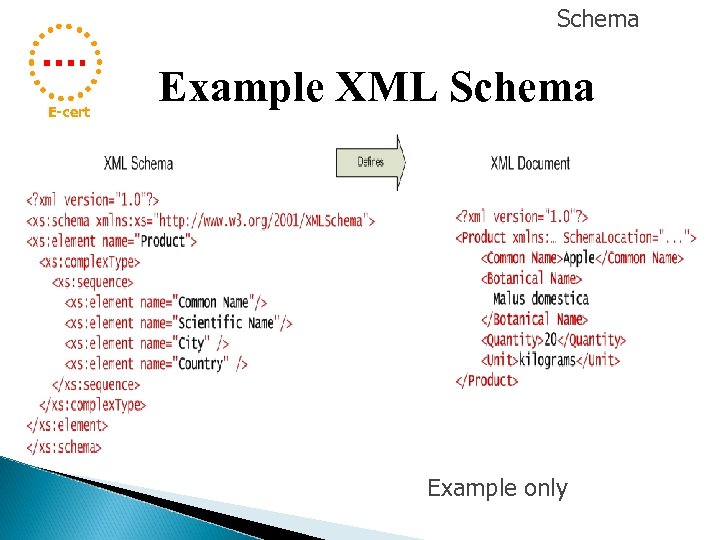
Schema E-cert Example XML Schema Example only
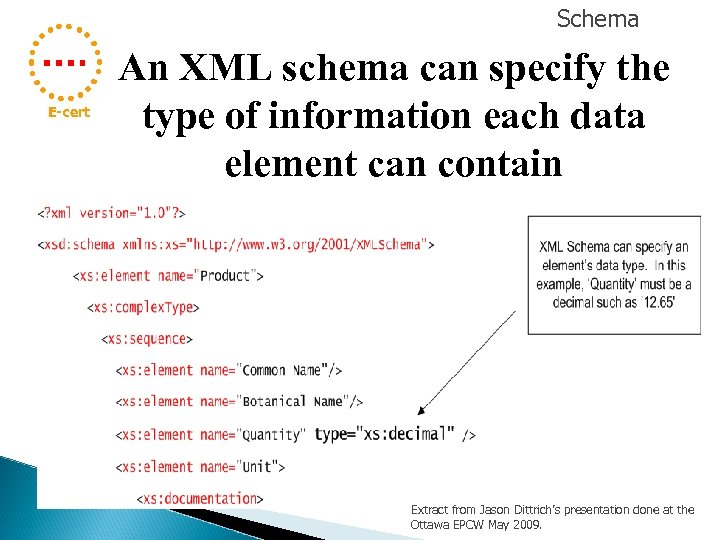
Schema E-cert An XML schema can specify the type of information each data element can contain Extract from Jason Dittrich’s presentation done at the Ottawa EPCW May 2009.
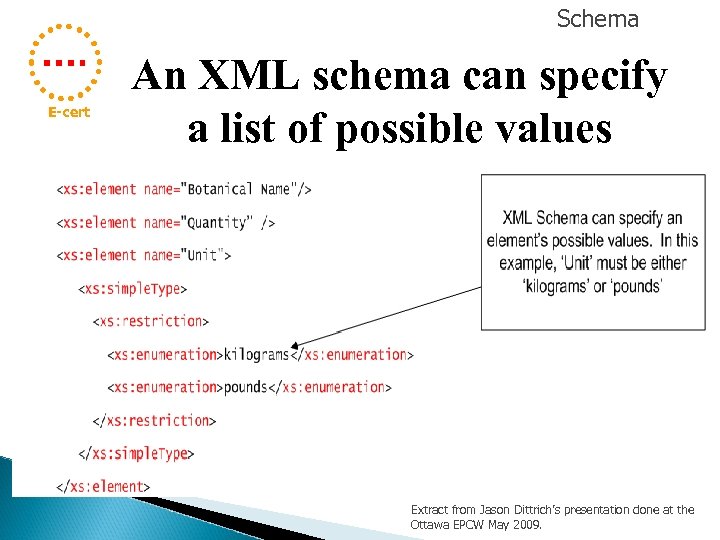
Schema E-cert An XML schema can specify a list of possible values Extract from Jason Dittrich’s presentation done at the Ottawa EPCW May 2009.
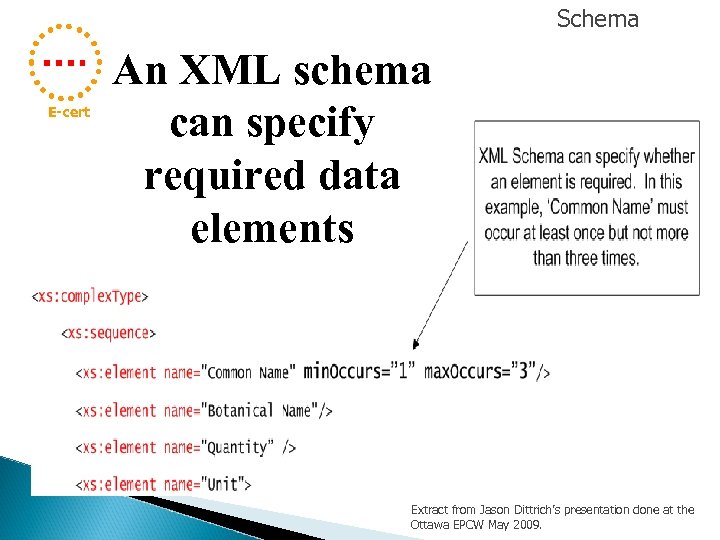
Schema E-cert An XML schema can specify required data elements Extract from Jason Dittrich’s presentation done at the Ottawa EPCW May 2009.
Standard Message E-cert A Standard E-Cert Message Using XML and Schema • Phytosanitary Certificate Data can be represented electronically using XML • This electronic representation of Certificate data is defined by an XML Schema
SPS Schema E-cert UN/CEFACT (SPS) Certificate Schema This standard adopts an XML Schema-based solution and uses data elements from the published UN/CEFACT core component library

SPS Schema E-cert Characteristics of the UN/CEFACT (SPS) Certificate Schema 1. Universal Schema was designed to allow for use with more than one type of certificate, e. g. phytosanitary certificates, live animal certificates, meat certificates, etc. 2. Because of this design, few restrictions are imposed by the schema itself and any ISPM 12 -specific requirements for phytosanitary certificates must defined separately.

Business Rules E-cert Challenges 1. Due to its universal design, the SPS Schema is complex and data elements are named generically. Every data item in ISPM 12 must be identified and mapped to the correct element within the SPS Certificate Schema. 2. Few ISPM 12 restrictions are imposed in the SPS Schema itself. How might these business rules be imposed?
Business Rules NAPPO Progress E-cert An “XML Datamap” and a UN/CEFACT implementation guide have been prepared. • Translates ISPM-12 to the SPS Certificate XML schema • Highlights mandatory vs. optional data requirements in the SPS Schema • Provides real life examples • Provides a single ‘go to’ point when defining the XML message content
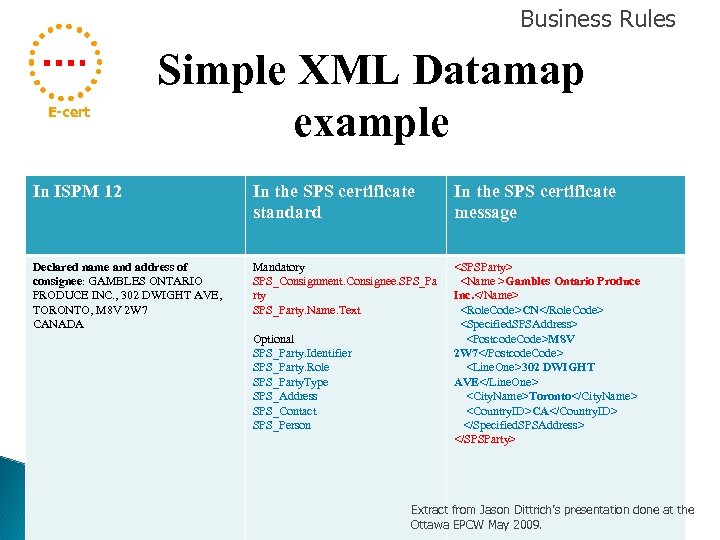
Business Rules E-cert Simple XML Datamap example In ISPM 12 In the SPS certificate standard In the SPS certificate message Declared name and address of consignee: GAMBLES ONTARIO PRODUCE INC. , 302 DWIGHT AVE, TORONTO, M 8 V 2 W 7 CANADA Mandatory SPS_Consignment. Consignee. SPS_Pa rty SPS_Party. Name. Text <SPSParty> <Name >Gambles Ontario Produce Inc. </Name> <Role. Code>CN</Role. Code> <Specified. SPSAddress> <Postcode. Code>M 8 V 2 W 7</Postcode. Code> <Line. One>302 DWIGHT AVE</Line. One> <City. Name>Toronto</City. Name> <Country. ID>CA</Country. ID> </Specified. SPSAddress> </SPSParty> Optional SPS_Party. Identifier SPS_Party. Role SPS_Party. Type SPS_Address SPS_Contact SPS_Person Extract from Jason Dittrich’s presentation done at the Ottawa EPCW May 2009.

Business Rules E-cert Challenge : ISPM 12 Requirements and the SPS Schema ISPM 12 -specific requirements are not imposed in the SPS Schema itself. These must be defined and implemented separately. How might this be accomplished?

Business Rules E-cert ISPM 12 Requirements and the SPS Schema Option 1: Each NPPO builds custom message validation into their internal systems International community creates a narrative (text) document describing the message requirements • Pros: Does not rely on a specific technology • Cons: Each participant must build their own validation system and may interpret the requirements differently

Business Rules E-cert ISPM 12 Requirements and the SPS Schema Option 2: Utilize a centralized system for validating requirements International Community creates a validation system all ECert messages must pass through • Pros: Single system ensures all participants are using the same set of requirements • Cons: Costly to build and maintain. Single point of failure.

Business Rules E-cert ISPM 12 Requirements and the SPS Schema Option 3: Use an additional technical document as an addendum to SPS Schema International Community drafts a technical (computer readable) addendum to the SPS Schema applying ISPM-12 message requirements • Pros: Technical document limits differences in interpretation of the standard • Cons: E-Cert standard would need to contain an additional specification in addition to SPS Schema

Business Rules E-cert • • E-Cert Requirements Summary Electronic transfer should contain all elements that the paper certificate contains, in accordance with ISPM 12. The authenticity of the message certification data should be assured by electronic means. It should be clear that the certification data are provided and supported by the NPPO of the exporting country. The electronic transfer should be in a protected way such that the data cannot be changed or read by any party during transfer. To facilitate communication, this transfer can best be done in a standardized format. The XML format, following an XML schema, is strongly recommended.
Validation E-Cert Validation is. . . E-cert The use of a computer system to automatically verify the contents of an electronic certificate meet the minimum requirements of a given NPPO
Validation Why is validation important? E-cert Ø The use of a computer system to perform certificate verification allows for automatic rejection of incomplete or invalid documents System validation provides significant cost savings to NPPOs by reducing the amount of time spent by government employees reviewing certificates The more detailed and complete automatic validation is, the greater efficiency and cost savings achieved. Reduces errors and allows for timely correction of certificates, increasing efficiency at ports of entry.

Business Rules E-cert Previous NAPPO efforts The NAPPO e. Certification panel’s previous efforts focused on creating a single phytosanitary certificate XML Schema. This single schema would encompass agreed upon business rules.

Business Rules Previous NAPPO efforts E-cert Single XML Schema for Phytosanitary Certificates Pros : • Customized schema provides simple validation Cons: • Schema not reusable • Attaining agreement on a common rule set extremely difficult • Bilateral agreements are not supported

Business Rules E-cert 1. 2. Current NAPPO Direction NAPPO is exploring the use of a common, generic schema for all electronic certificates (UN/CEFACT SPS Certificate) Perform content verification using a secondary set of business rules (ISO Schematron)
Business Rules Current NAPPO Direction E-cert Pros: • Common Schema can be reused for different certificate types • Validation separated from document format Cons: • Slightly more complex processing • No unified set of requirements (Our goal is to move towards ISPM 12 as the business requirements with schematron)
Schematron About ISO Schematron E-cert • • ISO Schematron is an ISO-standard syntax for describing the semantic rules a particular XML document must adhere to. More flexible and extensible than XML Schema, it can be used to conditionally validate document contents based on complex rules.
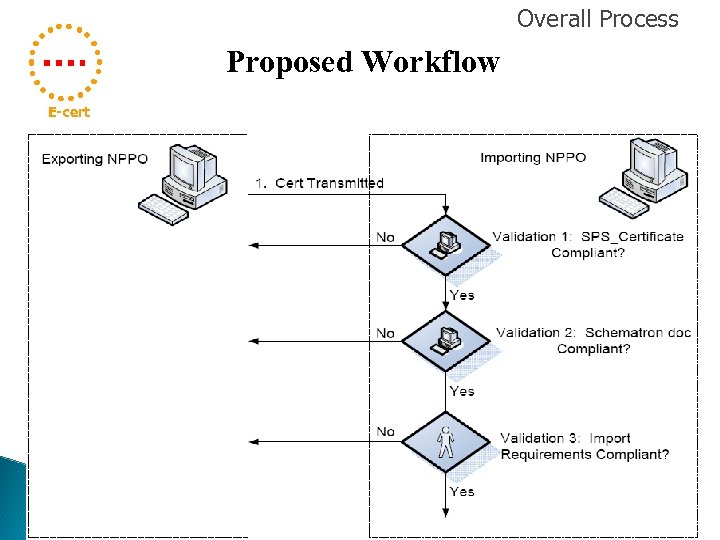
Overall Process Proposed Workflow E-cert

Schematron Example E-cert

Business Rules E-cert 1. 2. Steps to Implement Common Schema, the UN/CEFACT SPS Certificate has already been released. Business Rules documents, using ISO Schematron, and being ISPM 12 compliant, must be generated.

Business Rules E-cert ISO Schematron Implementation (Option 3) a) NPPOs agree on a common set of business rules (ISPM 12). A single schematron file is used by all participants or b) NPPOs each produce their own schematron file based on their individual import requirements. Allows for more flexibility. In either case, schematron documents could be hosted on an international site as part of the E-Cert ‘Directory’

Business Rules E-cert Schema and Schematron ISO Schematron, when used in combination with the UN/CEFACT SPS E-Certificate schema, will provide the maximum level of flexibility for automating enforcement of e. Cert business rules.
Use Cases Explained E-cert A use case defines a goal-oriented set of interactions between external actors and the system under consideration. Actors are parties outside the system that interact with the system. An actor may be a class of users, roles users can play, or other systems. Use Cases capture who (actor) does what (interaction) with the system, for what purpose (goal), without dealing with system internals

Use Cases E-cert Identified Use Cases For electronic Certification the Use Cases identified include: • • Original Phytosanitary Certificate Withdrawn Phytosanitary Certificate Replacement Phytosanitary Certificate The same Use Cases for Re-export Certificates may be needed

Use Cases E-cert • • • Original Phytosanitary Certificate This an issued certificate which has neither been withdrawn nor replaced The electronic message need only include the certificate information Based on Annex 1 of ISPM 12

Use Cases E-cert • • Withdrawn Phytosanitary Certificate An original certificate was issued The original certificate was subsequently withdrawn by the issuing NPPO Note: The certificate was withdrawn but no replacement certificate was ever been presented

Use Cases E-cert • • Replacement Phytosantiary Certificate An original certificate was issued by the NPPO The original certificate was subsequently replaced by the NPPO with a replacement certificate Note: A relationship between the original and replacement certificates must be maintained

Use Cases E-cert Re-export Phytosanitary Certificates Note: Each of the Use Cases might need to be copied for Re-export Certificates

Use Cases E-cert • • • Documenting Use Cases The NAPPO Panel has documented the identified Use Cases Documentation follows the UN/CEFACT Schema The panel used real certificate examples (with dummy data)
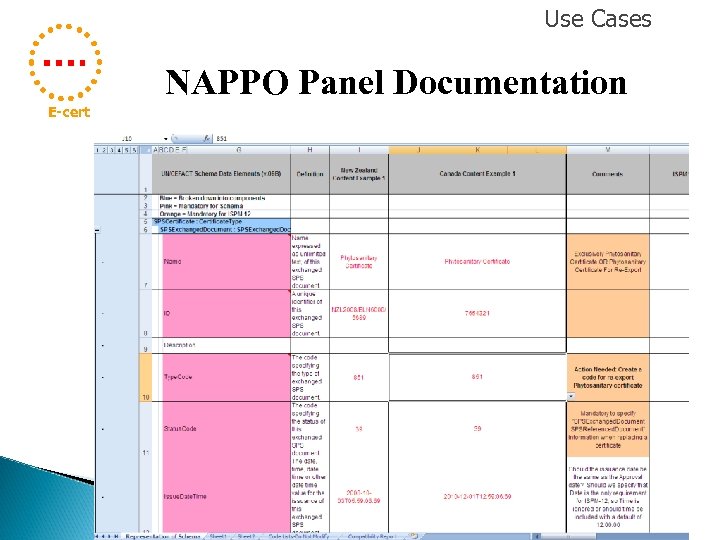
Use Cases NAPPO Panel Documentation E-cert

Use Cases E-cert • • Next Steps NAPPO will share documentation to date IPPC Working group could comment and improve upon NAPPO documentation Schema data map needs to be completed and agreed upon Generic ISO Schematron should be developed

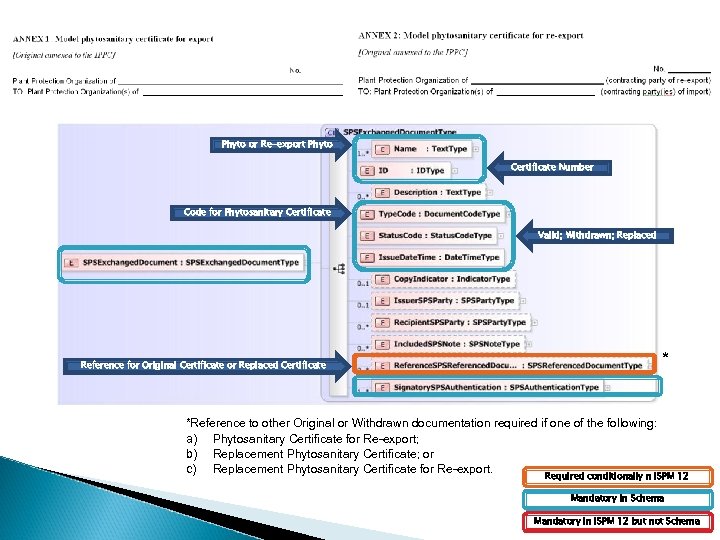
Phyto or Re-export Phyto Certificate Number Code for Phytosanitary Certificate Valid; Withdrawn; Replaced * Reference for Original Certificate or Replaced Certificate *Reference to other Original or Withdrawn documentation required if one of the following: a) Phytosanitary Certificate for Re-export; b) Replacement Phytosanitary Certificate; or c) Replacement Phytosanitary Certificate for Re-export. Required conditionally n ISPM 12 Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema

Outstanding Questions / Considerations A ‘Type’ code exists for Phytosanitary Certificates There is currently no code for a Phytosanitary Certificate for Re-export Is a code needed? ◦ Reference can always be made between SPS documents in the Schema, regardless of the ‘Type’ code ◦ There is no clear identifier for a Phytosanitary Certificate for Reexport In cases or re-export or replacement ◦ Is the entire original/withdrawn document referenced? ◦ Is the date issued and unique number sufficient?
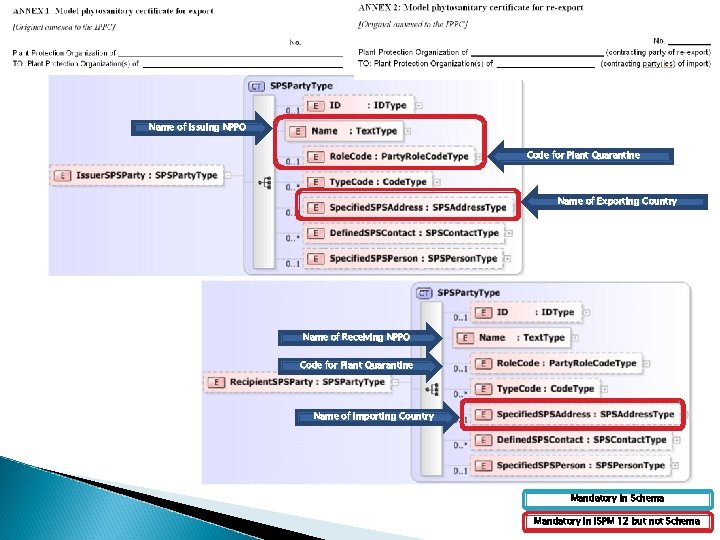
Name of Issuing NPPO Code for Plant Quarantine Name of Exporting Country Name of Receiving NPPO Code for Plant Quarantine Name of Importing Country Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema
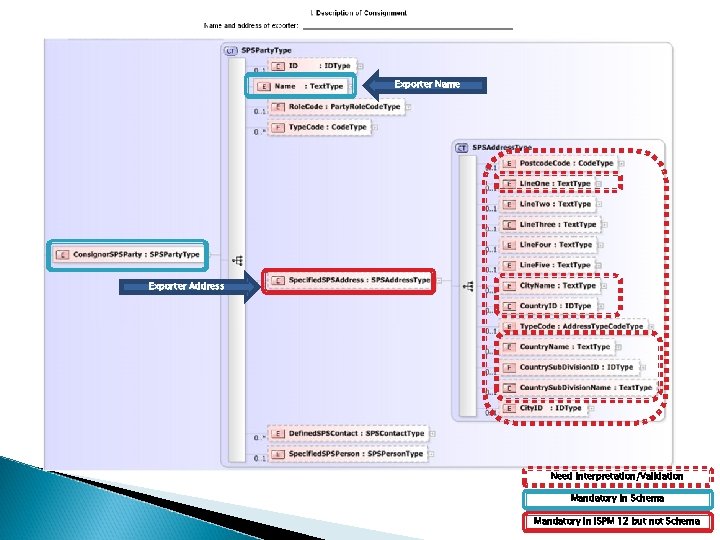
Exporter Name Exporter Address Need Interpretation/Validation Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema
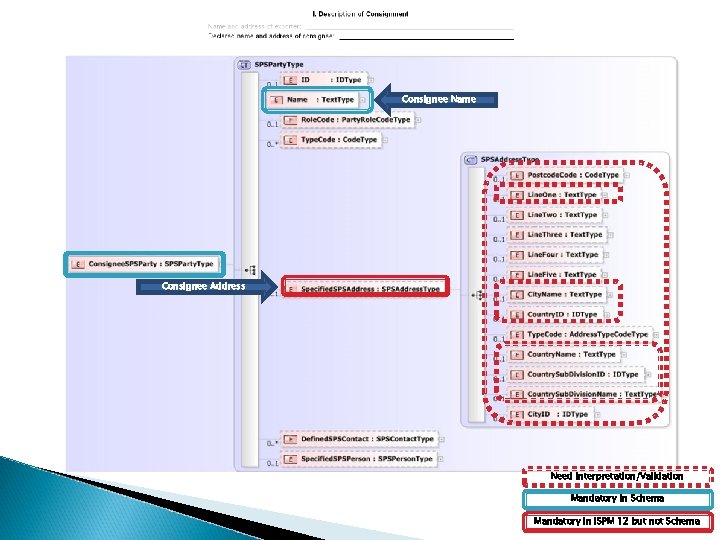
Consignee Name Consignee Address Need Interpretation/Validation Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema

Outstanding Questions / Considerations What is the minimal mandatory set of elements for an address as per ISPM 12? Post Code? Line 1? City? Country Subdivision (state, province, regions, territory, department, etc. )? ◦ All of the above? ◦ ◦ ◦
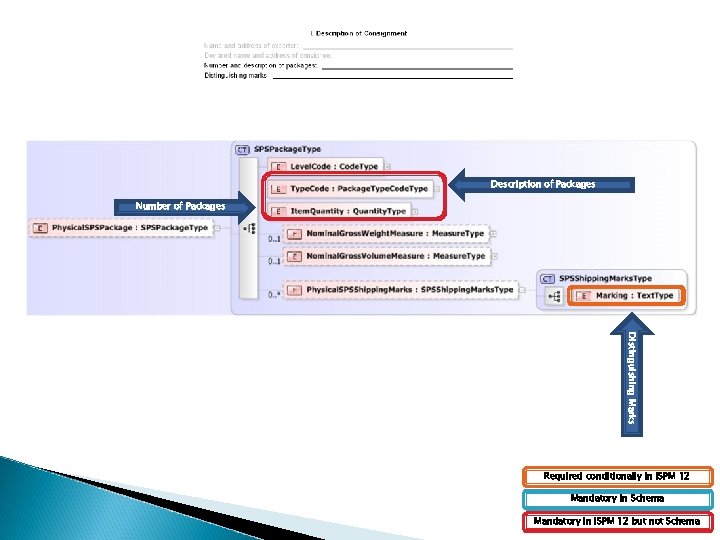
Description of Packages Number of Packages Distinguishing Marks Required conditionally in ISPM 12 Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema

Outstanding Questions / Considerations What if there are no distinguishing marks? ◦ ISPM 12 - “should be included if necessary for the identification of the consignment” ◦ On a printed certificate, the area contains ‘none’, is blocked out, or has a line drawn through it ◦ Electronically, is the element still required to appear and state ‘none’?
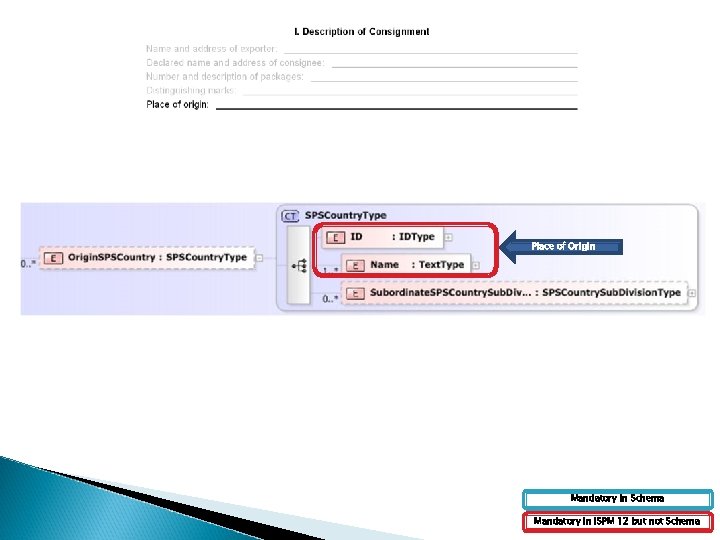
Place of Origin Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema

Outstanding Questions / Considerations Is a Place of Production required? ◦ Elements in the Schema allow for origin location at a level lower than country
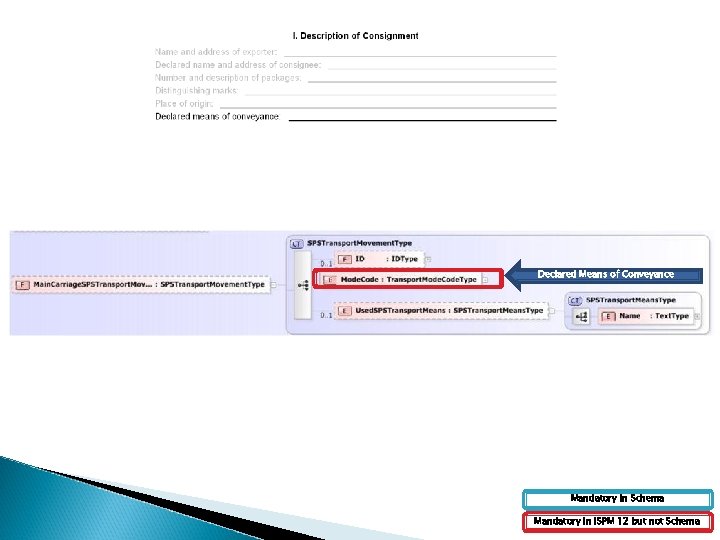
Declared Means of Conveyance Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema

Declared Point of Entry State, Province, etc. Optional Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema

Name of Produce Botanical Name Quantity Declared Need Interpretation/Validation Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema

Considerations / Outstanding Questions To appropriately define products and allow validation, a standardized classification is being proposed

Statement Title Statement Text Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema

Considerations / Outstanding Questions Two standard statements can be generated: ◦ One statement with the optional clause; and ◦ One statement without the optional clause. How do we handle the multiple options for a Phytosanitary Certificate for Re-export?

Considerations / Outstanding Questions This is to certify that the plants, plant products or other regulated articles described above ____ were 1 imported into (contracting party of re-export) ______ 2 from _______ (contracting party of origin) covered 3 by Phytosanitary certificate No. ____, *original certified true copy of which is attached to this certificate; that they are packed repacked in original *new containers, that based on the original phytosanitary certificate and additional inspection , they are considered to conform with the current phytosanitary requirements of the importing contracting party, and that 1 during storage in ________ (contracting party of re -export), the consignment has not been subjected to the risk of infestation or infection.
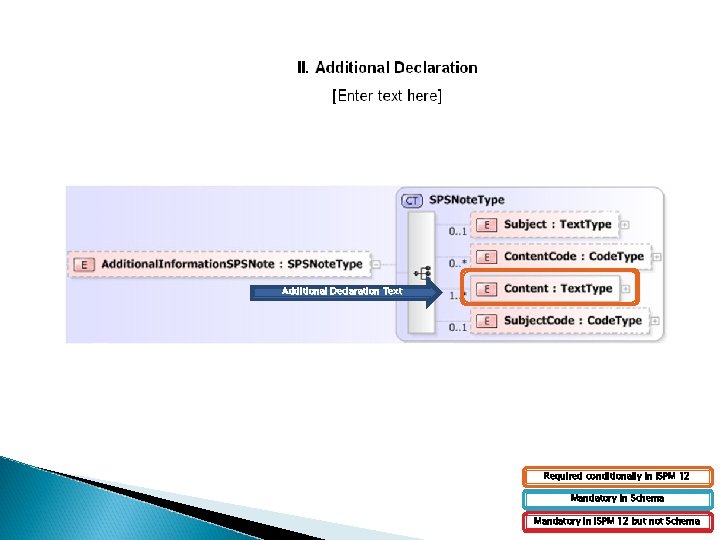
Additional Declaration Text Required conditionally in ISPM 12 Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema

Considerations / Outstanding Questions It is possible to completely separate the “Additional Declaration” from the “Additional Official Phytosanitary Information” What if there are no additional declarations? ◦ On a printed certificate, the area contains ‘none’, is blocked out, or has a line drawn through it ◦ Electronically, is the element still required to appear and state ‘none’?
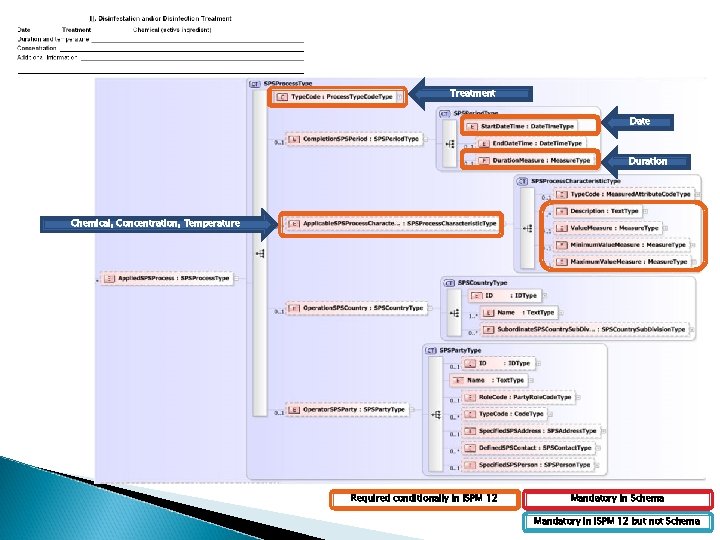
Treatment Date Duration Chemical, Concentration, Temperature Required conditionally in ISPM 12 Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema

Outstanding Questions / Considerations What if there is no treatment? ◦ On a printed certificate, the area contains ‘none’, is blocked out, or has a line drawn through it ◦ Electronically, is the element still required to appear and state ‘none’?
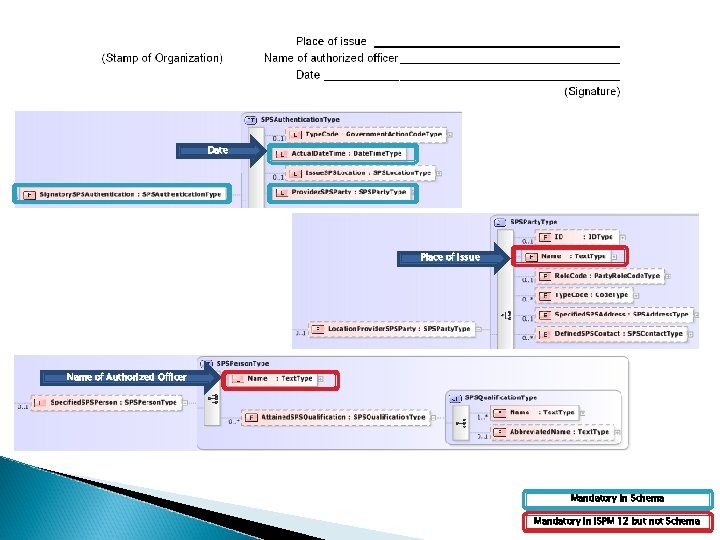
Date Place of Issue Name of Authorized Officer Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema
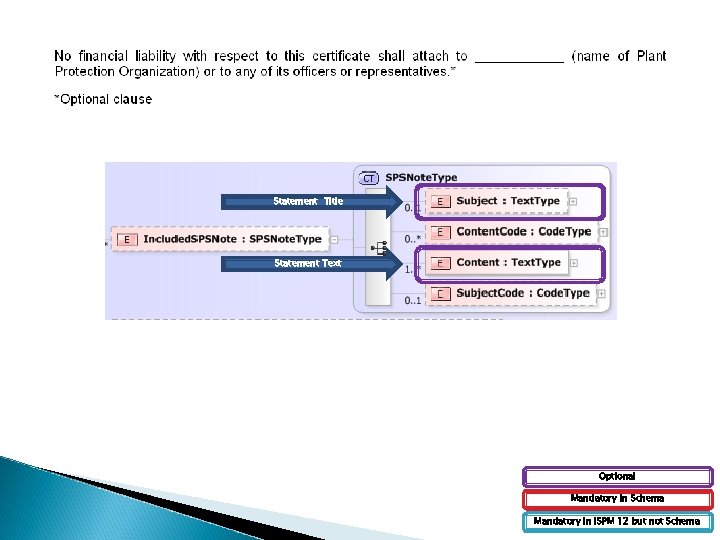
Statement Title Statement Text Optional Mandatory in Schema Mandatory in ISPM 12 but not Schema

E-cert Questions? Discussion

Credit Jason Dittrich – Materials and personal communications Ian Mc. Dowell – Information borrowed or adapted from his Ottawa presentation
d31ab803195981c2e0daaec6acc912cb.ppt