2cfe719986a5155ea992e6a9a116e242.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 INTRODUCTION § § AI - Artificial Intelligence What is AI? Problems with definition of AI Main difficulty: What is Intelligence?
INTRODUCTION § § AI - Artificial Intelligence What is AI? Problems with definition of AI Main difficulty: What is Intelligence?
 AI - Some Definitions § AI is the study of ideas which enable computers to do the things that make people seem intelligent (Winston’s book AI, 1 st edition, 1979) § But, what is human intelligence? Surely: (1) ability to reason (2) ability to learn (acquire and apply new knowledge) (3) ability to communicate ideas (. . . ) creativity, emotions, consciousness, . . . ?
AI - Some Definitions § AI is the study of ideas which enable computers to do the things that make people seem intelligent (Winston’s book AI, 1 st edition, 1979) § But, what is human intelligence? Surely: (1) ability to reason (2) ability to learn (acquire and apply new knowledge) (3) ability to communicate ideas (. . . ) creativity, emotions, consciousness, . . . ?
 AI, problems with definition § Definition of consciousness = ? § Searl: Chinese room argument § One’s ability of competent conversation in Chinese enough to say that he really knows Chinese? Understands, feels Chinese? § Chinese room argument too strong? It practically makes AI impossible § One view: “Who cares? ” (John Sowa)
AI, problems with definition § Definition of consciousness = ? § Searl: Chinese room argument § One’s ability of competent conversation in Chinese enough to say that he really knows Chinese? Understands, feels Chinese? § Chinese room argument too strong? It practically makes AI impossible § One view: “Who cares? ” (John Sowa)
 Winston’s updated definition of AI § AI is the study of the computations that make it possible to perceive, reason and act (Winston’s book on AI, 3 rd edition, 1992)
Winston’s updated definition of AI § AI is the study of the computations that make it possible to perceive, reason and act (Winston’s book on AI, 3 rd edition, 1992)
 GOALS OF AI (Winston 1992) § Engineering goal: Solve real-world problems using AI as an armamentarium of ideas about representing knowledge, using knowledge, and assembling systems § Scientific goal: Determine which ideas about representing knowledge, using knowledge and building systems explain various sorts of intelligence § AI helps us to become more intelligent.
GOALS OF AI (Winston 1992) § Engineering goal: Solve real-world problems using AI as an armamentarium of ideas about representing knowledge, using knowledge, and assembling systems § Scientific goal: Determine which ideas about representing knowledge, using knowledge and building systems explain various sorts of intelligence § AI helps us to become more intelligent.
 TURING TEST § When can we say that a computer is truly intelligent? § Alan Turing defined a test to decide whether a computer has achieved intelligence comparable to human: An observer, after 30 min of conversation, cannot distinguish intelligent computer from a human
TURING TEST § When can we say that a computer is truly intelligent? § Alan Turing defined a test to decide whether a computer has achieved intelligence comparable to human: An observer, after 30 min of conversation, cannot distinguish intelligent computer from a human
 A definition of AI with reference to Turing test § AI is the enterprise of constructing a physical symbol system that can reliably pass the Turing test (M. Ginsberg, Essential of Artificial Intelligence, Morgan Kaufmann 1993) Reference to logic
A definition of AI with reference to Turing test § AI is the enterprise of constructing a physical symbol system that can reliably pass the Turing test (M. Ginsberg, Essential of Artificial Intelligence, Morgan Kaufmann 1993) Reference to logic
 STRONG vs. WEAK AI § Mainly topic of philosophical discussion (Searl, Penrose, . . . ), not of so much interest to AI practitioners § What is strong AI? § Ginsberg’s definition of AI expresses the spirit of strong AI by referencing logic
STRONG vs. WEAK AI § Mainly topic of philosophical discussion (Searl, Penrose, . . . ), not of so much interest to AI practitioners § What is strong AI? § Ginsberg’s definition of AI expresses the spirit of strong AI by referencing logic
 Strong vs. Weak AI, comments by Donald Michie § Spirit of strong AI: By sufficiency of “logic crunching” we can program computers to out-think humans. § Spirit of weak AI: Humans don’t think logically anyway; so why not try neural nets, ultra parallelism, or accept that mechanising intelligence is impossible.
Strong vs. Weak AI, comments by Donald Michie § Spirit of strong AI: By sufficiency of “logic crunching” we can program computers to out-think humans. § Spirit of weak AI: Humans don’t think logically anyway; so why not try neural nets, ultra parallelism, or accept that mechanising intelligence is impossible.
 Strong vs. Weak AI, comments by Donald Michie, ctd. § Topics missed by “strong AI”: “visual thinking”, sub-cognitive mental skills, explanation as confabulation § “. . . both sides of this debate may find that their artillery is being wasted on positions that are not so much untenable as abandoned”.
Strong vs. Weak AI, comments by Donald Michie, ctd. § Topics missed by “strong AI”: “visual thinking”, sub-cognitive mental skills, explanation as confabulation § “. . . both sides of this debate may find that their artillery is being wasted on positions that are not so much untenable as abandoned”.
 AREAS OF AI § § § § § Problem solving and search Means-ends planning Knowledge representation Reasoning, inference Knowledge engineering Common sense reasoning Qualitative reasoning, naive physics Machine learning Data mining, knowledge discovery in data bases Neural networks
AREAS OF AI § § § § § Problem solving and search Means-ends planning Knowledge representation Reasoning, inference Knowledge engineering Common sense reasoning Qualitative reasoning, naive physics Machine learning Data mining, knowledge discovery in data bases Neural networks
 AREAS OF AI, cont. § § Natural language understanding Computer vision Robotics Evolutionary programming: genetic algorithms genetic programming artificial life § Simulated annealing
AREAS OF AI, cont. § § Natural language understanding Computer vision Robotics Evolutionary programming: genetic algorithms genetic programming artificial life § Simulated annealing
 EXAMPLE APPLICATIONS OF AI § Planning and search: production planning, scheduling, resource allocation, logistics § Machine learning: medical diagnosis in various medical domains. Diagnostic accuracy better than physicians’. § Synthesis of new scientific theories from measured data: automated construction of genetic network theories from genetic experimental data
EXAMPLE APPLICATIONS OF AI § Planning and search: production planning, scheduling, resource allocation, logistics § Machine learning: medical diagnosis in various medical domains. Diagnostic accuracy better than physicians’. § Synthesis of new scientific theories from measured data: automated construction of genetic network theories from genetic experimental data
 Breast Cancer Recurrence Degree of Malig <3 Tumor Size < 15 >= 3 Involved Nodes >= 15 no rec 125 recurr 39 Age <3 no rec 30 recurr 18 >= 3 recurr 27 no_rec 10 >45 no rec 4 recurr 1 no rec 32 recurr 0 Tree induced by Assistant Professional Interesting: Predictive accuracy of this tree better than medical specialists
Breast Cancer Recurrence Degree of Malig <3 Tumor Size < 15 >= 3 Involved Nodes >= 15 no rec 125 recurr 39 Age <3 no rec 30 recurr 18 >= 3 recurr 27 no_rec 10 >45 no rec 4 recurr 1 no rec 32 recurr 0 Tree induced by Assistant Professional Interesting: Predictive accuracy of this tree better than medical specialists
 PREDICTIVE ACCURACY § Accuracy : probability of correct classification of a randomly chosen new object
PREDICTIVE ACCURACY § Accuracy : probability of correct classification of a randomly chosen new object
 SOME ACCURACY RESULTS Classifier Primary Tumour Breast Cancer Thyroid Rheumatology Naive Bayes 49% 78% 70% 67% Decision tree 44% 77% 73% 61% Physician 42% 64% 56%
SOME ACCURACY RESULTS Classifier Primary Tumour Breast Cancer Thyroid Rheumatology Naive Bayes 49% 78% 70% 67% Decision tree 44% 77% 73% 61% Physician 42% 64% 56%
 APPLICATION OF AI IN GENETICS § Gene. Path, a system that helps biologists in functional genomics research § Collaboration between: Ljubljana University, Faculty of Computer and Info. Sc. (Zupan, Demšar, Juvan, Curk, Bratko) Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas (Kuspa, Shaulsky, Halter)
APPLICATION OF AI IN GENETICS § Gene. Path, a system that helps biologists in functional genomics research § Collaboration between: Ljubljana University, Faculty of Computer and Info. Sc. (Zupan, Demšar, Juvan, Curk, Bratko) Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas (Kuspa, Shaulsky, Halter)
 FUNCTIONAL GENOMICS § Determining gene function through genetic experiments: - What is the role of each gene in a genome? - How do the genes interact? - How do they influence the phenotype? § One way of modelling these relations: genetic networks
FUNCTIONAL GENOMICS § Determining gene function through genetic experiments: - What is the role of each gene in a genome? - How do the genes interact? - How do they influence the phenotype? § One way of modelling these relations: genetic networks
 DICTYOSTELIUM § A simple, but very interesting organism § A social amoeba: Can exist as single cell or multi cell organism § Has been attracting biologists for long § A topic of current research in functional genomics § Also used in this study
DICTYOSTELIUM § A simple, but very interesting organism § A social amoeba: Can exist as single cell or multi cell organism § Has been attracting biologists for long § A topic of current research in functional genomics § Also used in this study
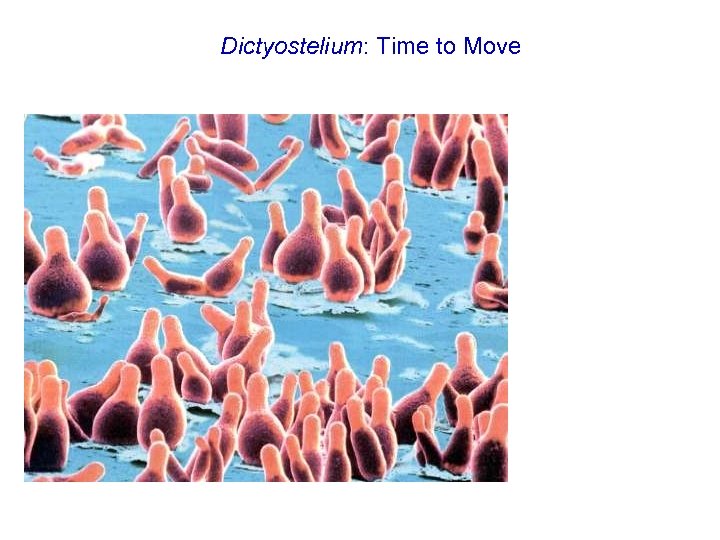 Dictyostelium: Time to Move When food is cleaned, Dictyostelium get together and converge in mound. Development: the mounds stretch into slugs, which topple over and crawl away.
Dictyostelium: Time to Move When food is cleaned, Dictyostelium get together and converge in mound. Development: the mounds stretch into slugs, which topple over and crawl away.
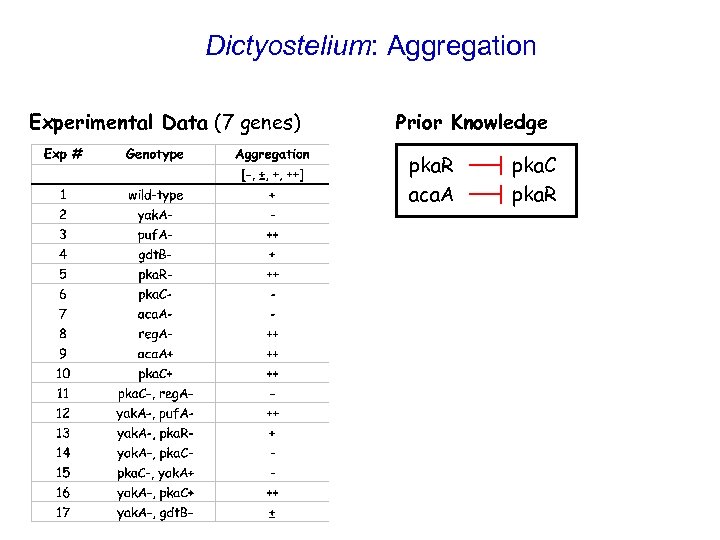 Dictyostelium: Aggregation Experimental Data (7 genes) Prior Knowledge pka. R aca. A pka. C pka. R
Dictyostelium: Aggregation Experimental Data (7 genes) Prior Knowledge pka. R aca. A pka. C pka. R
 Resulting Models for Dictyostelium yak. A puf. A reg. A pka. R pka. C aggregation yak. A aca. A reg. A aca. A yak. A reg. A puf. A aca. A puf. A pka. R pka. C aggregation yak. A puf. A aca. A pka. R reg. A pka. C aggregation
Resulting Models for Dictyostelium yak. A puf. A reg. A pka. R pka. C aggregation yak. A aca. A reg. A aca. A yak. A reg. A puf. A aca. A puf. A pka. R pka. C aggregation yak. A puf. A aca. A pka. R reg. A pka. C aggregation
 EXAMPLE APPLICATIONS OF AI, ctd. § Machine learning: synthesis of new knowledge from measured data - ecological modelling (Lagoon of Venice, Lake Glumsoe, Lake Bled) § Learning to predict river water quality from organisms living in river § Learning to predict deer population in a forest § Predicting biodegradability of chemicals
EXAMPLE APPLICATIONS OF AI, ctd. § Machine learning: synthesis of new knowledge from measured data - ecological modelling (Lagoon of Venice, Lake Glumsoe, Lake Bled) § Learning to predict river water quality from organisms living in river § Learning to predict deer population in a forest § Predicting biodegradability of chemicals
 EXAMPLE APPLICATIONS: Learning to predict weather § E. g. learn to predict temperature at noon next day § Students project 2001/2 (Žabkar, Vrabec, Indihar), data from Environment Agency § Take measured weather data and Aladin’s predictions, improve on Aladin’s prediction
EXAMPLE APPLICATIONS: Learning to predict weather § E. g. learn to predict temperature at noon next day § Students project 2001/2 (Žabkar, Vrabec, Indihar), data from Environment Agency § Take measured weather data and Aladin’s predictions, improve on Aladin’s prediction
 PREDICTION OF OZONE CONCENTRATION § Learn with ML to predict ozone concentration on the basis of measured air and weather parameters (Ljubljana, Nova Gorica; Zabkar et al. 2004) § Meteorological Agency required to issue these forecasts by European regulations
PREDICTION OF OZONE CONCENTRATION § Learn with ML to predict ozone concentration on the basis of measured air and weather parameters (Ljubljana, Nova Gorica; Zabkar et al. 2004) § Meteorological Agency required to issue these forecasts by European regulations
 SAVINJA NAPOVEDOVANJE POPLAV § Hudournik – težko napovedovati pretok, še posebno ekstremne vrednosti, ki pomenijo poplave => cilj: izboljšati napovedni model § Trenutno je v uporabi numerični model HBV, ki ne daje dobrih rezultatov (hidrologi: pomemben vhod so napovedi padavin, ki pa so slabe!) § HBV: aplikacija splošnega modela na konkretno domeno § Naš pristop: Uporaba podatkov določene domene za induciranje specifičnega modela
SAVINJA NAPOVEDOVANJE POPLAV § Hudournik – težko napovedovati pretok, še posebno ekstremne vrednosti, ki pomenijo poplave => cilj: izboljšati napovedni model § Trenutno je v uporabi numerični model HBV, ki ne daje dobrih rezultatov (hidrologi: pomemben vhod so napovedi padavin, ki pa so slabe!) § HBV: aplikacija splošnega modela na konkretno domeno § Naš pristop: Uporaba podatkov določene domene za induciranje specifičnega modela
 EXAMPLE APPLICATIONS OF AI, ctd. § Machine learning in mechanical engineering: § § prediction of surface roughness from acoustic data in machining Machine learning in textile industry: prediction of mechanical properties of thread from material mixture used in weaving Learning to predict aesthetic appearance of clothes Behavioural cloning: Reconstructing sub-cognitive skills from behaviour data Data mining in marketing: determining target population for advertisement
EXAMPLE APPLICATIONS OF AI, ctd. § Machine learning in mechanical engineering: § § prediction of surface roughness from acoustic data in machining Machine learning in textile industry: prediction of mechanical properties of thread from material mixture used in weaving Learning to predict aesthetic appearance of clothes Behavioural cloning: Reconstructing sub-cognitive skills from behaviour data Data mining in marketing: determining target population for advertisement
 Vizualizacija podatkov v sistemu za strojno učenje ORANGE § Nova vizualizacijska metodo, imenovana Viz. Rank, iz podatkov avtomatsko poišče zanimive točkovne geometrijske vizualizacije. § Vizrank za ocenjevanje vizualizacij in hevristično preiskovanje prostora možnih vizualizacij uporablja metode strojnega učenja. § Aplikacije metode Viz. Rank na področju bioinformatike (članek v reviji Bioinformatics, IF=6. 7, januar 2005) ter analize genskih izrazov rakastih tkiv (v 2005 dva prispevka s tega področja na odličnih konferencah AIME in KDD, članek za revijo je v pripravi).
Vizualizacija podatkov v sistemu za strojno učenje ORANGE § Nova vizualizacijska metodo, imenovana Viz. Rank, iz podatkov avtomatsko poišče zanimive točkovne geometrijske vizualizacije. § Vizrank za ocenjevanje vizualizacij in hevristično preiskovanje prostora možnih vizualizacij uporablja metode strojnega učenja. § Aplikacije metode Viz. Rank na področju bioinformatike (članek v reviji Bioinformatics, IF=6. 7, januar 2005) ter analize genskih izrazov rakastih tkiv (v 2005 dva prispevka s tega področja na odličnih konferencah AIME in KDD, članek za revijo je v pripravi).
 Levkemija; “naključni” scatterplot
Levkemija; “naključni” scatterplot
 Levkemija, Vizrank scatterplot
Levkemija, Vizrank scatterplot
 Genetski algoritem za optimizacijo procesnih parametrov § Optimiranje parametrov v ulivanju jekla. Za več primerov jekel v železarnah Acroni in Ruukki Steel (Finska) smo izboljšali nastavitve procesnih parametrov, predvsem pretokov hladil.
Genetski algoritem za optimizacijo procesnih parametrov § Optimiranje parametrov v ulivanju jekla. Za več primerov jekel v železarnah Acroni in Ruukki Steel (Finska) smo izboljšali nastavitve procesnih parametrov, predvsem pretokov hladil.
 OZON NAPOVEDOVANJE KONCENTRACIJE § Evropski predpisi: obvezno napovedovanje koncentracije ozona § Napovedovanje koncentracije ozona v LJ in NG (Q 2 učenje) in model za razlago procesov nastajanja O 3. § Izhodišče: • zapleteni meteorološki in kemijski procesi pri nastajanju ozona • ni napovednega modela • zelo pomembni lokalni dejavniki
OZON NAPOVEDOVANJE KONCENTRACIJE § Evropski predpisi: obvezno napovedovanje koncentracije ozona § Napovedovanje koncentracije ozona v LJ in NG (Q 2 učenje) in model za razlago procesov nastajanja O 3. § Izhodišče: • zapleteni meteorološki in kemijski procesi pri nastajanju ozona • ni napovednega modela • zelo pomembni lokalni dejavniki
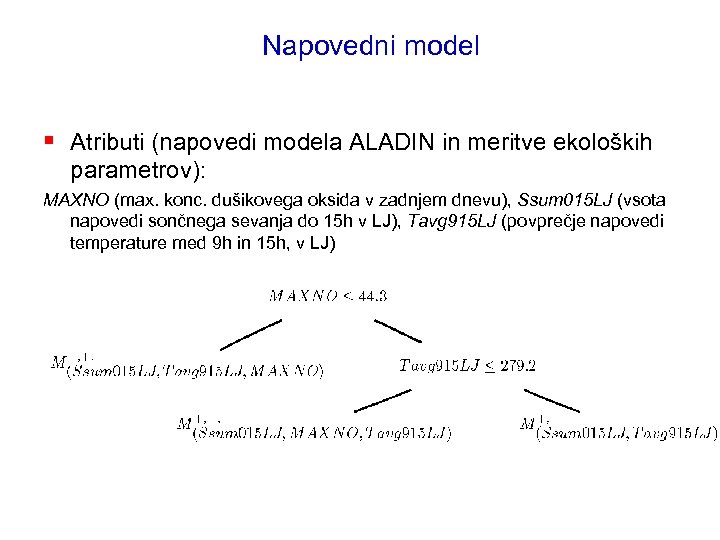 Napovedni model § Atributi (napovedi modela ALADIN in meritve ekoloških parametrov): MAXNO (max. konc. dušikovega oksida v zadnjem dnevu), Ssum 015 LJ (vsota napovedi sončnega sevanja do 15 h v LJ), Tavg 915 LJ (povprečje napovedi temperature med 9 h in 15 h, v LJ)
Napovedni model § Atributi (napovedi modela ALADIN in meritve ekoloških parametrov): MAXNO (max. konc. dušikovega oksida v zadnjem dnevu), Ssum 015 LJ (vsota napovedi sončnega sevanja do 15 h v LJ), Tavg 915 LJ (povprečje napovedi temperature med 9 h in 15 h, v LJ)
 Nekateri evropski projekti v Laboratoriu za umetno inteligenco FRI § ASPIC, Argumentation Services Platform with Integrated Components § XMEDIA, Knowledge Sharing and Reuse across Media § XPERO, Learning by Experimentation
Nekateri evropski projekti v Laboratoriu za umetno inteligenco FRI § ASPIC, Argumentation Services Platform with Integrated Components § XMEDIA, Knowledge Sharing and Reuse across Media § XPERO, Learning by Experimentation
 XMEDIA Consortium § § § § University of Sheffield, Shef, Prof. Fabio Ciravegna, Dr. Mark Stevenson, Dr. Daniela Petrelli 2 Centre for Research and Technology, Hellas, CERTH Dr. Yannis Avrithis Cogn. IT a. s Cogn. IT Dr. Robert Engels Instituto Trentino Di Cultura ITC-Irst Dott. Alberto Lavelli Universitaet Koblenz-Landau KOB Prof. Steffen Staab Laboratoire Bordelais Recherche en Informatique, Labri, Prof. Jenny Benois-Pineau Ontoprise Gmb. H Intelligente, Losungen fur das Wissensmanagement, Ontoprise Prof. Juergen Angele Open University, OU, Prof. Enrico Motta Quinary Spa, Quinary, Dott. Luca Gilardoni Rolls Royce plc, RR, Dr. Ian Jennions University of Freiburg, UFrei, Prof. Lars Schmidt-Thieme Universitat Karlsruhe, UKarl, Prof. Rudi Studer, Mr. Philip Cimiano Faculty of Computer and Information Science, University of Ljubljana, UL Prof. Ivan Bratko Centro Ricerche Fiat, Societa Consortile per Azior, C. R. F. , Fiat, Ing. Marialuisa Sanseverino Solcara Limited Solcara, Mr. Ray Jackson
XMEDIA Consortium § § § § University of Sheffield, Shef, Prof. Fabio Ciravegna, Dr. Mark Stevenson, Dr. Daniela Petrelli 2 Centre for Research and Technology, Hellas, CERTH Dr. Yannis Avrithis Cogn. IT a. s Cogn. IT Dr. Robert Engels Instituto Trentino Di Cultura ITC-Irst Dott. Alberto Lavelli Universitaet Koblenz-Landau KOB Prof. Steffen Staab Laboratoire Bordelais Recherche en Informatique, Labri, Prof. Jenny Benois-Pineau Ontoprise Gmb. H Intelligente, Losungen fur das Wissensmanagement, Ontoprise Prof. Juergen Angele Open University, OU, Prof. Enrico Motta Quinary Spa, Quinary, Dott. Luca Gilardoni Rolls Royce plc, RR, Dr. Ian Jennions University of Freiburg, UFrei, Prof. Lars Schmidt-Thieme Universitat Karlsruhe, UKarl, Prof. Rudi Studer, Mr. Philip Cimiano Faculty of Computer and Information Science, University of Ljubljana, UL Prof. Ivan Bratko Centro Ricerche Fiat, Societa Consortile per Azior, C. R. F. , Fiat, Ing. Marialuisa Sanseverino Solcara Limited Solcara, Mr. Ray Jackson
 XPERO: Robot gaining “insights” § A definition of insight in the spirit of XPERO: an insight is a new piece of knowledge that makes it possible to simplify the current agent’s theory about its environment § Examples of insights are discoveries of notions like: • absolute coordinate system, • arithmetic operations, • notion of gravity, • notion of support between objects • . . .
XPERO: Robot gaining “insights” § A definition of insight in the spirit of XPERO: an insight is a new piece of knowledge that makes it possible to simplify the current agent’s theory about its environment § Examples of insights are discoveries of notions like: • absolute coordinate system, • arithmetic operations, • notion of gravity, • notion of support between objects • . . .


