97fadf087642cbd6c399f3a40ec48a75.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Intro to SAP Enterprise Systems Configuration EGS 5622 Enterprise Systems Integration Spring, 2018
Intro to SAP Enterprise Systems Configuration EGS 5622 Enterprise Systems Integration Spring, 2018
 SAP ERP Introduction Central relational database ◦ Oracle, Informix, Microsoft SQL, etc. Client/Server – three-tiered for database, application, and presentation. ERP Central Components (ECC)– Oriented towards common identifiable business modules: ◦ MM, SD, PP, FI, CO, HR, WM, PM Add-ons: ◦ Customer Relationship Mgmt (CRM) ◦ Supplier Relationship Mgmt (SRM) ◦ Supply Chain Mgmt (SCM) ◦ Product Lifecycle Mgmt (PLM) 2
SAP ERP Introduction Central relational database ◦ Oracle, Informix, Microsoft SQL, etc. Client/Server – three-tiered for database, application, and presentation. ERP Central Components (ECC)– Oriented towards common identifiable business modules: ◦ MM, SD, PP, FI, CO, HR, WM, PM Add-ons: ◦ Customer Relationship Mgmt (CRM) ◦ Supplier Relationship Mgmt (SRM) ◦ Supply Chain Mgmt (SCM) ◦ Product Lifecycle Mgmt (PLM) 2
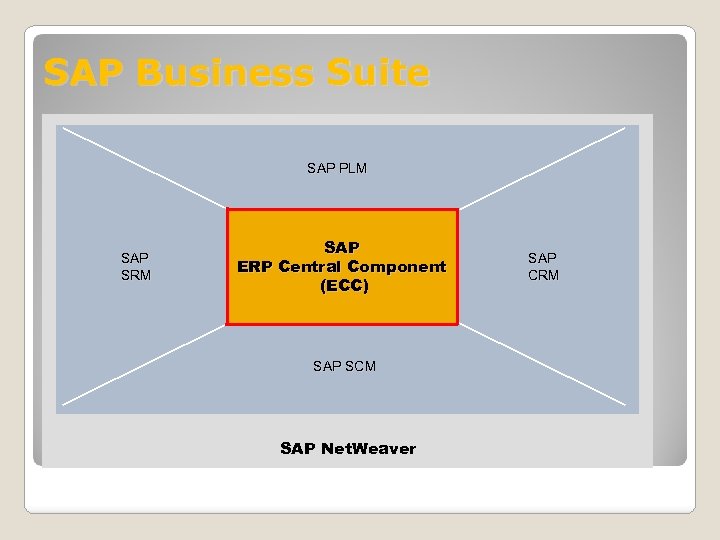 SAP Business Suite SAP PLM SAP SRM SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) SAP SCM SAP Net. Weaver SAP CRM
SAP Business Suite SAP PLM SAP SRM SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) SAP SCM SAP Net. Weaver SAP CRM
 Client/Server Environment Server ◦ Software/hardware combination that can provide services to a group of clients in a controlled environment Client ◦ Software/hardware combination that can make a request from a SAP customer for services from a central repository of resources 4
Client/Server Environment Server ◦ Software/hardware combination that can provide services to a group of clients in a controlled environment Client ◦ Software/hardware combination that can make a request from a SAP customer for services from a central repository of resources 4
 Three-Tier SAP Structure GUI – Graphical User Interface or Web Interface Application server (one or many) Database server (one single location)
Three-Tier SAP Structure GUI – Graphical User Interface or Web Interface Application server (one or many) Database server (one single location)
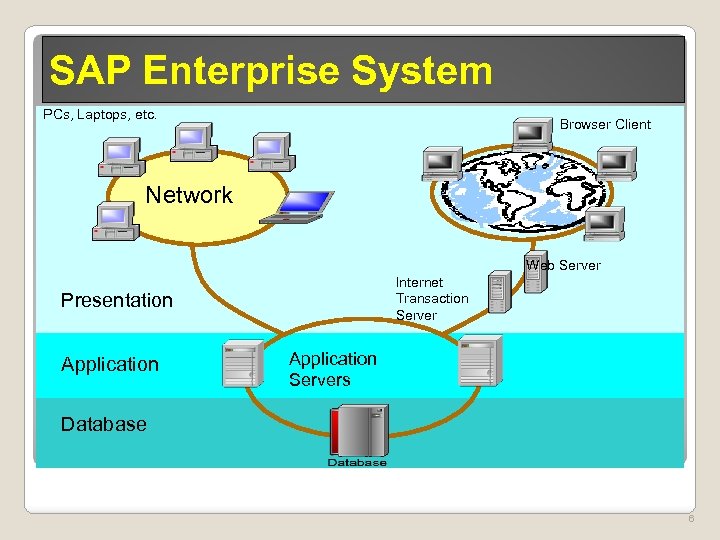 SAP Enterprise System PCs, Laptops, etc. Browser Client Network Web Server Internet Transaction Server Presentation Application Servers Database 6
SAP Enterprise System PCs, Laptops, etc. Browser Client Network Web Server Internet Transaction Server Presentation Application Servers Database 6
 SAP Data Types Required data types: Organizational levels (data, elements) Master data Transactional data (e. g. , documents)
SAP Data Types Required data types: Organizational levels (data, elements) Master data Transactional data (e. g. , documents)
 Data Type 1: Organizational Levels Defines the enterprise structure in terms of legal or business purposes, including legal entities, plants, storage areas, sales organizations, profit centers: Client (e. g. , 435) ◦ Highest organizational level ◦ Represents the enterprise consisting of many companies Business area (e. g. , BI##) ◦ An organizational unit within financial accounting. It corresponds to a defined business segment or area of responsibility, to which you can assign value movements recorded in Financial Accounting. Company Code (e. g. , US##) ◦ Identifies legal entities in an enterprise ◦ Central organizational element in financial accounting.
Data Type 1: Organizational Levels Defines the enterprise structure in terms of legal or business purposes, including legal entities, plants, storage areas, sales organizations, profit centers: Client (e. g. , 435) ◦ Highest organizational level ◦ Represents the enterprise consisting of many companies Business area (e. g. , BI##) ◦ An organizational unit within financial accounting. It corresponds to a defined business segment or area of responsibility, to which you can assign value movements recorded in Financial Accounting. Company Code (e. g. , US##) ◦ Identifies legal entities in an enterprise ◦ Central organizational element in financial accounting.
 Data Type 1: Organizational Levels Organizational levels in Logistics ◦ Plants (e. g. DL##, MI##, SD##) Represents factory, warehouse, office, distribution center, etc. ◦ Storage locations A location within a plant where materials are stored At plant DL##: FG##, SF##, RM##, MI## At MI##: FG##, MI##, TG## At SD##: FG##, MI##, TG##
Data Type 1: Organizational Levels Organizational levels in Logistics ◦ Plants (e. g. DL##, MI##, SD##) Represents factory, warehouse, office, distribution center, etc. ◦ Storage locations A location within a plant where materials are stored At plant DL##: FG##, SF##, RM##, MI## At MI##: FG##, MI##, TG## At SD##: FG##, MI##, TG##
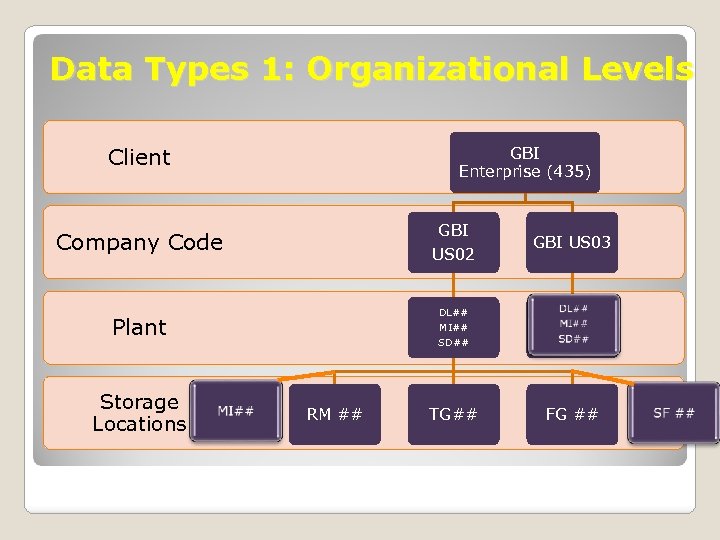 Data Types 1: Organizational Levels Client GBI Enterprise (435) GBI US 02 Company Code DL## MI## Plant Storage Locations GBI US 03 SD## RM ## TG## FG ##
Data Types 1: Organizational Levels Client GBI Enterprise (435) GBI US 02 Company Code DL## MI## Plant Storage Locations GBI US 03 SD## RM ## TG## FG ##
 Data Type 1: Organizational Levels § Organizational levels in Accounting § Client § Company code § Business area § Controlling area § Operating concern § Organizational levels in procurement § Purchasing organization § Purchasing group § Plant § Storage location n Organizational levels in fulfillment (sales) n Sales organizations n Divisions n Distribution channel n Sales areas n Shipping point n Plant n Storage location n Organizational levels in PP n Plant n Work Center n Storage location n Shipping Point
Data Type 1: Organizational Levels § Organizational levels in Accounting § Client § Company code § Business area § Controlling area § Operating concern § Organizational levels in procurement § Purchasing organization § Purchasing group § Plant § Storage location n Organizational levels in fulfillment (sales) n Sales organizations n Divisions n Distribution channel n Sales areas n Shipping point n Plant n Storage location n Organizational levels in PP n Plant n Work Center n Storage location n Shipping Point
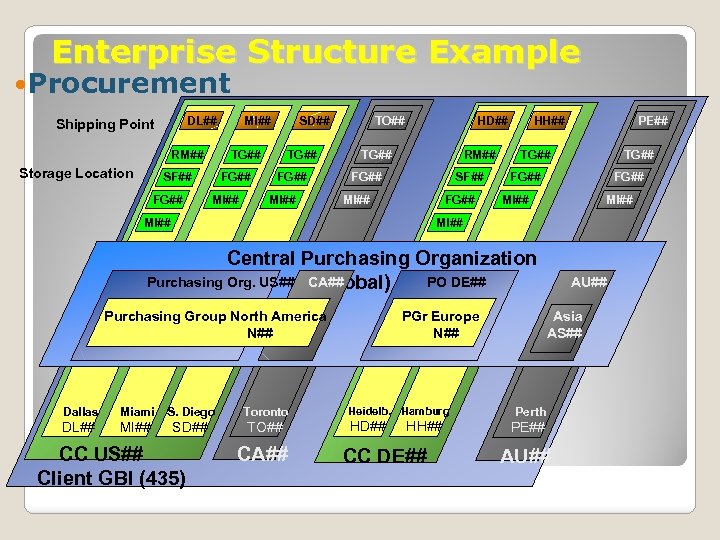 Enterprise Structure Example Procurement DL## Shipping Point RM## Storage Location SD## TG## SF## FG## MI## TO## HD## RM## TG## FG## SF## MI## FG## HH## PE## TG## FG## MI## Central Purchasing Organization Purchasing Org. US## CA## PO (global) GL## DE## Purchasing Group North America N## Dallas Miami S. Diego Toronto DL## MI## SD## TO## CC US## Client GBI (435) CA## PGr Europe N## Heidelb. Hamburg HD## HH## CC DE## AU## Asia AS## Perth PE## AU##
Enterprise Structure Example Procurement DL## Shipping Point RM## Storage Location SD## TG## SF## FG## MI## TO## HD## RM## TG## FG## SF## MI## FG## HH## PE## TG## FG## MI## Central Purchasing Organization Purchasing Org. US## CA## PO (global) GL## DE## Purchasing Group North America N## Dallas Miami S. Diego Toronto DL## MI## SD## TO## CC US## Client GBI (435) CA## PGr Europe N## Heidelb. Hamburg HD## HH## CC DE## AU## Asia AS## Perth PE## AU##
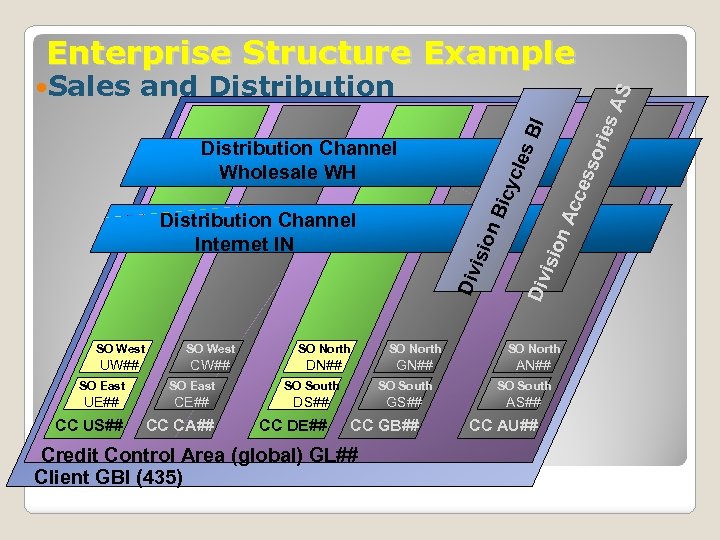 Enterprise Structure Example BI isio Div n. A n. B icy c les Distribution Channel Wholesale WH Distribution Channel Internet IN cce sso ries AS and Distribution Div Sales SO West SO North UW## CW## DN## GN## AN## SO East SO South UE## CE## DS## GS## AS## CC DE## CC GB## CC AU## CC US## CC CA## Credit Control Area (global) GL## Client GBI (435)
Enterprise Structure Example BI isio Div n. A n. B icy c les Distribution Channel Wholesale WH Distribution Channel Internet IN cce sso ries AS and Distribution Div Sales SO West SO North UW## CW## DN## GN## AN## SO East SO South UE## CE## DS## GS## AS## CC DE## CC GB## CC AU## CC US## CC CA## Credit Control Area (global) GL## Client GBI (435)
 Data Type 2: Master Data ◦ Long term data that represent entities of: Procurement ◦ Vendor ◦ Material ◦ Info records, source list Fulfillment (Sales & Distribution) ◦ Customer ◦ Material ◦ Conditions (pricing, output) Production ◦ Bills of material ◦ Work centers ◦ Product routings
Data Type 2: Master Data ◦ Long term data that represent entities of: Procurement ◦ Vendor ◦ Material ◦ Info records, source list Fulfillment (Sales & Distribution) ◦ Customer ◦ Material ◦ Conditions (pricing, output) Production ◦ Bills of material ◦ Work centers ◦ Product routings
 Types of Data 3: Transaction Data ◦ Data generated during executing process (steps) combining: Organizational levels Master data Situational data (who, what, when, and where) ◦ Example: sales order Organizational levels: customer, company code, sales area Master data: customer master, material master Situational data: date, time, person, quantities
Types of Data 3: Transaction Data ◦ Data generated during executing process (steps) combining: Organizational levels Master data Situational data (who, what, when, and where) ◦ Example: sales order Organizational levels: customer, company code, sales area Master data: customer master, material master Situational data: date, time, person, quantities
 Types of Data 3: Transaction Data • Document concept ◦ An electronic record of transactions ◦ Each transaction creates document(s) • Document types ◦ ◦ Financial accounting documents (FI) Management accounting documents (CO) Material documents (goods movement, MM) Others
Types of Data 3: Transaction Data • Document concept ◦ An electronic record of transactions ◦ Each transaction creates document(s) • Document types ◦ ◦ Financial accounting documents (FI) Management accounting documents (CO) Material documents (goods movement, MM) Others
 SAP ERP Document Principle Each business transaction that writes data to the database creates a uniquely numbered electronic document Each document contains information such as ◦ Responsible person ◦ Date and time of the transaction ◦ Commercial content Once created, a document can not be deleted from the database
SAP ERP Document Principle Each business transaction that writes data to the database creates a uniquely numbered electronic document Each document contains information such as ◦ Responsible person ◦ Date and time of the transaction ◦ Commercial content Once created, a document can not be deleted from the database
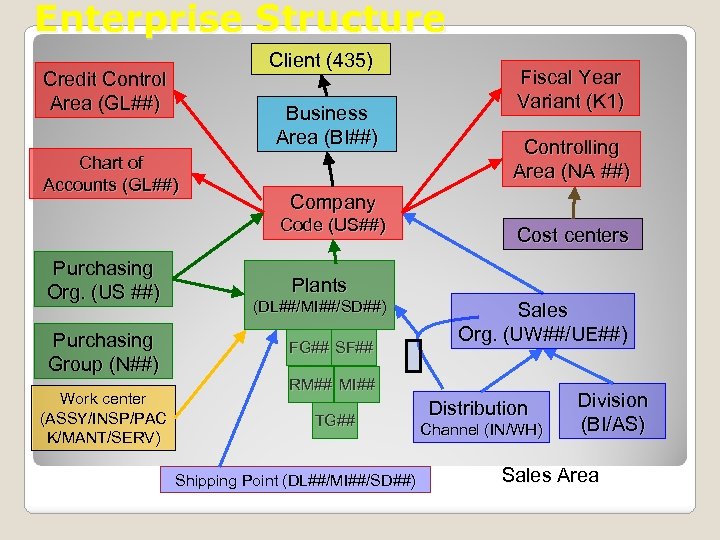 Enterprise Structure Client (435) Credit Control Area (GL##) Business Area (BI##) Chart of Accounts (GL##) Purchasing Group (N##) Work center (ASSY/INSP/PAC K/MANT/SERV) Controlling Area (NA ##) Company Code (US##) Purchasing Org. (US ##) Fiscal Year Variant (K 1) Cost centers Plants (DL##/MI##/SD##) FG## SF## Sales Org. (UW##/UE##) RM## MI## TG## Shipping Point (DL##/MI##/SD##) Distribution Channel (IN/WH) Division (BI/AS) Sales Area
Enterprise Structure Client (435) Credit Control Area (GL##) Business Area (BI##) Chart of Accounts (GL##) Purchasing Group (N##) Work center (ASSY/INSP/PAC K/MANT/SERV) Controlling Area (NA ##) Company Code (US##) Purchasing Org. (US ##) Fiscal Year Variant (K 1) Cost centers Plants (DL##/MI##/SD##) FG## SF## Sales Org. (UW##/UE##) RM## MI## TG## Shipping Point (DL##/MI##/SD##) Distribution Channel (IN/WH) Division (BI/AS) Sales Area
 GBI Inc. : Key Processes ◦ Procurement (buy) ◦ Fulfillment (sell) ◦ Production (make) ◦ Material forecast & demand planning (plan) ◦ Financial Accounting (track) ◦ Management Accounting (track) ◦ Inventory and Warehouse Management (store) ◦ Enterprise Asset Management (EAM, maintain) ◦ HCM (people)
GBI Inc. : Key Processes ◦ Procurement (buy) ◦ Fulfillment (sell) ◦ Production (make) ◦ Material forecast & demand planning (plan) ◦ Financial Accounting (track) ◦ Management Accounting (track) ◦ Inventory and Warehouse Management (store) ◦ Enterprise Asset Management (EAM, maintain) ◦ HCM (people)


