489d718f50278c5eb840774b073ca8ef.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
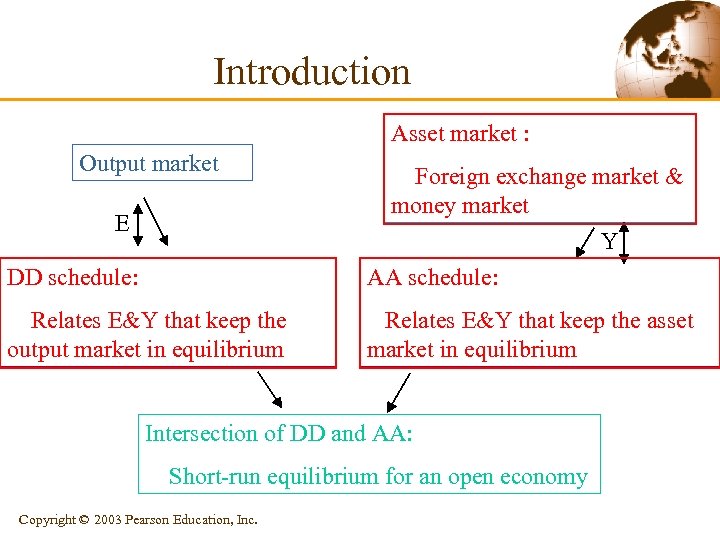
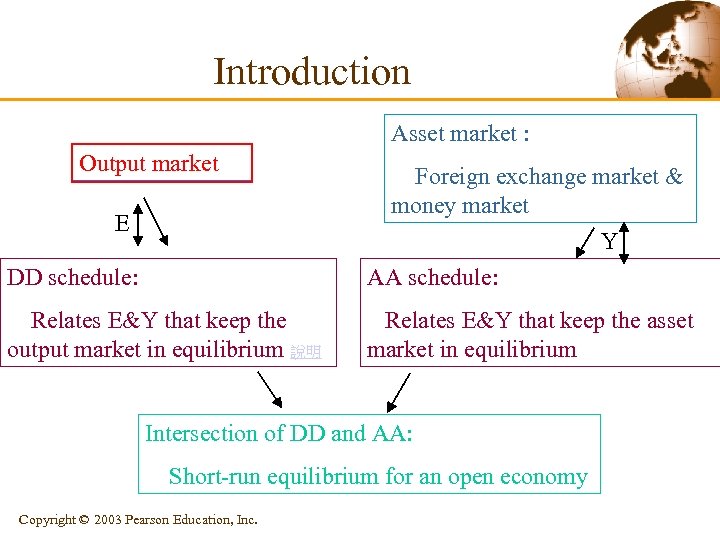 Introduction Asset market : Output market E Foreign exchange market & money market Y DD schedule: AA schedule: Relates E&Y that keep the output market in equilibrium 說明 Relates E&Y that keep the asset market in equilibrium Intersection of DD and AA: Short-run equilibrium for an open economy Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
Introduction Asset market : Output market E Foreign exchange market & money market Y DD schedule: AA schedule: Relates E&Y that keep the output market in equilibrium 說明 Relates E&Y that keep the asset market in equilibrium Intersection of DD and AA: Short-run equilibrium for an open economy Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
 學習經濟模型五步驟 §模型目的。 §內生變數:決定模型兩軸。 §行為法則:畫出模型曲線。 §均衡:決定均衡之內生變數。 §外生衝擊 • 判斷是否為外生變數改變? • 判斷此外生變數之改變將影響哪些行為法則? • 判斷此外生變數之改變造成行為法則何種影響? 3 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
學習經濟模型五步驟 §模型目的。 §內生變數:決定模型兩軸。 §行為法則:畫出模型曲線。 §均衡:決定均衡之內生變數。 §外生衝擊 • 判斷是否為外生變數改變? • 判斷此外生變數之改變將影響哪些行為法則? • 判斷此外生變數之改變造成行為法則何種影響? 3 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
 內生變數 Exchange Rate, E Output, Y Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
內生變數 Exchange Rate, E Output, Y Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
 學習經濟模型五步驟 §模型目的。 §內生變數:決定模型兩軸。 §行為法則:畫出模型曲線。 §均衡:決定均衡之內生變數。 §外生衝擊 • 判斷是否為外生變數改變? • 判斷此外生變數之改變將影響哪些行為法則? • 判斷此外生變數之改變造成行為法則何種影響? 5 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
學習經濟模型五步驟 §模型目的。 §內生變數:決定模型兩軸。 §行為法則:畫出模型曲線。 §均衡:決定均衡之內生變數。 §外生衝擊 • 判斷是否為外生變數改變? • 判斷此外生變數之改變將影響哪些行為法則? • 判斷此外生變數之改變造成行為法則何種影響? 5 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Output Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The DD Schedule § Deriving the DD Schedule • DD schedule – It shows all combinations of output and the exchange rate for which the output market is in short-run equilibrium (aggregate demand = aggregate output). 6 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
Output Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The DD Schedule § Deriving the DD Schedule • DD schedule – It shows all combinations of output and the exchange rate for which the output market is in short-run equilibrium (aggregate demand = aggregate output). 6 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
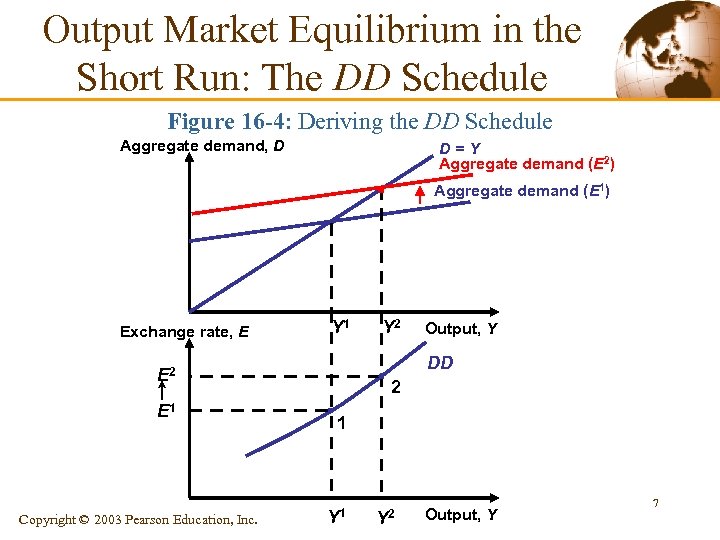 Output Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The DD Schedule Figure 16 -4: Deriving the DD Schedule Aggregate demand, D D=Y Aggregate demand (E 2) Aggregate demand (E 1) Exchange rate, E Y 1 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. Output, Y DD E 2 E 1 Y 2 2 1 Y 2 Output, Y 7
Output Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The DD Schedule Figure 16 -4: Deriving the DD Schedule Aggregate demand, D D=Y Aggregate demand (E 2) Aggregate demand (E 1) Exchange rate, E Y 1 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. Output, Y DD E 2 E 1 Y 2 2 1 Y 2 Output, Y 7
 Output Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The DD Schedule § § It slopes upward because a rise in the exchange rate causes output to rise. Factors that Shift the DD Schedule • • Government purchases Taxes Investment Domestic price levels Foreign price levels Consumption function Demand shift between foreign and domestic goods § This equation shows that aggregate demand for home output can be written as: D = D(EP*/P, Y – T, I, G) Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. (+) (+)(+) 8
Output Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The DD Schedule § § It slopes upward because a rise in the exchange rate causes output to rise. Factors that Shift the DD Schedule • • Government purchases Taxes Investment Domestic price levels Foreign price levels Consumption function Demand shift between foreign and domestic goods § This equation shows that aggregate demand for home output can be written as: D = D(EP*/P, Y – T, I, G) Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. (+) (+)(+) 8
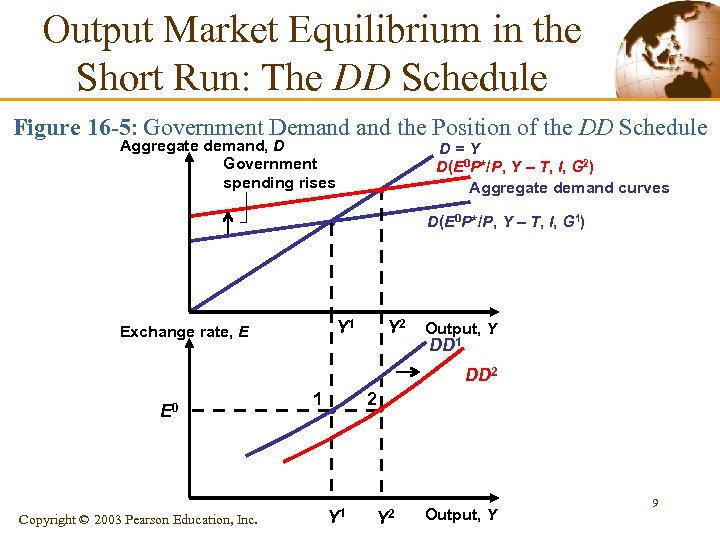 Output Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The DD Schedule Figure 16 -5: Government Demand the Position of the DD Schedule Aggregate demand, D Government spending rises D=Y D(E 0 P*/P, Y – T, I, G 2) Aggregate demand curves D(E 0 P*/P, Y – T, I, G 1) Y 1 Exchange rate, E Y 2 Output, Y DD 1 DD 2 E 0 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 2 Y 1 Y 2 Output, Y 9
Output Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The DD Schedule Figure 16 -5: Government Demand the Position of the DD Schedule Aggregate demand, D Government spending rises D=Y D(E 0 P*/P, Y – T, I, G 2) Aggregate demand curves D(E 0 P*/P, Y – T, I, G 1) Y 1 Exchange rate, E Y 2 Output, Y DD 1 DD 2 E 0 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 2 Y 1 Y 2 Output, Y 9
 Output Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The DD Schedule § A disturbance that raises (lowers) aggregate demand for domestic output shifts the DD schedule to the right (left). 10 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
Output Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The DD Schedule § A disturbance that raises (lowers) aggregate demand for domestic output shifts the DD schedule to the right (left). 10 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Output Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The DD Schedule § A disturbance that raises (lowers) aggregate demand for domestic output shifts the DD schedule to the right (left). 11 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
Output Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The DD Schedule § A disturbance that raises (lowers) aggregate demand for domestic output shifts the DD schedule to the right (left). 11 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Introduction Asset market : Output market E Foreign exchange market & money market Y DD schedule: AA schedule: Relates E&Y that keep the output market in equilibrium Relates E&Y that keep the asset market in equilibrium Intersection of DD and AA: Short-run equilibrium for an open economy Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
Introduction Asset market : Output market E Foreign exchange market & money market Y DD schedule: AA schedule: Relates E&Y that keep the output market in equilibrium Relates E&Y that keep the asset market in equilibrium Intersection of DD and AA: Short-run equilibrium for an open economy Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule § AA Schedule • It shows all combinations of exchange rate and output that are consistent with equilibrium in the domestic money market and the foreign exchange market. 13 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule § AA Schedule • It shows all combinations of exchange rate and output that are consistent with equilibrium in the domestic money market and the foreign exchange market. 13 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule § Output, the Exchange Rate, and Asset Market Equilibrium • We will combine the interest parity condition with the • money market to derive the asset market equilibrium in the short-run. The interest parity condition describing foreign exchange market equilibrium is: R = R* + (Ee – E)/E where: Ee is the expected future exchange rate R is the interest rate on domestic currency deposits R* is the interest rate on foreign currency deposits 14 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule § Output, the Exchange Rate, and Asset Market Equilibrium • We will combine the interest parity condition with the • money market to derive the asset market equilibrium in the short-run. The interest parity condition describing foreign exchange market equilibrium is: R = R* + (Ee – E)/E where: Ee is the expected future exchange rate R is the interest rate on domestic currency deposits R* is the interest rate on foreign currency deposits 14 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule • The R satisfying the interest parity condition must also • equate the real domestic money supply to aggregate real money demand: Ms/P = L(R, Y) Aggregate real money demand L(R, Y) rises when the interest rate falls because a fall in R makes interestbearing nonmoney assets less attractive to hold. 15 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule • The R satisfying the interest parity condition must also • equate the real domestic money supply to aggregate real money demand: Ms/P = L(R, Y) Aggregate real money demand L(R, Y) rises when the interest rate falls because a fall in R makes interestbearing nonmoney assets less attractive to hold. 15 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
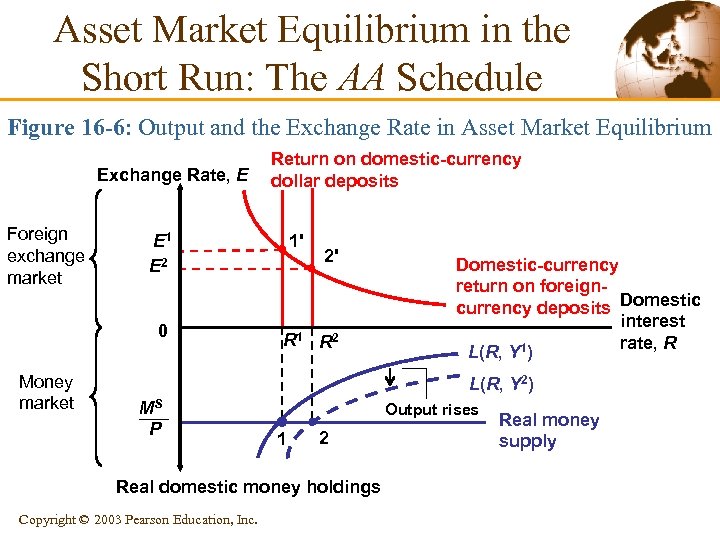 Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule Figure 16 -6: Output and the Exchange Rate in Asset Market Equilibrium Exchange Rate, E Foreign exchange market 1' E 1 E 2 0 Money market Return on domestic-currency dollar deposits 2' R 1 R 2 Domestic-currency return on foreigncurrency deposits Domestic interest rate, R L(R, Y 1) L(R, Y 2) MS P Output rises 1 2 Real domestic money holdings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. Real money supply
Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule Figure 16 -6: Output and the Exchange Rate in Asset Market Equilibrium Exchange Rate, E Foreign exchange market 1' E 1 E 2 0 Money market Return on domestic-currency dollar deposits 2' R 1 R 2 Domestic-currency return on foreigncurrency deposits Domestic interest rate, R L(R, Y 1) L(R, Y 2) MS P Output rises 1 2 Real domestic money holdings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. Real money supply
 Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule § For asset markets to remain in equilibrium: • A rise in domestic output must be accompanied by an • appreciation of the domestic currency. A fall in domestic output must be accompanied by a depreciation of the domestic currency. 17 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule § For asset markets to remain in equilibrium: • A rise in domestic output must be accompanied by an • appreciation of the domestic currency. A fall in domestic output must be accompanied by a depreciation of the domestic currency. 17 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule § Deriving the AA Schedule • It relates exchange rates and output levels that keep the • money and foreign exchange markets in equilibrium. It slopes downward because a rise in output causes a rise in the home interest rate and a domestic currency appreciation. 18 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule § Deriving the AA Schedule • It relates exchange rates and output levels that keep the • money and foreign exchange markets in equilibrium. It slopes downward because a rise in output causes a rise in the home interest rate and a domestic currency appreciation. 18 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
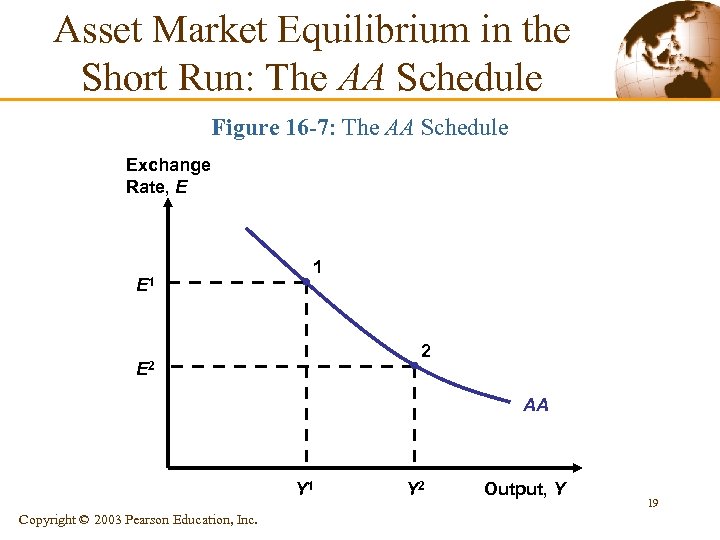 Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule Figure 16 -7: The AA Schedule Exchange Rate, E E 1 1 2 E 2 AA Y 1 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. Y 2 Output, Y 19
Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule Figure 16 -7: The AA Schedule Exchange Rate, E E 1 1 2 E 2 AA Y 1 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. Y 2 Output, Y 19
 Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule § Factors that Shift the AA Schedule 說明 • • • Domestic money supply Domestic price level Expected future exchange rate Foreign interest rate Shifts in the aggregate real money demand schedule 20 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule § Factors that Shift the AA Schedule 說明 • • • Domestic money supply Domestic price level Expected future exchange rate Foreign interest rate Shifts in the aggregate real money demand schedule 20 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
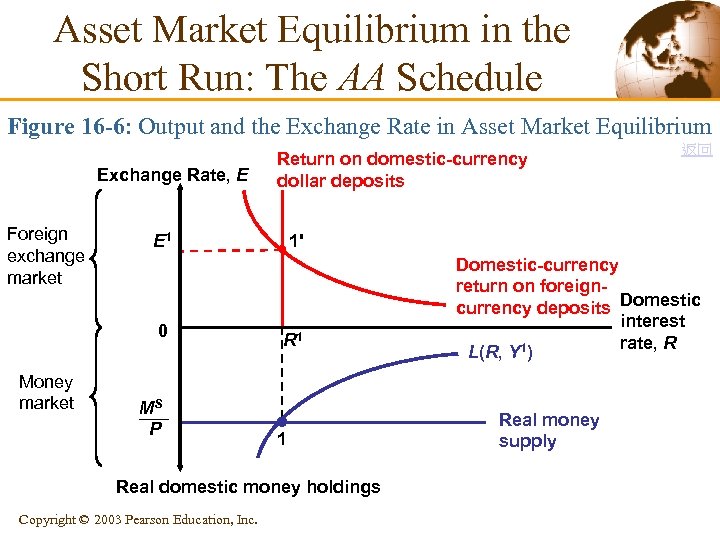 Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule Figure 16 -6: Output and the Exchange Rate in Asset Market Equilibrium Exchange Rate, E Foreign exchange market MS P R 1 1 Real domestic money holdings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. 返回 1' E 1 0 Money market Return on domestic-currency dollar deposits Domestic-currency return on foreigncurrency deposits Domestic interest rate, R L(R, Y 1) Real money supply
Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule Figure 16 -6: Output and the Exchange Rate in Asset Market Equilibrium Exchange Rate, E Foreign exchange market MS P R 1 1 Real domestic money holdings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. 返回 1' E 1 0 Money market Return on domestic-currency dollar deposits Domestic-currency return on foreigncurrency deposits Domestic interest rate, R L(R, Y 1) Real money supply
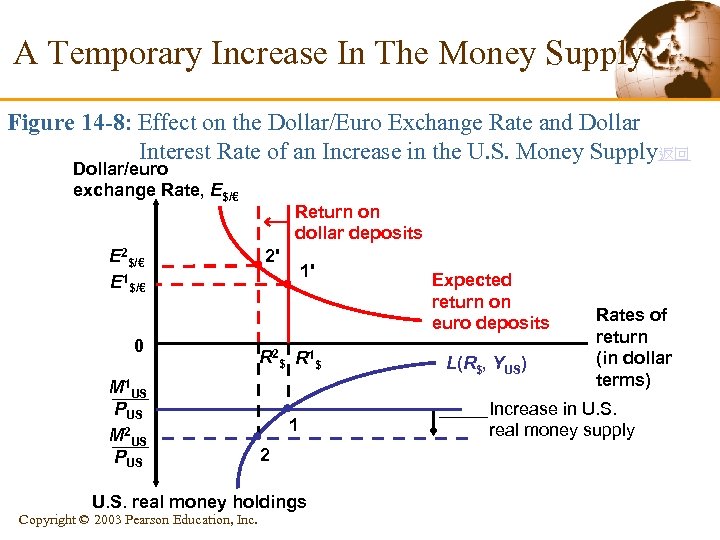 A Temporary Increase In The Money Supply Figure 14 -8: Effect on the Dollar/Euro Exchange Rate and Dollar Interest Rate of an Increase in the U. S. Money Supply返回 Dollar/euro exchange Rate, E$/€ E 2$/€ E 1$/€ 0 M 1 US PUS M 2 US PUS Return on dollar deposits 2' 1' R 2 $ R 1 $ 1 2 U. S. real money holdings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. Expected return on euro deposits L(R$, YUS) Rates of return (in dollar terms) Increase in U. S. real money supply
A Temporary Increase In The Money Supply Figure 14 -8: Effect on the Dollar/Euro Exchange Rate and Dollar Interest Rate of an Increase in the U. S. Money Supply返回 Dollar/euro exchange Rate, E$/€ E 2$/€ E 1$/€ 0 M 1 US PUS M 2 US PUS Return on dollar deposits 2' 1' R 2 $ R 1 $ 1 2 U. S. real money holdings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. Expected return on euro deposits L(R$, YUS) Rates of return (in dollar terms) Increase in U. S. real money supply
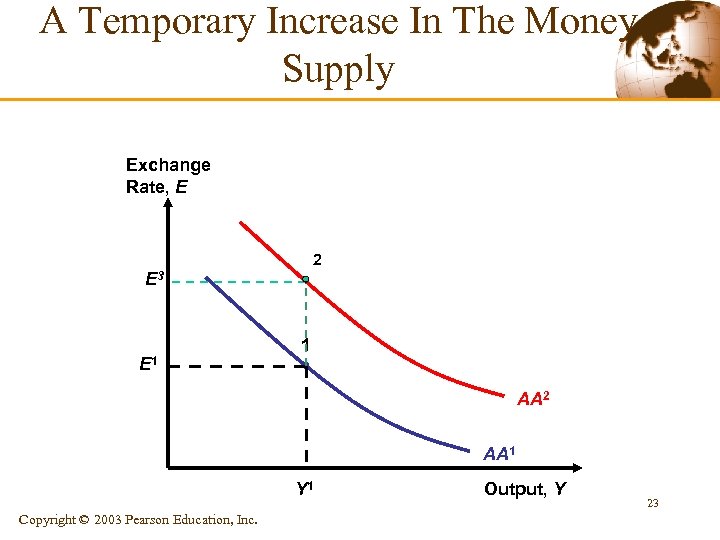 A Temporary Increase In The Money Supply Exchange Rate, E 2 E 3 E 1 1 AA 2 AA 1 Y 1 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. Output, Y 23
A Temporary Increase In The Money Supply Exchange Rate, E 2 E 3 E 1 1 AA 2 AA 1 Y 1 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. Output, Y 23
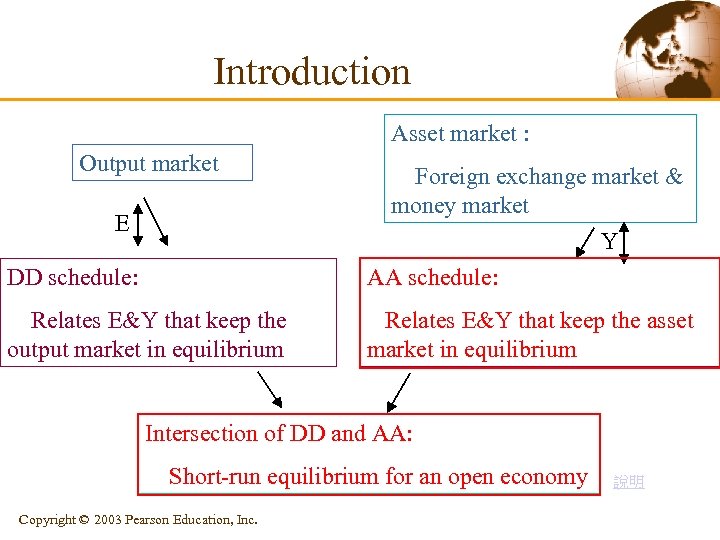 Introduction Asset market : Output market E Foreign exchange market & money market Y DD schedule: AA schedule: Relates E&Y that keep the output market in equilibrium Relates E&Y that keep the asset market in equilibrium Intersection of DD and AA: Short-run equilibrium for an open economy Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. 說明
Introduction Asset market : Output market E Foreign exchange market & money market Y DD schedule: AA schedule: Relates E&Y that keep the output market in equilibrium Relates E&Y that keep the asset market in equilibrium Intersection of DD and AA: Short-run equilibrium for an open economy Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. 說明
 Short-Run Equilibrium for an Open Economy: Putting the DD and AA Schedules Together § A short-run equilibrium for the economy as a whole must bring equilibrium simultaneously in the output and asset markets. • That is, it must lie on both DD and AA schedules. 25 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
Short-Run Equilibrium for an Open Economy: Putting the DD and AA Schedules Together § A short-run equilibrium for the economy as a whole must bring equilibrium simultaneously in the output and asset markets. • That is, it must lie on both DD and AA schedules. 25 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc.
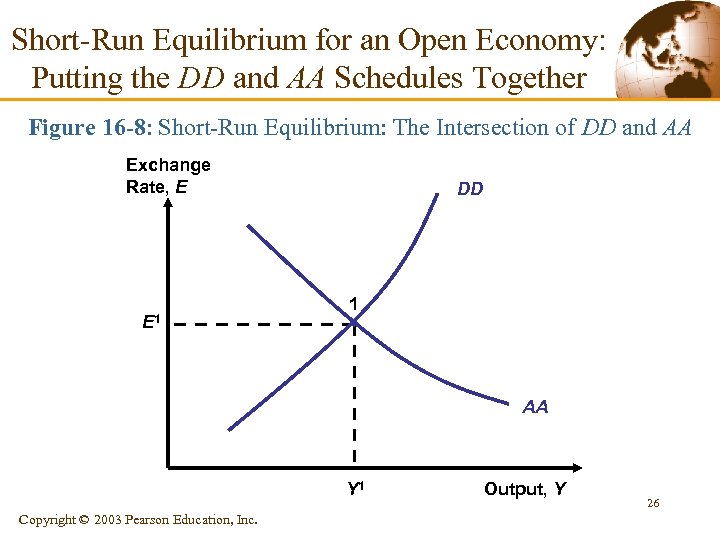 Short-Run Equilibrium for an Open Economy: Putting the DD and AA Schedules Together Figure 16 -8: Short-Run Equilibrium: The Intersection of DD and AA Exchange Rate, E E 1 DD 1 AA Y 1 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. Output, Y 26
Short-Run Equilibrium for an Open Economy: Putting the DD and AA Schedules Together Figure 16 -8: Short-Run Equilibrium: The Intersection of DD and AA Exchange Rate, E E 1 DD 1 AA Y 1 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. Output, Y 26


