a0d9961c9bbeac11ecf4cbabd4263a7d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Intro to Oligopoly & market concentrations A 2 Economics
Intro to Oligopoly & market concentrations A 2 Economics
 Key Issues • Meaning of oligopoly • Examples of oligopoly • Understand the different market concentration ratios
Key Issues • Meaning of oligopoly • Examples of oligopoly • Understand the different market concentration ratios
 What is an Oligopoly? • Oligopoly is best defined by the market conduct (behaviour) of firms • A market dominated by a few large firms I. e. “Competition amongst the few” • High level of market concentration – Concentration ratio is the market share of the leading firms • Each firm tends to produce branded / differentiated products ue is ey iss K few! b of aviour eh a
What is an Oligopoly? • Oligopoly is best defined by the market conduct (behaviour) of firms • A market dominated by a few large firms I. e. “Competition amongst the few” • High level of market concentration – Concentration ratio is the market share of the leading firms • Each firm tends to produce branded / differentiated products ue is ey iss K few! b of aviour eh a
 What is an Oligopoly? • Sets up Barriers to Entry • Aims to create long run supernormal profits • Mutual interdependence between competing firms (important) • Intensive non-price competition is common • Periodic aggressive price wars • Exploitation of economies of scale
What is an Oligopoly? • Sets up Barriers to Entry • Aims to create long run supernormal profits • Mutual interdependence between competing firms (important) • Intensive non-price competition is common • Periodic aggressive price wars • Exploitation of economies of scale
 Examples of Oligopolies • Petrol Retailing • National Food Retailers • Hotel Industry • DIY Retail Sector • Electrical Retailing • Package Holiday Companies Each of you are to take one of these business areas and see if you can name the top 5 companies! • Leading Commercial Banks • Telecommunications Industry • Pharmaceutical companies • Soft drinks manufacturers • Low cost airlines • Computer games console manufacturers Orange competes in an oligopoly – there is intense price and non-price competition for customers
Examples of Oligopolies • Petrol Retailing • National Food Retailers • Hotel Industry • DIY Retail Sector • Electrical Retailing • Package Holiday Companies Each of you are to take one of these business areas and see if you can name the top 5 companies! • Leading Commercial Banks • Telecommunications Industry • Pharmaceutical companies • Soft drinks manufacturers • Low cost airlines • Computer games console manufacturers Orange competes in an oligopoly – there is intense price and non-price competition for customers
 To name a few examples of oligopolies • Groceries - dominated in the UK by Asda/Wal Mart, Tesco, Sainsbury and Safeway/Morrisons • Chemicals/oils - wide definition of the term chemical but key players are Shell, Exxon, Glaxo. Smith Klein, ICI, Kodak, Astra-Zeneca, BP, Du. Pont, BASF and Bayer • Brewers - Interbrew, Scottish and Newcastle, Guinness, and Carlsberg Tetley have a four firm concentration ratio of 85%! • Fast food outlets - Mc. Donalds, Burger King, KFC • Bookstores - Amazon, Barnes & Noble, Borders, Blackwells, Waterstones • Detergents - Unilever and Proctor and Gamble • Music retailing - HMV, Tesco, I Tunes, Tower, Amazon, MVC • Banks - Nat. West, Barclays, HSBC, Lloyds TSB • Entertainment - Time-Warner, BMG, • Electrical retail - Dixons, Currys, Comet • Electrical goods - Sony, Hitachi, Panasonic, Canon, Bush, Fuji • Mobile phone networks - O 2, Vodafone, Orange, T-Mobile • Home DIY - B&Q, Focus, Homebase
To name a few examples of oligopolies • Groceries - dominated in the UK by Asda/Wal Mart, Tesco, Sainsbury and Safeway/Morrisons • Chemicals/oils - wide definition of the term chemical but key players are Shell, Exxon, Glaxo. Smith Klein, ICI, Kodak, Astra-Zeneca, BP, Du. Pont, BASF and Bayer • Brewers - Interbrew, Scottish and Newcastle, Guinness, and Carlsberg Tetley have a four firm concentration ratio of 85%! • Fast food outlets - Mc. Donalds, Burger King, KFC • Bookstores - Amazon, Barnes & Noble, Borders, Blackwells, Waterstones • Detergents - Unilever and Proctor and Gamble • Music retailing - HMV, Tesco, I Tunes, Tower, Amazon, MVC • Banks - Nat. West, Barclays, HSBC, Lloyds TSB • Entertainment - Time-Warner, BMG, • Electrical retail - Dixons, Currys, Comet • Electrical goods - Sony, Hitachi, Panasonic, Canon, Bush, Fuji • Mobile phone networks - O 2, Vodafone, Orange, T-Mobile • Home DIY - B&Q, Focus, Homebase
 Oligopoly & Concentration ratios! • An oligopoly is an industry where there is a high level of market concentration. • The concentration ratio measures the extent to which a market or industry is dominated by a few leading firms. Normally an oligopoly exists when the top five firms in the market account for more than 60% of total market demand/sales. Top 5 firms > 60%
Oligopoly & Concentration ratios! • An oligopoly is an industry where there is a high level of market concentration. • The concentration ratio measures the extent to which a market or industry is dominated by a few leading firms. Normally an oligopoly exists when the top five firms in the market account for more than 60% of total market demand/sales. Top 5 firms > 60%
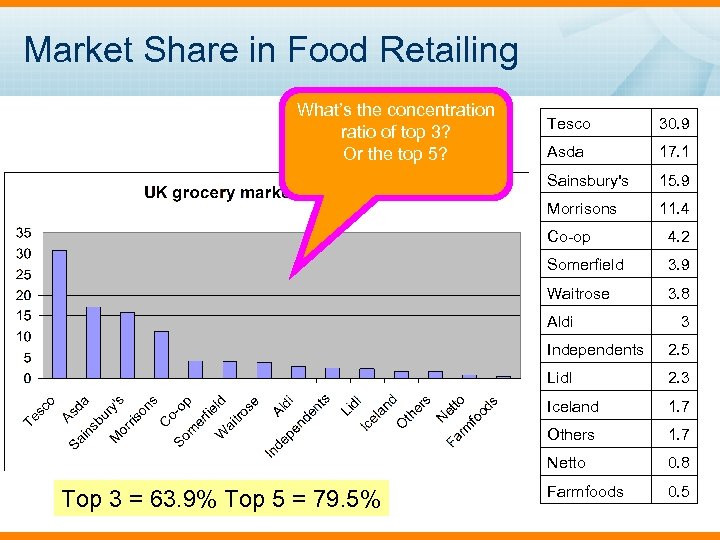 Market Share in Food Retailing What’s the concentration ratio of top 3? Or the top 5? Tesco 30. 9 Asda 17. 1 Sainsbury's 15. 9 Morrisons 11. 4 Co-op 4. 2 Somerfield 3. 9 Waitrose 3. 8 Aldi 3 Independents Lidl 2. 3 Iceland 1. 7 Others 1. 7 Netto Top 3 = 63. 9% Top 5 = 79. 5% 2. 5 0. 8 Farmfoods 0. 5
Market Share in Food Retailing What’s the concentration ratio of top 3? Or the top 5? Tesco 30. 9 Asda 17. 1 Sainsbury's 15. 9 Morrisons 11. 4 Co-op 4. 2 Somerfield 3. 9 Waitrose 3. 8 Aldi 3 Independents Lidl 2. 3 Iceland 1. 7 Others 1. 7 Netto Top 3 = 63. 9% Top 5 = 79. 5% 2. 5 0. 8 Farmfoods 0. 5
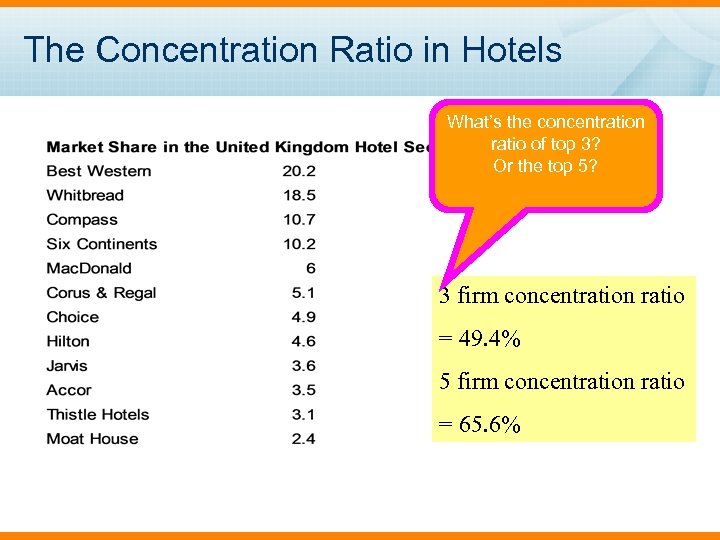 The Concentration Ratio in Hotels What’s the concentration ratio of top 3? Or the top 5? 3 firm concentration ratio = 49. 4% 5 firm concentration ratio = 65. 6%
The Concentration Ratio in Hotels What’s the concentration ratio of top 3? Or the top 5? 3 firm concentration ratio = 49. 4% 5 firm concentration ratio = 65. 6%
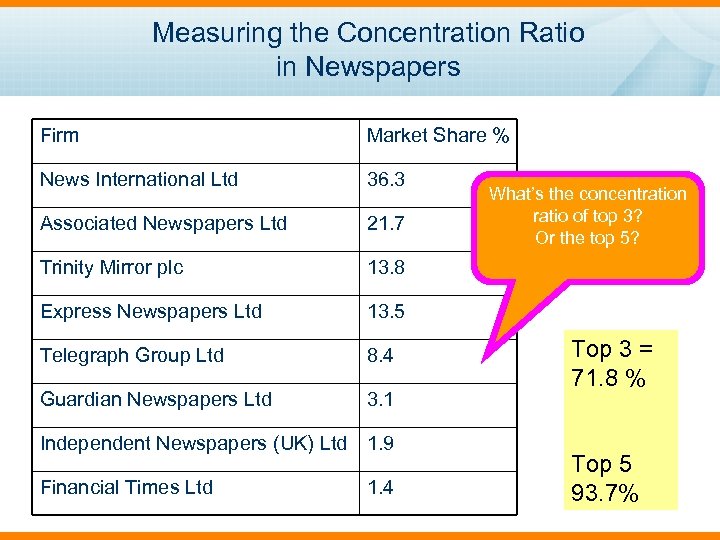 Measuring the Concentration Ratio in Newspapers Firm Market Share % News International Ltd 36. 3 Associated Newspapers Ltd 21. 7 Trinity Mirror plc 13. 8 Express Newspapers Ltd 13. 5 Telegraph Group Ltd 8. 4 Guardian Newspapers Ltd 3. 1 Independent Newspapers (UK) Ltd 1. 9 Financial Times Ltd 1. 4 What’s the concentration ratio of top 3? Or the top 5? Top 3 = 71. 8 % Top 5 93. 7%
Measuring the Concentration Ratio in Newspapers Firm Market Share % News International Ltd 36. 3 Associated Newspapers Ltd 21. 7 Trinity Mirror plc 13. 8 Express Newspapers Ltd 13. 5 Telegraph Group Ltd 8. 4 Guardian Newspapers Ltd 3. 1 Independent Newspapers (UK) Ltd 1. 9 Financial Times Ltd 1. 4 What’s the concentration ratio of top 3? Or the top 5? Top 3 = 71. 8 % Top 5 93. 7%
 So what’s the problem with a high concentration ratio? You need to think back to arguments against monopolies.
So what’s the problem with a high concentration ratio? You need to think back to arguments against monopolies.
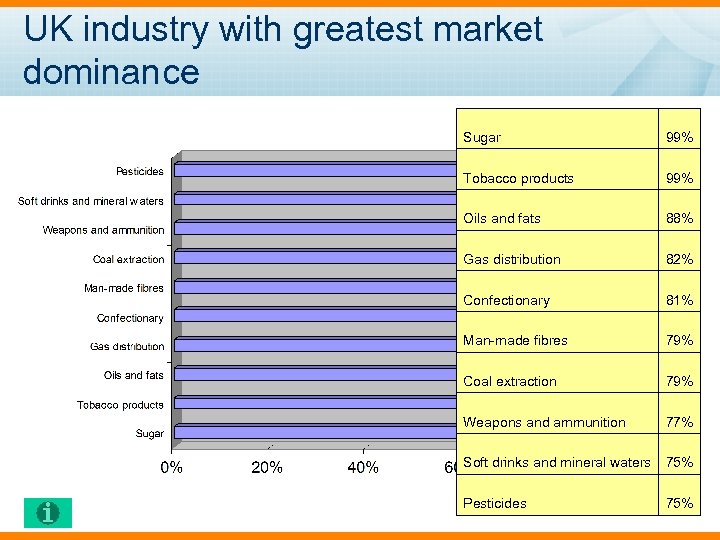 UK industry with greatest market dominance Sugar 99% Tobacco products 99% Oils and fats 88% Gas distribution 82% Confectionary 81% Man-made fibres 79% Coal extraction 79% Weapons and ammunition 77% Soft drinks and mineral waters 75% Pesticides 75%
UK industry with greatest market dominance Sugar 99% Tobacco products 99% Oils and fats 88% Gas distribution 82% Confectionary 81% Man-made fibres 79% Coal extraction 79% Weapons and ammunition 77% Soft drinks and mineral waters 75% Pesticides 75%
 Concentration ratio & market share • Market forms can often be classified by their concentration ratio. Listed, in ascending firm size, they are: • Perfect competition, with a very low concentration ratio. • Monopolistic competition, below 60% for the five-firm measurement. • Oligopoly, above 60% for the five-firm measurement. • Monopoly, with a near-100% four-firm measurement.
Concentration ratio & market share • Market forms can often be classified by their concentration ratio. Listed, in ascending firm size, they are: • Perfect competition, with a very low concentration ratio. • Monopolistic competition, below 60% for the five-firm measurement. • Oligopoly, above 60% for the five-firm measurement. • Monopoly, with a near-100% four-firm measurement.
 Oligopoly power • What harm can it do?
Oligopoly power • What harm can it do?
 Is your house loyal to one supermarket? Why? Supermarkets Oligopoly behaviour
Is your house loyal to one supermarket? Why? Supermarkets Oligopoly behaviour
 Supermarket non price competition • On line shopping • Supermarket store website • Opening hours • brand / product range • Non food products
Supermarket non price competition • On line shopping • Supermarket store website • Opening hours • brand / product range • Non food products
 Sainsburys
Sainsburys
 Waitrose
Waitrose
 Asda
Asda
 Tesco
Tesco
 So what extras do the supermarket websites offer?
So what extras do the supermarket websites offer?
 The main features of Oligopoly behaviour….
The main features of Oligopoly behaviour….
 Oligopoly behaviour • Non price competition • Can you remember some industries that are ‘oligopolistic’? • Price rigidity • Petrol • Hotel • DIY • Electrical Retailing • Package Holidays • Banks • Phone • Soft drinks • L shape cost curve (flat bottom!) • Collusion
Oligopoly behaviour • Non price competition • Can you remember some industries that are ‘oligopolistic’? • Price rigidity • Petrol • Hotel • DIY • Electrical Retailing • Package Holidays • Banks • Phone • Soft drinks • L shape cost curve (flat bottom!) • Collusion
 Price rigidity… • Despite changes in costs of production, oligopoly prices appear to remain at a constant level • Consider petrol prices…. Very rarely different within a geographical area… collusion or market forces?
Price rigidity… • Despite changes in costs of production, oligopoly prices appear to remain at a constant level • Consider petrol prices…. Very rarely different within a geographical area… collusion or market forces?
 L shape cost curve (flat bottom!) • Draw me a LRAC curve • Do you think that the optimum output is at just one point in output? • Not really a U for oligopolies… it tends to be a |____| shape – due to economies of scale over a wide range of products.
L shape cost curve (flat bottom!) • Draw me a LRAC curve • Do you think that the optimum output is at just one point in output? • Not really a U for oligopolies… it tends to be a |____| shape – due to economies of scale over a wide range of products.
 Formal Collusion – forming a cartel. • Oligopolies do compete against each other - known as non –collusive behaviour. • However, there is an incentive to collude. • Formal collusion - is where firms set up an agreement between each other – they create a cartel!
Formal Collusion – forming a cartel. • Oligopolies do compete against each other - known as non –collusive behaviour. • However, there is an incentive to collude. • Formal collusion - is where firms set up an agreement between each other – they create a cartel!
 Great milk robbery? Great milk robbery Supermarkets admit price fixing
Great milk robbery? Great milk robbery Supermarkets admit price fixing
 Tactic collusion • This is not illegal • It is where competitive firms monitor each other’s behaviour closely and refrain from competing on price. • This is often seen as price leadership where competitors follow the dominant firm’s lead.
Tactic collusion • This is not illegal • It is where competitive firms monitor each other’s behaviour closely and refrain from competing on price. • This is often seen as price leadership where competitors follow the dominant firm’s lead.
 Cartels • Where a few firms dominate they could set an agreement on price, quantities for supply, service standards etc • The collusion restricts output • The collusion raises prices • The collusion raises abnormal profits
Cartels • Where a few firms dominate they could set an agreement on price, quantities for supply, service standards etc • The collusion restricts output • The collusion raises prices • The collusion raises abnormal profits
 Famous cartels - OPEC • The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is a permanent intergovernmental organization, currently consisting of 12 oil producing and exporting countries, spread across three continents America, Asia and Africa. • The members are Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, the Islamic Republic of Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, the Socialist People’s Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates & Venezuela. • The organization’s principal objectives are: • 1. To co-ordinate and unify the petroleum policies of the Member Countries and to determine the best means for safeguarding their individual and collective interests; • 2. To seek ways and means of ensuring the stabilization of prices in international oil markets, with a view to eliminating harmful and unnecessary fluctuations; and • 3. To provide an efficient economic and regular supply of petroleum to consuming nations and a fair return on capital to those investing in the petroleum industry.
Famous cartels - OPEC • The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is a permanent intergovernmental organization, currently consisting of 12 oil producing and exporting countries, spread across three continents America, Asia and Africa. • The members are Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, the Islamic Republic of Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, the Socialist People’s Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates & Venezuela. • The organization’s principal objectives are: • 1. To co-ordinate and unify the petroleum policies of the Member Countries and to determine the best means for safeguarding their individual and collective interests; • 2. To seek ways and means of ensuring the stabilization of prices in international oil markets, with a view to eliminating harmful and unnecessary fluctuations; and • 3. To provide an efficient economic and regular supply of petroleum to consuming nations and a fair return on capital to those investing in the petroleum industry.
 Office of Fair trade definition… Typically, cartel members may agree on: • prices • output levels • discounts • credit terms Confess your cartel: Individuals can be sent to prison for up to five years and businesses can be fined up to 10 per cent of worldwide turnover. • which customers they will supply • which areas they will supply • who should win a contract (bid rigging).
Office of Fair trade definition… Typically, cartel members may agree on: • prices • output levels • discounts • credit terms Confess your cartel: Individuals can be sent to prison for up to five years and businesses can be fined up to 10 per cent of worldwide turnover. • which customers they will supply • which areas they will supply • who should win a contract (bid rigging).


