9f30cabf9152ad16ec18f1ca4fe1c32d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

Introduction ASL® Mark Smalley ASL Bi. SL Foundation Application Services Library ASL® is a registered trademark of the ASL Bi. SL Foundation
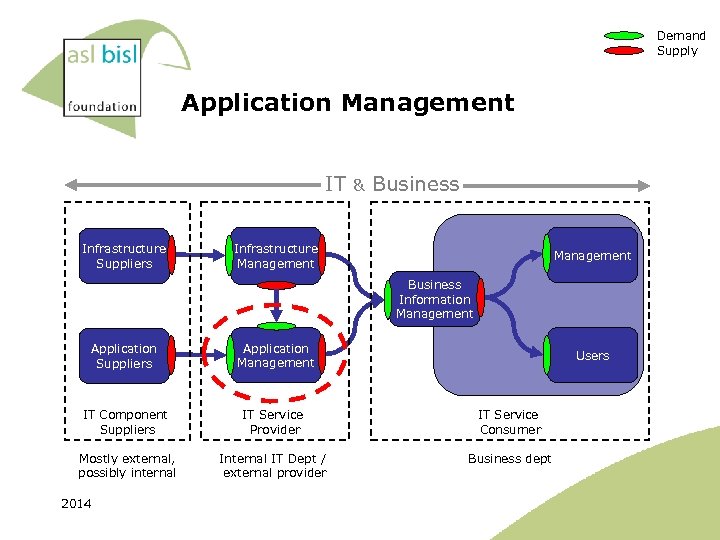
Demand Supply Application Management IT Infrastructure Suppliers & Business Infrastructure Management Business Information Management Application Suppliers Application Management IT Component Suppliers IT Service Provider IT Service Consumer Mostly external, possibly internal IT Dept / external provider Business dept 2014 Users

Pains IT Service Providers • • Delivery not under control Quality issues, outages and delays Misunderstandings with customers and IT partners Staff not motivated for Application Management Mugged by Application Development Complex application portfolio Business doesn’t know what it wants Business refuses to take responsibility 2014
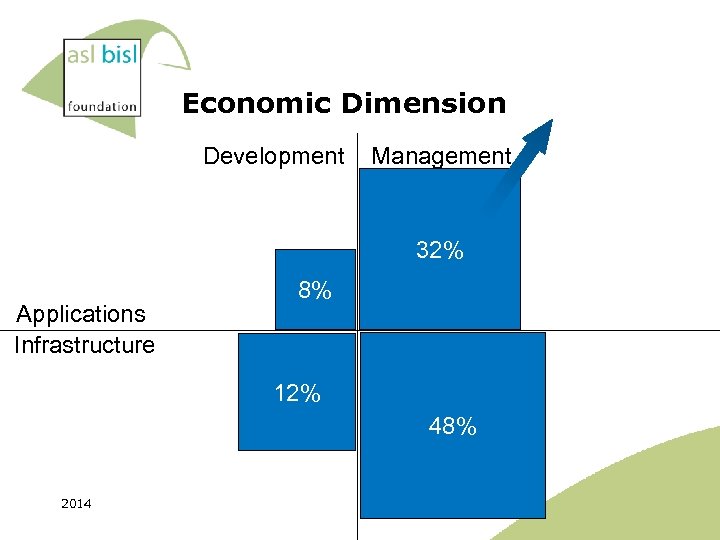
Economic Dimension Development Management 32% Applications Infrastructure 8% 12% 48% 2014
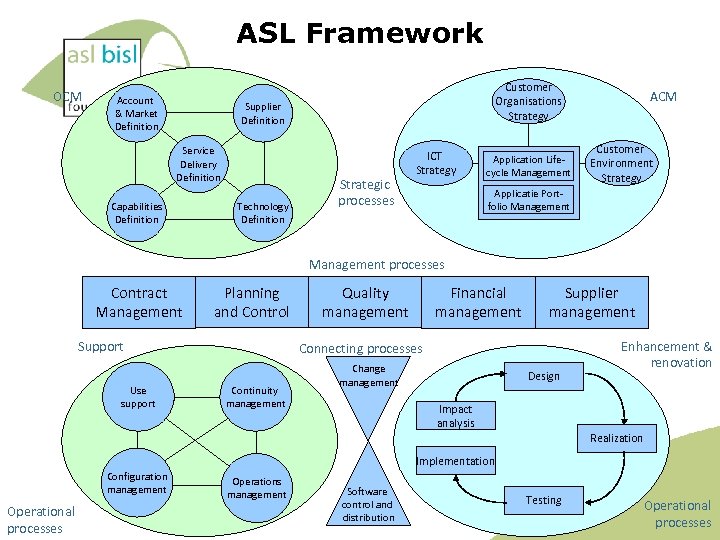
ASL Framework OCM Account & Market Definition Customer Organisations Strategy Supplier Definition Service Delivery Definition Capabilities Definition Technology Definition Strategic processes ICT Strategy Application Lifecycle Management ACM Customer Environment Strategy Applicatie Portfolio Management processes Contract Management Planning and Control Support Use support Quality management Financial management Supplier management Connecting processes Continuity management Change management Design Enhancement & renovation Impact analysis Realization Implementation Configuration management Operational processes Operations management Software control and distribution Testing Operational processes
ASL Framework 2010
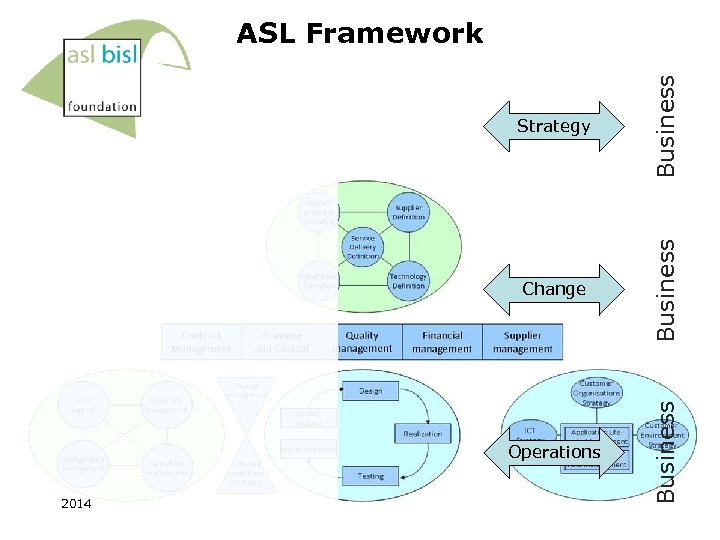
Change 2014 Business Operations Business Strategy Business ASL Framework
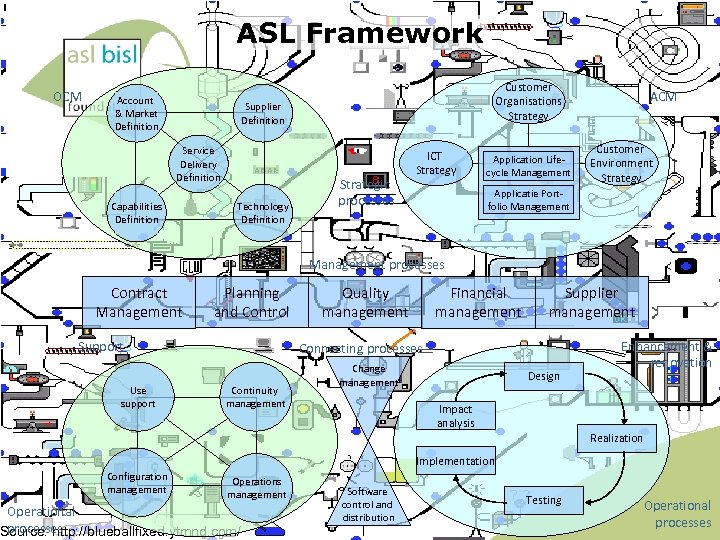
ASL Framework OCM Account & Market Definition Customer Organisations Strategy Supplier Definition Service Delivery Definition Capabilities Definition Technology Definition Strategic processes ICT Strategy Application Lifecycle Management ACM Customer Environment Strategy Applicatie Portfolio Management processes Contract Management Planning and Control Support Use support Quality management Financial management Supplier management Connecting processes Continuity management Change management Design Enhancement & renovation Impact analysis Realization Implementation Configuration management Operations management Operational processes Source: http: //blueballfixed. ytmnd. com/ Software control and distribution Testing Operational processes
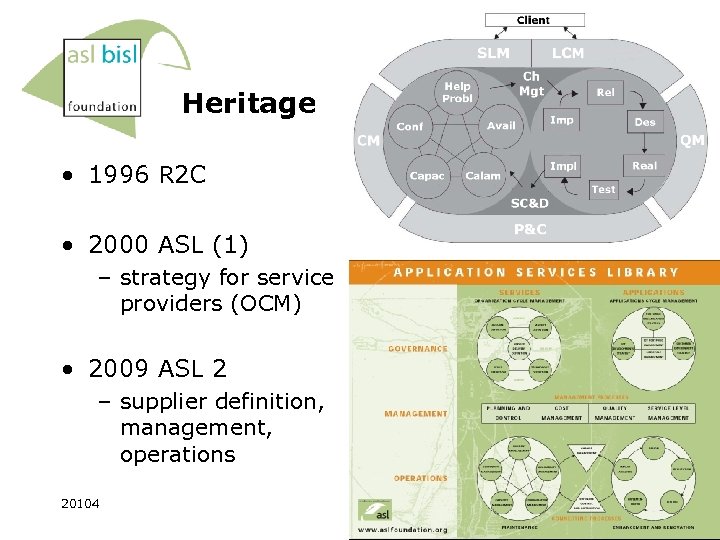
Heritage • 1996 R 2 C • 2000 ASL (1) – strategy for service providers (OCM) • 2009 ASL 2 – supplier definition, management, operations 20104
Underlying trends • Increased number of (standardized) application components • Increased number of AM providers • More diversification and specialization of AM providers Which position in the AM ecosystem? You can’t control the whole supply chain so just focus on the interfaces with the adjacent parties 2014
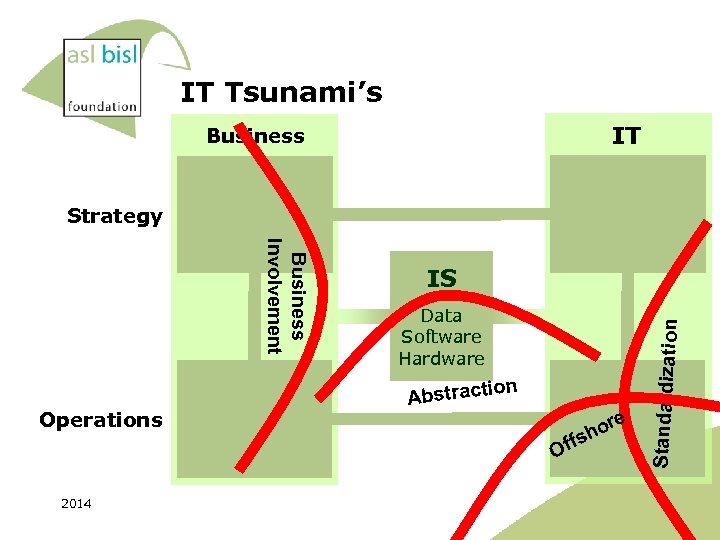
IT Tsunami’s IT Business Strategy Data Software Hardware on Operations Abstracti Of fs 2014 ore h Standardization Business Involvement IS
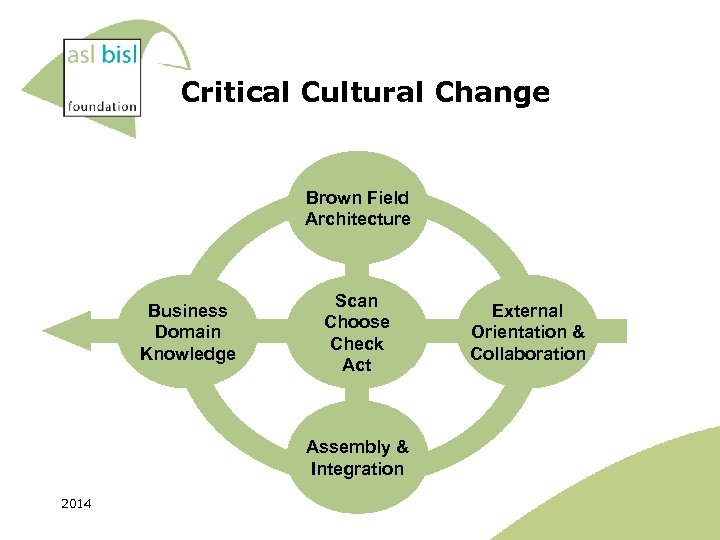
Critical Cultural Change Brown Field Architecture Business Domain Knowledge Scan Choose Check Act Assembly & Integration 2014 External Orientation & Collaboration
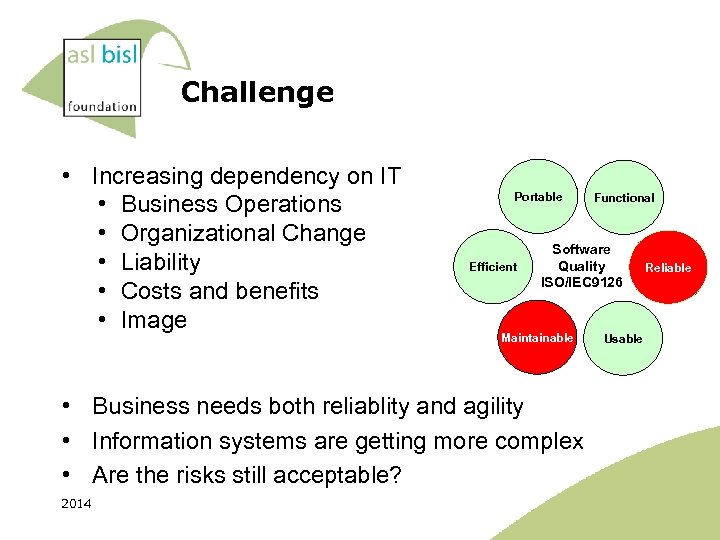
Challenge • Increasing dependency on IT • Business Operations • Organizational Change • Liability • Costs and benefits • Image Portable Efficient Software Quality ISO/IEC 9126 Maintainable • Business needs both reliablity and agility • Information systems are getting more complex • Are the risks still acceptable? 2014 Functional Usable Reliable
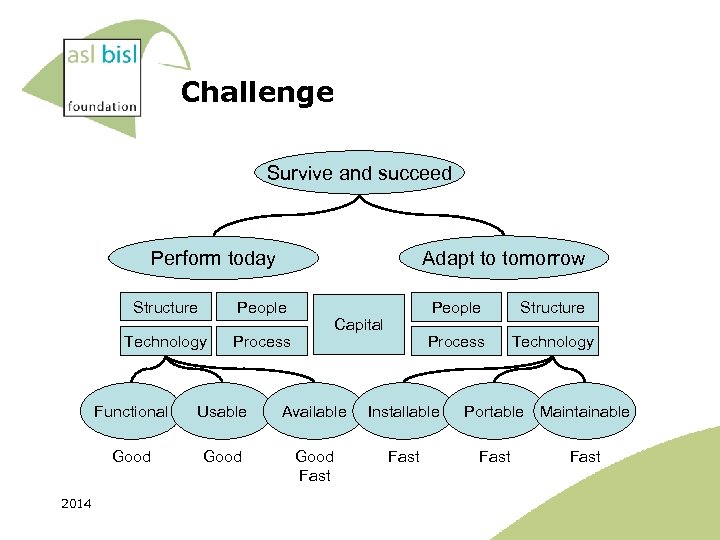
Challenge Survive and succeed Adapt to tomorrow Perform today Structure People Technology Process People Process Capital Structure Technology Functional Available Installable Good 2014 Usable Good Fast Portable Maintainable Fast
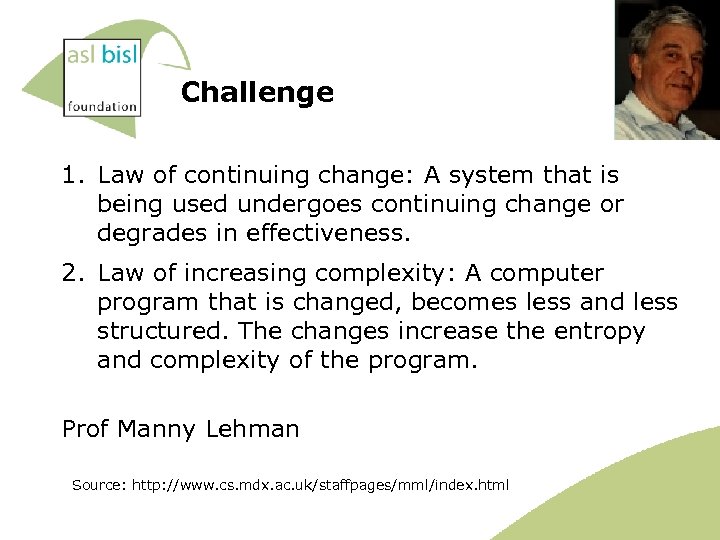
Challenge 1. Law of continuing change: A system that is being used undergoes continuing change or degrades in effectiveness. 2. Law of increasing complexity: A computer program that is changed, becomes less and less structured. The changes increase the entropy and complexity of the program. Prof Manny Lehman Source: http: //www. cs. mdx. ac. uk/staffpages/mml/index. html
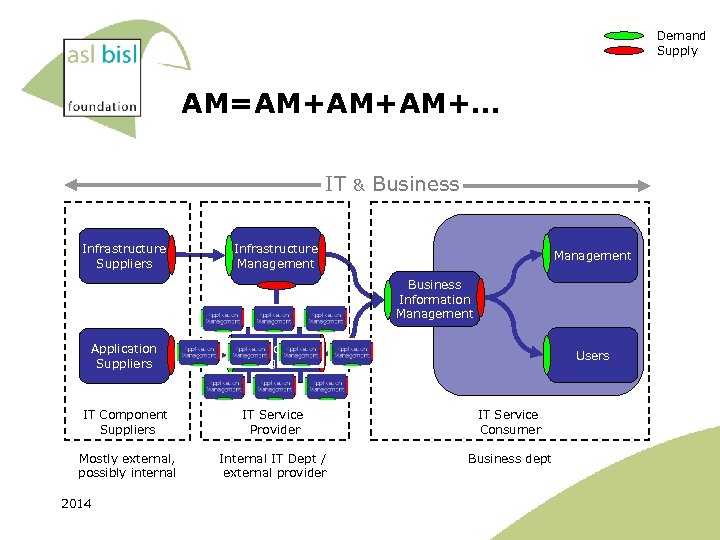
Demand Supply AM=AM+AM+AM+… IT Infrastructure Suppliers & Business Infrastructure Management Business Information Management Application Suppliers Application Management IT Component Suppliers IT Service Provider IT Service Consumer Mostly external, possibly internal IT Dept / external provider Business dept 2014 Users
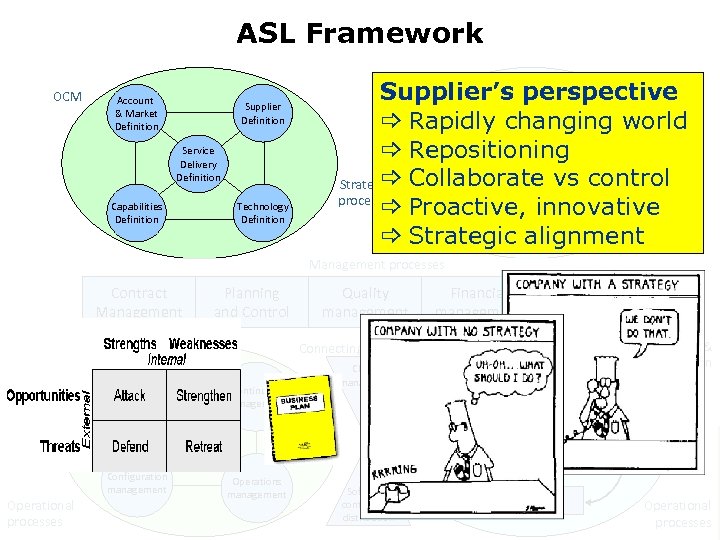
ASL Framework OCM Account & Market Definition Supplier Definition Service Delivery Definition Capabilities Definition Technology Definition Customer Supplier’s perspective ACM Organisations Strategy _ Rapidly changing world Business planning Customer _ Repositioning Environment ICT Application Lifethe AM Strategy for Management cycle _ Strategic Collaborate vs control Applicatie Portorganization processes folio Management _ Proactive, innovative _ Strategic alignment Management processes Contract Management Planning and Control Support Use support Quality management Financial management Supplier management Connecting processes Continuity management Change management Design Enhancement & renovation Impact analysis Realization Implementation 2010 Operational processes Configuration management Operations management Software control and distribution Testing Operational processes
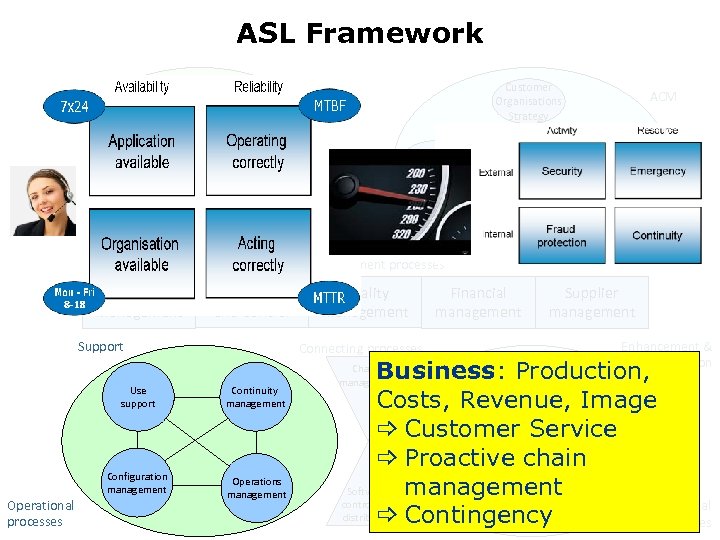
ASL Framework OCM Account & Market Definition Customer Organisations Strategy Supplier Definition Service Delivery Definition Capabilities Definition Technology Definition Strategic processes ICT Strategy Application Lifecycle Management ACM Customer Environment Strategy Applicatie Portfolio Management processes Contract Management Planning and Control Support Connecting processes Use support 2010 Operational processes Quality management Continuity management Configuration management Operations management Financial management Supplier management Enhancement & renovation Business: Production, Design Costs, Revenue, Image Impact analysis Keeping applications _ Customer Service Realization up and running Implementation _ Proactive chain management Software Testing control and Operational distribution Contingency _ processes Change management
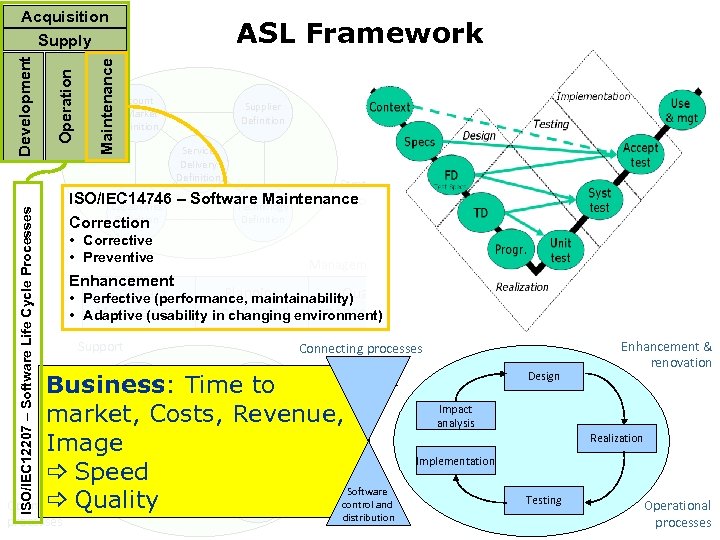
ISO/IEC 12207 – Software Life Cycle Processes ASL Framework Maintenance OCM Operation Development Acquisition Supply Account & Market Definition Customer Organisations Strategy Supplier Definition Service Delivery Definition Strategic ISO/IEC 14746 – Software Maintenance processes Capabilities Technology Definition Correction • Corrective • Preventive Customer Environment Strategy Management processes Enhancement Planning Quality Contract • Perfective (performance, maintainability) and Control management Management • Adaptive (usability in changing environment) Support Application Lifecycle Management Applicatie Portfolio Management Definition Financial management Supplier management Connecting processes Change management Business: Time to Use Continuity support management market, Costs, Revenue, Keeping applications Image up to date _ Speed Configuration Operations management Software management 2010 control and _ Operational. Quality processes ICT Strategy ACM distribution Design Enhancement & renovation Impact analysis Realization Implementation Testing Operational processes
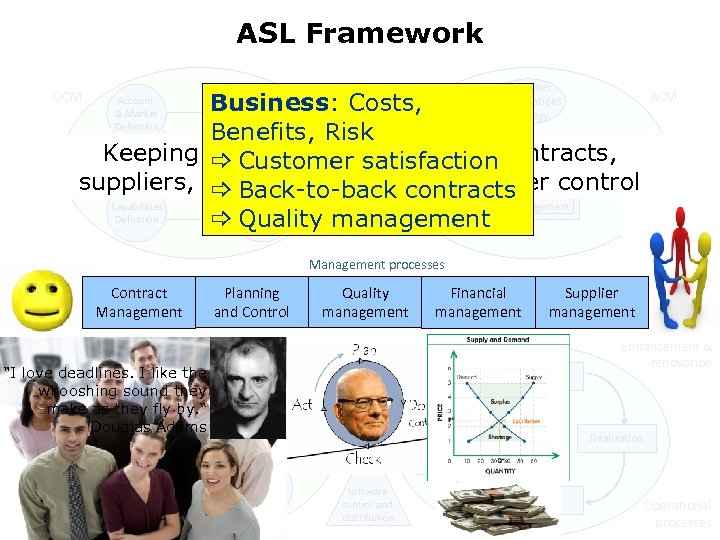
ASL Framework Customer Organisations Strategy ACM Supplier Business: Costs, Definition Benefits, Risk Customer Service ICT Keeping time, money, progress, Application Life- Environment contracts, Delivery _ Customer satisfaction Management Strategy cycle Definition Strategy Strategic suppliers, quality & expectations under control Applicatie _ Back-to-back contracts Portprocesses folio Management Capabilities Technology Definition _ Quality management OCM Account & Market Definition Management processes Contract Management Planning and Control Support "I love deadlines. I like the Use whooshing sound they support make as they fly by. “ Douglas Adams Quality management Financial management Supplier management Connecting processes Continuity management Change management Design Enhancement & renovation Impact analysis Realization Implementation 2010 Operational processes Configuration management Operations management Software control and distribution Testing Operational processes
Contracts Business 2014 IT
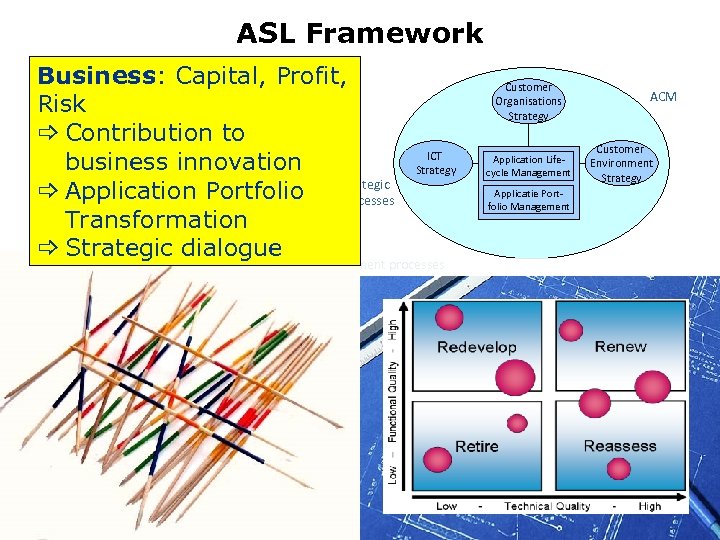
ASL Framework Business: Capital, Profit, OCM Account Supplier Risk & Market Definition Ensuring strategic _ Contribution to Service alignment of Delivery business Definition innovation Strategic business & IT _ Application Portfolio processes Capabilities Technology Definition Transformation _ Strategic dialogue Customer Organisations Strategy ICT Strategy Application Lifecycle Management ACM Customer Environment Strategy Applicatie Portfolio Management processes Contract Management Planning and Control Support Use support Quality management Financial management Supplier management Connecting processes Continuity management Change management Design Enhancement & renovation Impact analysis Realization Implementation 2010 Operational processes Configuration management Operations management Software control and distribution Testing Operational processes
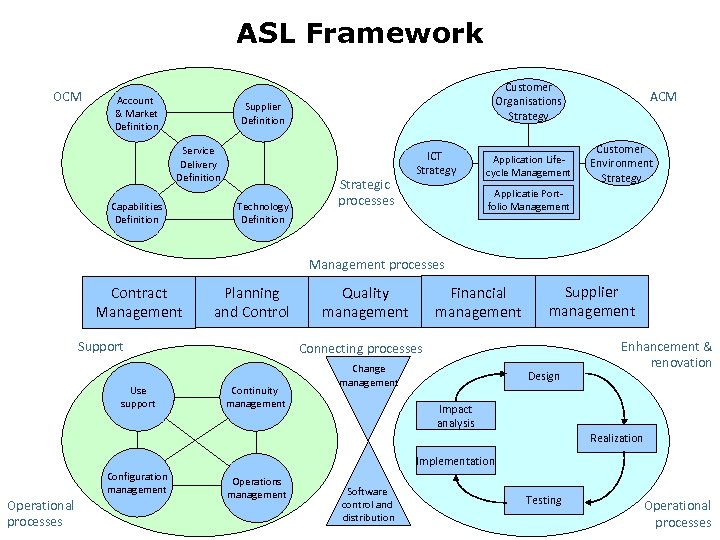
ASL Framework OCM Account & Market Definition Customer Organisations Strategy Supplier Definition Service Delivery Definition Capabilities Definition Technology Definition Strategic processes ICT Strategy Application Lifecycle Management ACM Customer Environment Strategy Applicatie Portfolio Management processes Contract Management Planning and Control Support Use support Financial management Quality management Supplier management Connecting processes Continuity management Change management Design Enhancement & renovation Impact analysis Realization Implementation 2010 Operational processes Configuration management Operations management Software control and distribution Testing Operational processes

Summary ASL • • • Organizations depend on applications Applications are getting more complex AM is also getting more complex AM is economically significant ASL offers guidance for AM organizations Operational, Management, Quality, Strategic 2010

ASL & ITIL®V 3 White Paper This presentation is based on a White Paper jointly commissioned by the OGC and the ASL Bi. SL Foundation, and authored by • Sharon Taylor (OGC), • Machteld Meijer and • Mark Smalley (ABF) The White Paper is available on • www. aslbislfoundation. org • www. best-management-practice. com • Best Management Practice stand (OGC, APMG and TSO) ITIL® is a registered trade mark of AXELOS Limited.
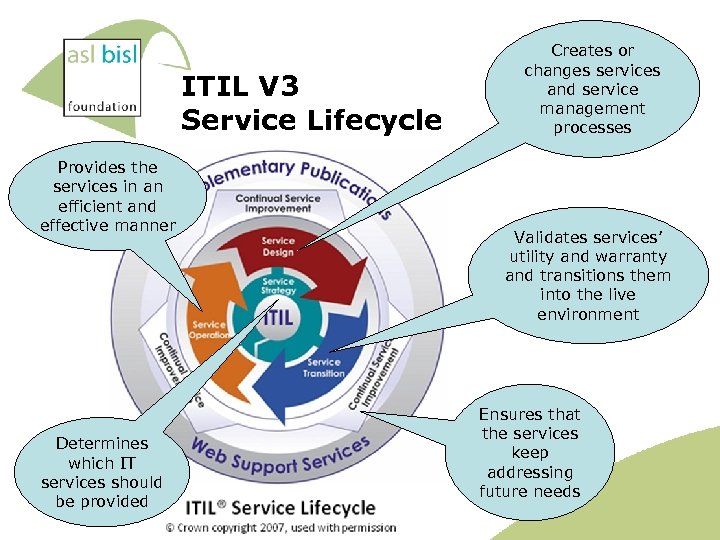
ITIL V 3 Service Lifecycle Provides the services in an efficient and effective manner Determines which IT services should be provided 2010 Creates or changes services and service management processes Validates services’ utility and warranty and transitions them into the live environment Ensures that the services keep addressing future needs
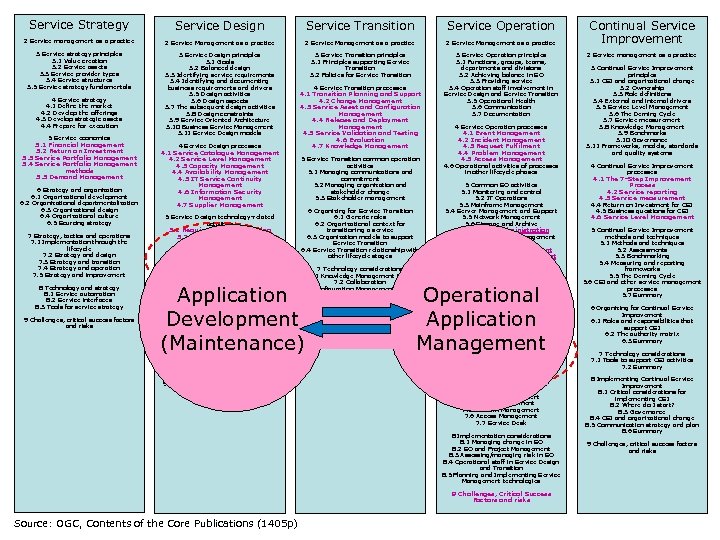
Service Strategy Service Design Service Transition Service Operation 2 Service management as a practice 2 Service Management as a practice 3 Service strategy principles 3. 1 Value creation 3. 2 Service assets 3. 3 Service provider types 3. 4 Service structures 3. 5 Service strategy fundamentals 3 Service Design principles 3. 1 Goals 3. 2 Balanced design 3. 3 Identifying service requirements 3. 4 Identifying and documenting business requirements and drivers 3. 5 Design activities 3. 6 Design aspects 3. 7 The subsequent design activities 3. 8 Design constraints 3. 9 Service Oriented Architecture 3. 10 Business Service Management 3. 11 Service Design models 3 Service Transition principles 3. 1 Principles supporting Service Transition 3. 2 Policies for Service Transition 3 Service Operation principles 3. 1 Functions, groups, teams, departments and divisions 3. 2 Achieving balance in SO 3. 3 Providing service 3. 4 Operation staff involvement in Service Design and Service Transition 3. 5 Operational Health 3. 6 Communication 3. 7 Documentation 4 Service strategy 4. 1 Define the market 4. 2 Develop the offerings 4. 3 Develop strategic assets 4. 4 Prepare for execution 5 Service economics 5. 1 Financial Management 5. 2 Return on Investment 5. 3 Service Portfolio Management 5. 4 Service Portfolio Management methods 5. 5 Demand Management 6 Strategy and organization 6. 1 Organizational development 6. 2 Organizational departmentalization 6. 3 Organizational design 6. 4 Organizational culture 6. 5 Sourcing strategy 7 Strategy, tactics and operations 7. 1 Implementation through the lifecycle 7. 2 Strategy and design 7. 3 Strategy and transition 7. 4 Strategy and operation 7. 5 Strategy and improvement 8 Technology and strategy 8. 1 Service automation 8. 2 Service interfaces 8. 3 Tools for service strategy 9 Challenges, critical success factors and risks 4 Service Design processes 4. 1 Service Catalogue Management 4. 2 Service Level Management 4. 3 Capacity Management 4. 4 Availability Management 4. 5 IT Service Continuity Management 4. 6 Information Security Management 4. 7 Supplier Management 5 Service Design technology-related activities 5. 1 Requirements engineering 5. 2 Data and Information Management 5. 3 Application Management 6 Organizing for Service Design 6. 1 Functional roles analysis 6. 2 Activity analysis 6. 3 Skills and attributes 6. 4 Roles and responsibilities 4 Service Transition processes 4. 1 Transition Planning and Support 4. 2 Change Management 4. 3 Service Asset and Configuration Management 4. 4 Release and Deployment Management 4. 5 Service Validation and Testing 4. 6 Evaluation 4. 7 Knowledge Management 5 Service Transition common operation activities 5. 1 Managing communications and commitment 5. 2 Managing organization and stakeholder change 5. 3 Stakeholder management 6 Organizing for Service Transition 6. 1 Generic roles 6. 2 Organizational context for transitioning a service 6. 3 Organization models to support Service Transition 6. 4 Service Transition relationship with other lifecycle stages 7 Technology considerations 7. 1 Knowledge Management tools 7. 2 Collaboration 7. 3 Configuration Management System Application Development (Maintenance) 7 Technology considerations 7. 1 Service Design tools 7. 2 Service Management tools 8 Implementing Service Design 8. 1 Business Impact Analysis 8. 2 Service Level Requirements 8. 3 Risks to the services and processes 8. 4 Implementing Service Design 8. 5 Measurement of Service Design 9 Challenges, Critical Success Factors and risks 8 Implementing Service Transition 8. 1 Stages of introducing Service Transition 9 Challenges, critical success factors and risks 4 Service Operation processes 4. 1 Event Management 4. 2 Incident Management 4. 3 Request Fulfilment 4. 4 Problem Management 4. 5 Access Management 4. 6 Operational activities of processes in other lifecycle phases 5 Common SO activities 5. 1 Monitoring and control 5. 2 IT Operations 5. 3 Mainframe Management 5. 4 Server Management and Support 5. 5 Network Management 5. 6 Storage and Archive 5. 7 Database Administration 5. 8 Directory Services Management 5. 9 Desktop Support 5. 10 Middleware Management 5. 11 Internet/Web Management 5. 12 Facilities and Data Centre Management 5. 13 Information Security Management and Service Operation 5. 14 Improvement of operational activities Operational Application Management 6 Organizing for Service Operation 6. 1 Functions 6. 2 Service Desk 6. 3 Technical Management 6. 4 IT Operations Management 6. 5 Application Management 6. 6 SO roles and responsibilities 6. 7 SO Organization Structures 7 Technology considerations 7. 1 Generic requirements 7. 2 Event Management 7. 3 Incident Management 7. 4 Request fulfilment 7. 5 Problem Management 7. 6 Access Management 7. 7 Service Desk 8 Implementation considerations 8. 1 Managing change in SO 8. 2 SO and Project Management 8. 3 Assessing/managing risk in SO 8. 4 Operational staff in Service Design and Transition 8. 5 Planning and Implementing Service Management technologies 2010 Source: OGC, Contents of the Core Publications (1405 p) 9 Challenges, Critical Success Factors and risks Continual Service Improvement 2 Service management as a practice 3 Continual Service Improvement principles 3. 1 CSI and organizational change 3. 2 Ownership 3. 3 Role definitions 3. 4 External and internal drivers 3. 5 Service Level Management 3. 6 The Deming Cycle 3. 7 Service measurement 3. 8 Knowledge Management 3. 9 Benchmarks 3. 10 Governance 3. 11 Frameworks, models, standards and quality systems 4 Continual Service Improvement processes 4. 1 The 7 -Step Improvement Process 4. 2 Service reporting 4. 3 Service measurement 4. 4 Return on Investment for CSI 4. 5 Business questions for CSI 4. 6 Service Level Management 5 Continual Service Improvement methods and techniques 5. 1 Methods and techniques 5. 2 Assessments 5. 3 Benchmarking 5. 4 Measuring and reporting frameworks 5. 5 The Deming Cycle 5. 6 CSI and other service management processes 5. 7 Summary 6 Organizing for Continual Service Improvement 6. 1 Roles and responsibilities that support CSI 6. 2 The authority matrix 6. 3 Summary 7 Technology considerations 7. 1 Tools to support CSI activities 7. 2 Summary 8 Implementing Continual Service Improvement 8. 1 Critical considerations for implementing CSI 8. 2 Where do I start? 8. 3 Governance 8. 4 CSI and organizational change 8. 5 Communication strategy and plan 8. 6 Summary 9 Challenges, critical success factors and risks

ITIL V 3 & Applications • Service and Service Lifecycle are dominant generic notions in ITIL V 3 • Applications are part of the service • There are packaged and customized applications • Development & maintenance of customized applications are part of IT Service Management • ITIL defines an Application Management Lifecycle 2014
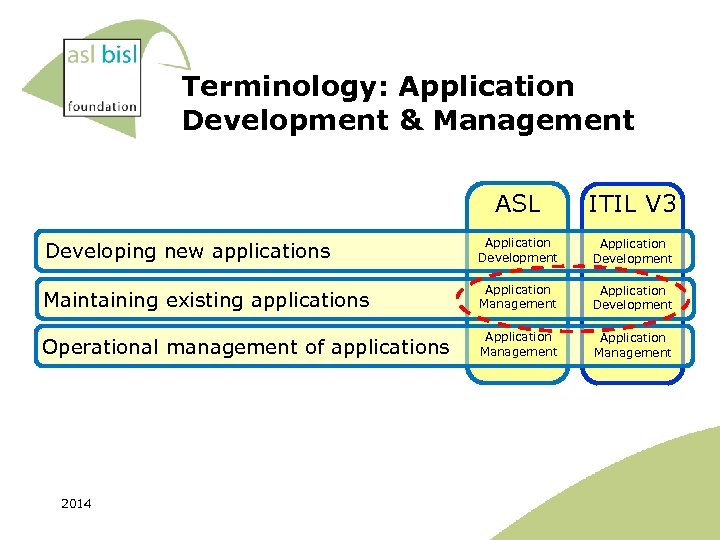
Terminology: Application Development & Management ASL ITIL V 3 Developing new applications Application Development Maintaining existing applications Application Management Application Development Operational management of applications Application Management 2014
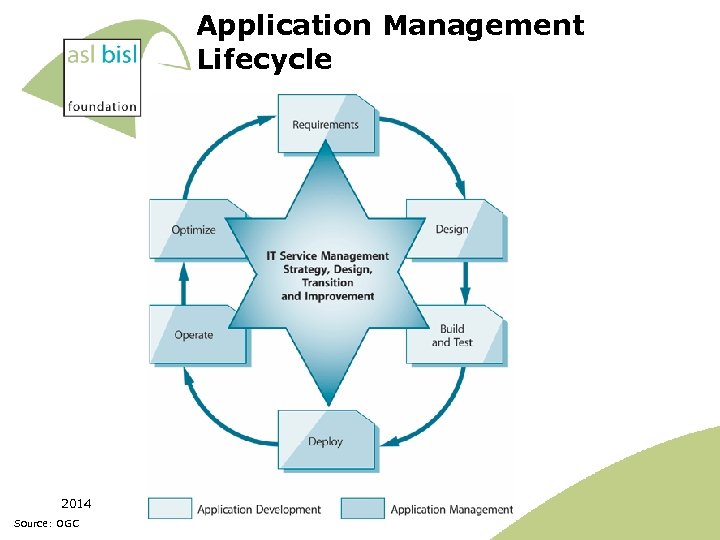
Application Management Lifecycle 2014 Source: OGC
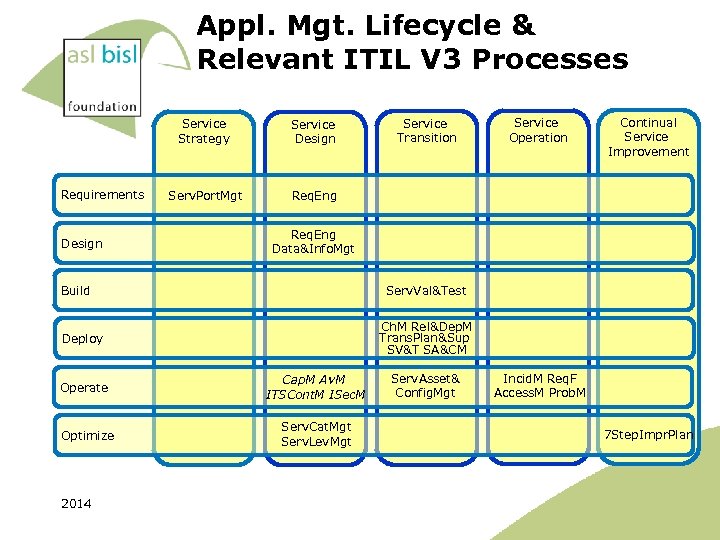
Appl. Mgt. Lifecycle & Relevant ITIL V 3 Processes Service Strategy Requirements Design Service Design Serv. Port. Mgt Service Operation Continual Service Improvement Req. Eng Data&Info. Mgt Serv. Val&Test Build Ch. M Rel&Dep. M Trans. Plan&Sup SV&T SA&CM Deploy Operate Cap. M Av. M ITSCont. M ISec. M Optimize Serv. Cat. Mgt Serv. Lev. Mgt 2014 Service Transition Serv. Asset& Config. Mgt Incid. M Req. F Access. M Prob. M 7 Step. Impr. Plan
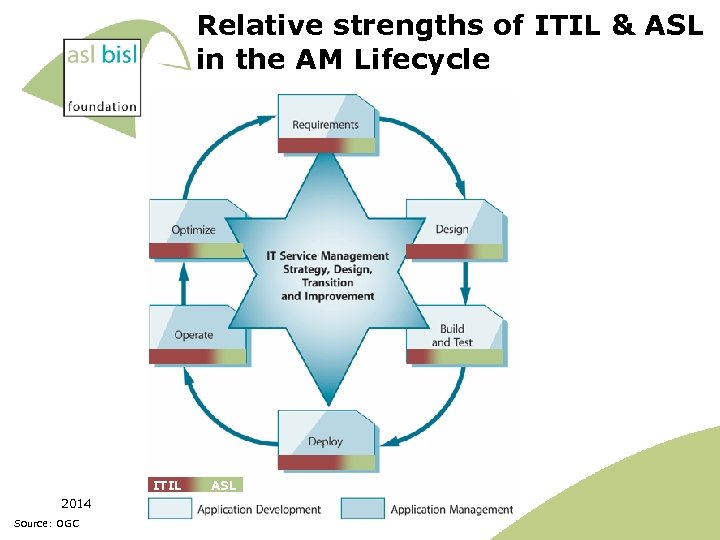
Relative strengths of ITIL & ASL in the AM Lifecycle ITIL 2014 Source: OGC ASL
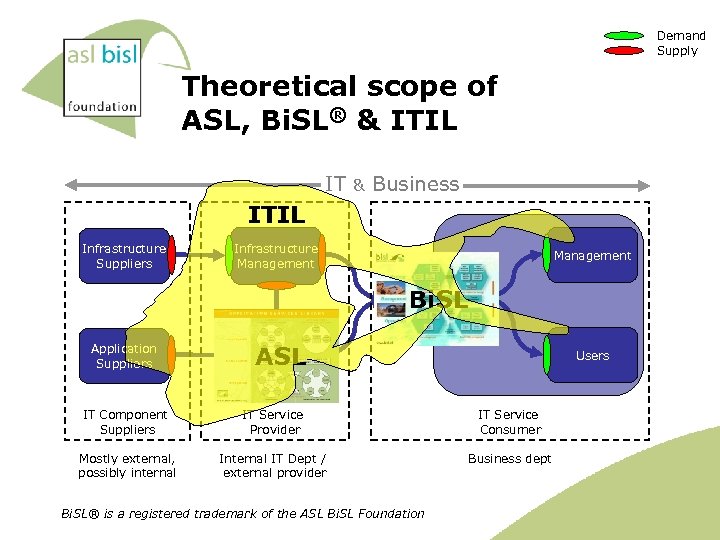
Demand Supply Theoretical scope of ASL, Bi. SL® & ITIL IT & Business ITIL Infrastructure Suppliers Infrastructure Management Business Information Management Bi. SL Application Suppliers Application Management IT Component Suppliers IT Service Provider IT Service Consumer Mostly external, possibly internal IT Dept / external provider Business dept ASL Bi. SL® is a registered trademark of the ASL Bi. SL Foundation Users
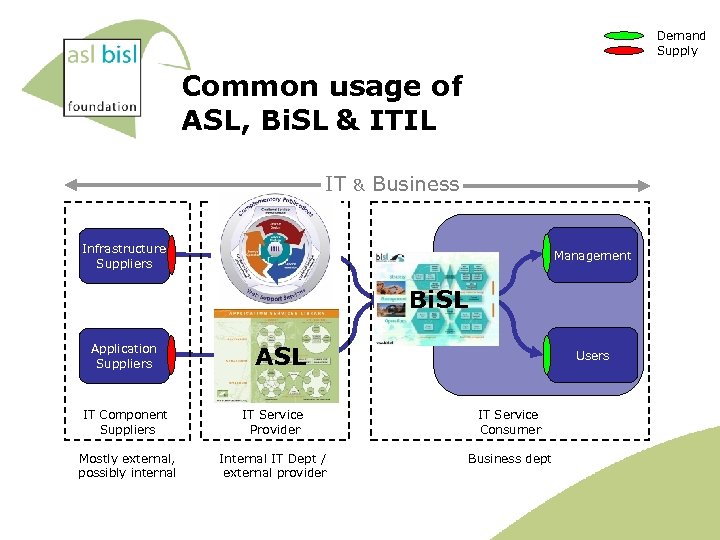
Demand Supply Common usage of ASL, Bi. SL & ITIL IT Infrastructure Suppliers & Business Infrastructure Management Business Information Management Bi. SL Application Suppliers Application Management IT Component Suppliers IT Service Provider IT Service Consumer Mostly external, possibly internal IT Dept / external provider Business dept ASL Users
Summary comparison ASL, Bi. SL & ITIL (1/2) ASL and ITIL V 3 • Similar domains, differing definitions • ITIL concentrates on IT services, ASL on application products and services • ASL gives more detailed guidance on – realization and testing of bespoke (additions to) applications – application strategy – planning & control and tactical level process quality (although less than CMMI) • ASL is dedicated to AM, more compact • ASL is written in AM language 2014
Summary comparison ASL, Bi. SL & ITIL (2/2) ITIL V 3 and V 2 • More coverage of AM in ITIL V 3 than V 2 • Generic guidance that is also useful for AM • ITIL helps to improve ‘service manageability’ Bi. SL and ITIL V 3 • Bi. SL provides guidance for demand not supply • ITIL also addresses demand, but from a supply perspective 2014
9f30cabf9152ad16ec18f1ca4fe1c32d.ppt