fa2f6420706eeab2421dfc0bcf362daa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
Introducing the Semantic Web Professor James Hendler http: //www. cs. umd. edu/~hendler Co-Director, Maryland Information and Network Dynamics Laboratory Semantic Web Agents Project http: //www. mindswap. org

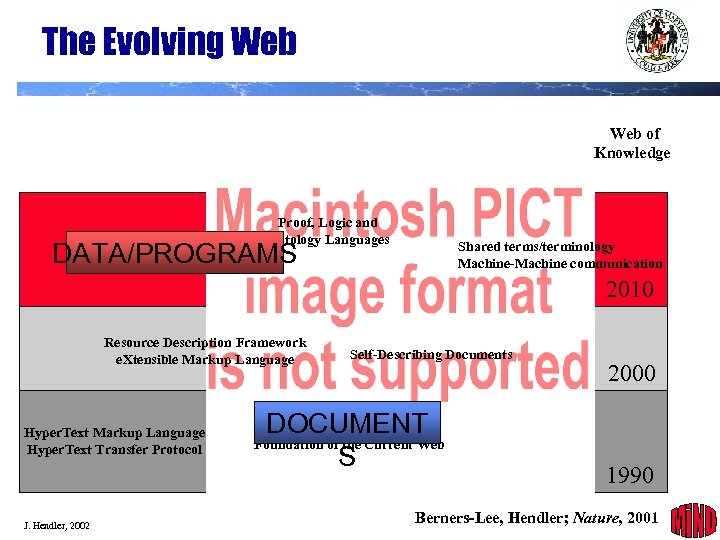
The Evolving Web of Knowledge Proof, Logic and Ontology Languages DATA/PROGRAMS Shared terms/terminology Machine-Machine communication 2010 Resource Description Framework e. Xtensible Markup Language Hyper. Text Transfer Protocol J. Hendler, 2002 Self-Describing Documents DOCUMENT Foundation of the Current Web S 2000 1990 Berners-Lee, Hendler; Nature, 2001 3
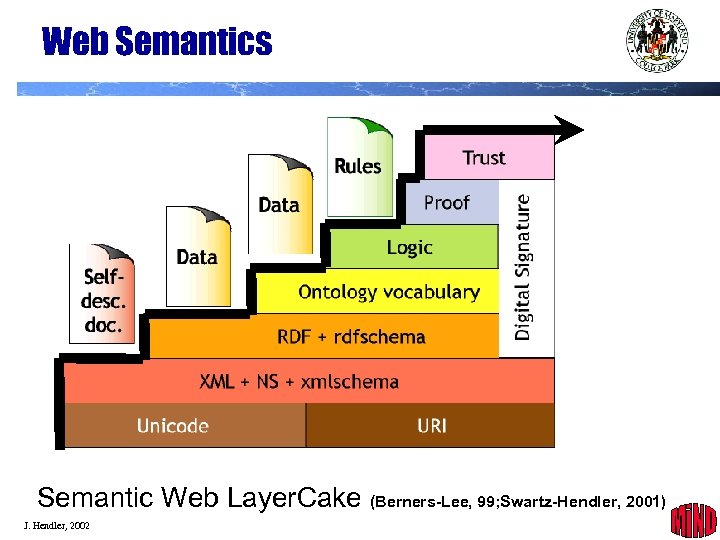
Web Semantics Semantic Web Layer. Cake (Berners-Lee, 99; Swartz-Hendler, 2001) J. Hendler, 2002 4

Can’t we just use XML? This is what a web-page in natural language looks like for a machine

XML helps XML allows “meaningful tags” to be added to parts of the text < name > < education> < work> < private > < CV >
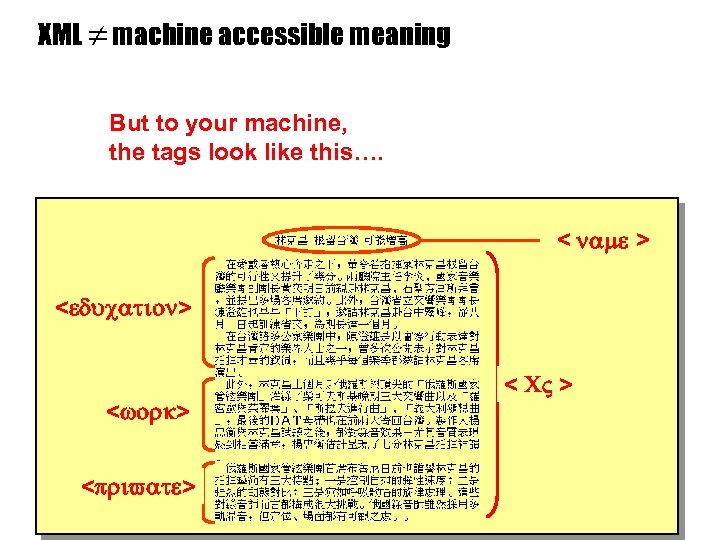
XML machine accessible meaning But to your machine, the tags look like this…. name < name > <education> <work> <private> < private > < CV > CV
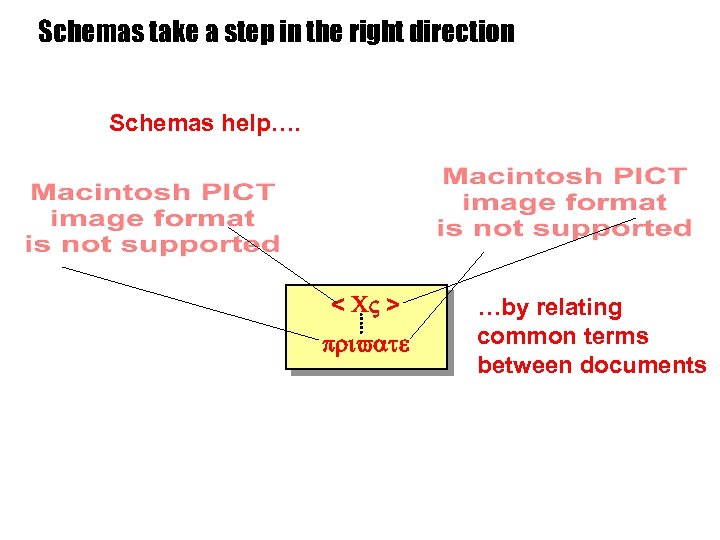
Schemas take a step in the right direction Schemas help…. < CV > private …by relating common terms between documents
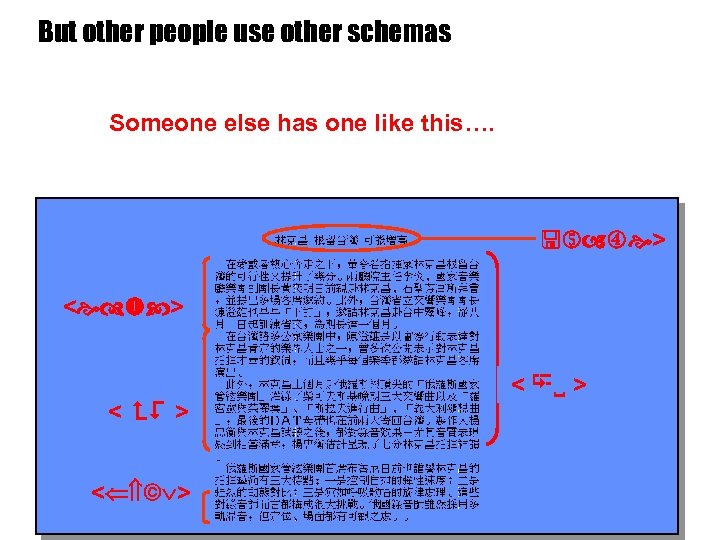
But other people use other schemas Someone else has one like this…. name> < name > <educ> < education> <> < work> < private > < CV > >
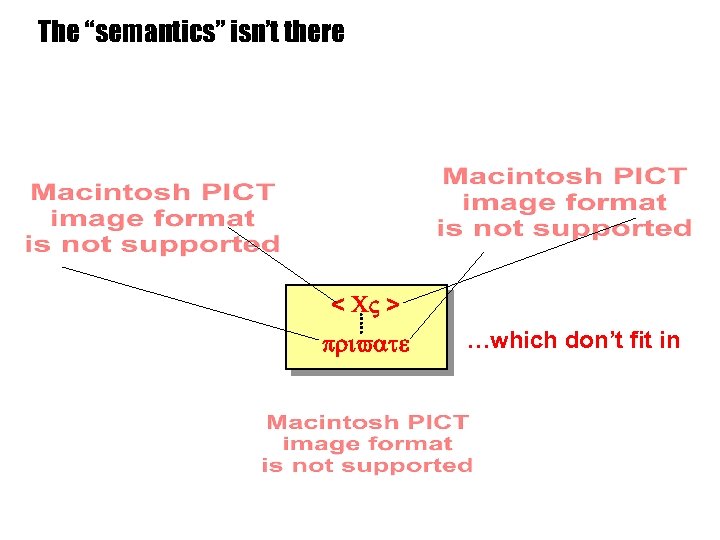
The “semantics” isn’t there < CV > private …which don’t fit in
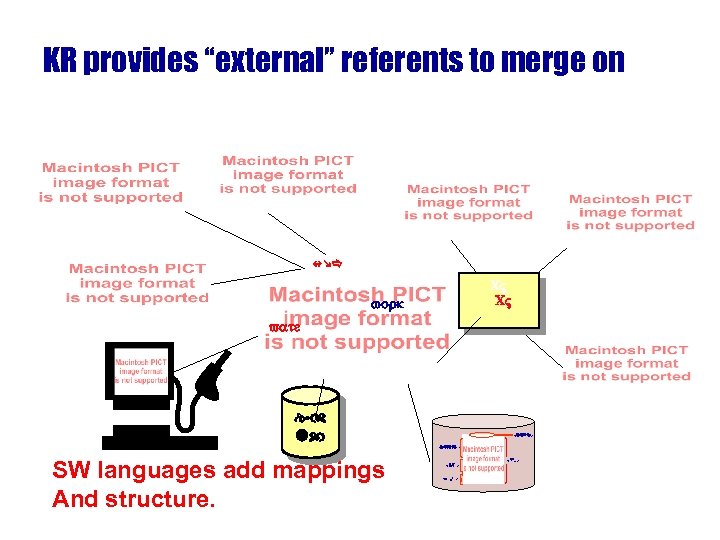
KR provides “external” referents to merge on nme CV CV work vate educ ed uc SW languages add mappings And structure. CV <name > <educ > < education> <> < work> < private < ‹› „⁄ >> < CV > <

Which is what the web was meant to be!! "This is a pity, as in fact documents on the web describe real objects and imaginary concepts, and give particular relationships between them. . . For example, a document might describe a person. The title document to a house describes a house and also the ownership relation with a person. . This means that machines, as well as people operating on the web of information, can do real things. For example, a program could search for a house and negotiate transfer of ownership of the house to a new owner. The land registry guarantees that the title actually represents reality. ” J. Hendler, 2002 Tim Berners-Lee plenary presentation at WWW Geneva, 1994 l 12

Putting semantics on the web J. Hendler, 2002 13

(and making it machine-readable) J. Hendler, 2002 14

J. Hendler, 2002 15
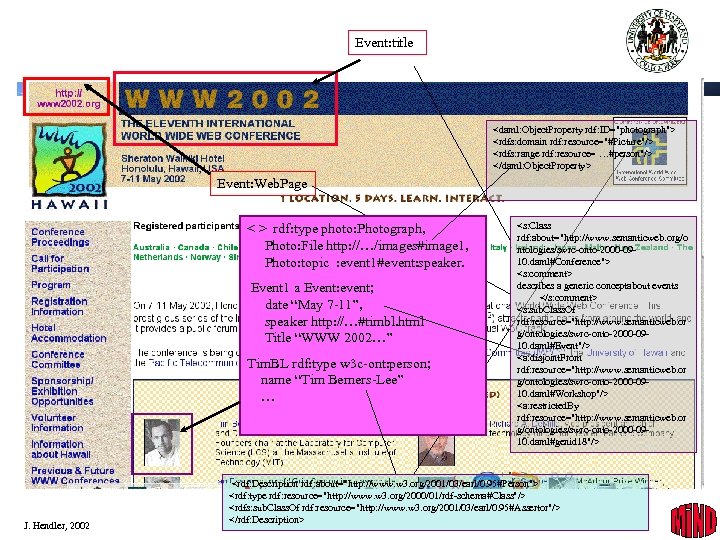
Event: title <daml: Object. Property rdf: ID="photograph"> <rdfs: domain rdf: resource="#Picture"/> <rdfs: range rdf: resource= …#person"/> </daml: Object. Property> Event: Web. Page < > rdf: type photo: Photograph, Photo: File http: //…/images#image 1, Photo: topic : event 1#event: speaker. Event 1 a Event: event; date “May 7 -11”, speaker http: //…#timbl. html Title “WWW 2002…” Tim. BL rdf: type w 3 c-ont: person; name “Tim Berners-Lee” … J. Hendler, 2002 <s: Class rdf: about="http: //www. semanticweb. org/o ntologies/swrc-onto-2000 -0910. daml#Conference"> <s: comment> describes a generic conceptabout events </s: comment> <s: sub. Class. Of rdf: resource="http: //www. semanticweb. or g/ontologies/swrc-onto-2000 -0910. daml#Event"/> <a: disjoint. From rdf: resource="http: //www. semanticweb. or g/ontologies/swrc-onto-2000 -0910. daml#Workshop"/> <a: restricted. By rdf: resource="http: //www. semanticweb. or g/ontologies/swrc-onto-2000 -0910. daml#genid 18"/> <rdf: Description rdf: about="http: //www. w 3. org/2001/03/earl/0. 95#Person"> <rdf: type rdf: resource="http: //www. w 3. org/2000/01/rdf-schema#Class"/> <rdfs: sub. Class. Of rdf: resource="http: //www. w 3. org/2001/03/earl/0. 95#Assertor"/> </rdf: Description> 16
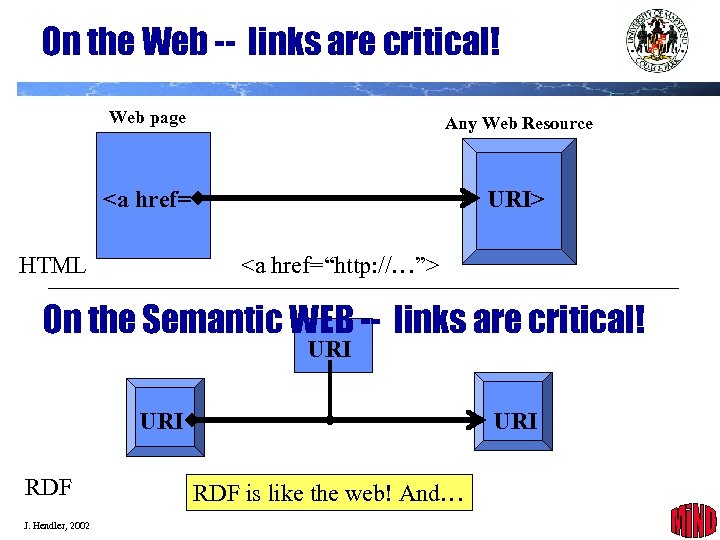
On the Web -- links are critical! Web page Any Web Resource <a href= URI> HTML <a href=“http: //…”> On the Semantic WEB -- links are critical! URI RDF J. Hendler, 2002 URI RDF is like the web! And… 17
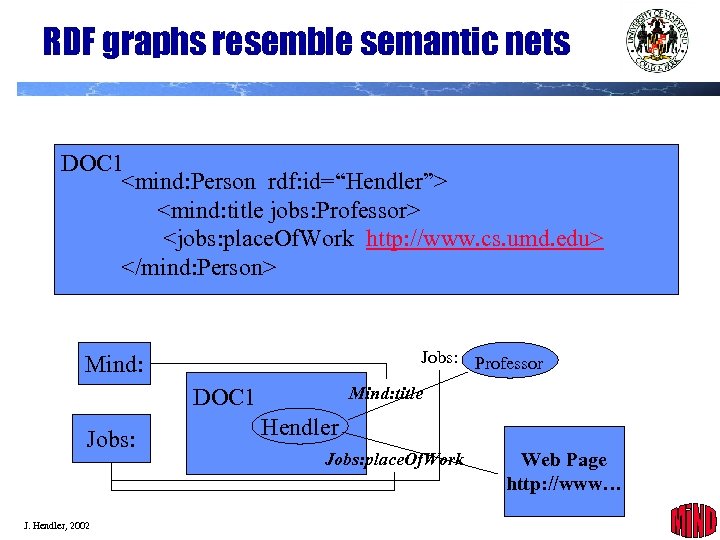
RDF graphs resemble semantic nets DOC 1 <mind: Person rdf: id=“Hendler”> <mind: title jobs: Professor> <jobs: place. Of. Work http: //www. cs. umd. edu> </mind: Person> Jobs: Professor Mind: title DOC 1 Jobs: J. Hendler, 2002 Hendler Jobs: place. Of. Work Web Page http: //www… 18
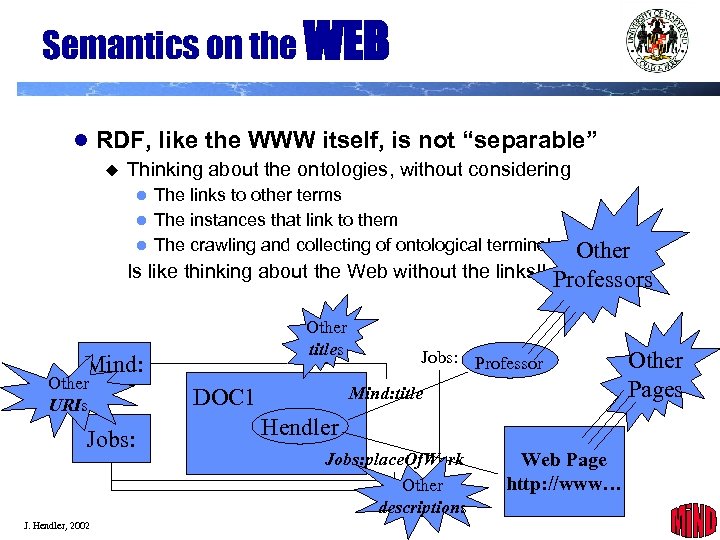
Semantics on the WEB l RDF, like the WWW itself, is not “separable” Thinking about the ontologies, without considering l The links to other terms l The instances that link to them l The crawling and collecting of ontological terminologues Other Is like thinking about the Web without the links!! Other titles Mind: Other URIs Jobs: J. Hendler, 2002 Professors Jobs: Professor Mind: title DOC 1 Other Pages Hendler Jobs: place. Of. Work Other descriptions Web Page http: //www… 19
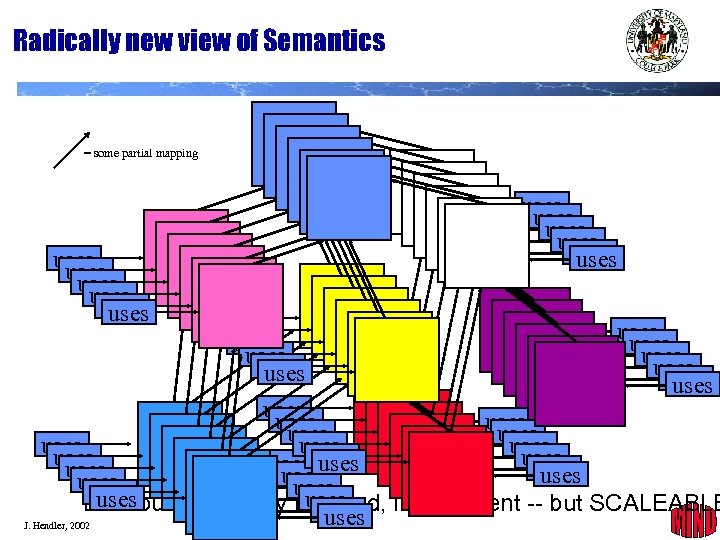
Radically new view of Semantics = some partial mapping uses uses uses uses uses uses uses uses uses uses uses uses Distributed, partially mapped, inconsistent -- but SCALEABLE uses J. Hendler, 2002 20

Real examples l Examples from http: //dormouse. cs. umd. edu: 8080/wiki/cmsc 498 wi ki. wiki l Students violated every rule in the KR book Extended existing ontologies Linked instances directly to terms from multiple ontologies Mixed “real KR” and NL l We can learn from their lessons http: //dormouse. cs. umd. edu: 8080/wiki/assignment 1_collecte d_les. wiki J. Hendler, 2002 21
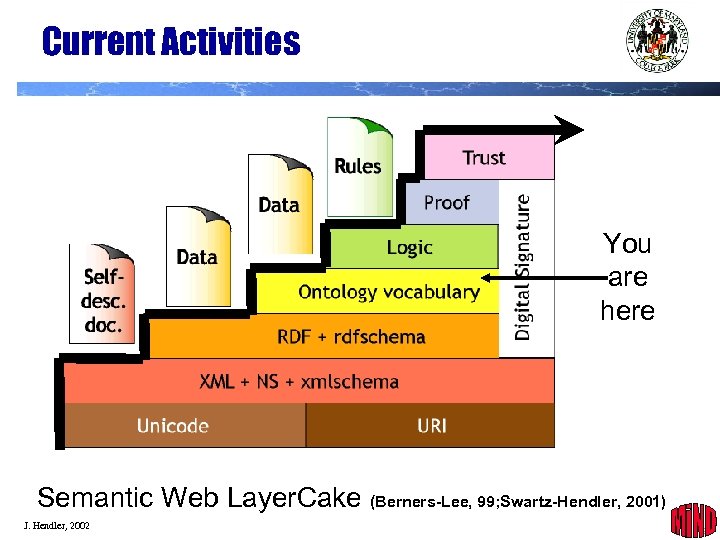
Current Activities You are here Semantic Web Layer. Cake (Berners-Lee, 99; Swartz-Hendler, 2001) J. Hendler, 2002 22

W 3 C Web Ontology Working Group l Web Ontology Working Group in the W 3 C Semantic Web Activity aimed at “extending the semantic reach of current XML and RDF meta-data efforts. “ l History J. Hendler, 2002 DAML+OIL is submitted as a joint committee effort published as a W 3 C note. W 3 C WG Announcement in November 2001 http: //lists. w 3. org/Archives/Public/www-rdflogic/2001 Nov/0000. html Weekly teleconferences started in November 2001 First Face to Face Meeting - New Jersey (Lucent), Jan ‘ 02; 2 nd Amsterdam April (W 3 C); 3 rd - CA (Fujitsu/Stanford host) July; 4 th in Bristol UK (HP Host) Oct. Four Working Drafts to date l Requirements/Use cases - March 2002 l 3 Technical Documents - July 2002 (Language renamed OWL) 23

Membership l Current Working Group includes over 50 members from over 30 organizations. Chairs l J. Hendler, MIND Lab UMCP l G. Schreiber, Univ. of Amsterdam Industry including: l Large companies - Daimler Chrysler, IBM, HP, Intel, EDS, Fujitsu, Lucent, Motorola, Nokia, Philips Electronics, Sun, Unisys l Newer/smaller companies - IVIS Group, Network Inference, Stilo Technology, Unicorn Solutions Government and Not-For-Profits: l US Defense Information Systems Agency, Interoperability Technology Association for Information Processing, Japan (INTAP) , Electricite De France, Mitre, NIST Universities and Research Centers: l University of Bristol, University of Maryland, University of Southamptom, Stanford University l DFKI (German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence), Forschungszentrum Informatik, Ontoweb J. Hendler, 2002 Invited Experts 24

But will it fly? l DAML+OIL is already the most used ontology language ever!! http: //www. daml. org (3. 5 M statements on 25, 000 web pages) l Gaining acceptance by web players Semantic Web Track being offered at WWW 2002 3 x more people attended WWW 2002 Developer Day on SW than attended KR l Significant (international) Govt Support US DARPA/NSF; EU IST Framework 5, 6 Japan, Germany, Australia considering significant investments US National Cancer Institute to publish cancer vocabulary in DAML+OIL l Much New Startup activity (even in this economic climate) l Many tools being developed J. Hendler, 2002 Many of them aimed at developers, not just AI literate types 25
Making Markup Easier J. Hendler, 2002 26
Machine worries about the syntax J. Hendler, 2002 27
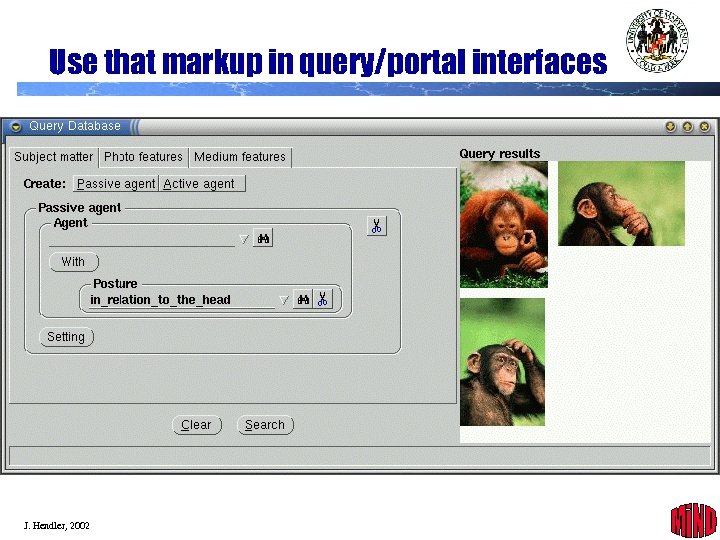
Use that markup in query/portal interfaces J. Hendler, 2002 28
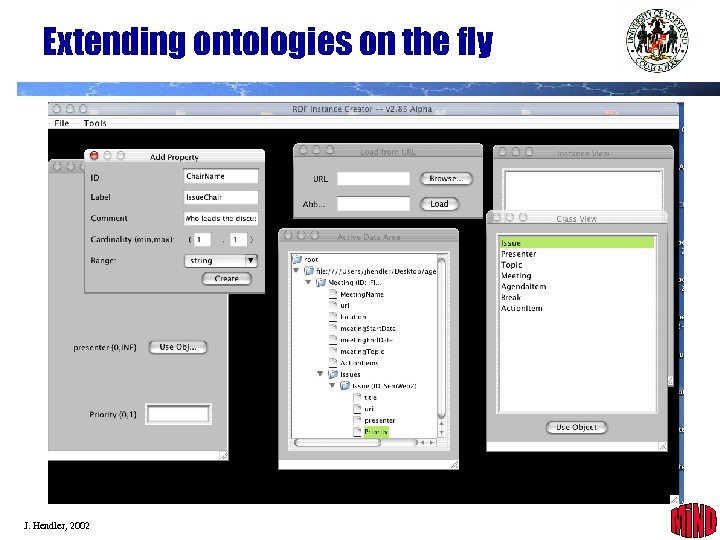
Extending ontologies on the fly J. Hendler, 2002 29
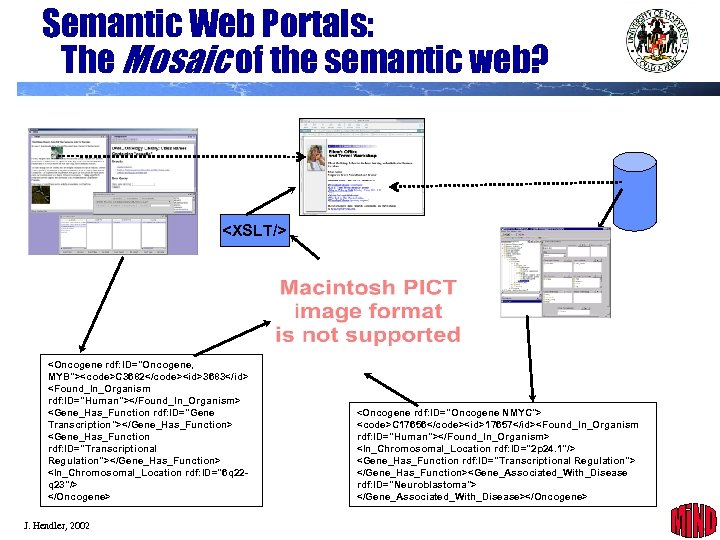
Semantic Web Portals: The Mosaic of the semantic web? <XSLT/> <Oncogene rdf: ID="Oncogene, MYB"><code>C 3682</code><id>3683</id> <Found_In_Organism rdf: ID="Human"></Found_In_Organism> <Gene_Has_Function rdf: ID="Gene Transcription"></Gene_Has_Function> <Gene_Has_Function rdf: ID="Transcriptional Regulation"></Gene_Has_Function> <In_Chromosomal_Location rdf: ID="6 q 22 q 23"/> </Oncogene> J. Hendler, 2002 <Oncogene rdf: ID="Oncogene NMYC"> <code>C 17656</code><id>17657</id><Found_In_Organism rdf: ID="Human"></Found_In_Organism> <In_Chromosomal_Location rdf: ID="2 p 24. 1"/> <Gene_Has_Function rdf: ID="Transcriptional Regulation"> </Gene_Has_Function><Gene_Associated_With_Disease rdf: ID="Neuroblastoma"> </Gene_Associated_With_Disease></Oncogene> 30
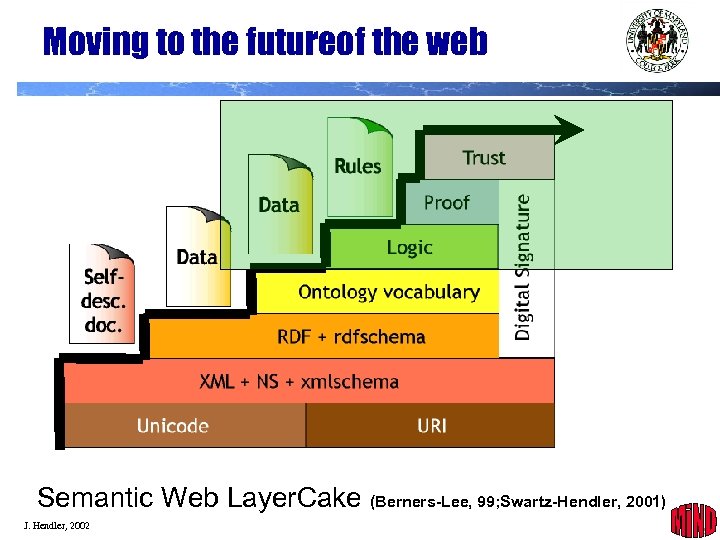
Moving to the futureof the web Semantic Web Layer. Cake (Berners-Lee, 99; Swartz-Hendler, 2001) J. Hendler, 2002 31

Web “travel agents” How many cows are there in Texas? Query processed: 73 answers found Google document search finds 235, 312 possible page hits. Http: //www…/Cow. Texas. html claims the answer is 289, 921, 836 A database entitled “Texas Cattle Association” can be queried for the answer, but you will need “authorization as a state employee. ” A computer program that can compute that number is offered by the State of Texas Cattleman’s Cooperative, click here to run program. . J. Hendler, 2002 The “sex network” can answer anything that troubles you, click here for relief. . . The “UFO network” claims the “all cows in Texas have been replaced by aliens 32

Allows new capabilities J. Hendler, 2002 33
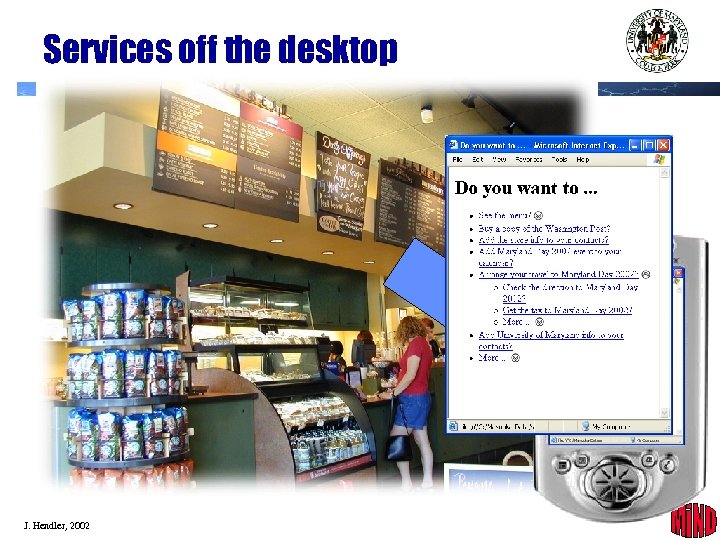
Services off the desktop J. Hendler, 2002 34
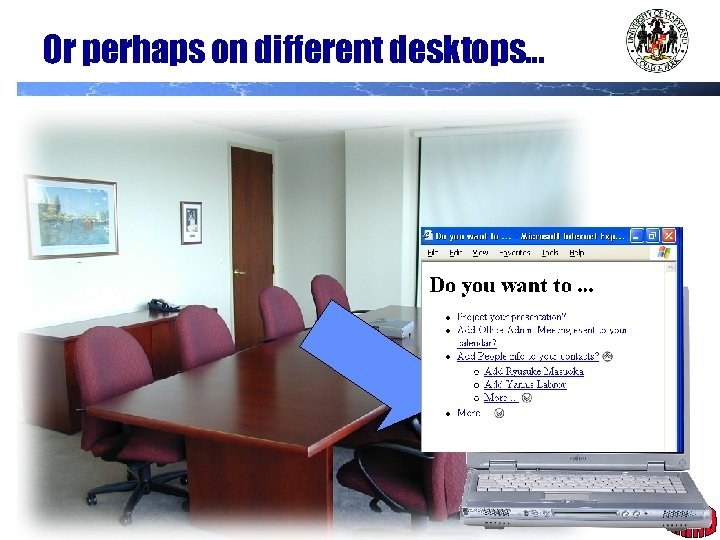
Or perhaps on different desktops… J. Hendler, 2002 35
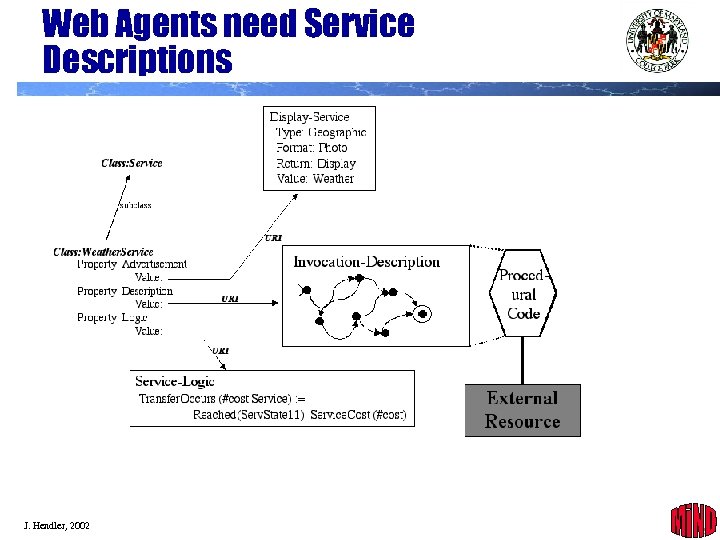
Web Agents need Service Descriptions J. Hendler, 2002 36

Semantic Web Service Description J. Hendler, 2002 37
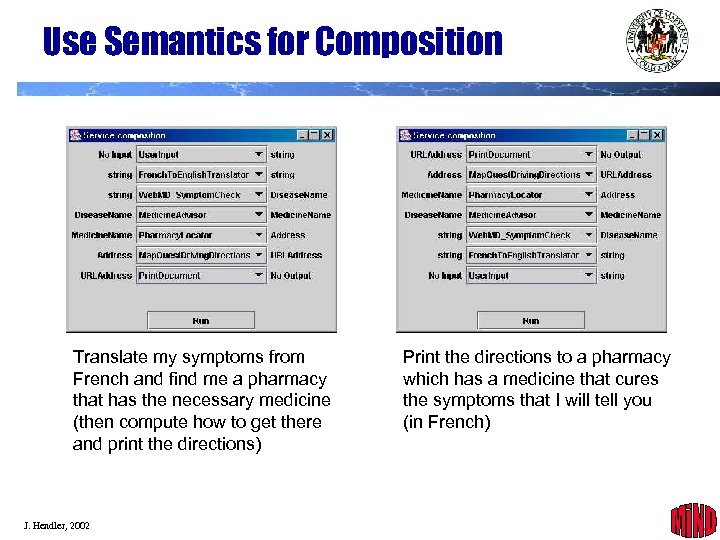
Use Semantics for Composition Translate my symptoms from French and find me a pharmacy that has the necessary medicine (then compute how to get there and print the directions) J. Hendler, 2002 Print the directions to a pharmacy which has a medicine that cures the symptoms that I will tell you (in French) 38

Or, translate to Planning Operators J. Hendler, 2002 39

For goal-based service composition J. Hendler, 2002 Buy the French version of a book from amazon. fr and have it sent to Mom’s address 40
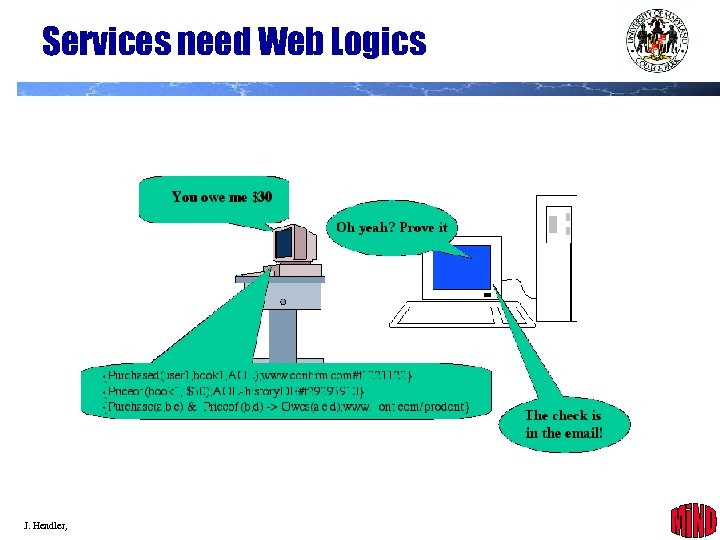
Services need Web Logics J. Hendler, 2002 41

Web of Trust l Claims can be verified if there is supporting evidence from another (trusted) source We only believe that someone is a professor at a university if the university also claims that person is a professor, and the university is on a list I trust. believe(c 1) : - claims(x, c 1) ^ predicate(c 1, professor. At) ^ arg 1(c 1, x) ^ arg 2(c 1, y) ^ claims(c 2, y) ^ predicate(c 2, professor. At) ^ arg 1(c 2, x) ^ arg 2(c 2, y) ^ Accredited. University(y) Acknowledged. University(u) : - link-from(“http: //www. cs. umd. edu/university-list”, u) Notice this one J. Hendler, 2002 42
Distributed Trust J. Hendler, 2002 43

Conclusion l It is no longer a question of whether the semantic web will come into being, it is already here! l We’re already well past the starting gate Web ontologies, term languages, “shims” to DB and services, research in proofs/rules/trust Standardization providing a common denominator for KR researchers as well as web developers Small companies starting to form, Big companies starting to move l The current environment is open, encouraging, moving fast, and exciting as heck Come play! J. Hendler, 2002 44
fa2f6420706eeab2421dfc0bcf362daa.ppt