8937d214da01b7ef32932edda06cc1a7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

INTRO TO MANAGEMENT SUPPORT SYSTEMS IS 340 BY CHANDRA S. AMARAVADI

IN THIS PRESENTATION. . Introduction to MSS l Decisions & types of decisions l DSS l EIS l GDSS l 2

INTRO TO MSS 3

INTRODUCTION (FYI) l More competition l Globalization l Complexity More decision making (D. M) 4

MANAGEMENT SUPPORT SYSTEMS MSS: collection of tools/systems to support managerial activity. Characteristics (FYI): u Interactive u Customizable u Model based u Support rather than automate 5
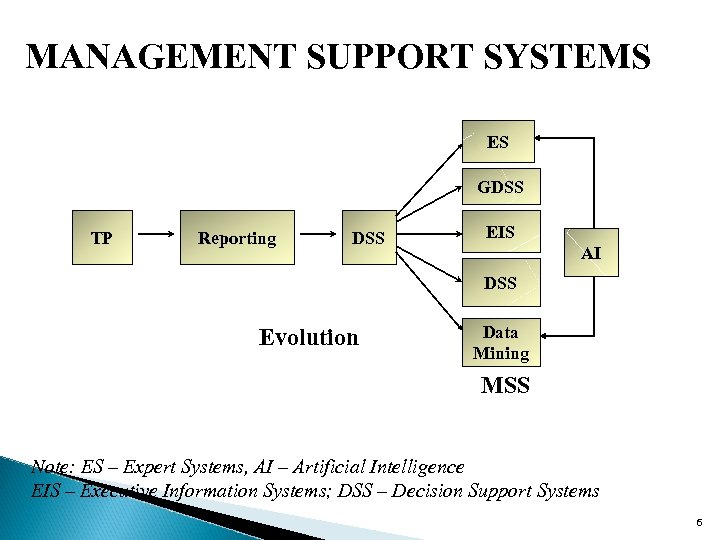
MANAGEMENT SUPPORT SYSTEMS ES GDSS TP Reporting DSS EIS AI DSS Evolution Data Mining MSS Note: ES – Expert Systems, AI – Artificial Intelligence EIS – Executive Information Systems; DSS – Decision Support Systems 6

EXAMPLES OF DECISIONS n. Whether to approve a loan? n. Whether to promote an employee? n. How much of an increase to allocate to employees? n. Where to advertise? Allocation to media? n. How to finance a capital expansion project? n. How much to produce? When to produce? n. What products to produce? What markets? n. What production techniques to use? 7
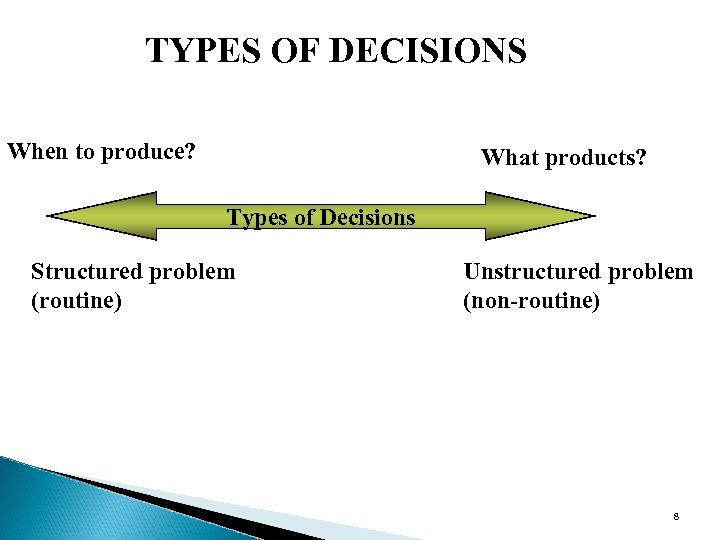
TYPES OF DECISIONS When to produce? What products? Types of Decisions Structured problem (routine) Unstructured problem (non-routine) 8
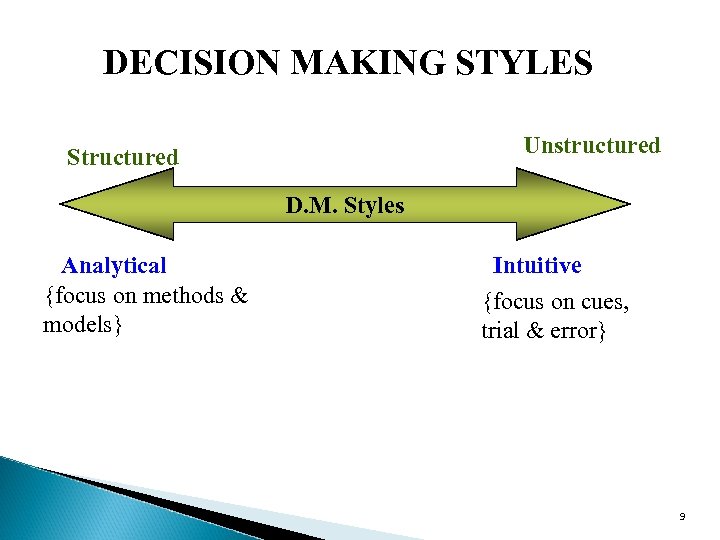
DECISION MAKING STYLES Unstructured Structured D. M. Styles Analytical {focus on methods & models} Intuitive {focus on cues, trial & error} 9
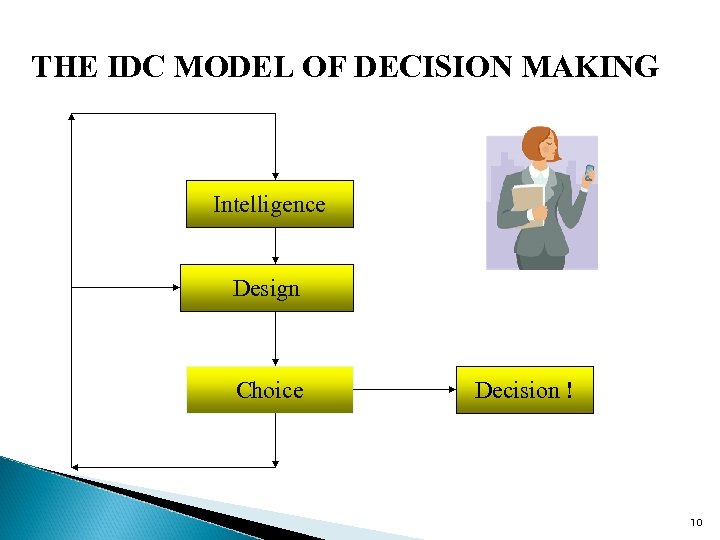
THE IDC MODEL OF DECISION MAKING Intelligence Design Choice Decision ! 10
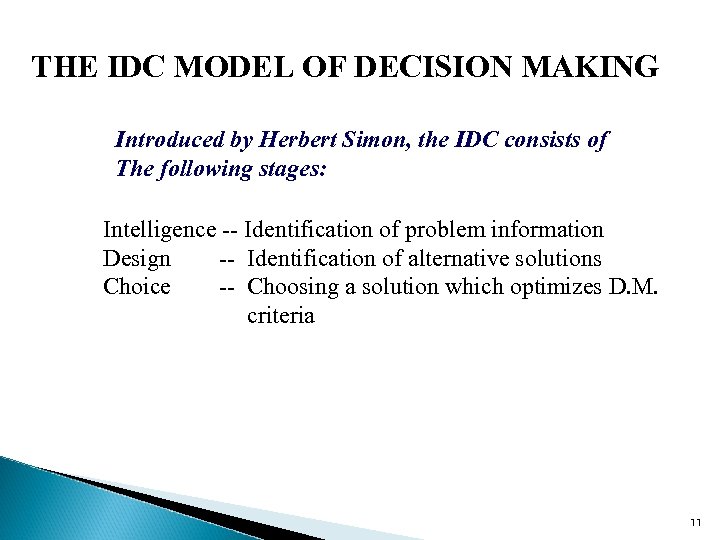
THE IDC MODEL OF DECISION MAKING Introduced by Herbert Simon, the IDC consists of The following stages: Intelligence -- Identification of problem information Design -- Identification of alternative solutions Choice -- Choosing a solution which optimizes D. M. criteria 11

DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS 12

DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS A system that supports structured and semistructured decision making by managers in their own personalized way. 13
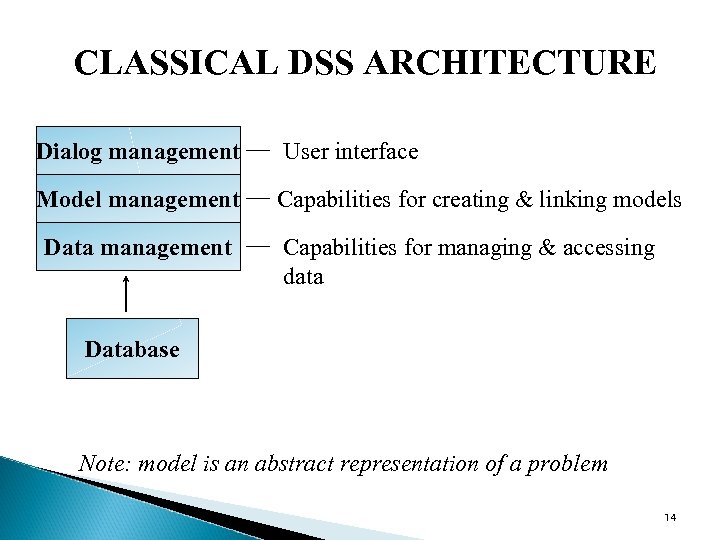
CLASSICAL DSS ARCHITECTURE Dialog management User interface Model management Capabilities for creating & linking models Data management Capabilities for managing & accessing data Database Note: model is an abstract representation of a problem 14

DSS ANALYSIS CAPABILITIES u “What - if “ u Sensitivity u Goal-seeking u Optimization 15

DSS ANALYSIS CAPABILITIES What if - change one or more variables Sensitivity - change one variable Goal seeking - finding a solution to satisfy constraints Optimization- find best solution under a given set of constraints 16

DSS MODELS (FYI) u Financial e. g. portfolio, NPV u Statistical e. g. : forecasting u Marketing e. g. : product mix, advertising u Production e. g. capacity planning, inventory u Simulation e. g. production process, bank tellers etc. 17
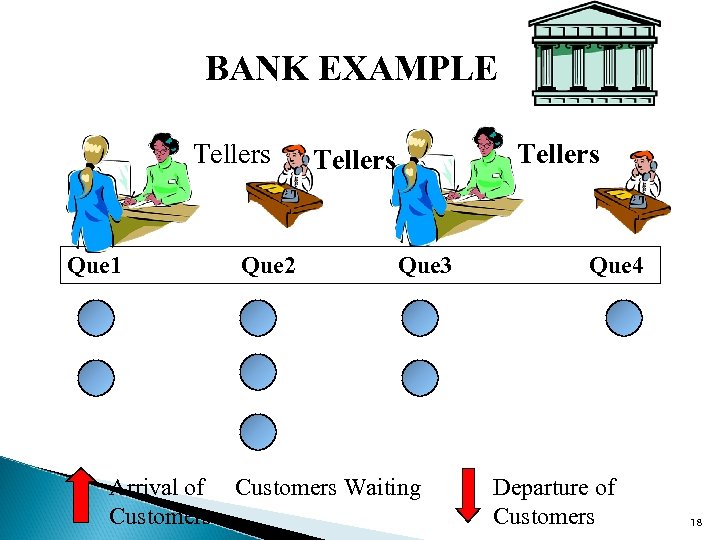
BANK EXAMPLE Tellers Que 1 Que 2 Tellers Que 3 Arrival of Customers Waiting Customers Que 4 Departure of Customers 18
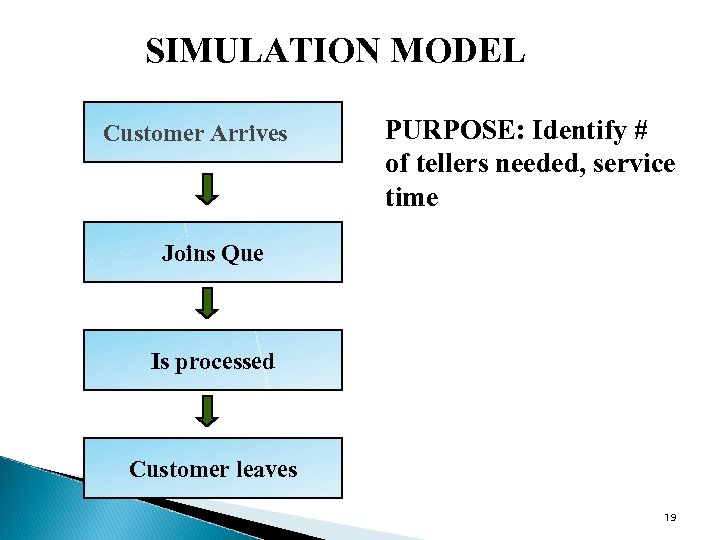
SIMULATION MODEL Customer Arrives PURPOSE: Identify # of tellers needed, service time Joins Que Is processed Customer leaves 19

CASE OF THE S. S. KUNIANG (FYI) l Ship ran aground l Owners wanted to sell it l Coast guard was the authority l Sealed bid l Scrap value ($5 m) l Repair cost ($15 m) 20

NEW ENGLAND ELECTRIC SYSTEM l Utility company needs coal l 4 m tons/year l Purchased a $70 m General Dynamics vessel l Capacity 36, 250 tons (self loading) l Bid for Kuniang? l How much? 21

DECISION COMPLICATIONS l Type of coal: Egypt or PA? l Jones Act and round trip time l Exception to Jones Act l Self unloader reduces cargo capacity l Buy a sister vessel? Tug barge? 22

DECISION OPTIONS (FYI) Options are l. Kuniang (w crane), l. Kuniang (no crane), l. General dynamics vessel, or ltug barge 23
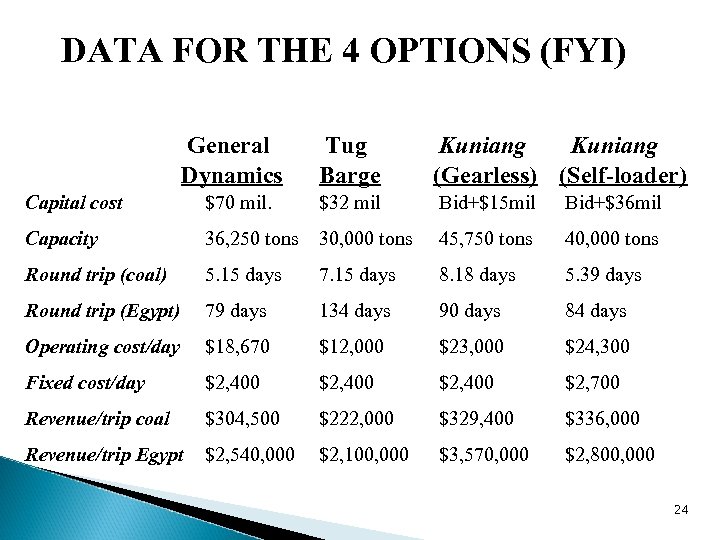
DATA FOR THE 4 OPTIONS (FYI) General Dynamics Tug Barge Kuniang (Gearless) (Self-loader) Capital cost $70 mil. $32 mil Bid+$15 mil Bid+$36 mil Capacity 36, 250 tons 30, 000 tons 45, 750 tons 40, 000 tons Round trip (coal) 5. 15 days 7. 15 days 8. 18 days 5. 39 days Round trip (Egypt) 79 days 134 days 90 days 84 days Operating cost/day $18, 670 $12, 000 $23, 000 $24, 300 Fixed cost/day $2, 400 $2, 700 Revenue/trip coal $304, 500 $222, 000 $329, 400 $336, 000 Revenue/trip Egypt $2, 540, 000 $2, 100, 000 $3, 570, 000 $2, 800, 000 24
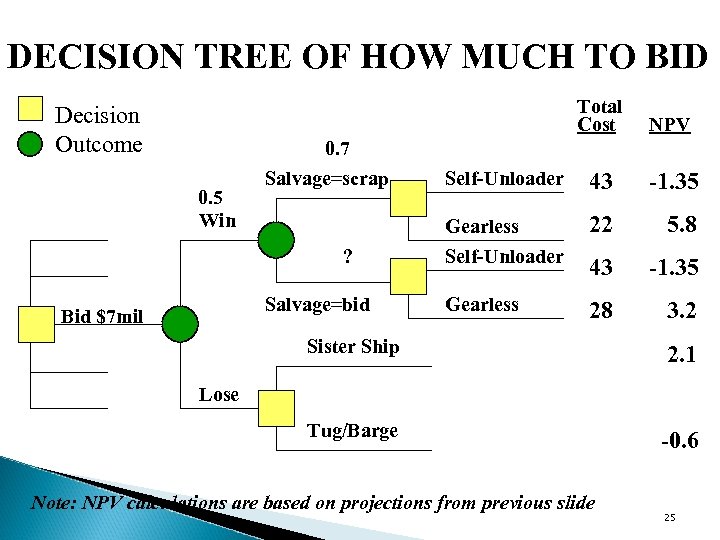
DECISION TREE OF HOW MUCH TO BID Total Cost Decision Outcome NPV Self-Unloader 43 -1. 35 Gearless 22 5. 8 Self-Unloader 43 -1. 35 Gearless 28 3. 2 0. 7 0. 5 Win Salvage=scrap ? Salvage=bid Bid $7 mil Sister Ship 2. 1 Tug/Barge -0. 6 Lose Note: NPV calculations are based on projections from previous slide 25

CONCLUSIONS (FYI) Ø NEES ended up bidding $6. 7 million for the Kuniang, but lost to a bid of $10 million Ø Coast Guard valued ship as scrap metal Ø Decision tree a useful tool; parameters unknown 26

DSS APPLICATIONS l l l l Cash forecasting Fire-fighting Portfolio selection Evaluate lending risk Event scheduling School location Police beat 27

DATA MINING 28

DATA MINING Search for relationships and global patterns that exist in large databases but are hidden in the vast amounts of data. e. g. sequence/association, classification, and clustering 29

SOME DATA MINING APPLICATIONS u Predicting the probability of default for consumer loans u Predicting audience response to TV advertisements u Predicting the probability that a cancer patient will respond to radiation therapy. u Predicting the probability that an offshore well is going to produce oil 30
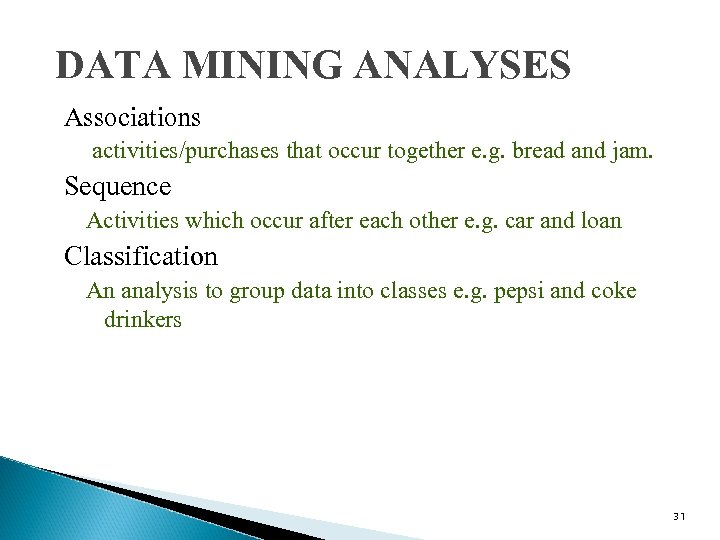
DATA MINING ANALYSES Associations activities/purchases that occur together e. g. bread and jam. Sequence Activities which occur after each other e. g. car and loan Classification An analysis to group data into classes e. g. pepsi and coke drinkers 31

BI SYSTEMS (ALSO EXECUTIVE INFORMATION SYSTEMS) 32

BI SYSTEMS & DASHBOARDS BI System: Systems that provide information to executives on the business environment. Executive Dashboard: An interface that displays information needed to effectively run an enterprise. Does more information lead to better quality decisions? 33
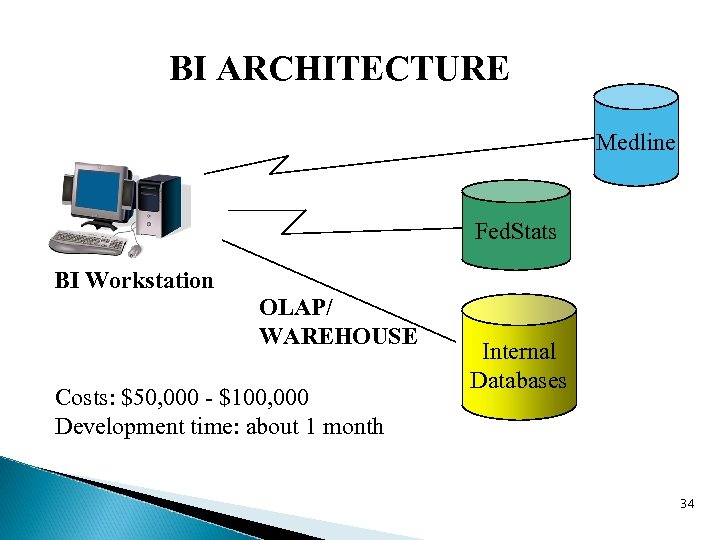
BI ARCHITECTURE Medline Fed. Stats BI Workstation OLAP/ WAREHOUSE Costs: $50, 000 - $100, 000 Development time: about 1 month Internal Databases 34

BI CHARACTERISTICS An intuitive easy-to-navigate graphical display A logical structure for easy access Little or no user training is required Data displays that can be customized Regular and frequent automatic updates of dashboard information Information from multiple sources, departments, or markets can be viewed simultaneously
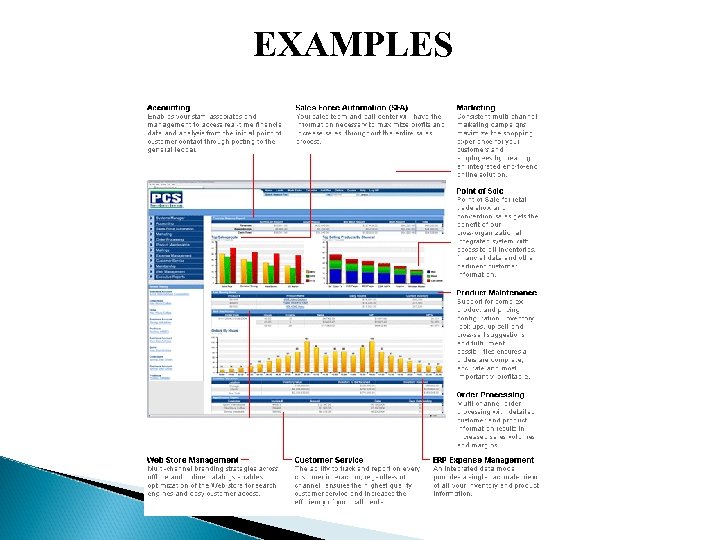
EXAMPLES
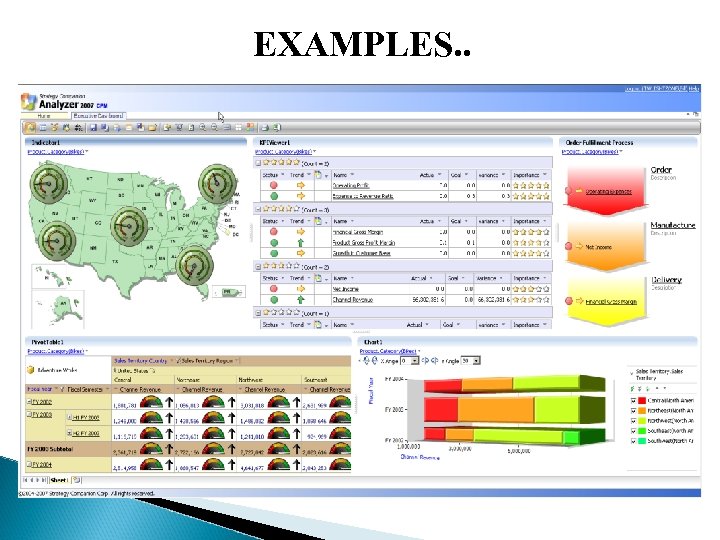
EXAMPLES. .

COLLABORATIVE SYSTEMS (GDSS) 38

COLLABORATIVE SYSTEMS An interactive computer based system which facilitates solution of unstructured problems by a set of D. M. working together as a group. Other terms - GDSS, Electronic Meeting Systems. 39

CURRENT BUSINESS TRENDS (FYI) l More competition l Shift towards flat/virtual organizations l More mergers [industry consolidations] l Globalization of markets and products l More strategic alliances Group D. M. Is it necessary for org. decisions to be made in groups? Why cannot it be handled by individuals? 40

CHARACTERISTICS OF GROUP D. M. l l Participants of equal rank 5 -20 Time limits Requires knowledge from participants 41
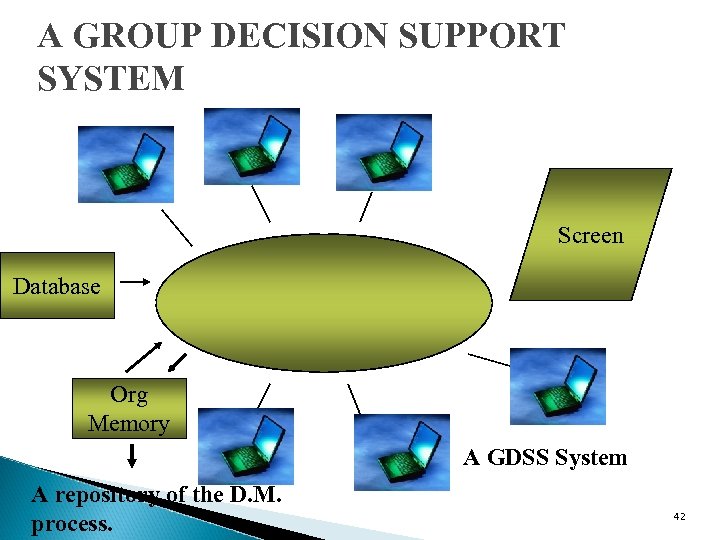
A GROUP DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM Screen Database Org Memory A GDSS System A repository of the D. M. process. 42

GROUP DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS 43
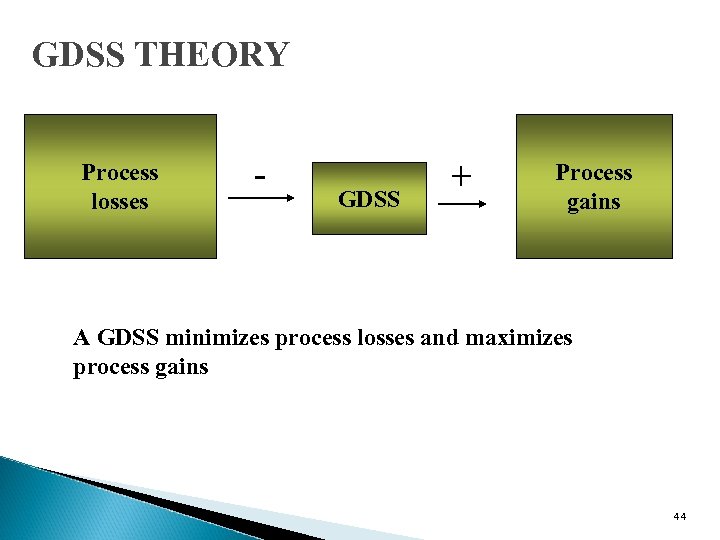
GDSS THEORY Process losses - GDSS + Process gains A GDSS minimizes process losses and maximizes process gains 44

ADVANTAGES OF GDSS n Time n Anonymity n Democratic participation n Satisfaction n Record of decision 45

THE END 46
8937d214da01b7ef32932edda06cc1a7.ppt