babb89d16929087f36fbcc0ebb115e33.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 Intro to MIS – MGS 351 Computer Hardware and Software Extended Learning Module A
Intro to MIS – MGS 351 Computer Hardware and Software Extended Learning Module A
 Chapter Overview m m Overview and History Binary and Digital Communications Hardware – CPU, Memory, Storage Devices, Input Devices, Output Devices Software – Operating Systems, Application Software, Programming Languages
Chapter Overview m m Overview and History Binary and Digital Communications Hardware – CPU, Memory, Storage Devices, Input Devices, Output Devices Software – Operating Systems, Application Software, Programming Languages
 Computers
Computers
 Other Computer Form Factors
Other Computer Form Factors
 Computers? ? ?
Computers? ? ?
 Essence of a Computer “If we can build something that adds, we’re well on our way to building something that uses addition to also subtract, multiply, divide, calculate mortgage payments, guide rockets to Mars, play chess and foul up our phone bills. ” - Charles Petzold, CODE p 131
Essence of a Computer “If we can build something that adds, we’re well on our way to building something that uses addition to also subtract, multiply, divide, calculate mortgage payments, guide rockets to Mars, play chess and foul up our phone bills. ” - Charles Petzold, CODE p 131
 Mechanical Computers
Mechanical Computers
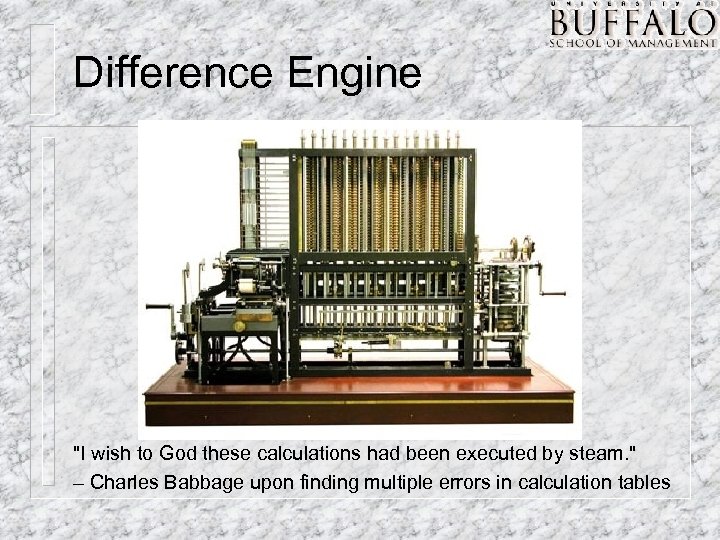 Difference Engine "I wish to God these calculations had been executed by steam. " – Charles Babbage upon finding multiple errors in calculation tables
Difference Engine "I wish to God these calculations had been executed by steam. " – Charles Babbage upon finding multiple errors in calculation tables
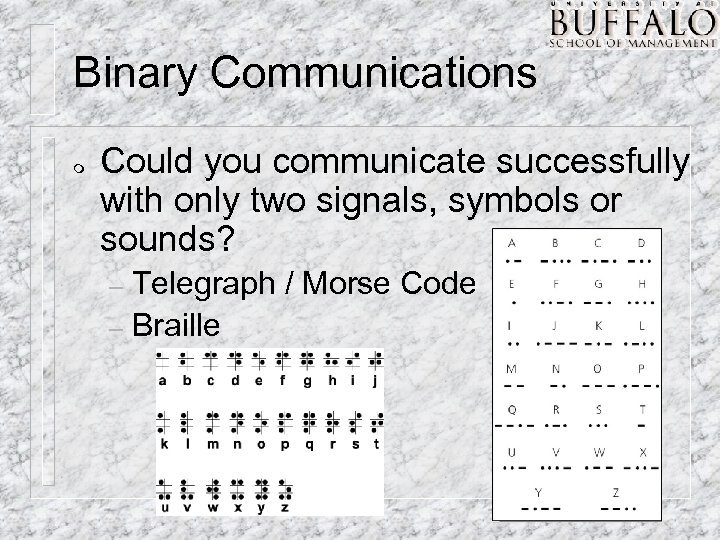 Binary Communications m Could you communicate successfully with only two signals, symbols or sounds? Telegraph / Morse Code – Braille –
Binary Communications m Could you communicate successfully with only two signals, symbols or sounds? Telegraph / Morse Code – Braille –
 Can a Machine do Binary Math?
Can a Machine do Binary Math?
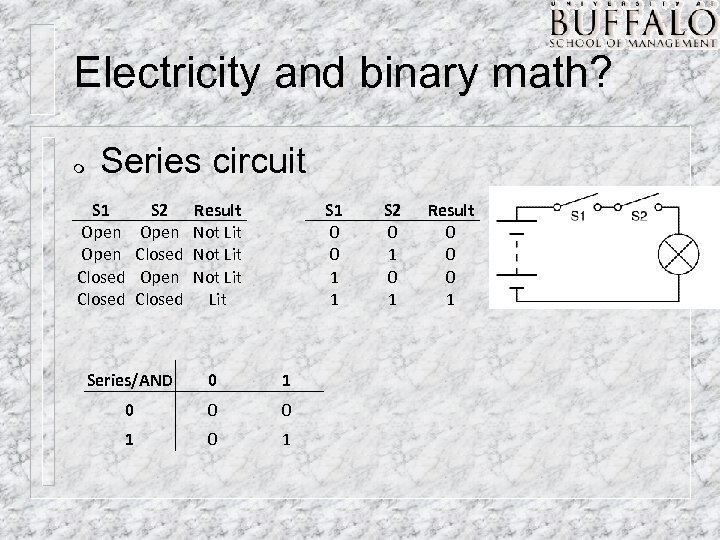 Electricity and binary math? m Series circuit S 1 Open Closed S 2 Open Closed Result Not Lit S 1 0 0 1 1 Series/AND 0 1 0 0 0 1 S 2 0 1 Result 0 0 0 1
Electricity and binary math? m Series circuit S 1 Open Closed S 2 Open Closed Result Not Lit S 1 0 0 1 1 Series/AND 0 1 0 0 0 1 S 2 0 1 Result 0 0 0 1
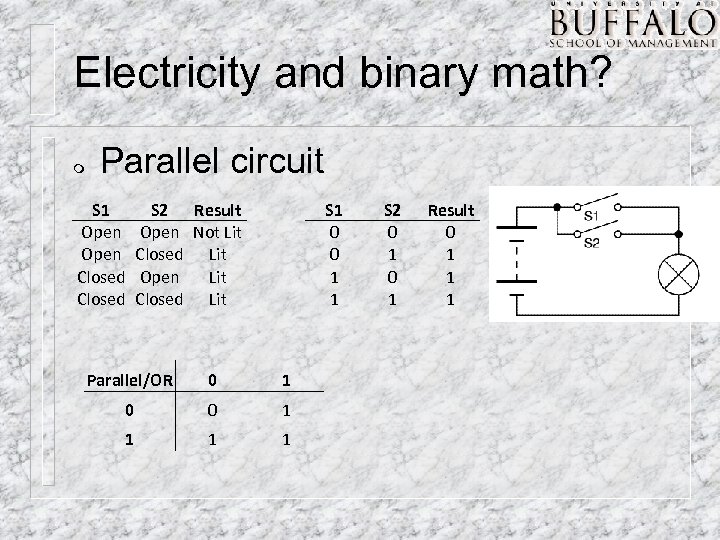 Electricity and binary math? m Parallel circuit S 1 Open Closed S 2 Result Open Not Lit Closed Lit Open Lit Closed Lit S 1 0 0 1 1 Parallel/OR 0 1 0 0 1 1 S 2 0 1 Result 0 1 1 1
Electricity and binary math? m Parallel circuit S 1 Open Closed S 2 Result Open Not Lit Closed Lit Open Lit Closed Lit S 1 0 0 1 1 Parallel/OR 0 1 0 0 1 1 S 2 0 1 Result 0 1 1 1
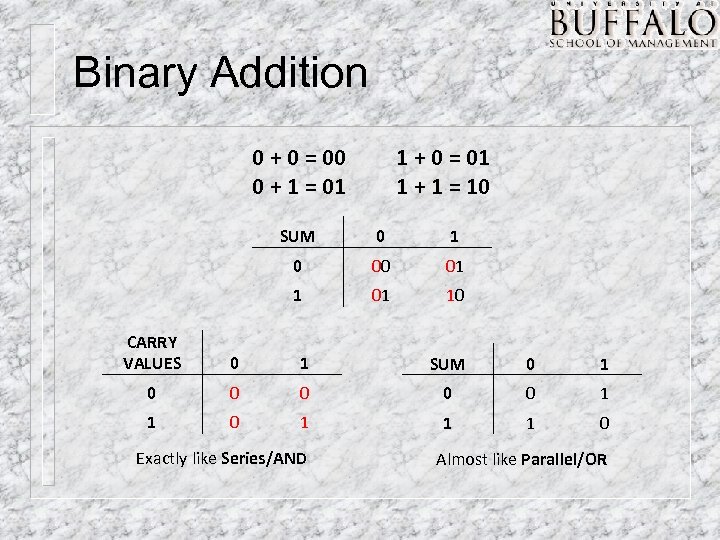 Binary Addition 0 + 0 = 00 0 + 1 = 01 1 + 0 = 01 1 + 1 = 10 SUM 0 1 0 00 01 10 CARRY VALUES 0 1 SUM 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 Exactly like Series/AND Almost like Parallel/OR
Binary Addition 0 + 0 = 00 0 + 1 = 01 1 + 0 = 01 1 + 1 = 10 SUM 0 1 0 00 01 10 CARRY VALUES 0 1 SUM 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 Exactly like Series/AND Almost like Parallel/OR
 Stibitz 1 -Bit Model K Adder "We wouldn't have our i. Phones today, if we didn't start out with stuff like this. " - Steve Wozniak
Stibitz 1 -Bit Model K Adder "We wouldn't have our i. Phones today, if we didn't start out with stuff like this. " - Steve Wozniak
 Digital Communications Bit (binary digit) Represents smallest unit of data in the form of either 0 or 1 m Byte String of bits, usually eight m m Stores one number or character
Digital Communications Bit (binary digit) Represents smallest unit of data in the form of either 0 or 1 m Byte String of bits, usually eight m m Stores one number or character
 Digital Communications
Digital Communications
 Sentence written in ASCII 0100000101010011010000110 10010010010000001 101001011100100000011 01110011011101000010 000001100111010101101 110000001110100011011 1100100000011101000111100 10111000001100101110
Sentence written in ASCII 0100000101010011010000110 10010010010000001 101001011100100000011 01110011011101000010 000001100111010101101 110000001110100011011 1100100000011101000111100 10111000001100101110
 What is this?
What is this?
 What is this?
What is this?
 Hardware m The physical electronic components and peripherals of a computer that do the “work” of computing.
Hardware m The physical electronic components and peripherals of a computer that do the “work” of computing.
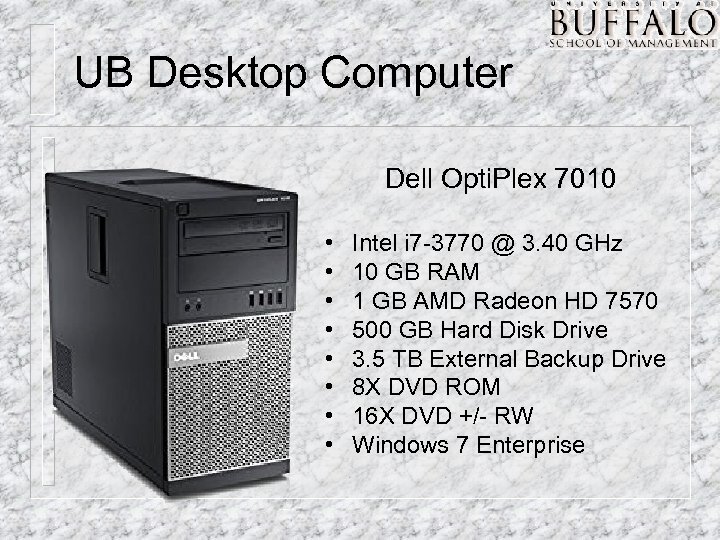 UB Desktop Computer Dell Opti. Plex 7010 • • Intel i 7 -3770 @ 3. 40 GHz 10 GB RAM 1 GB AMD Radeon HD 7570 500 GB Hard Disk Drive 3. 5 TB External Backup Drive 8 X DVD ROM 16 X DVD +/- RW Windows 7 Enterprise
UB Desktop Computer Dell Opti. Plex 7010 • • Intel i 7 -3770 @ 3. 40 GHz 10 GB RAM 1 GB AMD Radeon HD 7570 500 GB Hard Disk Drive 3. 5 TB External Backup Drive 8 X DVD ROM 16 X DVD +/- RW Windows 7 Enterprise
 UB Laptop Computer Dell Latitude E 7440 • • • Intel i 7 -4600 U @ 2. 10 GHz 16 GB RAM Intel HD Graphics (Integrated) 256 GB Solid State Drive Windows 7 Enterprise
UB Laptop Computer Dell Latitude E 7440 • • • Intel i 7 -4600 U @ 2. 10 GHz 16 GB RAM Intel HD Graphics (Integrated) 256 GB Solid State Drive Windows 7 Enterprise
 Personal Laptop Computer Microsoft Surface Book • • • Intel i 7 -6600 U @ 2. 60 GHz 16 GB RAM NVIDIA Ge. Force GPU 500 GB Solid State Drive Windows 10 Professional
Personal Laptop Computer Microsoft Surface Book • • • Intel i 7 -6600 U @ 2. 60 GHz 16 GB RAM NVIDIA Ge. Force GPU 500 GB Solid State Drive Windows 10 Professional
 CPU (processor) m Interprets and carries out basic instructions that operate a computer. Controls other parts of the computer system. m Gigahertz and Multicore m Moore’s Law
CPU (processor) m Interprets and carries out basic instructions that operate a computer. Controls other parts of the computer system. m Gigahertz and Multicore m Moore’s Law
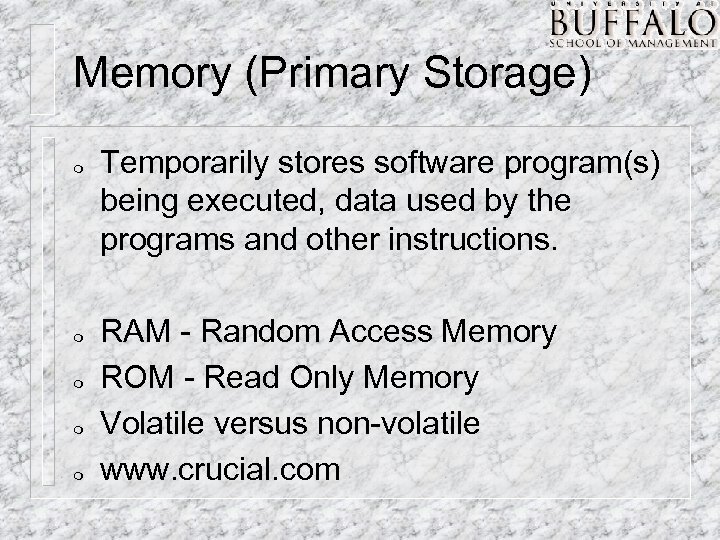 Memory (Primary Storage) m m m Temporarily stores software program(s) being executed, data used by the programs and other instructions. RAM - Random Access Memory ROM - Read Only Memory Volatile versus non-volatile www. crucial. com
Memory (Primary Storage) m m m Temporarily stores software program(s) being executed, data used by the programs and other instructions. RAM - Random Access Memory ROM - Read Only Memory Volatile versus non-volatile www. crucial. com
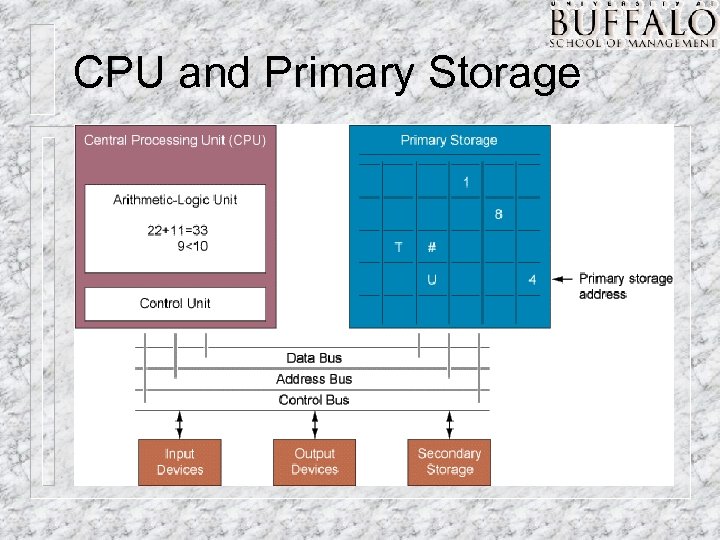 CPU and Primary Storage
CPU and Primary Storage
 What is this?
What is this?
 Storage Devices m m Sequential versus direct access Magnetic disk: Floppy disk, Hard disk m Solid state drive m Optical disks: CD-ROM, DVDs m Magnetic tape: Inexpensive, older secondary-storage medium
Storage Devices m m Sequential versus direct access Magnetic disk: Floppy disk, Hard disk m Solid state drive m Optical disks: CD-ROM, DVDs m Magnetic tape: Inexpensive, older secondary-storage medium


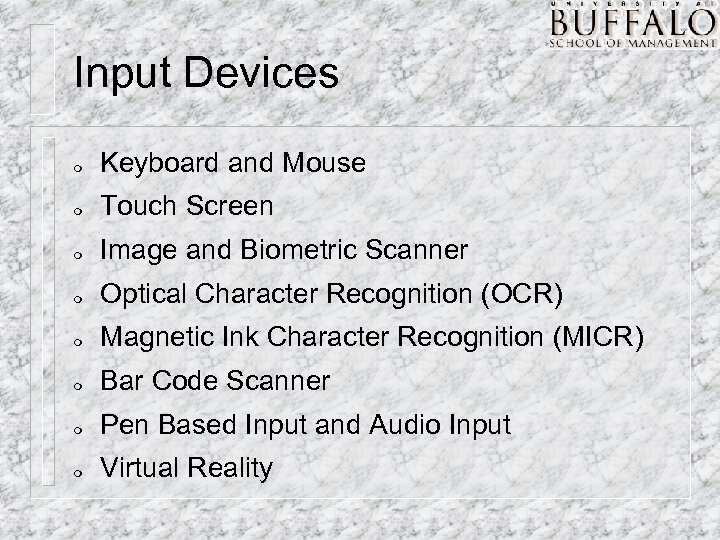 Input Devices m Keyboard and Mouse m Touch Screen m Image and Biometric Scanner m Optical Character Recognition (OCR) m Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) m Bar Code Scanner m Pen Based Input and Audio Input m Virtual Reality
Input Devices m Keyboard and Mouse m Touch Screen m Image and Biometric Scanner m Optical Character Recognition (OCR) m Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) m Bar Code Scanner m Pen Based Input and Audio Input m Virtual Reality
 Output Devices m Monitor m Printer m Audio Output m Microfilm and Microfiche m Virtual Reality
Output Devices m Monitor m Printer m Audio Output m Microfilm and Microfiche m Virtual Reality
 Software m The electronic instructions that tell the computer hardware what to do. Software is useless without hardware and vice versa.
Software m The electronic instructions that tell the computer hardware what to do. Software is useless without hardware and vice versa.
 Software • Software program: Series of statements or instructions to the computer • System software: Generalized programs, manages computer’s resources • Application software: Programs written to perform functions specified by end users
Software • Software program: Series of statements or instructions to the computer • System software: Generalized programs, manages computer’s resources • Application software: Programs written to perform functions specified by end users
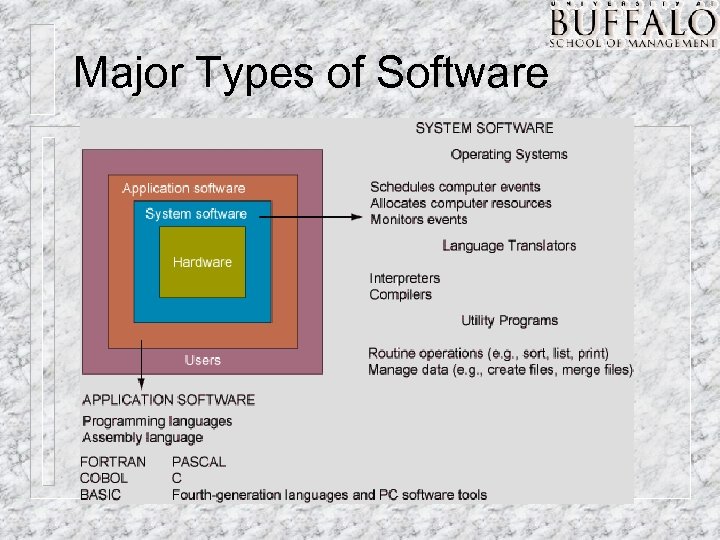 Major Types of Software
Major Types of Software
 What is an Operating System? m A set of programs that manages the operations of a computer and functions as an interface between the user, the application programs and the computer hardware. – Windows (XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10, Server) Mac OS, DOS, UNIX, Linux, OS/2, MVS and more!
What is an Operating System? m A set of programs that manages the operations of a computer and functions as an interface between the user, the application programs and the computer hardware. – Windows (XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10, Server) Mac OS, DOS, UNIX, Linux, OS/2, MVS and more!
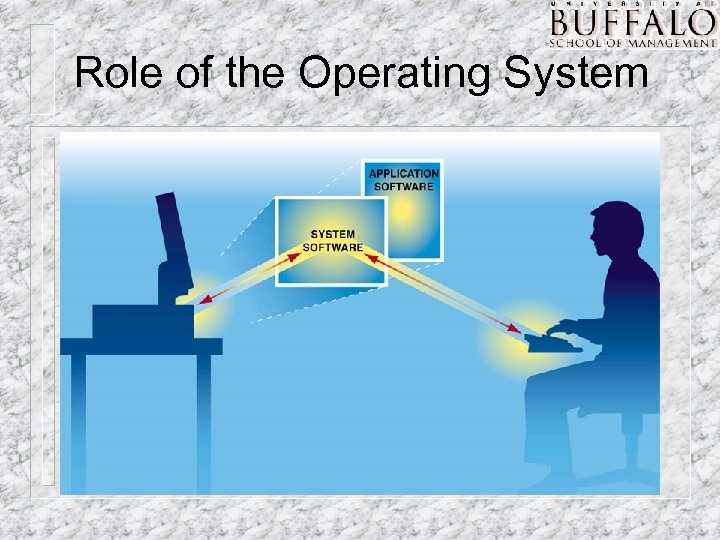 Role of the Operating System
Role of the Operating System
 Operating System Functions • Allocates and assigns system resources • Schedules use of computer resources • Monitors computer system activities • Provides locations in primary memory for data and programs • Controls the input and output devices
Operating System Functions • Allocates and assigns system resources • Schedules use of computer resources • Monitors computer system activities • Provides locations in primary memory for data and programs • Controls the input and output devices
 Linux m Operating system originally developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991 m Software is freely available and open source m Contributions made by over 12, 000 developers m Used to power – New York Stock Exchange – Particle accelerator at CERN – Toyota’s Vehicle Infotainment – Nearly all of the fastest 500 supercomputers
Linux m Operating system originally developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991 m Software is freely available and open source m Contributions made by over 12, 000 developers m Used to power – New York Stock Exchange – Particle accelerator at CERN – Toyota’s Vehicle Infotainment – Nearly all of the fastest 500 supercomputers
 Popular Linux Distributions m m m Ubuntu - www. ubuntu. com Linux Mint - linuxmint. com Zorin OS - www. zorin-os. com Hundreds more at distrowatch. com Can try Linux without installing it using a Linux Live. CD - www. livecdlist. com
Popular Linux Distributions m m m Ubuntu - www. ubuntu. com Linux Mint - linuxmint. com Zorin OS - www. zorin-os. com Hundreds more at distrowatch. com Can try Linux without installing it using a Linux Live. CD - www. livecdlist. com
 Application Software m m Software designed to perform peoplerelated tasks such as payroll, inventory, and sales analysis. Questions when Selecting Software – – Proprietary or Common Off the Shelf (COTS) Software? Build or Buy? Open Source or Commercial?
Application Software m m Software designed to perform peoplerelated tasks such as payroll, inventory, and sales analysis. Questions when Selecting Software – – Proprietary or Common Off the Shelf (COTS) Software? Build or Buy? Open Source or Commercial?
 Popular Programming Languages • Java, Javascript, C, C++, PHP, Python, C#, Visual Basic, Objective C, Perl, Ruby, Delphi
Popular Programming Languages • Java, Javascript, C, C++, PHP, Python, C#, Visual Basic, Objective C, Perl, Ruby, Delphi
 Programming Languages • Machine language: Consists of 1 s and 0 s of binary code • Assembly language: Resembles machine language, substitutes mnemonics for numeric codes • Third-generation languages: FORTRAN, COBOL, BASIC, Pascal, and C
Programming Languages • Machine language: Consists of 1 s and 0 s of binary code • Assembly language: Resembles machine language, substitutes mnemonics for numeric codes • Third-generation languages: FORTRAN, COBOL, BASIC, Pascal, and C
 Programming Languages • Fourth-generation language: Employed directly by end users nonprocedural • Natural languages: Similar to human language • Query languages: Retrieve data stored in databases or files (eg SQL)
Programming Languages • Fourth-generation language: Employed directly by end users nonprocedural • Natural languages: Similar to human language • Query languages: Retrieve data stored in databases or files (eg SQL)
 Programming Languages • Machine code 01001010 111010 001011 • Assembly language AR 5, 3 • FORTRAN READ (5, 100) ID, QUANT, PRICE TOTAL = QUANT * PRICE • COBOL MULTIPLY QUANT-SOLD BY UNIT-PRICE GIVING SALES-TOTAL
Programming Languages • Machine code 01001010 111010 001011 • Assembly language AR 5, 3 • FORTRAN READ (5, 100) ID, QUANT, PRICE TOTAL = QUANT * PRICE • COBOL MULTIPLY QUANT-SOLD BY UNIT-PRICE GIVING SALES-TOTAL
 Language Translation Software • Translates high-level language programs into machine language (1 s and 0 s) binary executables • Compilers • Interpreters
Language Translation Software • Translates high-level language programs into machine language (1 s and 0 s) binary executables • Compilers • Interpreters
 Is newer technology better? When should you upgrade?
Is newer technology better? When should you upgrade?
 Quote “We should be impressed by technology, but we shouldn’t be distracted by it or fooled into thinking that technology, unto itself, is the solution to anything. ” -Lou Gerstner
Quote “We should be impressed by technology, but we shouldn’t be distracted by it or fooled into thinking that technology, unto itself, is the solution to anything. ” -Lou Gerstner


