81328b634c16ed8b14faafb0f5bd0575.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Introducing Computer Systems Mc. Graw-Hill Technology Education Copyright © 2006 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Introducing Computer Systems Mc. Graw-Hill Technology Education Copyright © 2006 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Computer Defined • A Computer is an electronic machine which is fast, accurate and controllable. • A computer is a device that accepts data, then perform arithmetic or logical operations that manipulate or change the data, and finally produces new results from that data. 1 A-2
The Computer Defined • A Computer is an electronic machine which is fast, accurate and controllable. • A computer is a device that accepts data, then perform arithmetic or logical operations that manipulate or change the data, and finally produces new results from that data. 1 A-2
 Information Technology Hardware, software, telecommunications, database management and other information processing technologies used in computer based information systems. 1 A-3
Information Technology Hardware, software, telecommunications, database management and other information processing technologies used in computer based information systems. 1 A-3
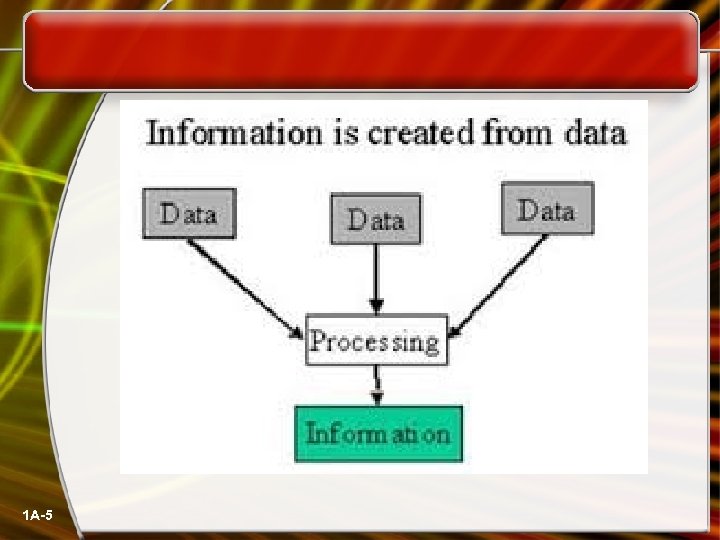
 Data and Information Data are facts. The raw material of information. Information is data arranged in ordered and useful form. 1 A-4
Data and Information Data are facts. The raw material of information. Information is data arranged in ordered and useful form. 1 A-4
 1 A-5
1 A-5
 1 A-6
1 A-6
 Software and Hardware Software: Any program (set of instructions) that causes a computer to carry out a task or function. Hardware: The physical elements of the computer system. 1 A-7
Software and Hardware Software: Any program (set of instructions) that causes a computer to carry out a task or function. Hardware: The physical elements of the computer system. 1 A-7
 Number Systems Decimal : Base 10, 0 -9 Binary: Base 2, 0 -1 Octal: Base 8, 0 -7 Hexadecimal: Base 16, 0 -9 & A-F 1 A-8
Number Systems Decimal : Base 10, 0 -9 Binary: Base 2, 0 -1 Octal: Base 8, 0 -7 Hexadecimal: Base 16, 0 -9 & A-F 1 A-8
 Bits and Bytes 1 Byte = 8 Bits 1 KB(Kilobyte)= 1024 bytes 1 MB(megabyte)= 1024 KB 1 GB(gigabyte)= 1024 MB 1 TB(terabyte)= 1024 GB 1 A-9
Bits and Bytes 1 Byte = 8 Bits 1 KB(Kilobyte)= 1024 bytes 1 MB(megabyte)= 1024 KB 1 GB(gigabyte)= 1024 MB 1 TB(terabyte)= 1024 GB 1 A-9
 Computers For Individual Use • Desktop computers – The most common type of computer – Sits on the desk or floor – Performs a variety of tasks • Workstations – Specialized computers – Optimized for science or graphics – More powerful than a desktop 1 A-10
Computers For Individual Use • Desktop computers – The most common type of computer – Sits on the desk or floor – Performs a variety of tasks • Workstations – Specialized computers – Optimized for science or graphics – More powerful than a desktop 1 A-10
 Computers For Individual Use • Notebook computers – Small portable computers – Weighs between 3 and 8 pounds – About 8 ½ by 11 inches – Typically as powerful as a desktop – Can include a docking station 1 A-11
Computers For Individual Use • Notebook computers – Small portable computers – Weighs between 3 and 8 pounds – About 8 ½ by 11 inches – Typically as powerful as a desktop – Can include a docking station 1 A-11
 Computers For Individual Use • Tablet computers – Newest development in portable computers – Input is through a pen – Run specialized versions of office products 1 A-12
Computers For Individual Use • Tablet computers – Newest development in portable computers – Input is through a pen – Run specialized versions of office products 1 A-12
 Computers For Individual Use • Handheld computers – Very small computers – Personal Digital Assistants (PDA) – Note taking or contact management – Data can synchronize with a desktop • Smart phones – Hybrid of cell phone and PDA – Web surfing, e-mail access 1 A-13
Computers For Individual Use • Handheld computers – Very small computers – Personal Digital Assistants (PDA) – Note taking or contact management – Data can synchronize with a desktop • Smart phones – Hybrid of cell phone and PDA – Web surfing, e-mail access 1 A-13
 Computers For Organizations • Network servers – Centralized computer – All other computers connect – Provides access to network resources – Multiple servers are called server farms – Often simply a powerful desktop 1 A-14
Computers For Organizations • Network servers – Centralized computer – All other computers connect – Provides access to network resources – Multiple servers are called server farms – Often simply a powerful desktop 1 A-14
 Computers For Organizations • Mainframes – Used in large organizations – Handle thousands of users – Users access through a terminal 1 A-15
Computers For Organizations • Mainframes – Used in large organizations – Handle thousands of users – Users access through a terminal 1 A-15
 Computers For Organizations • Minicomputers – Called midrange computers – Power between mainframe and desktop – Handle hundreds of users – Used in smaller organizations – Users access through a terminal 1 A-16
Computers For Organizations • Minicomputers – Called midrange computers – Power between mainframe and desktop – Handle hundreds of users – Used in smaller organizations – Users access through a terminal 1 A-16
 Computers For Organizations • Supercomputers – The most powerful computers made – Handle large and complex calculations – Process trillions of operations per second – Found in research organizations 1 A-17
Computers For Organizations • Supercomputers – The most powerful computers made – Handle large and complex calculations – Process trillions of operations per second – Found in research organizations 1 A-17
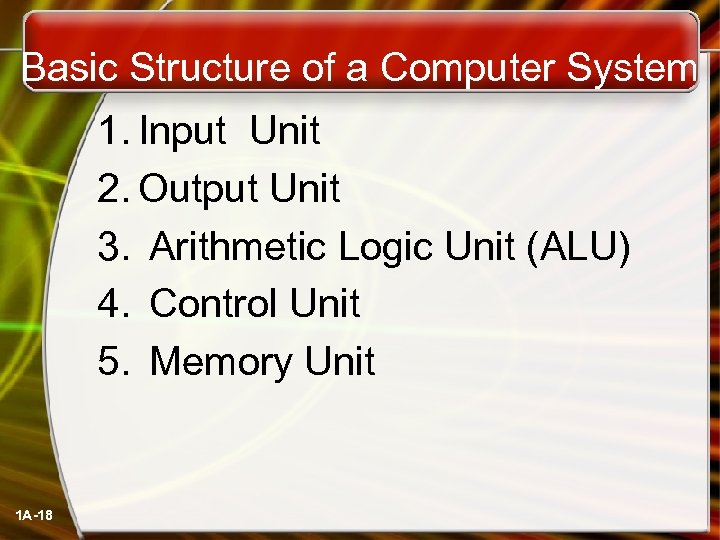 Basic Structure of a Computer System 1. Input Unit 2. Output Unit 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. Control Unit 5. Memory Unit 1 A-18
Basic Structure of a Computer System 1. Input Unit 2. Output Unit 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. Control Unit 5. Memory Unit 1 A-18
 Input Unit Enter data into the computer. Output Unit Extract data from the computer. 1 A-19
Input Unit Enter data into the computer. Output Unit Extract data from the computer. 1 A-19
 Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Calculates data and compares data. Basic arithmetic operations (add, subtract, multiply, divide etc. ) Logical operations (AND, OR). 1 A-20
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Calculates data and compares data. Basic arithmetic operations (add, subtract, multiply, divide etc. ) Logical operations (AND, OR). 1 A-20
 Control Unit (CU) Selects, interprets and carries out the execution of program instructions in their proper sequence 1 A-21
Control Unit (CU) Selects, interprets and carries out the execution of program instructions in their proper sequence 1 A-21
 Memory Unit Holds data, instructions and results of processing 1 A-22
Memory Unit Holds data, instructions and results of processing 1 A-22
 Computer Clock Speed • (Hz) is a measure of cycles per second. • Megahertz (MHz) means “millions of cycles per second” • Gigahertz (GHz) means “Billions of cycle per second”. 1 A-23
Computer Clock Speed • (Hz) is a measure of cycles per second. • Megahertz (MHz) means “millions of cycles per second” • Gigahertz (GHz) means “Billions of cycle per second”. 1 A-23
 • A processor can execute an instruction in a given number of clock cycles. As the system’s clock speed increases, so does the number of instructions it can carry out each second. 1 A-24
• A processor can execute an instruction in a given number of clock cycles. As the system’s clock speed increases, so does the number of instructions it can carry out each second. 1 A-24
 Input and Output Devices • Input Devices - Keyboard - Pointing Devices- Mouse, Trackball, Joystick - Scanners 1 A-25
Input and Output Devices • Input Devices - Keyboard - Pointing Devices- Mouse, Trackball, Joystick - Scanners 1 A-25
 Input and Output Devices • Output Devices - Display Screen CRT – Cathode Ray Tube LCD – Liquid crystal display 1 A-26
Input and Output Devices • Output Devices - Display Screen CRT – Cathode Ray Tube LCD – Liquid crystal display 1 A-26
 Input and Output Devices • Output Devices - Printers Dot-matrix printer Laser Printer Ink-jet Printer - Plotter 1 A-27
Input and Output Devices • Output Devices - Printers Dot-matrix printer Laser Printer Ink-jet Printer - Plotter 1 A-27
 Computer Memory • Main Memory RAM (Random Access Memory) - Volatile memory - Read-write memory Everything stored there is lost when the computer’s power is shut off 1 A-28
Computer Memory • Main Memory RAM (Random Access Memory) - Volatile memory - Read-write memory Everything stored there is lost when the computer’s power is shut off 1 A-28
 Computer Memory • Read Only Memory ROM - Non-Volatile memory - Read only memory ROM holds the start up program that begins when the computer is turned on 1 A-29
Computer Memory • Read Only Memory ROM - Non-Volatile memory - Read only memory ROM holds the start up program that begins when the computer is turned on 1 A-29
 Secondary Storage Media & Devices • Sequential Access Storage Devices Sequential Access Storage means the data is stored in particular order. So the computer must sequentially search for data. Today sequential access storage devices are most commonly used for backup purposes. Magnetic Tape Cartridges 1 A-30
Secondary Storage Media & Devices • Sequential Access Storage Devices Sequential Access Storage means the data is stored in particular order. So the computer must sequentially search for data. Today sequential access storage devices are most commonly used for backup purposes. Magnetic Tape Cartridges 1 A-30
 Secondary Storage Media & Devices • Direct Access Storage Devices Direct access means the data is stored in a particular memory location with a specific address so that any data can be found quickly. Direct access storage devices are magnetic disk drives used for secondary storage. Floppy Disk Hard Disk Drive Optical Disk 1 A-31
Secondary Storage Media & Devices • Direct Access Storage Devices Direct access means the data is stored in a particular memory location with a specific address so that any data can be found quickly. Direct access storage devices are magnetic disk drives used for secondary storage. Floppy Disk Hard Disk Drive Optical Disk 1 A-31
 BUS The term bus refers to the paths between the components of a Computer. Data Bus Address Bus 1 A-32
BUS The term bus refers to the paths between the components of a Computer. Data Bus Address Bus 1 A-32
 CACHE MEMORY • High-speed memory that resides between the CPU and RAM in a computer. Cache memory stores data and instructions that the CPU is likely to need next. The CPU can retrieve data or instructions more quickly from cache than it can from RAM or a disk. 1 A-33
CACHE MEMORY • High-speed memory that resides between the CPU and RAM in a computer. Cache memory stores data and instructions that the CPU is likely to need next. The CPU can retrieve data or instructions more quickly from cache than it can from RAM or a disk. 1 A-33
 1 A-34
1 A-34
 INPUT/OUTPUT PORTS • Every device that is external to the 1 A-35 system unit must be attached by a cable to the bus. This point of attachment is called a port or connector. There are six common types of ports and they are keyboard port, video port (for the display), mouse port, parallel port, serial port and USB port. •
INPUT/OUTPUT PORTS • Every device that is external to the 1 A-35 system unit must be attached by a cable to the bus. This point of attachment is called a port or connector. There are six common types of ports and they are keyboard port, video port (for the display), mouse port, parallel port, serial port and USB port. •
 1 A-36
1 A-36
 DISPLAYS • The resolution of a computer monitor is classified by the number of pixels on the screen, expressed as a matrix. 1 A-37
DISPLAYS • The resolution of a computer monitor is classified by the number of pixels on the screen, expressed as a matrix. 1 A-37
 • A resolution of 640 X 480 means that there are 640 pixels horizontally across the screen and 480 pixels vertically down the screen. The higher the resolution, the sharper and crisper the characters or image formed • 800 x 600 pixels • 1024 x 768 pixels • 1280 x 1024 pixels 1 A-38
• A resolution of 640 X 480 means that there are 640 pixels horizontally across the screen and 480 pixels vertically down the screen. The higher the resolution, the sharper and crisper the characters or image formed • 800 x 600 pixels • 1024 x 768 pixels • 1280 x 1024 pixels 1 A-38
 VIDEO CARDS • The quality of the images that a monitor can display is defines as much by the Video card /video controller as by the monitor itself. The video controller is an intermediary device between the CPU and the monitor, It contains the video-dedicated memory and other circuitry necessary to send information to the monitor to display on the screen 1 A-39
VIDEO CARDS • The quality of the images that a monitor can display is defines as much by the Video card /video controller as by the monitor itself. The video controller is an intermediary device between the CPU and the monitor, It contains the video-dedicated memory and other circuitry necessary to send information to the monitor to display on the screen 1 A-39
 MOTHERBOARD The main circuit board of the computer, which contains the processor, memory, expansion slots, bus, and video controller. Also called the system board or mainboard 1 A-40
MOTHERBOARD The main circuit board of the computer, which contains the processor, memory, expansion slots, bus, and video controller. Also called the system board or mainboard 1 A-40
 1 A-41
1 A-41


