ce72f062e78f32c9da6ecca97425d989.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Introducing the ‘Semantic Wave’ The making use of the Internet, the Web, and Service Orientated Architecture to define and query data in a new way Andy Mulholland CTO, Capgemini
Introducing the ‘Semantic Wave’ The making use of the Internet, the Web, and Service Orientated Architecture to define and query data in a new way Andy Mulholland CTO, Capgemini
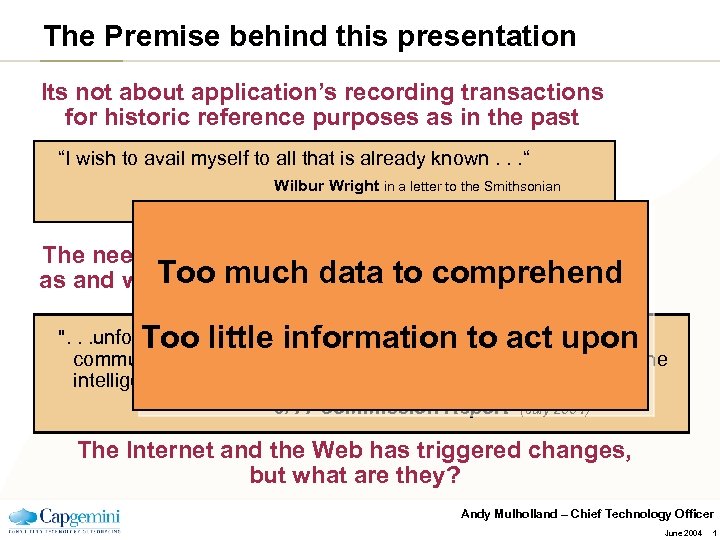 The Premise behind this presentation Its not about application’s recording transactions for historic reference purposes as in the past “I wish to avail myself to all that is already known. . . “ Wilbur Wright in a letter to the Smithsonian about flight (100 years ago) The need is for disparate facts to become associated Too much data to or unknown needs as and when events trigger known comprehend Too little information to act upon ". . . unfortunately, we suffered from a persistent problem of not communicating the intelligence we had or being able to analyze the intelligence based on conventional models. . . " 9/11 Commission Report (July 2004) The Internet and the Web has triggered changes, but what are they? Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 1
The Premise behind this presentation Its not about application’s recording transactions for historic reference purposes as in the past “I wish to avail myself to all that is already known. . . “ Wilbur Wright in a letter to the Smithsonian about flight (100 years ago) The need is for disparate facts to become associated Too much data to or unknown needs as and when events trigger known comprehend Too little information to act upon ". . . unfortunately, we suffered from a persistent problem of not communicating the intelligence we had or being able to analyze the intelligence based on conventional models. . . " 9/11 Commission Report (July 2004) The Internet and the Web has triggered changes, but what are they? Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 1
 Some scene setting on Business and Technology The drivers and background
Some scene setting on Business and Technology The drivers and background
 The Business Headlines; its on line and its now! ‘e’ has had it’s day Electronic interaction internally or externally is the norm Everyone, every system, every device is connected at no cost Redefines business communication Redesign of Process Industry sectors and Enterprises can be dramatically more efficient Standards suddenly become the most important aspect of IT Redefines interaction & collaboration New Technology Emerges The ‘Internet / Web’ model is leading to a new wave of technology & products ‘Client – Services’ bring competitive edge to business solutions Service Orientated Architecture lowers IT costs and integrates the new with old Converged communications is occurring Genuine Innovation has become possible Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 3
The Business Headlines; its on line and its now! ‘e’ has had it’s day Electronic interaction internally or externally is the norm Everyone, every system, every device is connected at no cost Redefines business communication Redesign of Process Industry sectors and Enterprises can be dramatically more efficient Standards suddenly become the most important aspect of IT Redefines interaction & collaboration New Technology Emerges The ‘Internet / Web’ model is leading to a new wave of technology & products ‘Client – Services’ bring competitive edge to business solutions Service Orientated Architecture lowers IT costs and integrates the new with old Converged communications is occurring Genuine Innovation has become possible Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 3
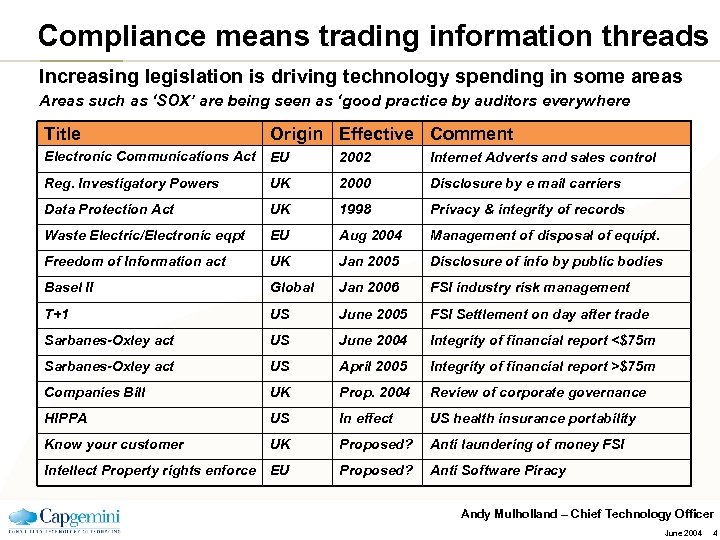 Compliance means trading information threads Increasing legislation is driving technology spending in some areas Areas such as ‘SOX’ are being seen as ‘good practice by auditors everywhere Title Origin Effective Comment Electronic Communications Act EU 2002 Internet Adverts and sales control Reg. Investigatory Powers UK 2000 Disclosure by e mail carriers Data Protection Act UK 1998 Privacy & integrity of records Waste Electric/Electronic eqpt EU Aug 2004 Management of disposal of equipt. Freedom of Information act UK Jan 2005 Disclosure of info by public bodies Basel II Global Jan 2006 FSI industry risk management T+1 US June 2005 FSI Settlement on day after trade Sarbanes-Oxley act US June 2004 Integrity of financial report <$75 m Sarbanes-Oxley act US April 2005 Integrity of financial report >$75 m Companies Bill UK Prop. 2004 Review of corporate governance HIPPA US In effect US health insurance portability Know your customer UK Proposed? Anti laundering of money FSI Intellect Property rights enforce EU Proposed? Anti Software Piracy Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 4
Compliance means trading information threads Increasing legislation is driving technology spending in some areas Areas such as ‘SOX’ are being seen as ‘good practice by auditors everywhere Title Origin Effective Comment Electronic Communications Act EU 2002 Internet Adverts and sales control Reg. Investigatory Powers UK 2000 Disclosure by e mail carriers Data Protection Act UK 1998 Privacy & integrity of records Waste Electric/Electronic eqpt EU Aug 2004 Management of disposal of equipt. Freedom of Information act UK Jan 2005 Disclosure of info by public bodies Basel II Global Jan 2006 FSI industry risk management T+1 US June 2005 FSI Settlement on day after trade Sarbanes-Oxley act US June 2004 Integrity of financial report <$75 m Sarbanes-Oxley act US April 2005 Integrity of financial report >$75 m Companies Bill UK Prop. 2004 Review of corporate governance HIPPA US In effect US health insurance portability Know your customer UK Proposed? Anti laundering of money FSI Intellect Property rights enforce EU Proposed? Anti Software Piracy Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 4
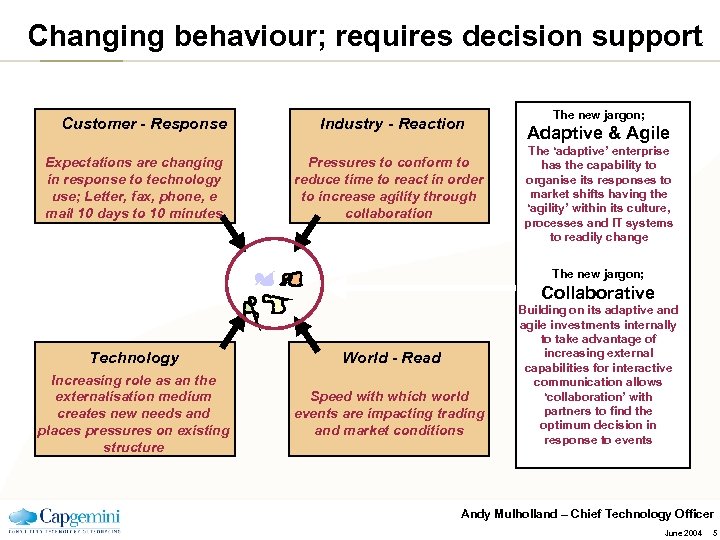 Changing behaviour; requires decision support Customer - Response Expectations are changing in response to technology use; Letter, fax, phone, e mail 10 days to 10 minutes Industry - Reaction Pressures to conform to reduce time to react in order to increase agility through collaboration The new jargon; Adaptive & Agile The ‘adaptive’ enterprise has the capability to organise its responses to market shifts having the ‘agility’ within its culture, processes and IT systems to readily change The new jargon; Collaborative Technology World - Read Increasing role as an the externalisation medium creates new needs and places pressures on existing structure Speed with which world events are impacting trading and market conditions Building on its adaptive and agile investments internally to take advantage of increasing external capabilities for interactive communication allows ‘collaboration’ with partners to find the optimum decision in response to events Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 5
Changing behaviour; requires decision support Customer - Response Expectations are changing in response to technology use; Letter, fax, phone, e mail 10 days to 10 minutes Industry - Reaction Pressures to conform to reduce time to react in order to increase agility through collaboration The new jargon; Adaptive & Agile The ‘adaptive’ enterprise has the capability to organise its responses to market shifts having the ‘agility’ within its culture, processes and IT systems to readily change The new jargon; Collaborative Technology World - Read Increasing role as an the externalisation medium creates new needs and places pressures on existing structure Speed with which world events are impacting trading and market conditions Building on its adaptive and agile investments internally to take advantage of increasing external capabilities for interactive communication allows ‘collaboration’ with partners to find the optimum decision in response to events Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 5
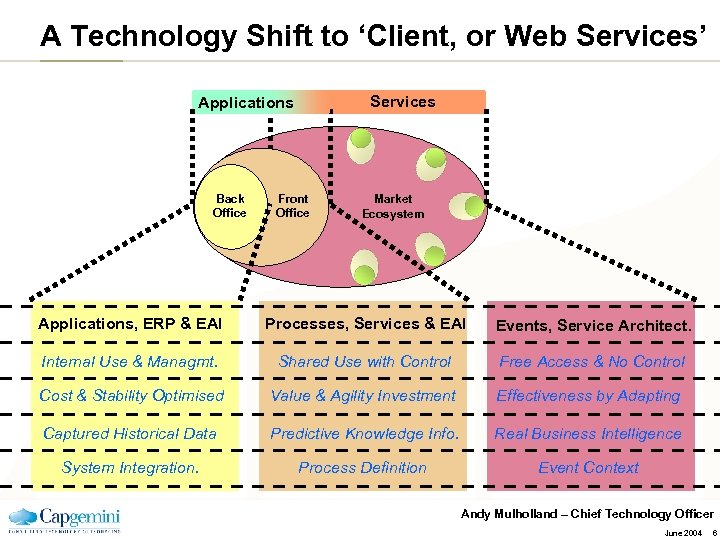 A Technology Shift to ‘Client, or Web Services’ Services Applications Back Office Front Office Market Ecosystem Applications, ERP & EAI Processes, Services & EAI Events, Service Architect. Internal Use & Managmt. Shared Use with Control Free Access & No Control Cost & Stability Optimised Value & Agility Investment Effectiveness by Adapting Captured Historical Data Predictive Knowledge Info. Real Business Intelligence System Integration. Process Definition Event Context Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 6
A Technology Shift to ‘Client, or Web Services’ Services Applications Back Office Front Office Market Ecosystem Applications, ERP & EAI Processes, Services & EAI Events, Service Architect. Internal Use & Managmt. Shared Use with Control Free Access & No Control Cost & Stability Optimised Value & Agility Investment Effectiveness by Adapting Captured Historical Data Predictive Knowledge Info. Real Business Intelligence System Integration. Process Definition Event Context Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 6
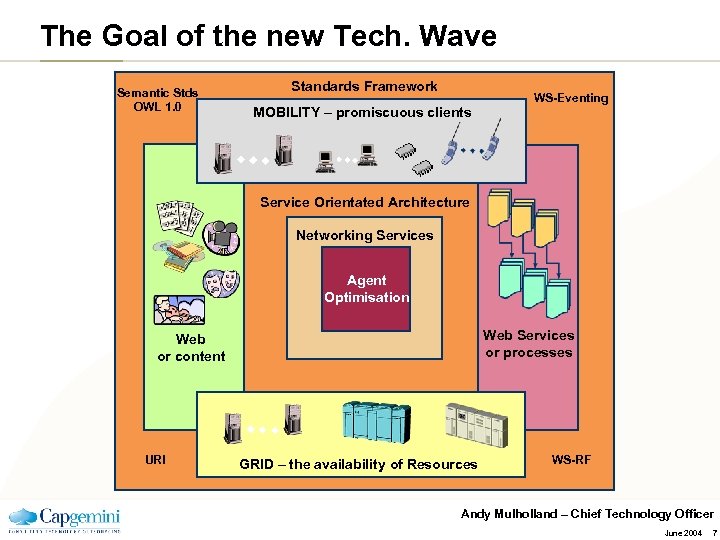 The Goal of the new Tech. Wave Semantic Stds OWL 1. 0 Standards Framework MOBILITY – promiscuous clients WS-Eventing Service Orientated Architecture Networking Services Agent Optimisation Web Services or processes Web or content URI GRID – the availability of Resources WS-RF Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 7
The Goal of the new Tech. Wave Semantic Stds OWL 1. 0 Standards Framework MOBILITY – promiscuous clients WS-Eventing Service Orientated Architecture Networking Services Agent Optimisation Web Services or processes Web or content URI GRID – the availability of Resources WS-RF Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 7
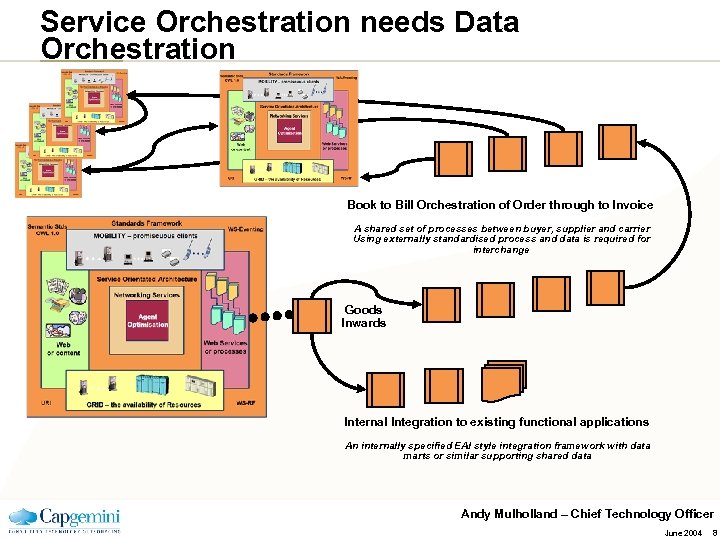 Service Orchestration needs Data Orchestration Book to Bill Orchestration of Order through to Invoice A shared set of processes between buyer, supplier and carrier Using externally standardised process and data is required for interchange Goods Inwards Internal Integration to existing functional applications An internally specified EAI style integration framework with data marts or similar supporting shared data Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 8
Service Orchestration needs Data Orchestration Book to Bill Orchestration of Order through to Invoice A shared set of processes between buyer, supplier and carrier Using externally standardised process and data is required for interchange Goods Inwards Internal Integration to existing functional applications An internally specified EAI style integration framework with data marts or similar supporting shared data Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 8
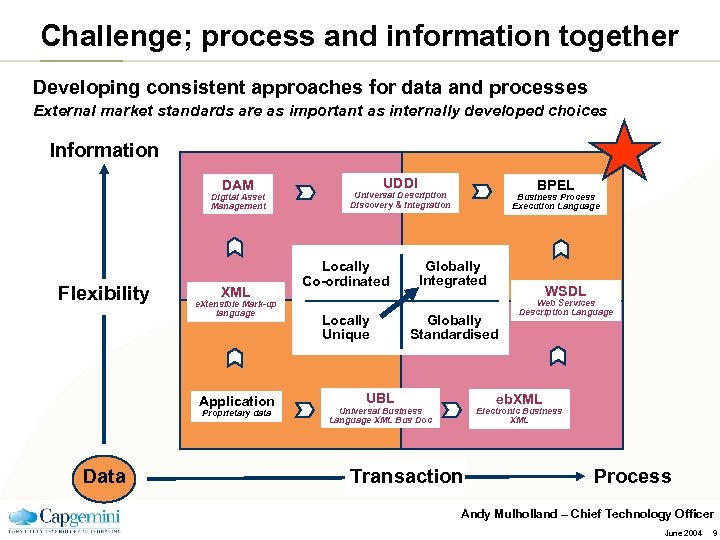 Challenge; process and information together Developing consistent approaches for data and processes External market standards are as important as internally developed choices Information DAM Digital Asset Management Flexibility XML e. Xtensible Mark-up language Application Proprietary data Data UDDI BPEL Universal Description Discovery & Integration Locally Co-ordinated Locally Unique Business Process Execution Language Globally Integrated WSDL Globally Standardised UBL Web Services Description Language eb. XML Universal Business Language XML Bus Doc Electronic Business XML Transaction Process Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 9
Challenge; process and information together Developing consistent approaches for data and processes External market standards are as important as internally developed choices Information DAM Digital Asset Management Flexibility XML e. Xtensible Mark-up language Application Proprietary data Data UDDI BPEL Universal Description Discovery & Integration Locally Co-ordinated Locally Unique Business Process Execution Language Globally Integrated WSDL Globally Standardised UBL Web Services Description Language eb. XML Universal Business Language XML Bus Doc Electronic Business XML Transaction Process Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 9
 Moving from Proprietary Data to Standardised Data What XML does and does not do
Moving from Proprietary Data to Standardised Data What XML does and does not do
 XML is a starting point by providing a Format e. Xtensible Markup Language is designed to provide a Syntax for computers to exchange and read data § XML itself conveys only content and structure, not presentation, behaviour, or meaning, and it’s Tags have no predefined meaning § The meaning or language must be specified outside of XML • prose, namespace, ontology, UML diagram. . …. ’Semantic’ § XML provides a standard framework for making agreements about communication, but XML does not make those agreements. § It’s flexibility, and widespread adoption can also be seen as its problem; List a number of versions Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 11
XML is a starting point by providing a Format e. Xtensible Markup Language is designed to provide a Syntax for computers to exchange and read data § XML itself conveys only content and structure, not presentation, behaviour, or meaning, and it’s Tags have no predefined meaning § The meaning or language must be specified outside of XML • prose, namespace, ontology, UML diagram. . …. ’Semantic’ § XML provides a standard framework for making agreements about communication, but XML does not make those agreements. § It’s flexibility, and widespread adoption can also be seen as its problem; List a number of versions Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 11
 UBL adds a Language for common processes Universal Business Language defines standard Book to Bill sequences to use XML data interchange • OASIS has now worked for 2 years to try and unify the chaotic world of XML formats with the UBL effort (Universal Business Language). • UBL now includes specifications (XML schemas) for the following transactions: ú ú ú Order and responses (simple and complex) Order cancellation Shipping notice (Dispatch advice) Receipt advice Invoice Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 12
UBL adds a Language for common processes Universal Business Language defines standard Book to Bill sequences to use XML data interchange • OASIS has now worked for 2 years to try and unify the chaotic world of XML formats with the UBL effort (Universal Business Language). • UBL now includes specifications (XML schemas) for the following transactions: ú ú ú Order and responses (simple and complex) Order cancellation Shipping notice (Dispatch advice) Receipt advice Invoice Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 12
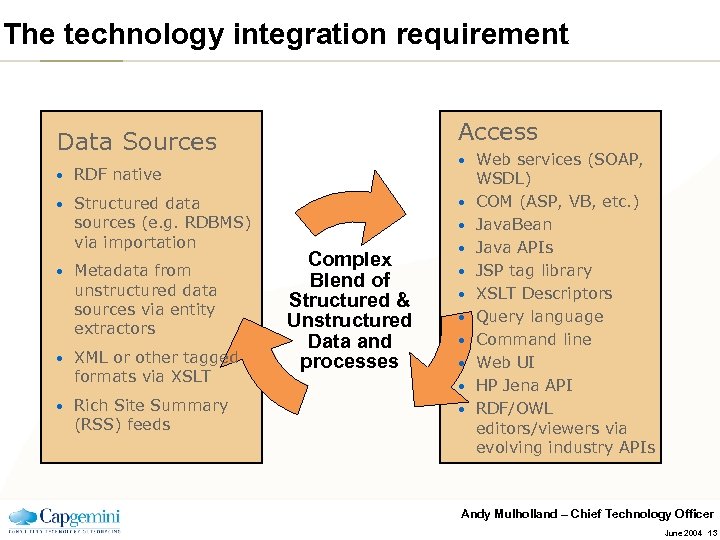 The technology integration requirement Access Data Sources • RDF native • Structured data sources (e. g. RDBMS) via importation • • Metadata from unstructured data sources via entity extractors XML or other tagged formats via XSLT Rich Site Summary (RSS) feeds • • Complex Blend of Structured & Unstructured Data and processes • • Web services (SOAP, WSDL) COM (ASP, VB, etc. ) Java. Bean Java APIs JSP tag library XSLT Descriptors Query language Command line Web UI HP Jena API RDF/OWL editors/viewers via evolving industry APIs Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 13
The technology integration requirement Access Data Sources • RDF native • Structured data sources (e. g. RDBMS) via importation • • Metadata from unstructured data sources via entity extractors XML or other tagged formats via XSLT Rich Site Summary (RSS) feeds • • Complex Blend of Structured & Unstructured Data and processes • • Web services (SOAP, WSDL) COM (ASP, VB, etc. ) Java. Bean Java APIs JSP tag library XSLT Descriptors Query language Command line Web UI HP Jena API RDF/OWL editors/viewers via evolving industry APIs Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 13
 Creating complex descriptions that can be understood Introducing the Semantic Wave
Creating complex descriptions that can be understood Introducing the Semantic Wave
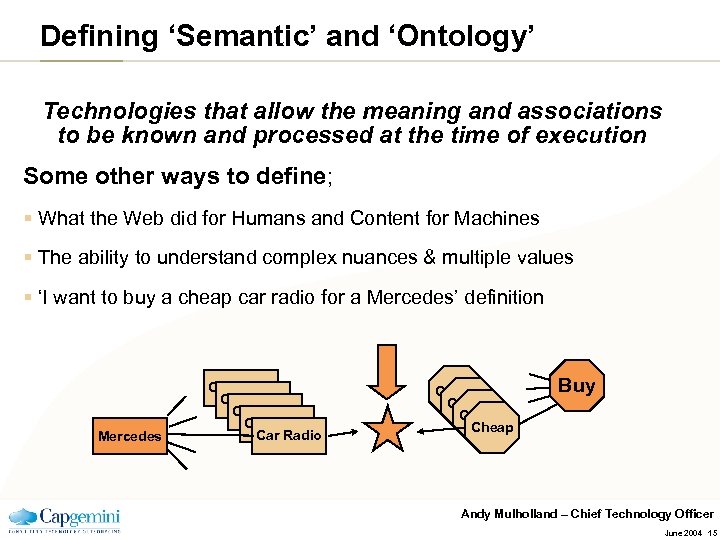 Defining ‘Semantic’ and ‘Ontology’ Technologies that allow the meaning and associations to be known and processed at the time of execution Some other ways to define; § What the Web did for Humans and Content for Machines § The ability to understand complex nuances & multiple values § ‘I want to buy a cheap car radio for a Mercedes’ definition Mercedes Car Radio Car Radio Cheap Buy Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 15
Defining ‘Semantic’ and ‘Ontology’ Technologies that allow the meaning and associations to be known and processed at the time of execution Some other ways to define; § What the Web did for Humans and Content for Machines § The ability to understand complex nuances & multiple values § ‘I want to buy a cheap car radio for a Mercedes’ definition Mercedes Car Radio Car Radio Cheap Buy Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 15
 Resource Description Framework, RDF § RDF is a collaboration from multiple W 3 c streams • PICSSPEC, PICSNG, XMLData, MCFXXML, WF, URI 2 etc § Therefore it emerged to handle the ‘new’ requirements § Its use is embedded in Web Services, WS, standards § Major vendors support it; Microsoft, IBM, etc Abstract; Resource Description Framework, RDF, is a mechanism for the encoding, exchange and reuse of structural metadata built using XML, but imposing structural constraints to ensure that there is a full unambiguous method to express semantic meanings. Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 16
Resource Description Framework, RDF § RDF is a collaboration from multiple W 3 c streams • PICSSPEC, PICSNG, XMLData, MCFXXML, WF, URI 2 etc § Therefore it emerged to handle the ‘new’ requirements § Its use is embedded in Web Services, WS, standards § Major vendors support it; Microsoft, IBM, etc Abstract; Resource Description Framework, RDF, is a mechanism for the encoding, exchange and reuse of structural metadata built using XML, but imposing structural constraints to ensure that there is a full unambiguous method to express semantic meanings. Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 16
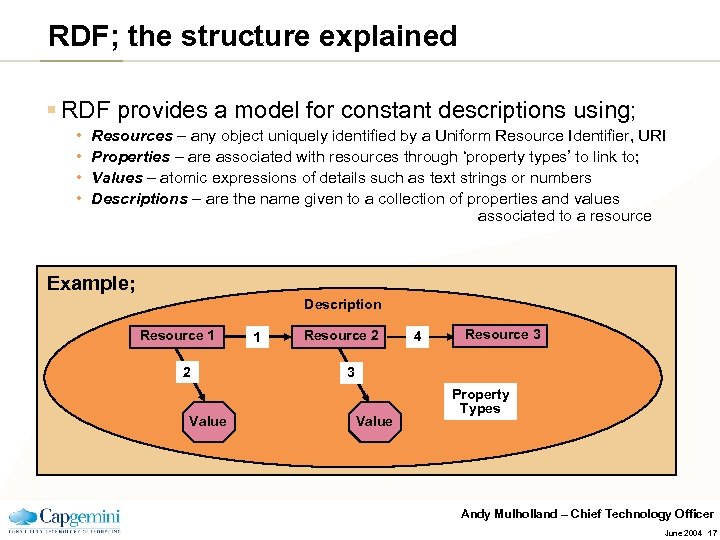 RDF; the structure explained § RDF provides a model for constant descriptions using; • • Resources – any object uniquely identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier, URI Properties – are associated with resources through ‘property types’ to link to; Values – atomic expressions of details such as text strings or numbers Descriptions – are the name given to a collection of properties and values associated to a resource Example; Description Resource 1 2 Value 1 Resource 2 4 Resource 3 3 Value Property Types Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 17
RDF; the structure explained § RDF provides a model for constant descriptions using; • • Resources – any object uniquely identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier, URI Properties – are associated with resources through ‘property types’ to link to; Values – atomic expressions of details such as text strings or numbers Descriptions – are the name given to a collection of properties and values associated to a resource Example; Description Resource 1 2 Value 1 Resource 2 4 Resource 3 3 Value Property Types Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 17
 Introducing Ontology Web Language, OWL § OWL emerged for use with the Web building on; • SHOE and DAML+OIL, but particularly Description Logic or DL § It is designed to be used with XML and RDF § OWL is specified in six major W 3 C documents • Overview, Semantics/Abstracts, Use Cases & Requirements, Test Cases, Reference, & Guide § A formal release OWL version 1. 0 made in 2003 Abstract; OWL is designed to provide applications that need to interpret content in forms normally understood by humans with expressive details by using a formal language vocabulary with defined semantic meanings to the words and a grammatical structure. Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 18
Introducing Ontology Web Language, OWL § OWL emerged for use with the Web building on; • SHOE and DAML+OIL, but particularly Description Logic or DL § It is designed to be used with XML and RDF § OWL is specified in six major W 3 C documents • Overview, Semantics/Abstracts, Use Cases & Requirements, Test Cases, Reference, & Guide § A formal release OWL version 1. 0 made in 2003 Abstract; OWL is designed to provide applications that need to interpret content in forms normally understood by humans with expressive details by using a formal language vocabulary with defined semantic meanings to the words and a grammatical structure. Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 18
 OWL; the structure explained § OWL offers flexibility in use through three sub languages; • OWL Lite – a simple version providing classification hierarchy with simple constraints that provides a quick migration for existing Thesauri and Taxonomies • OWL DL – providing maximum expressiveness but with computational success guarantee produced by ensuring all classes are complete and closed therefore computationally complete with in a defined time • OWL Full – offering maximum expressiveness to provide a full ontology augmenting any RDF description but open to allowing computational extensions to run indefinitely and therefore currently only used for research purposes Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 19
OWL; the structure explained § OWL offers flexibility in use through three sub languages; • OWL Lite – a simple version providing classification hierarchy with simple constraints that provides a quick migration for existing Thesauri and Taxonomies • OWL DL – providing maximum expressiveness but with computational success guarantee produced by ensuring all classes are complete and closed therefore computationally complete with in a defined time • OWL Full – offering maximum expressiveness to provide a full ontology augmenting any RDF description but open to allowing computational extensions to run indefinitely and therefore currently only used for research purposes Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 19
 Summary; XML, RDF and OWL relationships § XML – provides a surface syntax for structured documents, but imposes no semantic control on the meaning of those documents § XML Schema – is a language for restricting the structure of XML documents and allows XML to be extended with data types § RDF – is a data model for objects categorised as resources and the relationships between them providing simple semantics that can be represented using XML syntax § RDF Schema – is a vocabulary for describing properties and classes of RDF resources with a semantic structure for general hierarchies of properties and classes § OWL – adds extensive vocabulary for enriching the descriptions of properties and classes in a highly specific manner Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 20
Summary; XML, RDF and OWL relationships § XML – provides a surface syntax for structured documents, but imposes no semantic control on the meaning of those documents § XML Schema – is a language for restricting the structure of XML documents and allows XML to be extended with data types § RDF – is a data model for objects categorised as resources and the relationships between them providing simple semantics that can be represented using XML syntax § RDF Schema – is a vocabulary for describing properties and classes of RDF resources with a semantic structure for general hierarchies of properties and classes § OWL – adds extensive vocabulary for enriching the descriptions of properties and classes in a highly specific manner Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 20
 Using the Semantic Wave Complex data and complex queries become possible
Using the Semantic Wave Complex data and complex queries become possible
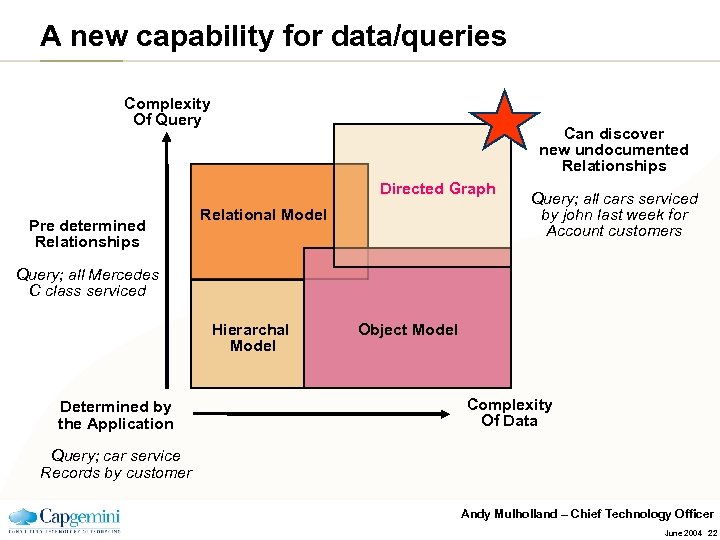 A new capability for data/queries Complexity Of Query Can discover new undocumented Relationships Directed Graph Pre determined Relationships Relational Model Query; all cars serviced by john last week for Account customers Query; all Mercedes C class serviced Hierarchal Model Determined by the Application Object Model Complexity Of Data Query; car service Records by customer Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 22
A new capability for data/queries Complexity Of Query Can discover new undocumented Relationships Directed Graph Pre determined Relationships Relational Model Query; all cars serviced by john last week for Account customers Query; all Mercedes C class serviced Hierarchal Model Determined by the Application Object Model Complexity Of Data Query; car service Records by customer Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 22
 What is Relationship Discovery? § “Find all organizations that have a relationship with Acme Corp. ” § How would you “google” this? § It can only be found by exploring relationships Example • XYZ Corp
What is Relationship Discovery? § “Find all organizations that have a relationship with Acme Corp. ” § How would you “google” this? § It can only be found by exploring relationships Example • XYZ Corp
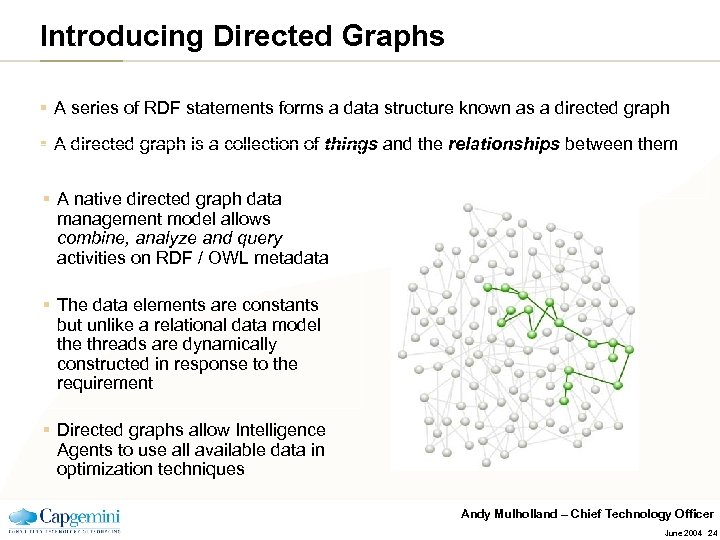 Introducing Directed Graphs § A series of RDF statements forms a data structure known as a directed graph § A directed graph is a collection of things and the relationships between them § A native directed graph data management model allows combine, analyze and query activities on RDF / OWL metadata § The data elements are constants but unlike a relational data model the threads are dynamically constructed in response to the requirement § Directed graphs allow Intelligence Agents to use all available data in optimization techniques Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 24
Introducing Directed Graphs § A series of RDF statements forms a data structure known as a directed graph § A directed graph is a collection of things and the relationships between them § A native directed graph data management model allows combine, analyze and query activities on RDF / OWL metadata § The data elements are constants but unlike a relational data model the threads are dynamically constructed in response to the requirement § Directed graphs allow Intelligence Agents to use all available data in optimization techniques Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 24
 Summary plus some thoughts
Summary plus some thoughts
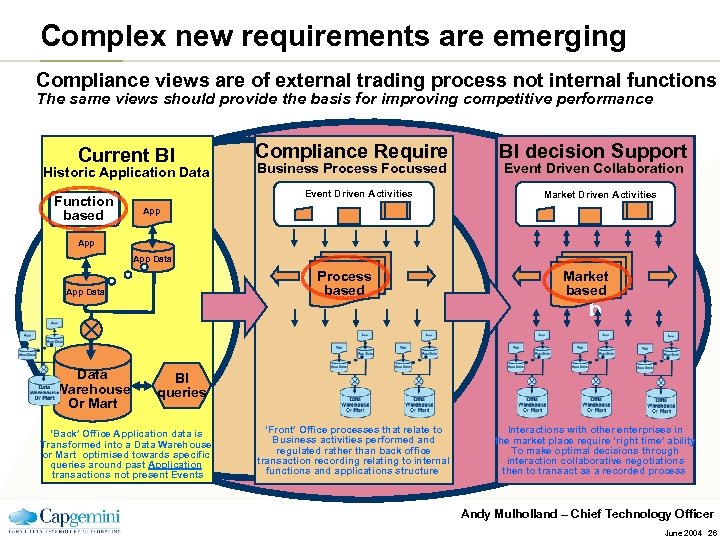 Complex new requirements are emerging Compliance views are of external trading process not internal functions The same views should provide the basis for improving competitive performance Current BI Historic Application Data Function based Compliance Require Business Process Focussed Event Driven Activities BI decision Support Event Driven Collaboration Market Driven Activities App App Data Warehouse Or Mart d Process based Market based b BI queries ‘Back’ Office Application data is Transformed into a Data Warehouse or Mart optimised towards specific queries around past Application transactions not present Events ‘Front’ Office processes that relate to Business activities performed and regulated rather than back office transaction recording relating to internal functions and applications structure Interactions with other enterprises in the market place require ‘right time’ ability To make optimal decisions through interaction collaborative negotiations then to transact as a recorded process Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 26
Complex new requirements are emerging Compliance views are of external trading process not internal functions The same views should provide the basis for improving competitive performance Current BI Historic Application Data Function based Compliance Require Business Process Focussed Event Driven Activities BI decision Support Event Driven Collaboration Market Driven Activities App App Data Warehouse Or Mart d Process based Market based b BI queries ‘Back’ Office Application data is Transformed into a Data Warehouse or Mart optimised towards specific queries around past Application transactions not present Events ‘Front’ Office processes that relate to Business activities performed and regulated rather than back office transaction recording relating to internal functions and applications structure Interactions with other enterprises in the market place require ‘right time’ ability To make optimal decisions through interaction collaborative negotiations then to transact as a recorded process Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 26
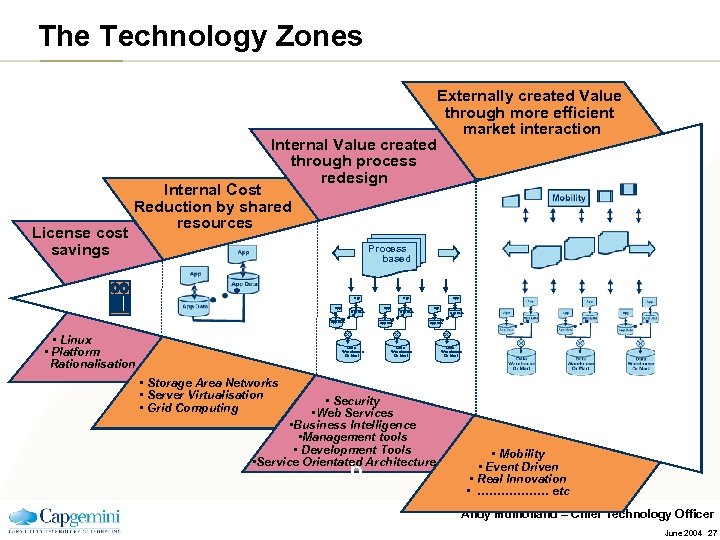 The Technology Zones Internal Value created through process redesign License cost savings Internal Cost Reduction by shared resources Process based App App • Linux • Platform Rationalisation App Data Warehouse Or Mart App App Data R Externally created Value through more efficient market interaction App Data Warehouse Or Mart • Storage Area Networks • Server Virtualisation • Grid Computing • Security • Web Services • Business Intelligence • Management tools • Development Tools • Service Orientated Architecture b • Mobility • Event Driven • Real Innovation • ……………… etc Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 27
The Technology Zones Internal Value created through process redesign License cost savings Internal Cost Reduction by shared resources Process based App App • Linux • Platform Rationalisation App Data Warehouse Or Mart App App Data R Externally created Value through more efficient market interaction App Data Warehouse Or Mart • Storage Area Networks • Server Virtualisation • Grid Computing • Security • Web Services • Business Intelligence • Management tools • Development Tools • Service Orientated Architecture b • Mobility • Event Driven • Real Innovation • ……………… etc Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 27
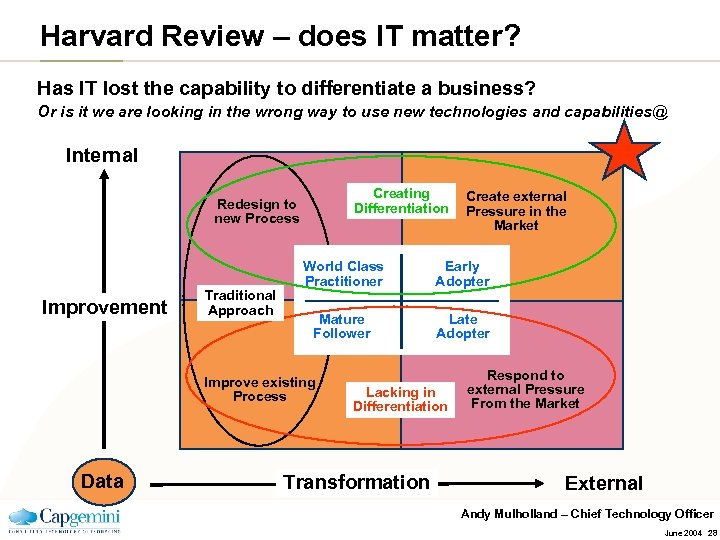 Harvard Review – does IT matter? Has IT lost the capability to differentiate a business? Or is it we are looking in the wrong way to use new technologies and capabilities@ Internal Creating Differentiation Redesign to new Process Improvement Traditional Approach World Class Practitioner Early Adopter Mature Follower Late Adopter Improve existing Process Data Create external Pressure in the Market Lacking in Differentiation Transformation Respond to external Pressure From the Market External Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 28
Harvard Review – does IT matter? Has IT lost the capability to differentiate a business? Or is it we are looking in the wrong way to use new technologies and capabilities@ Internal Creating Differentiation Redesign to new Process Improvement Traditional Approach World Class Practitioner Early Adopter Mature Follower Late Adopter Improve existing Process Data Create external Pressure in the Market Lacking in Differentiation Transformation Respond to external Pressure From the Market External Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 28
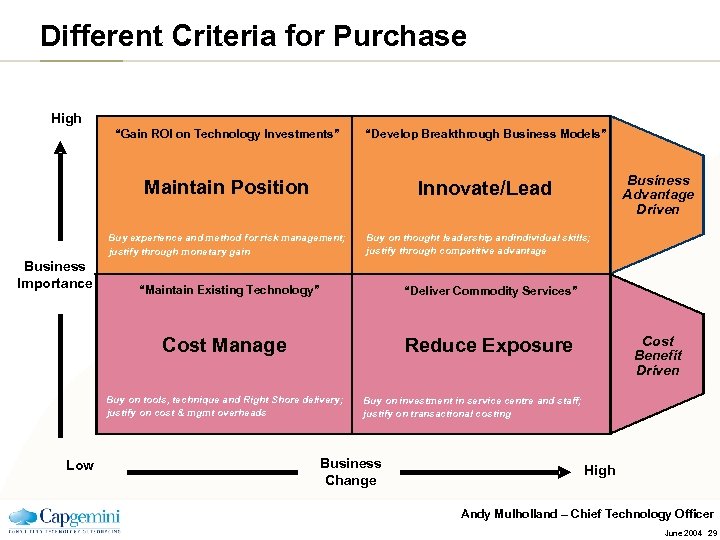 Different Criteria for Purchase High “Gain ROI on Technology Investments” “Develop Breakthrough Business Models” Maintain Position Innovate/Lead Buy experience and method for risk management; justify through monetary gain Business Importance Buy on thought leadership andindividual skills; justify through competitive advantage “Maintain Existing Technology” “Deliver Commodity Services” Cost Manage Cost Benefit Driven Reduce Exposure Buy on tools, technique and Right Shore delivery; justify on cost & mgmt overheads Low Business Advantage Driven Buy on investment in service centre and staff; justify on transactional costing Business Change High Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 29
Different Criteria for Purchase High “Gain ROI on Technology Investments” “Develop Breakthrough Business Models” Maintain Position Innovate/Lead Buy experience and method for risk management; justify through monetary gain Business Importance Buy on thought leadership andindividual skills; justify through competitive advantage “Maintain Existing Technology” “Deliver Commodity Services” Cost Manage Cost Benefit Driven Reduce Exposure Buy on tools, technique and Right Shore delivery; justify on cost & mgmt overheads Low Business Advantage Driven Buy on investment in service centre and staff; justify on transactional costing Business Change High Andy Mulholland – Chief Technology Officer June 2004 29


