04a70c584c383a5db33e6e63b8761d13.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 120
 Intro to Info Tech System Development Extra Credit Assg This presentation can be viewed on line at: http: //web. fscj. edu/Janson/cgs 1060/wk 12. System. Dev. ppt Copyright 2003 by Janson Industries 1
Intro to Info Tech System Development Extra Credit Assg This presentation can be viewed on line at: http: //web. fscj. edu/Janson/cgs 1060/wk 12. System. Dev. ppt Copyright 2003 by Janson Industries 1
 Objectives ▀ Expl. ain ♦ ♦ ▀ The System Development Cycle The Program Development Cycle Introduce technologies used to create systems ♦ ♦ Programming languages Development tools Scripting languages Application generators 2 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Objectives ▀ Expl. ain ♦ ♦ ▀ The System Development Cycle The Program Development Cycle Introduce technologies used to create systems ♦ ♦ Programming languages Development tools Scripting languages Application generators 2 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 System Development ▀ Need a defined process to create a complex info system ♦ ▀ System Development Cycle ♦ ♦ ▀ If you were building a skyscraper you would follow a process As in "the life-cycle of the NA otter" Cycle = Process Many steps and many people involved 3 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
System Development ▀ Need a defined process to create a complex info system ♦ ▀ System Development Cycle ♦ ♦ ▀ If you were building a skyscraper you would follow a process As in "the life-cycle of the NA otter" Cycle = Process Many steps and many people involved 3 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 SDC ▀ In general, broken into five phases ♦ ♦ ♦ ▀ Planning Analysis Design Implementation Operation/Support Each phase further broken down into activities 4 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
SDC ▀ In general, broken into five phases ♦ ♦ ♦ ▀ Planning Analysis Design Implementation Operation/Support Each phase further broken down into activities 4 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 SDC Participants ▀ Users ♦ People who will use the system ► Customers, ♦ employees Provide the system requirements ► What the system should do ► How it should work ▀ IT employees ♦ Create/install the system from system specifications ► Programmers, DBAs, Web Masters, Security experts, Network Designers Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 5
SDC Participants ▀ Users ♦ People who will use the system ► Customers, ♦ employees Provide the system requirements ► What the system should do ► How it should work ▀ IT employees ♦ Create/install the system from system specifications ► Programmers, DBAs, Web Masters, Security experts, Network Designers Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 5
 SDC Participants ▀ System Analyst(s) ♦ Designs the system ♦ Acts as liaison between users and IT ♦ Converts user requirements into technical specifications ► Diagrams, reports, pseudo-code ► Acts as a blueprint of the system ♦ Must have excellent communication skills and understand both the business and technical sides 6 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
SDC Participants ▀ System Analyst(s) ♦ Designs the system ♦ Acts as liaison between users and IT ♦ Converts user requirements into technical specifications ► Diagrams, reports, pseudo-code ► Acts as a blueprint of the system ♦ Must have excellent communication skills and understand both the business and technical sides 6 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 SDC Organization ▀ ▀ Selected users, systems analysts, and IT staff grouped into a project team One person assigned as project leader ♦ Creates a project plan ► Defines all activities and time/cost estimates for each ► Schedules and assigns activities ♦ ♦ Reports on plan progress to steering committee/management Represents the project to outside orgs ► Auditors, Finance, Interfacing systems 7 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
SDC Organization ▀ ▀ Selected users, systems analysts, and IT staff grouped into a project team One person assigned as project leader ♦ Creates a project plan ► Defines all activities and time/cost estimates for each ► Schedules and assigns activities ♦ ♦ Reports on plan progress to steering committee/management Represents the project to outside orgs ► Auditors, Finance, Interfacing systems 7 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 SDC ▀ Usually starts with a user request ♦ ▀ However, external events can cause ♦ ♦ ▀ RSS – request for system services New legal requirement Company merger Y 2 K New technology: Web, handheld devices Initiates the 1 st phase, Planning 8 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
SDC ▀ Usually starts with a user request ♦ ▀ However, external events can cause ♦ ♦ ▀ RSS – request for system services New legal requirement Company merger Y 2 K New technology: Web, handheld devices Initiates the 1 st phase, Planning 8 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Planning ▀ Broken into four activities ♦ ♦ ▀ Review Prioritize Allocate resources Create project team The initial review: ♦ ♦ ♦ Essentially triage (No, Must, Maybe) Done on a periodic basis (quarterly) By a senior IT member 9 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Planning ▀ Broken into four activities ♦ ♦ ▀ Review Prioritize Allocate resources Create project team The initial review: ♦ ♦ ♦ Essentially triage (No, Must, Maybe) Done on a periodic basis (quarterly) By a senior IT member 9 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Planning ▀ Senior staff then: ♦ ♦ ♦ ▀ Estimates resources for must dos Prioritizes/estimates maybes Presents results to steering committee Committee ♦ ♦ ♦ Reviews priorities and estimates Thumbs up and down Approves and allocates resources ► Creates project team, buys equipment, approves overtime, etc. Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 10
Planning ▀ Senior staff then: ♦ ♦ ♦ ▀ Estimates resources for must dos Prioritizes/estimates maybes Presents results to steering committee Committee ♦ ♦ ♦ Reviews priorities and estimates Thumbs up and down Approves and allocates resources ► Creates project team, buys equipment, approves overtime, etc. Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 10
 Phase 2: Analysis ▀ Broken into two activities ♦ ♦ ▀ Preliminary Investigation Detailed Analysis Preliminary Investigation ♦ Purpose: clearly define the change ► Interview the user(s) ► Examine existing documentation ♦ Conduct a feasibility study ► Confirm ♦ that project should be done Create and present feasibility report 11 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Phase 2: Analysis ▀ Broken into two activities ♦ ♦ ▀ Preliminary Investigation Detailed Analysis Preliminary Investigation ♦ Purpose: clearly define the change ► Interview the user(s) ► Examine existing documentation ♦ Conduct a feasibility study ► Confirm ♦ that project should be done Create and present feasibility report 11 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Phase 2: Analysis ▀ Feasibility report should contain ♦ ♦ Short description of problem For each possible solution: ► Benefits (quantifiable) ► Costs ► Factors that may affect ► Operational feasibility • how well it solves problem ► Schedule feasibility • can it be done ► Technical feasibility • are needed resources available Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries ♦ Recommendation 12
Phase 2: Analysis ▀ Feasibility report should contain ♦ ♦ Short description of problem For each possible solution: ► Benefits (quantifiable) ► Costs ► Factors that may affect ► Operational feasibility • how well it solves problem ► Schedule feasibility • can it be done ► Technical feasibility • are needed resources available Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries ♦ Recommendation 12
 Phase 2: Analysis ▀ If approved detailed analysis is begun ▀ Detailed analysis' purpose is to create ♦ A logical model of the new system ♦ A system proposal 13 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Phase 2: Analysis ▀ If approved detailed analysis is begun ▀ Detailed analysis' purpose is to create ♦ A logical model of the new system ♦ A system proposal 13 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Phase 2: Analysis ▀ ▀ Logical model describes what has to be done not how Create by: ♦ ♦ ▀ Investigating how the current system works Incorporating the desired change How do you find out how current system works? ♦ Several techniques 14 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Phase 2: Analysis ▀ ▀ Logical model describes what has to be done not how Create by: ♦ ♦ ▀ Investigating how the current system works Incorporating the desired change How do you find out how current system works? ♦ Several techniques 14 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Logical Model ▀ Review documentation ▀ Questionnaire ▀ Interview ♦ JAD (Joint Application Design) ▀ Observation ▀ Advantages and disadvantages? 15 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Logical Model ▀ Review documentation ▀ Questionnaire ▀ Interview ♦ JAD (Joint Application Design) ▀ Observation ▀ Advantages and disadvantages? 15 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Logical Model ▀ Describes the flow of data through the new system ♦ ♦ ▀ ▀ What data is required as input What is the source of that data How data is transformed into info What info is stored Does not dictate what is automated or manual Does not indicate technologies to be used 16 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Logical Model ▀ Describes the flow of data through the new system ♦ ♦ ▀ ▀ What data is required as input What is the source of that data How data is transformed into info What info is stored Does not dictate what is automated or manual Does not indicate technologies to be used 16 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
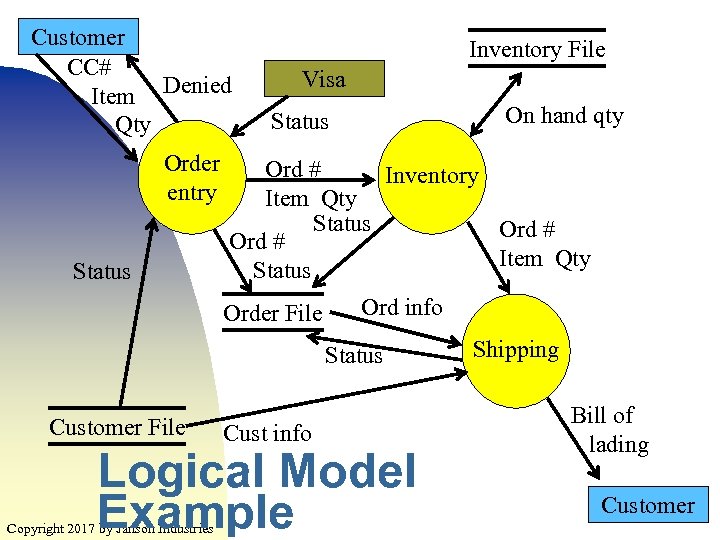 Customer CC# Item Denied Qty Order entry Status Inventory File Visa On hand qty Status Ord # Inventory Item Qty Status Ord # Item Qty Status Order File Ord info Status Customer File Cust info Logical Model Example Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Shipping Bill of lading Customer 17
Customer CC# Item Denied Qty Order entry Status Inventory File Visa On hand qty Status Ord # Inventory Item Qty Status Ord # Item Qty Status Order File Ord info Status Customer File Cust info Logical Model Example Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Shipping Bill of lading Customer 17
 System Proposal ▀ List alternatives for implementing ♦ ♦ ♦ H/W S/W Technologies ► Database ► Network ► Programming ♦ ♦ language Buy vs. build Who? 18 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
System Proposal ▀ List alternatives for implementing ♦ ♦ ♦ H/W S/W Technologies ► Database ► Network ► Programming ♦ ♦ language Buy vs. build Who? 18 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 System Proposal ▀ Buy vs. build ♦ Prepackaged apps ► Horizontal – can be used across different industries • Word, Excel, etc. ► Vertical – specific to an industry • Desktop publishing, MRP system ♦ Custom apps ► Build in house ► Outsource 19 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
System Proposal ▀ Buy vs. build ♦ Prepackaged apps ► Horizontal – can be used across different industries • Word, Excel, etc. ► Vertical – specific to an industry • Desktop publishing, MRP system ♦ Custom apps ► Build in house ► Outsource 19 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 System Proposal ▀ ▀ Buy vs. build adv and disadv? What's the advs and disadvs to building your own car? ♦ ♦ ♦ Cost? Time? Meet requirements? Repairs/modify? Quality? 20 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
System Proposal ▀ ▀ Buy vs. build adv and disadv? What's the advs and disadvs to building your own car? ♦ ♦ ♦ Cost? Time? Meet requirements? Repairs/modify? Quality? 20 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Phase 3: Design ▀ Two activities: ♦ ♦ Acquire h/w and s/w Detailed design of new system ▀ Can be done simultaneously ▀ To get h/w and s/w ♦ ♦ Define technical specs Get vendor proposals Evaluate proposals Make decision 21 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Phase 3: Design ▀ Two activities: ♦ ♦ Acquire h/w and s/w Detailed design of new system ▀ Can be done simultaneously ▀ To get h/w and s/w ♦ ♦ Define technical specs Get vendor proposals Evaluate proposals Make decision 21 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Phase 3: Design ▀ List technical specs ♦ Analyst fleshes out the details (or hire IT consultant to do) ♦ How "fleshy" depends on the type of proposal ► RFQ – great detail, asking for a price (quote) ► RFP – not great detail, let vendor come up with how and a price ► RFI – great detail, get specs of their products for comparison to needs 22 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Phase 3: Design ▀ List technical specs ♦ Analyst fleshes out the details (or hire IT consultant to do) ♦ How "fleshy" depends on the type of proposal ► RFQ – great detail, asking for a price (quote) ► RFP – not great detail, let vendor come up with how and a price ► RFI – great detail, get specs of their products for comparison to needs 22 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Phase 3: Design ▀ ▀ Send out requests and get vendor proposals Lots of different types of vendors ♦ ♦ ♦ H/W S/W VAR (value added reseller) ► Company sells a particular type of h/w or s/w and bundles with the other required pieces ► IBM business partners • Sell IBM equipment with non-IBM s/w Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 23
Phase 3: Design ▀ ▀ Send out requests and get vendor proposals Lots of different types of vendors ♦ ♦ ♦ H/W S/W VAR (value added reseller) ► Company sells a particular type of h/w or s/w and bundles with the other required pieces ► IBM business partners • Sell IBM equipment with non-IBM s/w Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 23
 Phase 3: Design ▀ Evaluate proposals ♦ ♦ Speed in MS ♦ ▀ Research online, mags, white papers Talk to customers already using Benchmark test evaluation copies Make decision ♦ Tally all the findings ► Weighted checklist 24 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Phase 3: Design ▀ Evaluate proposals ♦ ♦ Speed in MS ♦ ▀ Research online, mags, white papers Talk to customers already using Benchmark test evaluation copies Make decision ♦ Tally all the findings ► Weighted checklist 24 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Detailed Design ▀ ▀ Also called the physical design All details specified ♦ Input and output sources and targets ► How many digits for a phone number ► Validity checks for dates ♦ ♦ DB and tables defined User interface mockups ► Windows, ♦ menus, web pages, reports Individual programs defined ► pseudocode, flowcharts 25 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Detailed Design ▀ ▀ Also called the physical design All details specified ♦ Input and output sources and targets ► How many digits for a phone number ► Validity checks for dates ♦ ♦ DB and tables defined User interface mockups ► Windows, ♦ menus, web pages, reports Individual programs defined ► pseudocode, flowcharts 25 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Detailed Design ▀ CASE (computer aided software engineering) s/w ♦ ▀ ▀ Prototyping used to get user input Quality review ♦ ♦ Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Helps analyst generate program and documentation Read and verify the design is valid and complete Users, analysts, IT personal 26
Detailed Design ▀ CASE (computer aided software engineering) s/w ♦ ▀ ▀ Prototyping used to get user input Quality review ♦ ♦ Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Helps analyst generate program and documentation Read and verify the design is valid and complete Users, analysts, IT personal 26
 Phase 4: Implementation ▀ Most time consuming and costly phase ▀ Comprised of ♦ ♦ ▀ Creating programs Testing and installing Training users Converting to new system Again, some of these can be done simultaneously ♦ Training can be done while testing ► Can even use training as testing 27 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Phase 4: Implementation ▀ Most time consuming and costly phase ▀ Comprised of ♦ ♦ ▀ Creating programs Testing and installing Training users Converting to new system Again, some of these can be done simultaneously ♦ Training can be done while testing ► Can even use training as testing 27 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Phase 4: Implementation ▀ Create programs ♦ ♦ Lots of things to do Follow the Program Development Cycle ► Will explain later ► Just realize PDC is part of SDC ▀ Test and install ♦ ♦ Create test data Create and execute test scripts ► Developed models Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries from logical and physical 28
Phase 4: Implementation ▀ Create programs ♦ ♦ Lots of things to do Follow the Program Development Cycle ► Will explain later ► Just realize PDC is part of SDC ▀ Test and install ♦ ♦ Create test data Create and execute test scripts ► Developed models Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries from logical and physical 28
 Phase 4: Implementation ▀ Lots of different kinds of testing ♦ Unit testing – individual program works ♦ Functional – new programs work together ♦ Integration – new programs work with other applications ♦ Performance – functions are timely and consistently available ♦ Beta – pre-install for users to verify 29 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Phase 4: Implementation ▀ Lots of different kinds of testing ♦ Unit testing – individual program works ♦ Functional – new programs work together ♦ Integration – new programs work with other applications ♦ Performance – functions are timely and consistently available ♦ Beta – pre-install for users to verify 29 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Phase 4: Implementation ▀ User training ♦ ♦ Classes, computer- or web-based training Should include: ► Step-by-step instructions ► Hands on with system ► Realistic data ♦ ▀ Manuals, documentation Conversion ♦ Some activities can be done before hand ► Copy data to new database ► Install h/w Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 30
Phase 4: Implementation ▀ User training ♦ ♦ Classes, computer- or web-based training Should include: ► Step-by-step instructions ► Hands on with system ► Realistic data ♦ ▀ Manuals, documentation Conversion ♦ Some activities can be done before hand ► Copy data to new database ► Install h/w Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 30
 Phase 4: Implementation ▀ Conversion types ♦ Direct (or Big Bang) ► Stop using the old, use the new ► Advs: • Minimal transition costs • Fast ► Disadvs: • Possibility of catastrophic failure if new system does not work 31 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Phase 4: Implementation ▀ Conversion types ♦ Direct (or Big Bang) ► Stop using the old, use the new ► Advs: • Minimal transition costs • Fast ► Disadvs: • Possibility of catastrophic failure if new system does not work 31 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
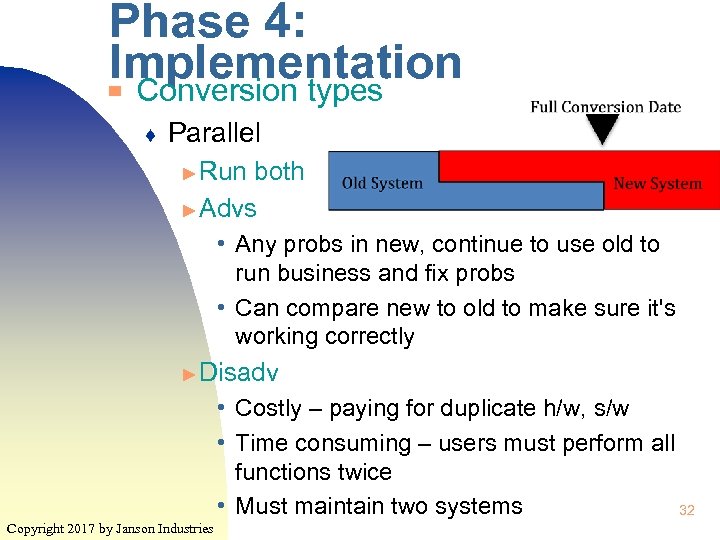 Phase 4: Implementation Conversion types ▀ ♦ Parallel ► Run both ► Advs • Any probs in new, continue to use old to run business and fix probs • Can compare new to old to make sure it's working correctly ► Disadv • Costly – paying for duplicate h/w, s/w • Time consuming – users must perform all functions twice • Must maintain two systems 32 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Phase 4: Implementation Conversion types ▀ ♦ Parallel ► Run both ► Advs • Any probs in new, continue to use old to run business and fix probs • Can compare new to old to make sure it's working correctly ► Disadv • Costly – paying for duplicate h/w, s/w • Time consuming – users must perform all functions twice • Must maintain two systems 32 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
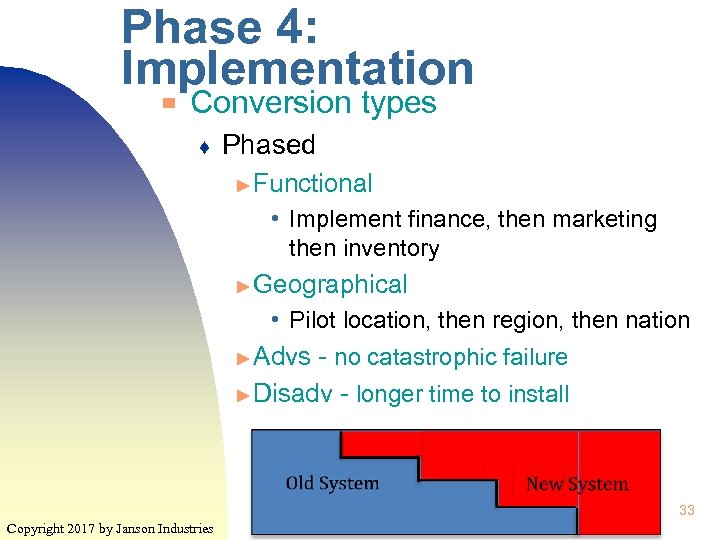 Phase 4: Implementation ▀ Conversion types ♦ Phased ► Functional • Implement finance, then marketing then inventory ► Geographical • Pilot location, then region, then nation ► Advs - no catastrophic failure ► Disadv - longer time to install 33 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Phase 4: Implementation ▀ Conversion types ♦ Phased ► Functional • Implement finance, then marketing then inventory ► Geographical • Pilot location, then region, then nation ► Advs - no catastrophic failure ► Disadv - longer time to install 33 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Phase 5: Support ▀ Comprised of : ♦ ♦ ♦ Maintenance ► Enhancements, fixes Monitor performance ► Insure availability and timeliness Monitor security ► Review security reports • # of unauthorized sign on attempts • Who attempted to access the payroll file ► Update security s/w • Install latest version of firewall, antivirus s/w ▀ Continues for the life of the system 34 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Phase 5: Support ▀ Comprised of : ♦ ♦ ♦ Maintenance ► Enhancements, fixes Monitor performance ► Insure availability and timeliness Monitor security ► Review security reports • # of unauthorized sign on attempts • Who attempted to access the payroll file ► Update security s/w • Install latest version of firewall, antivirus s/w ▀ Continues for the life of the system 34 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Program Development Cycle Requirements analysis ▀ ♦ ▀ Solution design ♦ ▀ Coding Test the program ♦ ♦ ▀ Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Review the program design Design implementation ♦ ▀ How the program will be structured Design validation ♦ ▀ Understand the analysts design Code review – compare code to design Programmer tests Document the program 35
Program Development Cycle Requirements analysis ▀ ♦ ▀ Solution design ♦ ▀ Coding Test the program ♦ ♦ ▀ Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Review the program design Design implementation ♦ ▀ How the program will be structured Design validation ♦ ▀ Understand the analysts design Code review – compare code to design Programmer tests Document the program 35
 Program Development Cycle ▀ Example, the logical design says: ♦ Users enter the amount of heating oil being purchased and the cost of oil is displayed ♦ The cost is determined by the amount that is ordered ♦ The first 150 gals costs $2. 25 per gal ♦ Qtys over that get charged $2. 10 for the next 100 gals ♦ Anything more gets billed at $1. 99 36 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Program Development Cycle ▀ Example, the logical design says: ♦ Users enter the amount of heating oil being purchased and the cost of oil is displayed ♦ The cost is determined by the amount that is ordered ♦ The first 150 gals costs $2. 25 per gal ♦ Qtys over that get charged $2. 10 for the next 100 gals ♦ Anything more gets billed at $1. 99 36 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Program Development Cycle ▀ To make absolutely clear, programmer translates the requirements into a diagram and/or pseudocode ♦ ♦ ▀ Most common diagram is a flowchart Pseudocode also called Structured English Both tools must be able to show ♦ Sequence – order actions/instructions are performed ♦ Selection – conditional instructions ♦ Iteration – repeated instructions Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 37
Program Development Cycle ▀ To make absolutely clear, programmer translates the requirements into a diagram and/or pseudocode ♦ ♦ ▀ Most common diagram is a flowchart Pseudocode also called Structured English Both tools must be able to show ♦ Sequence – order actions/instructions are performed ♦ Selection – conditional instructions ♦ Iteration – repeated instructions Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 37
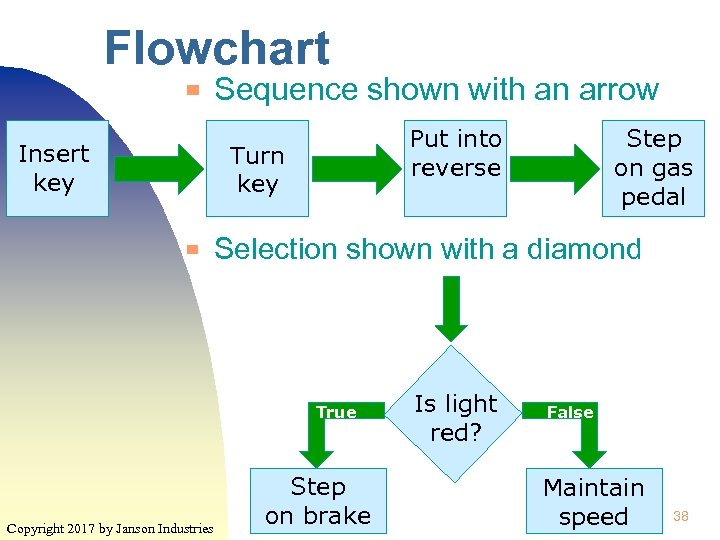 Flowchart ▀ Insert key Sequence shown with an arrow Put into reverse Turn key ▀ Selection shown with a diamond True Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Step on gas pedal Step on brake Is light red? False Maintain speed 38
Flowchart ▀ Insert key Sequence shown with an arrow Put into reverse Turn key ▀ Selection shown with a diamond True Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Step on gas pedal Step on brake Is light red? False Maintain speed 38
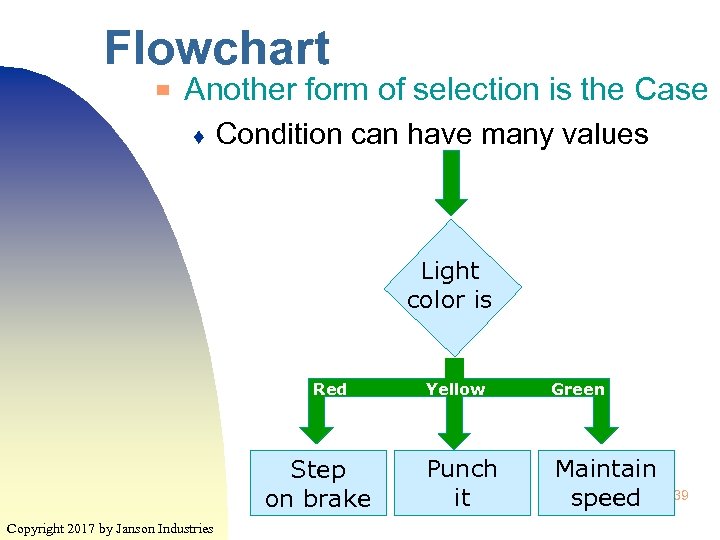 Flowchart ▀ Another form of selection is the Case ♦ Condition can have many values Light color is Red Step on brake Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries False Yellow Green Punch it Maintain speed 39
Flowchart ▀ Another form of selection is the Case ♦ Condition can have many values Light color is Red Step on brake Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries False Yellow Green Punch it Maintain speed 39
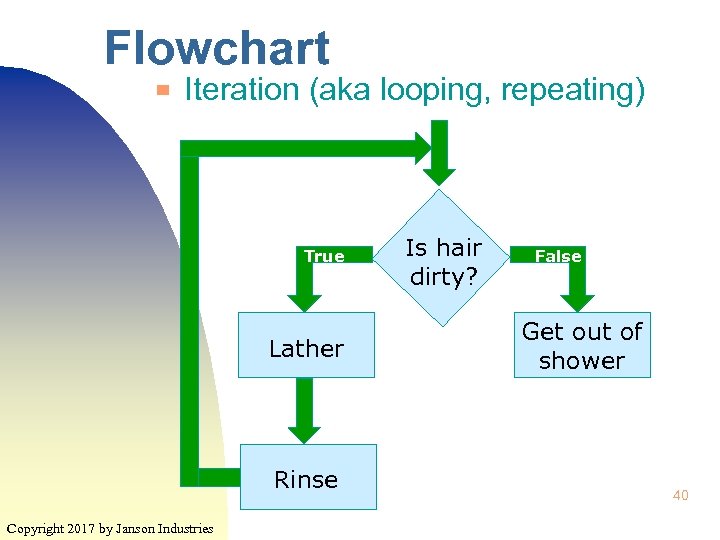 Flowchart ▀ Iteration (aka looping, repeating) True Lather Rinse Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Is hair dirty? False Get out of shower 40
Flowchart ▀ Iteration (aka looping, repeating) True Lather Rinse Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Is hair dirty? False Get out of shower 40
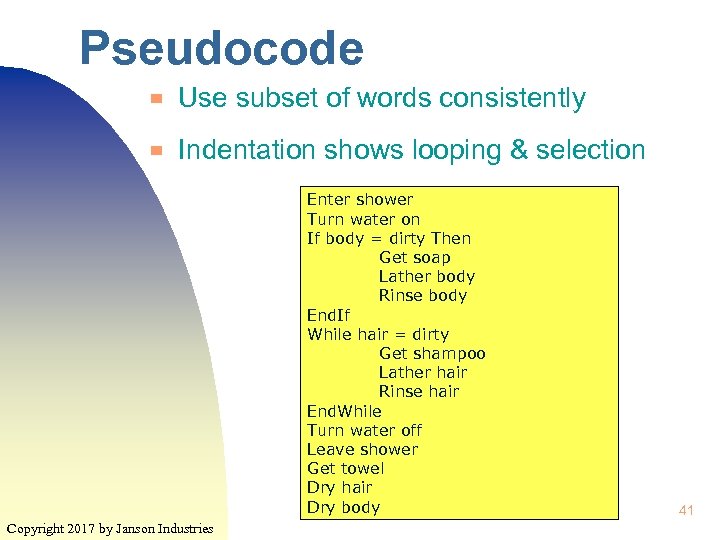 Pseudocode ▀ Use subset of words consistently ▀ Indentation shows looping & selection Enter shower Turn water on If body = dirty Then Get soap Lather body Rinse body End. If While hair = dirty Get shampoo Lather hair Rinse hair End. While Turn water off Leave shower Get towel Dry hair Dry body Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 41
Pseudocode ▀ Use subset of words consistently ▀ Indentation shows looping & selection Enter shower Turn water on If body = dirty Then Get soap Lather body Rinse body End. If While hair = dirty Get shampoo Lather hair Rinse hair End. While Turn water off Leave shower Get towel Dry hair Dry body Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 41
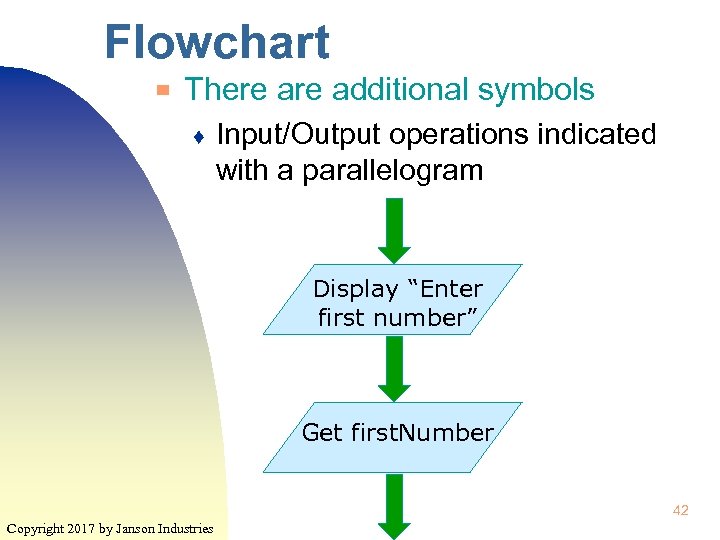 Flowchart ▀ There additional symbols ♦ Input/Output operations indicated with a parallelogram Display “Enter first number” Get first. Number 42 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Flowchart ▀ There additional symbols ♦ Input/Output operations indicated with a parallelogram Display “Enter first number” Get first. Number 42 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
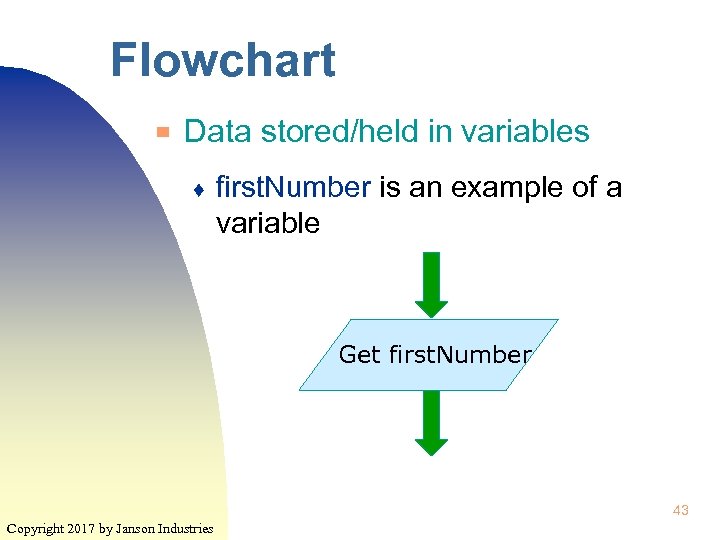 Flowchart ▀ Data stored/held in variables ♦ first. Number is an example of a variable Get first. Number 43 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Flowchart ▀ Data stored/held in variables ♦ first. Number is an example of a variable Get first. Number 43 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
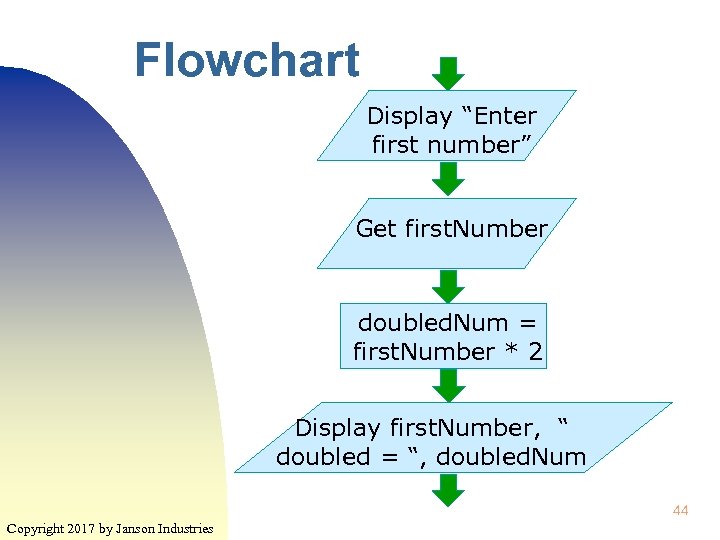 Flowchart Display “Enter first number” Get first. Number doubled. Num = first. Number * 2 Display first. Number, “ doubled = “, doubled. Num 44 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Flowchart Display “Enter first number” Get first. Number doubled. Num = first. Number * 2 Display first. Number, “ doubled = “, doubled. Num 44 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 In Class Assg ▀ Create a flow chart for the Oil Calc program ♦ ▀ Solution Create pseudocode for the Oil Calc program ♦ Solution 45 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
In Class Assg ▀ Create a flow chart for the Oil Calc program ♦ ▀ Solution Create pseudocode for the Oil Calc program ♦ Solution 45 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Alternative Resource ▀ ▀ Code. org Uses videos and games to get across the basic programming structures ♦ http: //learn. code. org/hoc/1 46 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Alternative Resource ▀ ▀ Code. org Uses videos and games to get across the basic programming structures ♦ http: //learn. code. org/hoc/1 46 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
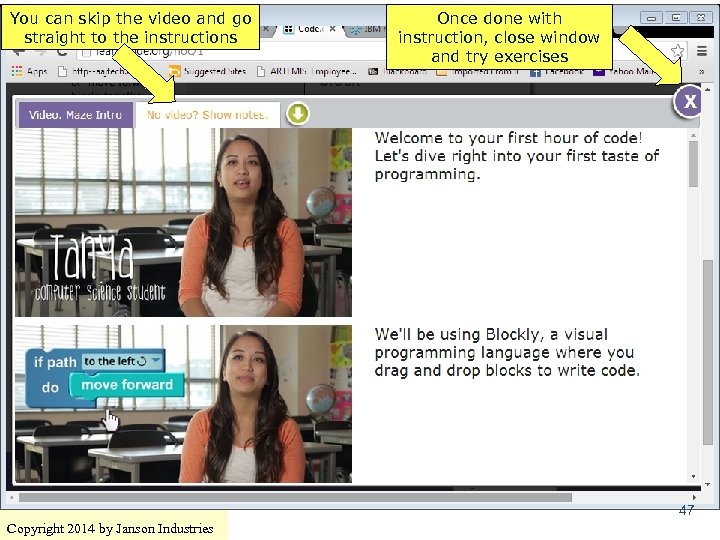 You can skip the video and go straight to the instructions Once done with instruction, close window and try exercises 47 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
You can skip the video and go straight to the instructions Once done with instruction, close window and try exercises 47 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
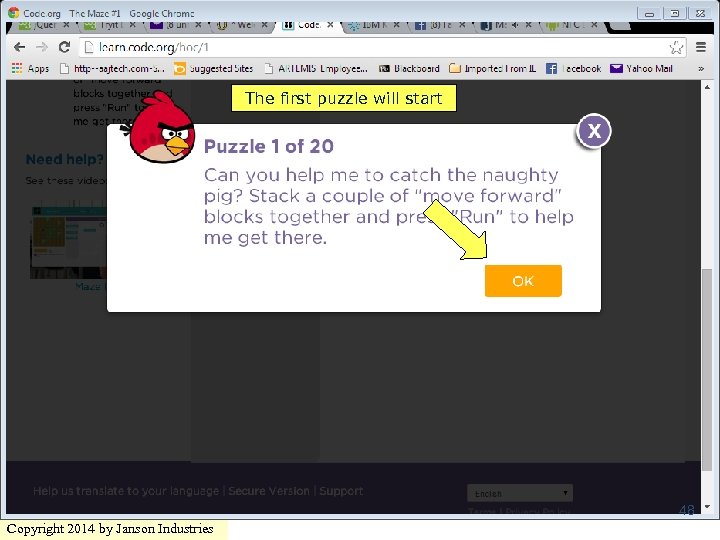 The first puzzle will start 48 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
The first puzzle will start 48 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
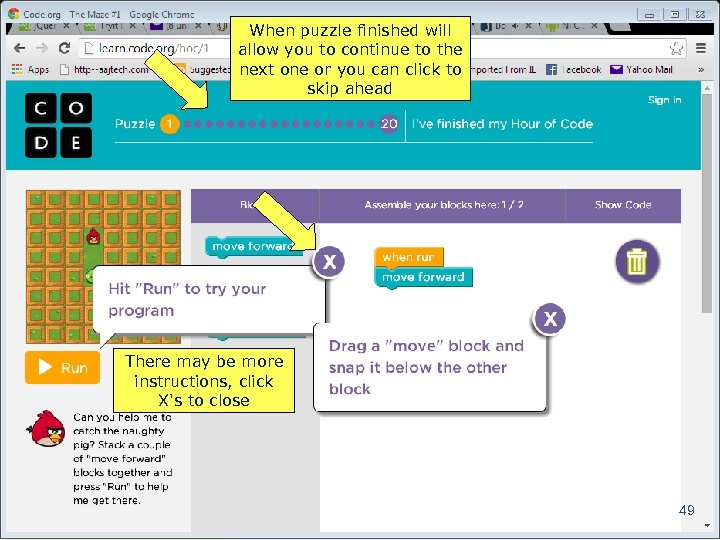 When puzzle finished will allow you to continue to the next one or you can click to skip ahead There may be more instructions, click X's to close 49 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
When puzzle finished will allow you to continue to the next one or you can click to skip ahead There may be more instructions, click X's to close 49 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
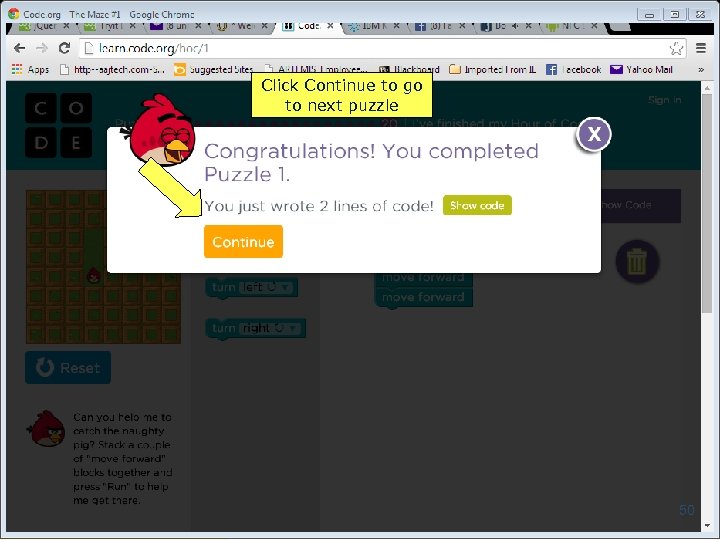 Click Continue to go to next puzzle 50 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Click Continue to go to next puzzle 50 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Click Continue to go to next puzzle 51 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Click Continue to go to next puzzle 51 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 If you can't figure it out, scroll down and click the help links 52 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
If you can't figure it out, scroll down and click the help links 52 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Code. org ▀ If you go through all twenty puzzles they will greatly help you understanding the concepts of ♦ ♦ Selection ♦ ▀ Sequential processing Iteration There's several sets of lessons at http: //learn. code. org/ 53 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Code. org ▀ If you go through all twenty puzzles they will greatly help you understanding the concepts of ♦ ♦ Selection ♦ ▀ Sequential processing Iteration There's several sets of lessons at http: //learn. code. org/ 53 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Unplugged activites have theory – good to read first Then tackle the puzzles 54 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Unplugged activites have theory – good to read first Then tackle the puzzles 54 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
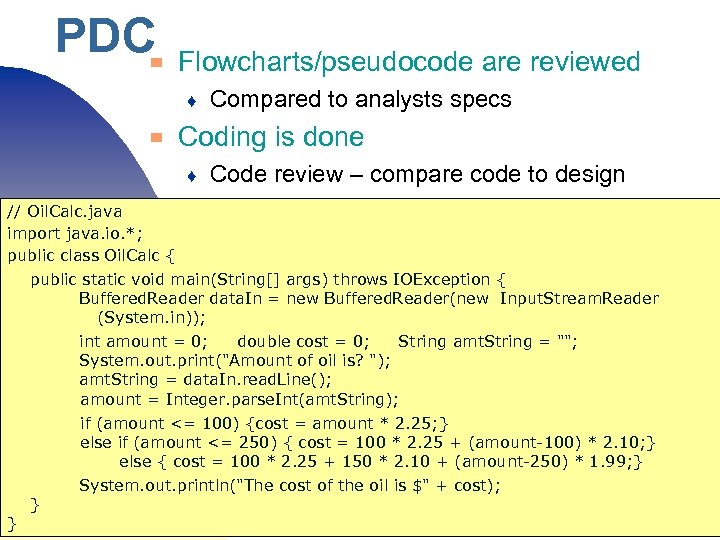 PDC ▀ Flowcharts/pseudocode are reviewed ♦ ▀ Compared to analysts specs Coding is done ♦ Code review – compare code to design // Oil. Calc. java import java. io. *; public class Oil. Calc { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Buffered. Reader data. In = new Buffered. Reader(new Input. Stream. Reader (System. in)); int amount = 0; double cost = 0; String amt. String = ""; System. out. print("Amount of oil is? "); amt. String = data. In. read. Line(); amount = Integer. parse. Int(amt. String); } if (amount <= 100) {cost = amount * 2. 25; } ♦ Programmer tests else if (amount <= 250) { cost = 100 * 2. 25 + (amount-100) * 2. 10; } else { cost = 100 * 2. 25 + 150 * 2. 10 + (amount-250) * 1. 99; } System. out. println("The cost of the oil is $" + cost); } Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 55
PDC ▀ Flowcharts/pseudocode are reviewed ♦ ▀ Compared to analysts specs Coding is done ♦ Code review – compare code to design // Oil. Calc. java import java. io. *; public class Oil. Calc { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Buffered. Reader data. In = new Buffered. Reader(new Input. Stream. Reader (System. in)); int amount = 0; double cost = 0; String amt. String = ""; System. out. print("Amount of oil is? "); amt. String = data. In. read. Line(); amount = Integer. parse. Int(amt. String); } if (amount <= 100) {cost = amount * 2. 25; } ♦ Programmer tests else if (amount <= 250) { cost = 100 * 2. 25 + (amount-100) * 2. 10; } else { cost = 100 * 2. 25 + 150 * 2. 10 + (amount-250) * 1. 99; } System. out. println("The cost of the oil is $" + cost); } Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 55
 PDC ▀ Programmer tests ♦ ▀ ▀ Run program What do you think the users think of this? What happened? ♦ No physical model (external design) to describe how it should be done 56 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
PDC ▀ Programmer tests ♦ ▀ ▀ Run program What do you think the users think of this? What happened? ♦ No physical model (external design) to describe how it should be done 56 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Program Development Cycle ▀ Example, the external design says: ♦ ♦ Users have hyperlink to start program Window appears with ► Text ► Input field ► Calc button ♦ When Calc button pressed ► Cost is displayed ► Input field is cleared ♦ When close window button pressed ► Window disappears 57 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Program Development Cycle ▀ Example, the external design says: ♦ ♦ Users have hyperlink to start program Window appears with ► Text ► Input field ► Calc button ♦ When Calc button pressed ► Cost is displayed ► Input field is cleared ♦ When close window button pressed ► Window disappears 57 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
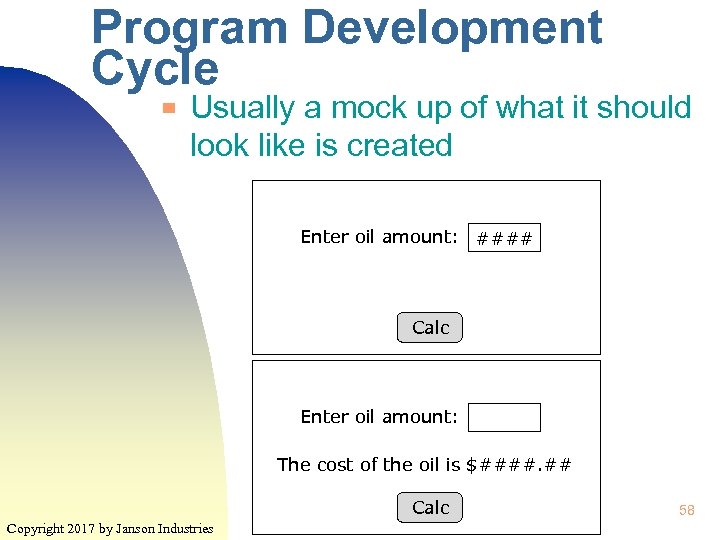 Program Development Cycle ▀ Usually a mock up of what it should look like is created Enter oil amount: #### Calc Enter oil amount: The cost of the oil is $####. ## Calc Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 58
Program Development Cycle ▀ Usually a mock up of what it should look like is created Enter oil amount: #### Calc Enter oil amount: The cost of the oil is $####. ## Calc Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 58
 PDC import import /* /* ▀ New code java. awt. Frame; java. awt. event. Action. Event; java. awt. event. Action. Listener; java. awt. event. Window. Event; java. awt. event. Window. Listener; java. awt. Label; java. awt. Text. Field; java. awt. Button; Created on Oct 31, 2010 */ @author rjanson ♦ Programmer */ tests class Oil. Calc. GUI extends Frame implements Window. Listener, Action. Listener { private double cost; private Label label = null; private Text. Field text. Field = null; private Label label 1 = null; private Button button = null; public Oil. Calc. GUI() { super(); initialize(); } Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 59
PDC import import /* /* ▀ New code java. awt. Frame; java. awt. event. Action. Event; java. awt. event. Action. Listener; java. awt. event. Window. Event; java. awt. event. Window. Listener; java. awt. Label; java. awt. Text. Field; java. awt. Button; Created on Oct 31, 2010 */ @author rjanson ♦ Programmer */ tests class Oil. Calc. GUI extends Frame implements Window. Listener, Action. Listener { private double cost; private Label label = null; private Text. Field text. Field = null; private Label label 1 = null; private Button button = null; public Oil. Calc. GUI() { super(); initialize(); } Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 59
 PDC ▀ New code private void initialize() { label 1 = new Label(); label = new Label(); this. set. Layout(null); this. set. Title("Oil Calculation"); this. set. Size(294, 180); label. set. Bounds(68, 103, 23); label. set. Text("Enter oil amount: "); label. set. Alignment(java. awt. Label. RIGHT); label 1. set. Bounds(51, 110, 191, 23); ♦ Programmer tests label 1. set. Text(""); this. add(label, null); this. add(get. Text. Field(), null); this. add(label 1, null); this. add(get. Button(), null); this. set. Visible(true); public void window. Opened(Window. Event e) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } public void window. Closing(Window. Event e) { dispose(); } Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 60
PDC ▀ New code private void initialize() { label 1 = new Label(); label = new Label(); this. set. Layout(null); this. set. Title("Oil Calculation"); this. set. Size(294, 180); label. set. Bounds(68, 103, 23); label. set. Text("Enter oil amount: "); label. set. Alignment(java. awt. Label. RIGHT); label 1. set. Bounds(51, 110, 191, 23); ♦ Programmer tests label 1. set. Text(""); this. add(label, null); this. add(get. Text. Field(), null); this. add(label 1, null); this. add(get. Button(), null); this. set. Visible(true); public void window. Opened(Window. Event e) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } public void window. Closing(Window. Event e) { dispose(); } Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 60
 PDC ▀ New code public void window. Closed(Window. Event e) { } public void window. Iconified(Window. Event e) { public void window. Deiconified(Window. Event e) { public void window. Activated(Window. Event e) { public void window. Deactivated(Window. Event e) { } } public void action. Performed(Action. Event e) { int amount = Integer. parse. Int(text. Field. get. Text()); if (amount <= 100)Programmer tests ♦ {cost = amount * 2. 25; } else if (amount <= 250) { cost = 150 * 2. 25 + (amount-100) * 2. 10; } else { cost = 150 * 2. 25 + 150 * 2. 10 + (amount-250) * 1. 99; } label 1. set. Text("The cost of the oil is $" + cost); } private Text. Field get. Text. Field() { if (text. Field == null) { text. Field = new Text. Field(); text. Field. set. Bounds(181, 68, 38, 23); } return text. Field; } Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 61
PDC ▀ New code public void window. Closed(Window. Event e) { } public void window. Iconified(Window. Event e) { public void window. Deiconified(Window. Event e) { public void window. Activated(Window. Event e) { public void window. Deactivated(Window. Event e) { } } public void action. Performed(Action. Event e) { int amount = Integer. parse. Int(text. Field. get. Text()); if (amount <= 100)Programmer tests ♦ {cost = amount * 2. 25; } else if (amount <= 250) { cost = 150 * 2. 25 + (amount-100) * 2. 10; } else { cost = 150 * 2. 25 + 150 * 2. 10 + (amount-250) * 1. 99; } label 1. set. Text("The cost of the oil is $" + cost); } private Text. Field get. Text. Field() { if (text. Field == null) { text. Field = new Text. Field(); text. Field. set. Bounds(181, 68, 38, 23); } return text. Field; } Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 61
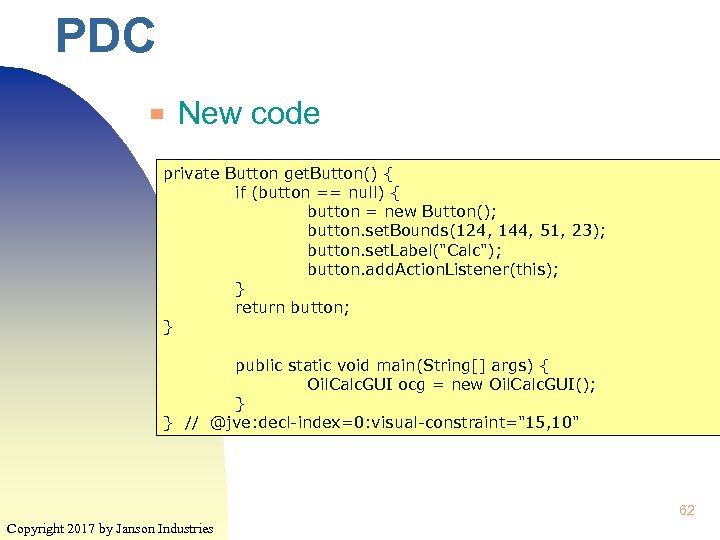 PDC ▀ New code private Button get. Button() { if (button == null) { button = new Button(); button. set. Bounds(124, 144, 51, 23); button. set. Label("Calc"); button. add. Action. Listener(this); } return button; } ♦ Programmer tests public static void main(String[] args) { Oil. Calc. GUI ocg = new Oil. Calc. GUI(); } } // @jve: decl-index=0: visual-constraint="15, 10" 62 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
PDC ▀ New code private Button get. Button() { if (button == null) { button = new Button(); button. set. Bounds(124, 144, 51, 23); button. set. Label("Calc"); button. add. Action. Listener(this); } return button; } ♦ Programmer tests public static void main(String[] args) { Oil. Calc. GUI ocg = new Oil. Calc. GUI(); } } // @jve: decl-index=0: visual-constraint="15, 10" 62 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
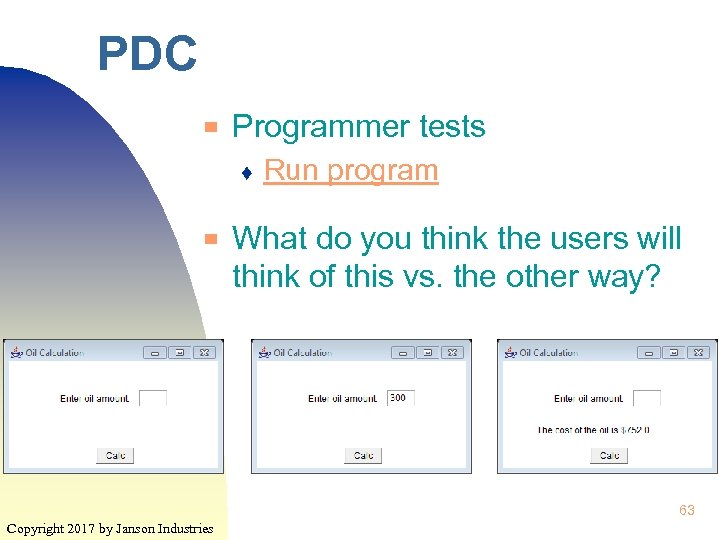 PDC ▀ Programmer tests ♦ ▀ Run program What do you think the users will think of this vs. the other way? 63 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
PDC ▀ Programmer tests ♦ ▀ Run program What do you think the users will think of this vs. the other way? 63 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Development Technologies ▀ Programming languages ▀ Development tools ▀ Mark up languages ▀ Scripting languages 64 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Development Technologies ▀ Programming languages ▀ Development tools ▀ Mark up languages ▀ Scripting languages 64 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Programming Languages ▀ In the beginning: Machine Language ♦ ▀ Problem with ML: ♦ ♦ ▀ The actual 0's and 1's Long time to code Error prone So, Assembly Level languages created ♦ ♦ English character/acronyms act as commands Specific syntax 65 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Programming Languages ▀ In the beginning: Machine Language ♦ ▀ Problem with ML: ♦ ♦ ▀ The actual 0's and 1's Long time to code Error prone So, Assembly Level languages created ♦ ♦ English character/acronyms act as commands Specific syntax 65 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Programming Languages ▀ Problem with AL: ♦ ♦ ♦ Programmer manage internal memory Syntax not easy Must be converted into ML ► An ▀ Assembler is used to do this This also creates two versions of the program ♦ ♦ The source code (AL code) The executable code (ML code) 66 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Programming Languages ▀ Problem with AL: ♦ ♦ ♦ Programmer manage internal memory Syntax not easy Must be converted into ML ► An ▀ Assembler is used to do this This also creates two versions of the program ♦ ♦ The source code (AL code) The executable code (ML code) 66 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Programming Languages ▀ 3 GL or Procedural Languages ♦ ♦ ♦ English words and math symbols Tells computer what to do but does not manage internal memory Must be converted into ML ►A ▀ Lots of 3 GLs ♦ ▀ Compiler is used to do this Cobol, C, Fortran, BASIC Each has pros and cons 67 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Programming Languages ▀ 3 GL or Procedural Languages ♦ ♦ ♦ English words and math symbols Tells computer what to do but does not manage internal memory Must be converted into ML ►A ▀ Lots of 3 GLs ♦ ▀ Compiler is used to do this Cobol, C, Fortran, BASIC Each has pros and cons 67 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Programming Languages ▀ COBOL (COmmon Business Oriented Language) ♦ ▀ FORTRAN (FORmula TRANslator) ♦ ▀ Great for scientific apps C ♦ ▀ Great for business apps Very efficient BASIC (Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) ♦ Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Very English-like and easy to learn 68
Programming Languages ▀ COBOL (COmmon Business Oriented Language) ♦ ▀ FORTRAN (FORmula TRANslator) ♦ ▀ Great for scientific apps C ♦ ▀ Great for business apps Very efficient BASIC (Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) ♦ Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Very English-like and easy to learn 68
 Programming Languages ▀ Object-oriented languages ♦ ♦ ♦ ▀ A subset of 3 GLs Objects are easily re-useable Create apps out of already existing objects Speeds up app development Java (Oracle), C+ (Bell Labs), C# (MS) Are free but companies compete for customers to use ♦ Why? It's the other stuff that they sell ► Servers, Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries security, networking, etc. 69
Programming Languages ▀ Object-oriented languages ♦ ♦ ♦ ▀ A subset of 3 GLs Objects are easily re-useable Create apps out of already existing objects Speeds up app development Java (Oracle), C+ (Bell Labs), C# (MS) Are free but companies compete for customers to use ♦ Why? It's the other stuff that they sell ► Servers, Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries security, networking, etc. 69
 Alice ▀ A “programming language” used to create 3 dimensional animations ♦ ▀ Uses the same logic structures (sequence, selection, and looping) as standard programming languages But instead of typing in code, functions selected from menus, lists, buttons, etc. 70 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Alice ▀ A “programming language” used to create 3 dimensional animations ♦ ▀ Uses the same logic structures (sequence, selection, and looping) as standard programming languages But instead of typing in code, functions selected from menus, lists, buttons, etc. 70 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Got to the Assignments area in Black. Board and click on the Alice 2. 2. zip link 71 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Got to the Assignments area in Black. Board and click on the Alice 2. 2. zip link 71 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
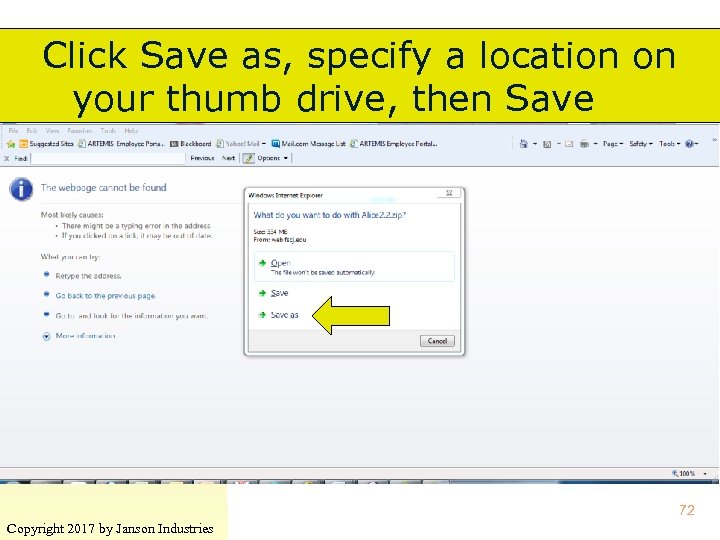 Click Save as, specify a location on your thumb drive, then Save 72 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Click Save as, specify a location on your thumb drive, then Save 72 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
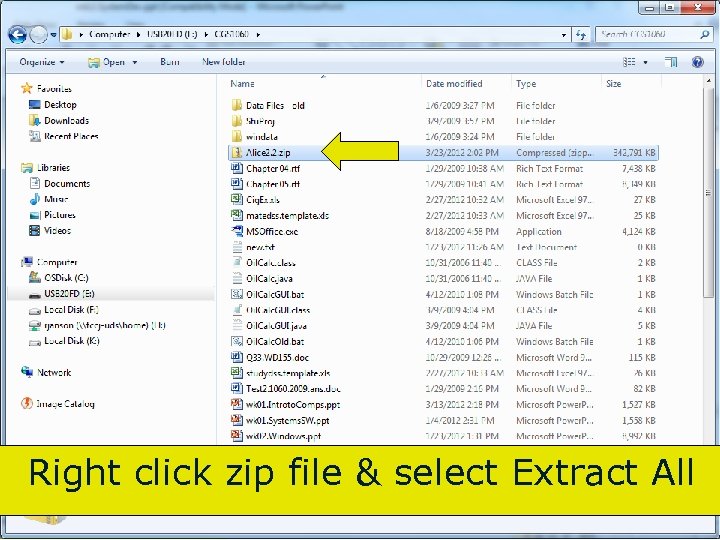 Right click zip file & select Extract All 73 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Right click zip file & select Extract All 73 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
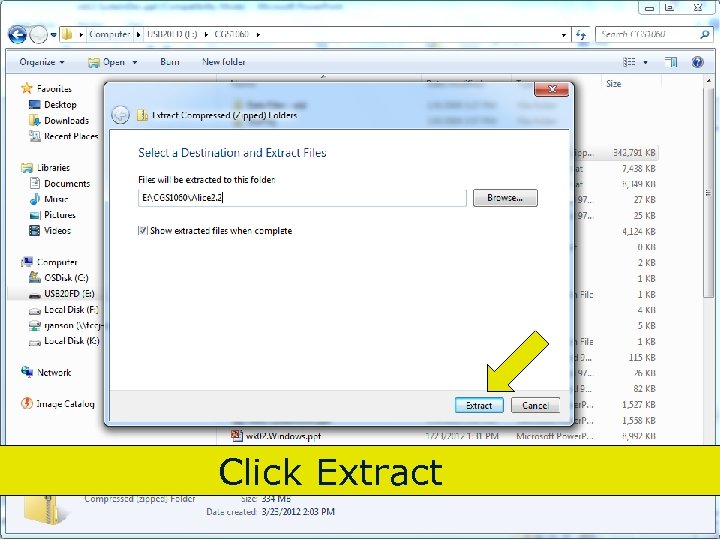 Click Extract 74 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Click Extract 74 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
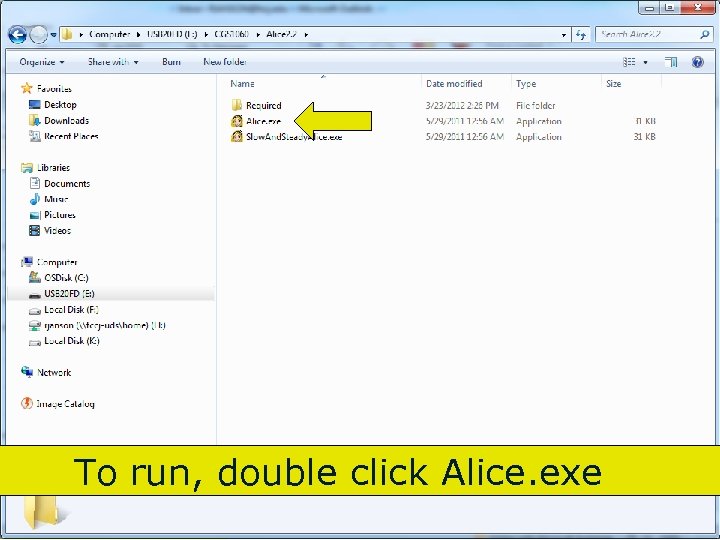 To run, double click Alice. exe 75 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
To run, double click Alice. exe 75 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
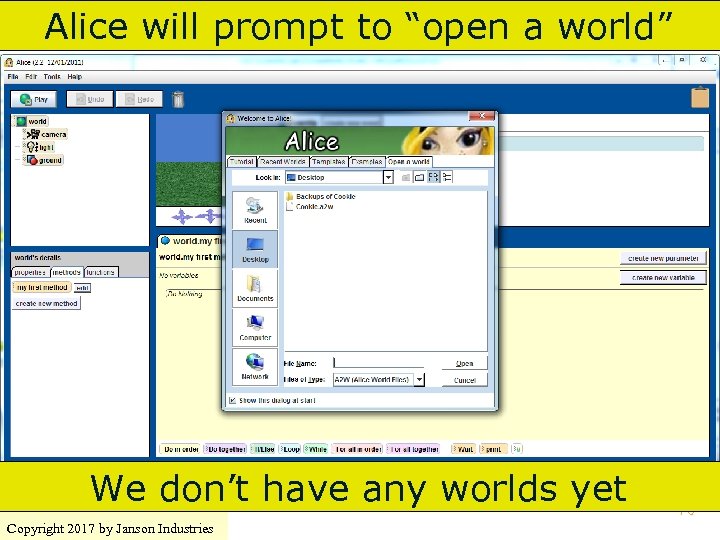 Alice will prompt to “open a world” We don’t have any worlds yet Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 76
Alice will prompt to “open a world” We don’t have any worlds yet Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 76
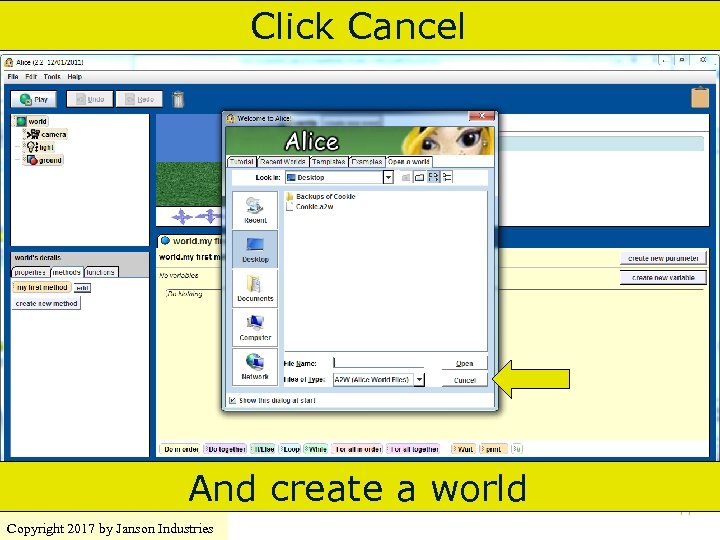 Click Cancel And create a world Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 77
Click Cancel And create a world Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 77
 Alice World ▀ ▀ Consists of objects and methods Methods consist of executable statements ♦ Move/change objects ♦ Math functions 78 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Alice World ▀ ▀ Consists of objects and methods Methods consist of executable statements ♦ Move/change objects ♦ Math functions 78 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Alice World ▀ Objects have: ♦ Properties ► Color, ♦ size, location, etc. Methods and functions ► Executable statements that can manipulate the object and its properties ▀ First step in creating a world – add an object 79 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Alice World ▀ Objects have: ♦ Properties ► Color, ♦ size, location, etc. Methods and functions ► Executable statements that can manipulate the object and its properties ▀ First step in creating a world – add an object 79 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
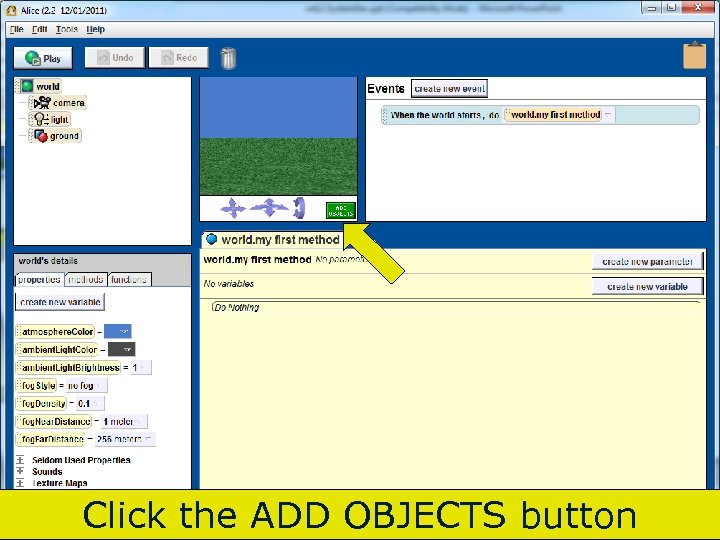 Click the ADD OBJECTS button Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 80
Click the ADD OBJECTS button Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 80
 Lots of categories 81 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Lots of categories 81 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
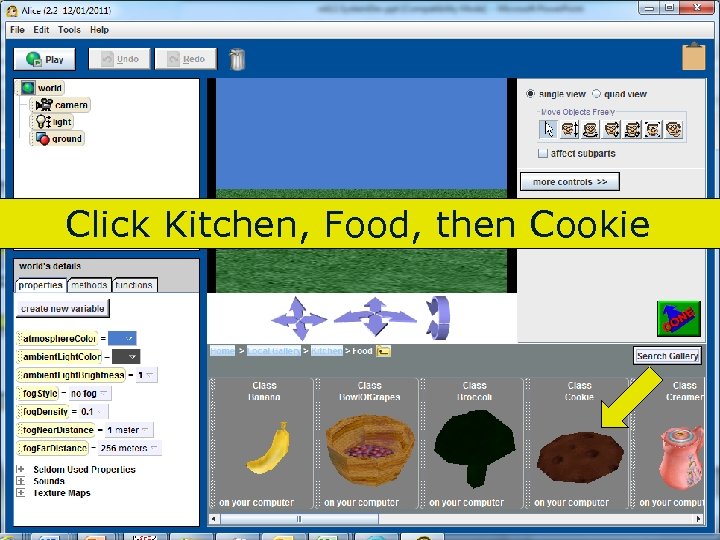 Click Kitchen, Food, then Cookie 82 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Click Kitchen, Food, then Cookie 82 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
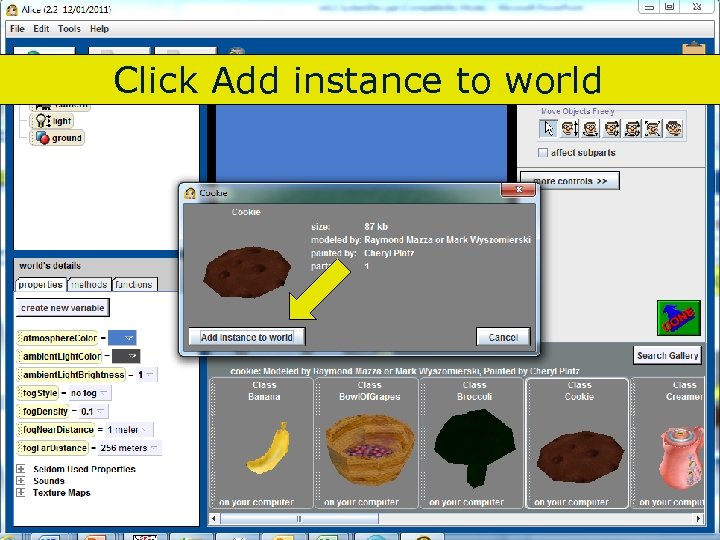 Click Add instance to world 83 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Click Add instance to world 83 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
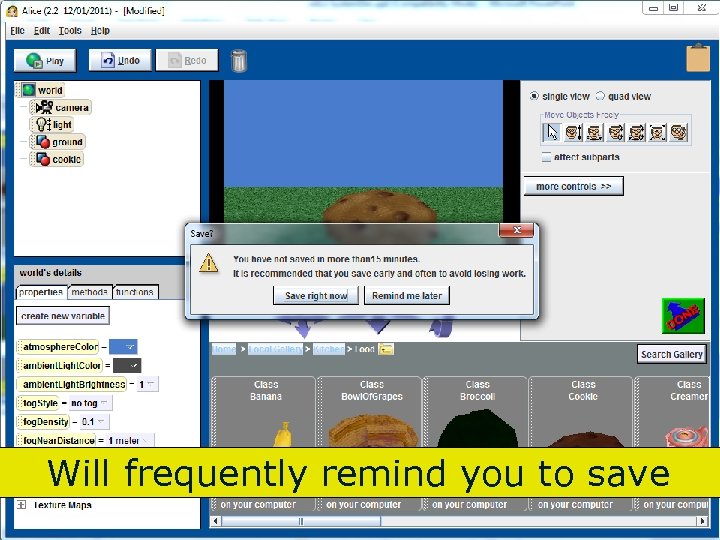 Will frequently remind you to save 84 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Will frequently remind you to save 84 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 85 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
85 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
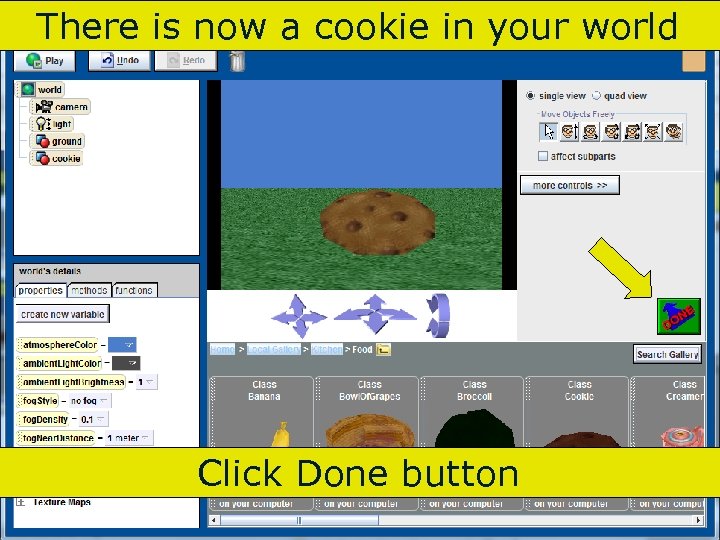 There is now a cookie in your world Click Done button 86 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
There is now a cookie in your world Click Done button 86 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
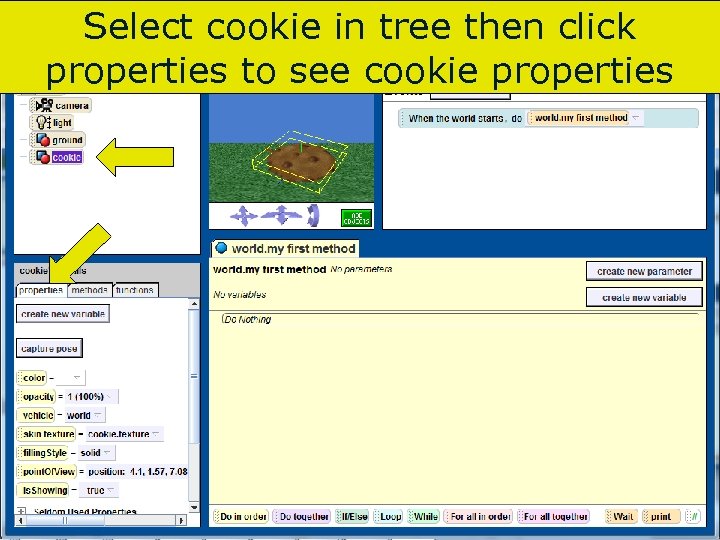 Select cookie in tree then click properties to see cookie properties 87 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Select cookie in tree then click properties to see cookie properties 87 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
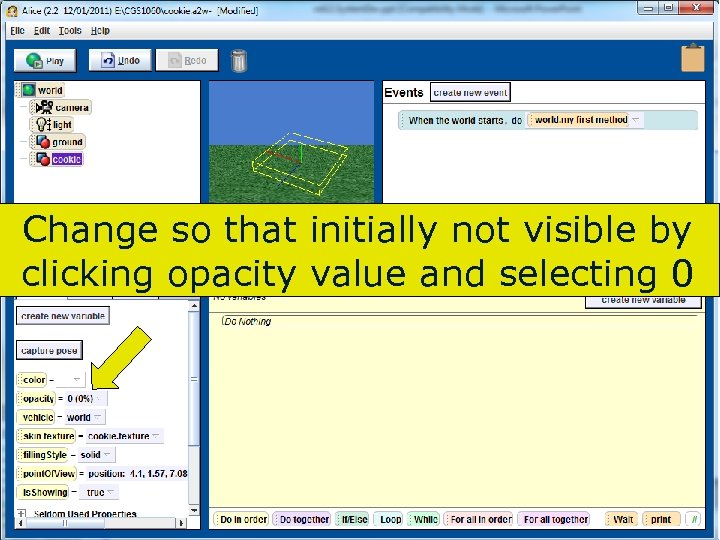 Change so that initially not visible by clicking opacity value and selecting 0 88 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Change so that initially not visible by clicking opacity value and selecting 0 88 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Alice ▀ ▀ We are going to ask the user if he/she wants a cookie Need a variable to hold the users input 89 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Alice ▀ ▀ We are going to ask the user if he/she wants a cookie Need a variable to hold the users input 89 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
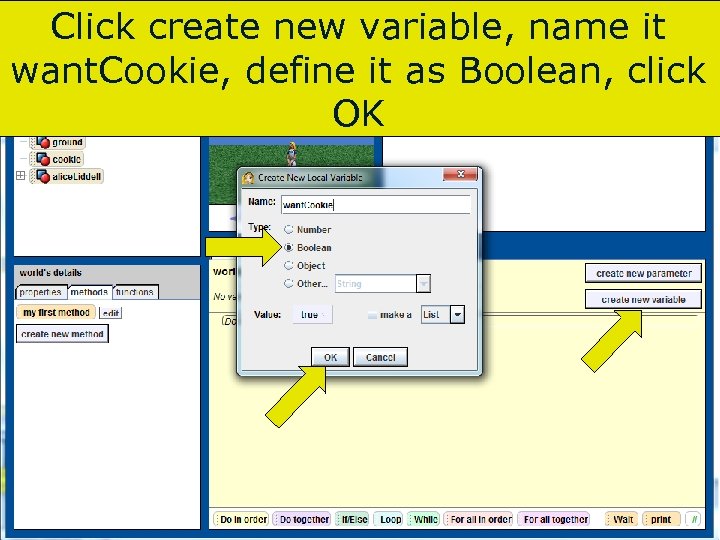 Click create new variable, name it want. Cookie, define it as Boolean, click OK 90 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Click create new variable, name it want. Cookie, define it as Boolean, click OK 90 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
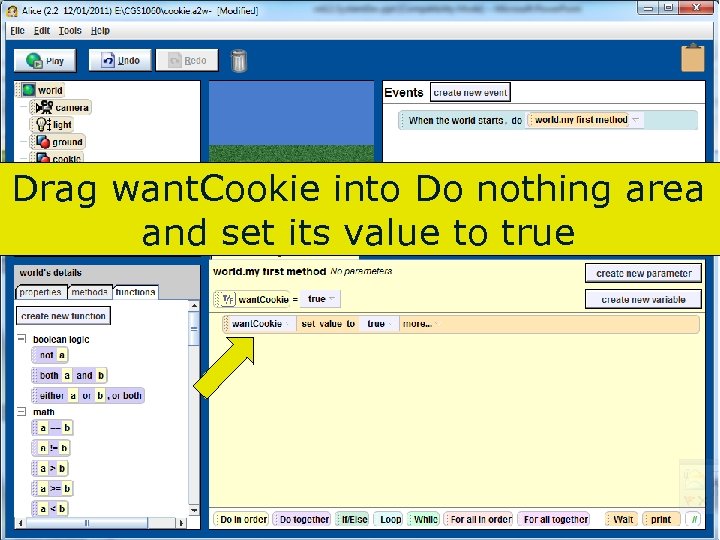 Drag want. Cookie into Do nothing area and set its value to true 91 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Drag want. Cookie into Do nothing area and set its value to true 91 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
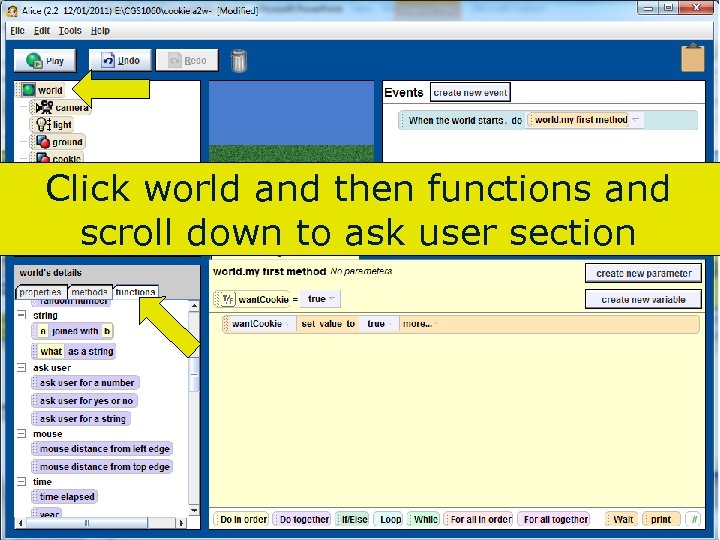 Click world and then functions and scroll down to ask user section 92 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Click world and then functions and scroll down to ask user section 92 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
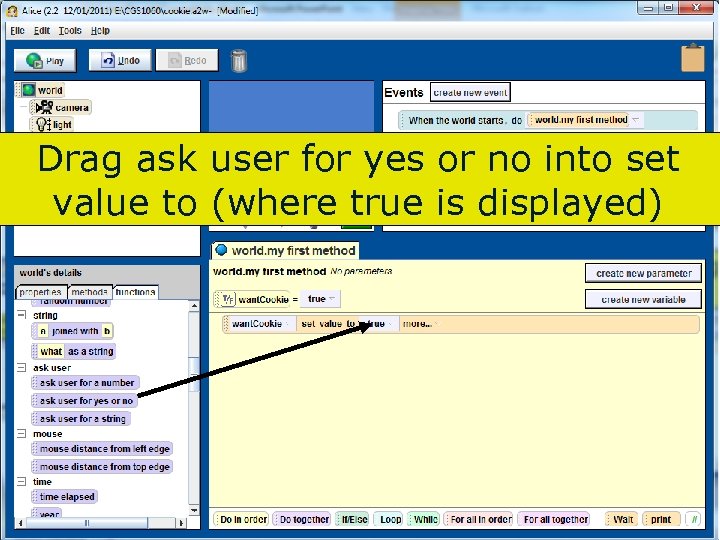 Drag ask user for yes or no into set value to (where true is displayed) 93 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Drag ask user for yes or no into set value to (where true is displayed) 93 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
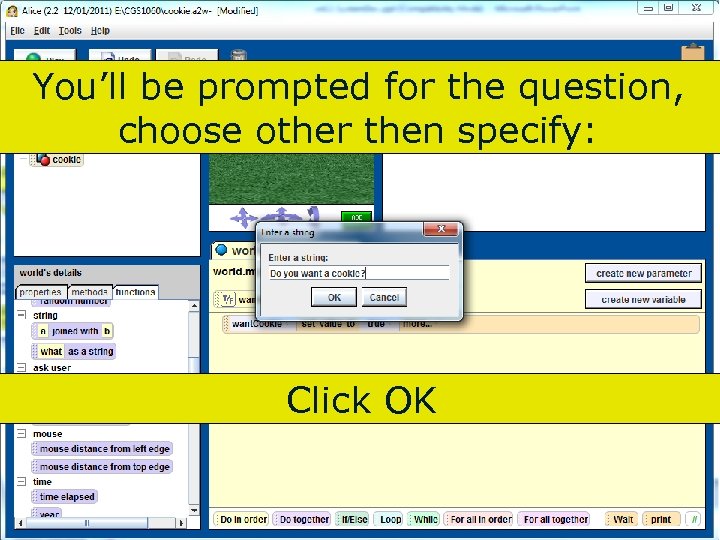 You’ll be prompted for the question, choose other then specify: Click OK 94 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
You’ll be prompted for the question, choose other then specify: Click OK 94 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
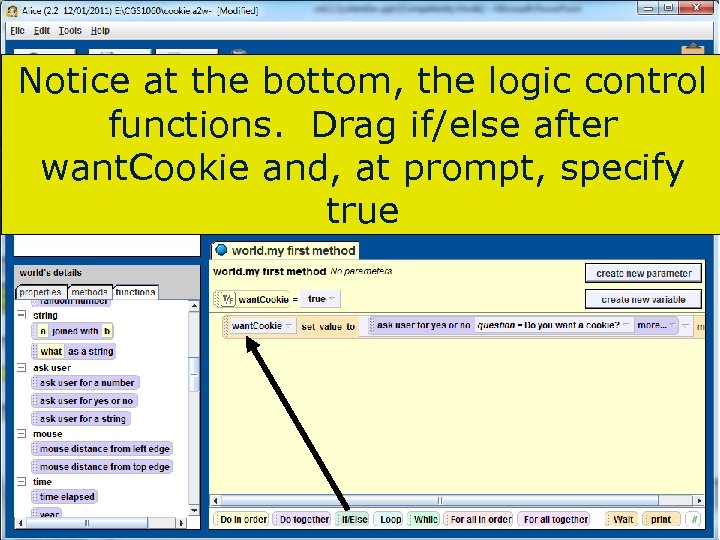 Notice at the bottom, the logic control functions. Drag if/else after want. Cookie and, at prompt, specify true 95 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Notice at the bottom, the logic control functions. Drag if/else after want. Cookie and, at prompt, specify true 95 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
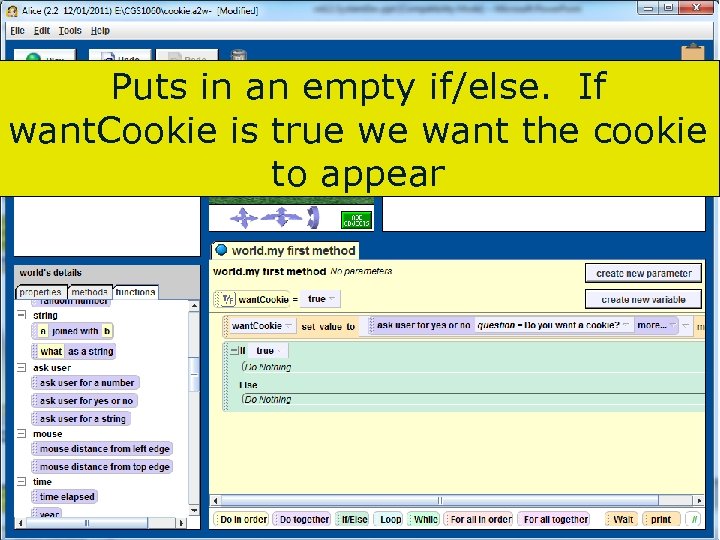 Puts in an empty if/else. If want. Cookie is true we want the cookie to appear 96 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Puts in an empty if/else. If want. Cookie is true we want the cookie to appear 96 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
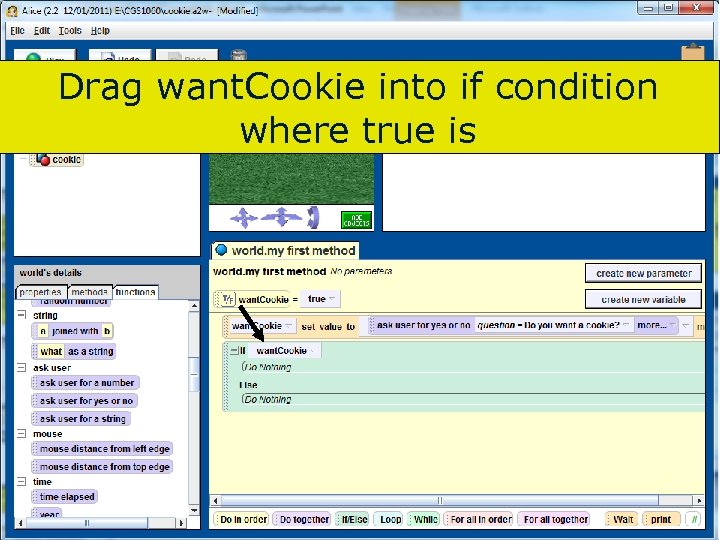 Drag want. Cookie into if condition where true is 97 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Drag want. Cookie into if condition where true is 97 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
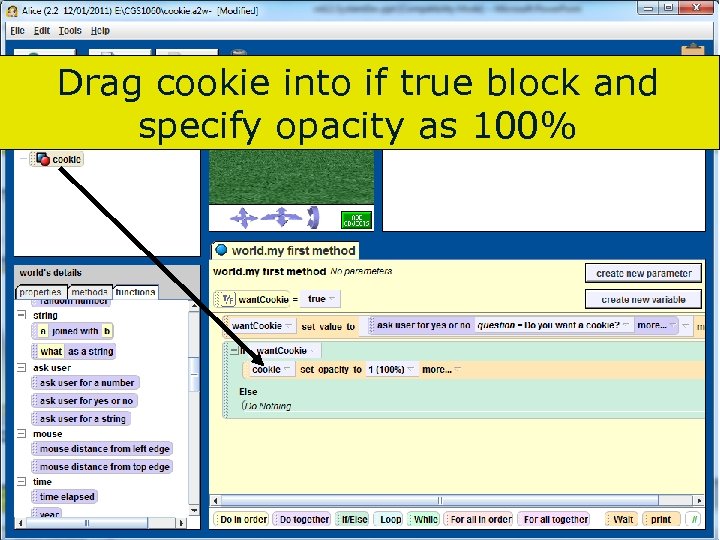 Drag cookie into if true block and specify opacity as 100% 98 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Drag cookie into if true block and specify opacity as 100% 98 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
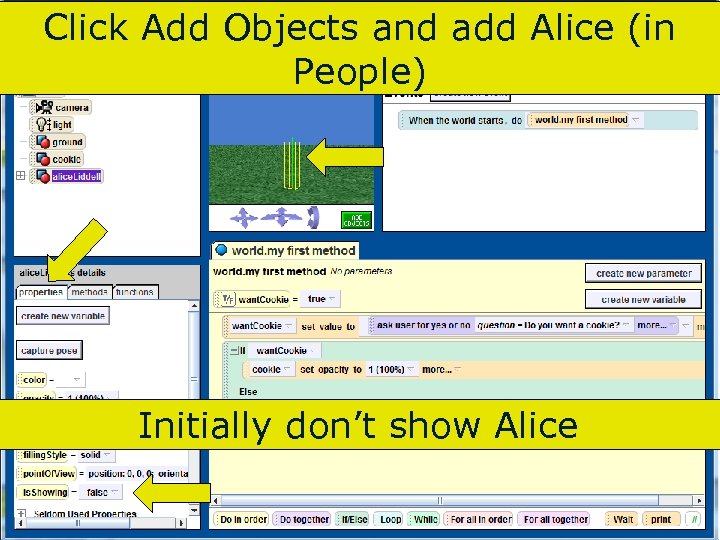 Click Add Objects and add Alice (in People) Initially don’t show Alice 99 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Click Add Objects and add Alice (in People) Initially don’t show Alice 99 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
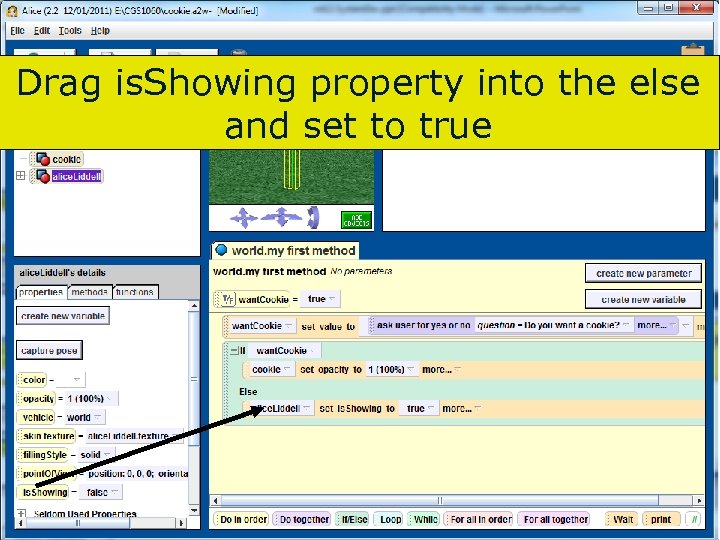 Drag is. Showing property into the else and set to true 100 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Drag is. Showing property into the else and set to true 100 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
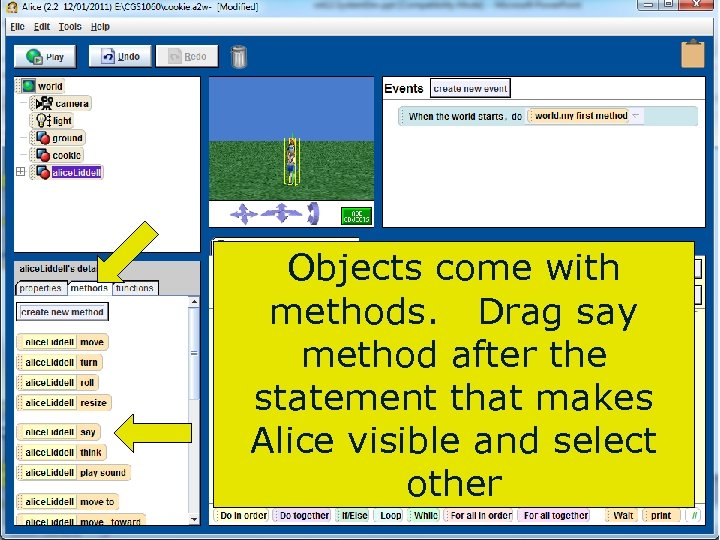 Objects come with methods. Drag say method after the statement that makes Alice visible and select other Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 101
Objects come with methods. Drag say method after the statement that makes Alice visible and select other Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 101
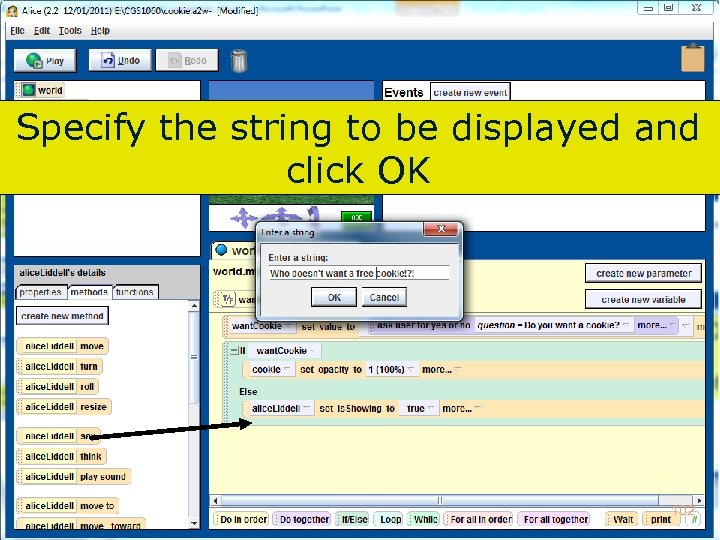 Specify the string to be displayed and click OK 102 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Specify the string to be displayed and click OK 102 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
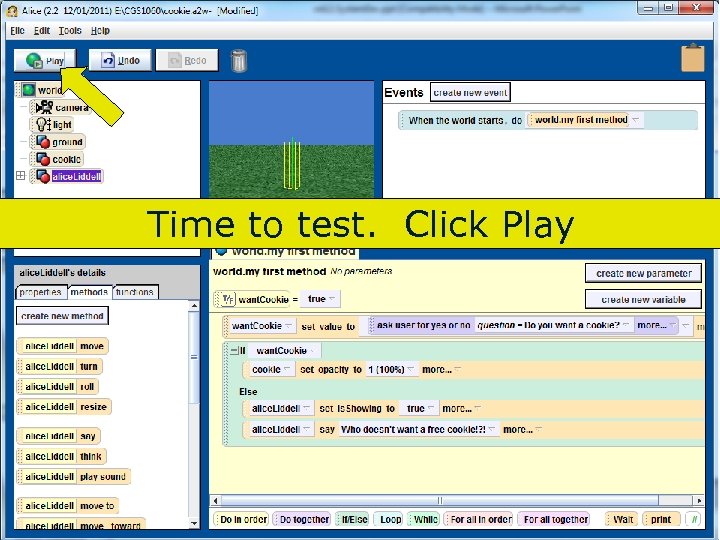 Time to test. Click Play 103 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Time to test. Click Play 103 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
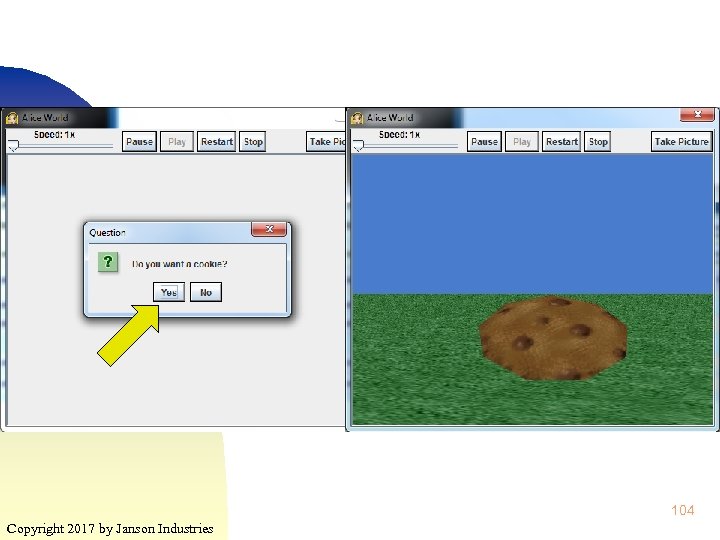 104 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
104 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
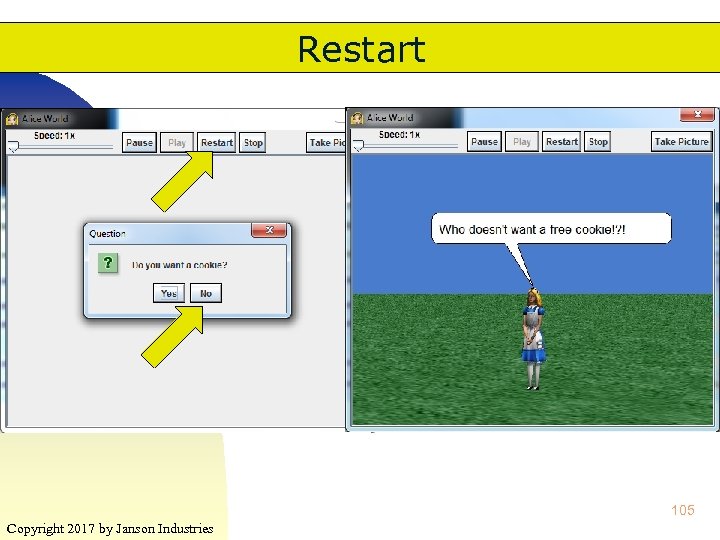 Restart 105 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Restart 105 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
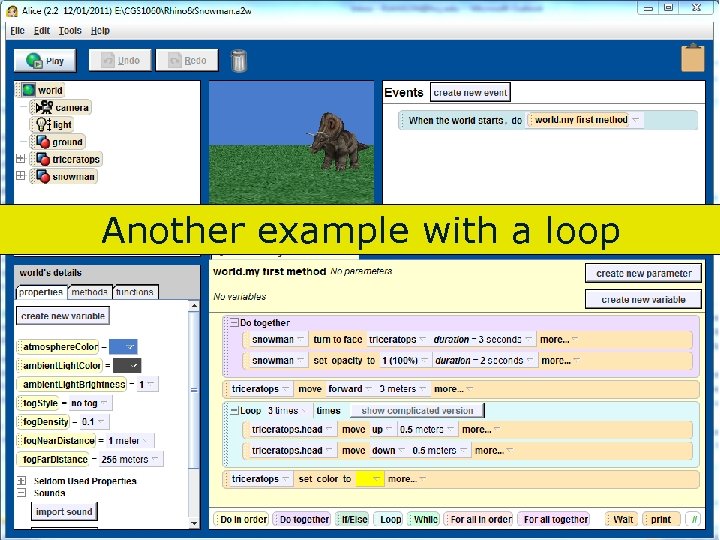 Another example with a loop 106 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Another example with a loop 106 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Extra Credit ▀ Create a storyboard (external design) for a world that uses ♦ At least 5 sequence steps ♦ At least one selection (if/then/else) ♦ At least one loop (any type) that loops at least 2 times ▀ Email the storyboard for approval ▀ After approval ♦ Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Create world and email me the file 107
Extra Credit ▀ Create a storyboard (external design) for a world that uses ♦ At least 5 sequence steps ♦ At least one selection (if/then/else) ♦ At least one loop (any type) that loops at least 2 times ▀ Email the storyboard for approval ▀ After approval ♦ Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Create world and email me the file 107
 Design Tools ▀ S/W that makes it easier to generate program designs ♦ ♦ ▀ Flowchart generator Storyboard tools Example ♦ SFC (Structured Flow Chart editor) 108 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Design Tools ▀ S/W that makes it easier to generate program designs ♦ ♦ ▀ Flowchart generator Storyboard tools Example ♦ SFC (Structured Flow Chart editor) 108 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
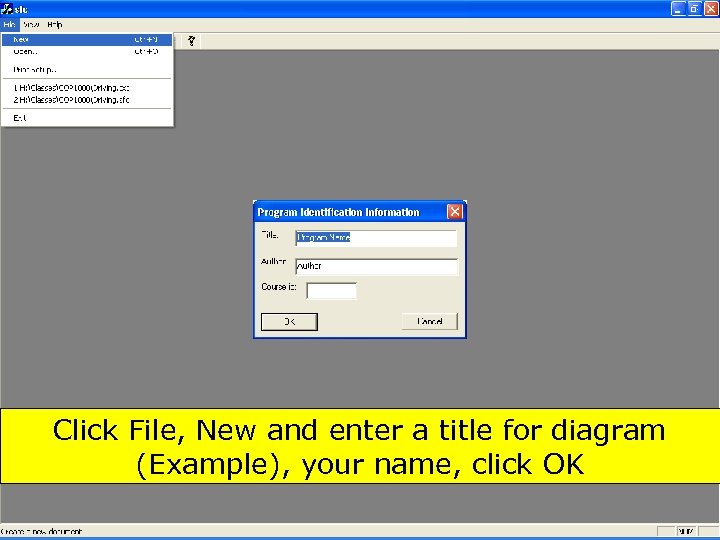 Click File, New and enter a title for diagram (Example), your name, click OK 109 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Click File, New and enter a title for diagram (Example), your name, click OK 109 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Lots of options 110 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Lots of options 110 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
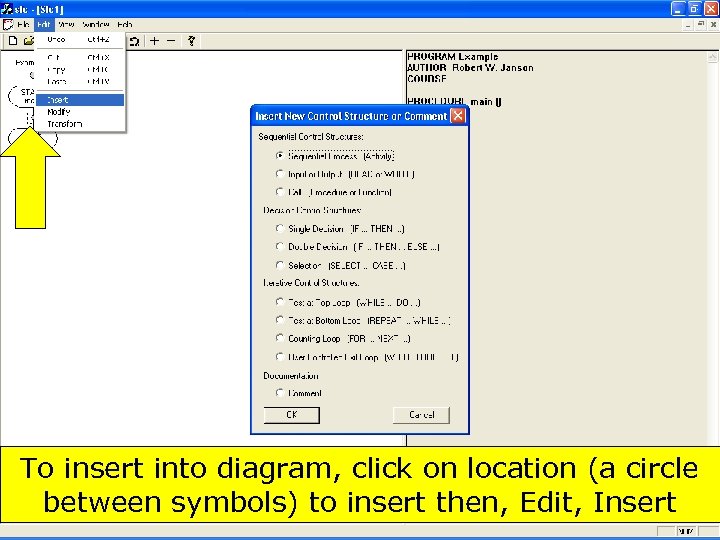 To insert into diagram, click on location (a circle between symbols) to insert then, Edit, Insert 111 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
To insert into diagram, click on location (a circle between symbols) to insert then, Edit, Insert 111 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
![] ] 112 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries ] ] 112 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries](https://present5.com/presentation/04a70c584c383a5db33e6e63b8761d13/image-112.jpg) ] ] 112 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
] ] 112 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
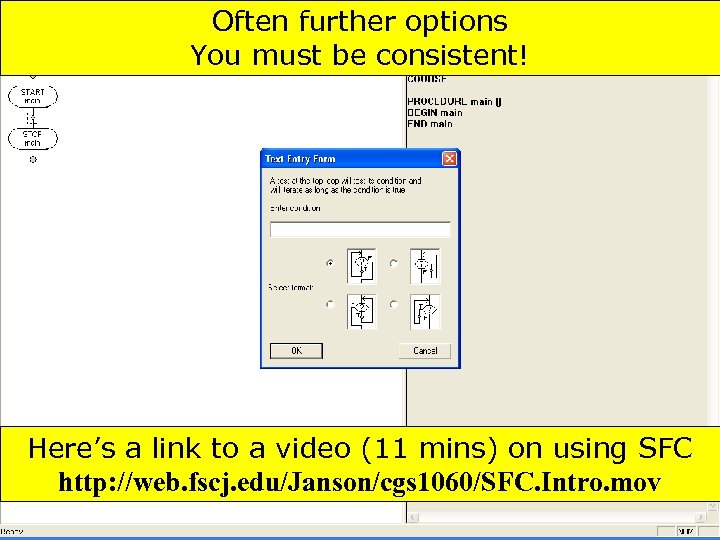 Often further options You must be consistent! Here’s a link to a video (11 mins) on using SFC http: //web. fscj. edu/Janson/cgs 1060/SFC. Intro. mov 113 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Often further options You must be consistent! Here’s a link to a video (11 mins) on using SFC http: //web. fscj. edu/Janson/cgs 1060/SFC. Intro. mov 113 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 App Development Tools ▀ S/W that makes it easier to program ♦ ♦ ▀ Syntax checkers Debugging utilities Visual editors Test environments Examples ♦ ♦ ♦ MS: . NET (Visual Studio) Oracle: Net. Beans IBM: Web. Sphere (Rational Application Developer) 114 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
App Development Tools ▀ S/W that makes it easier to program ♦ ♦ ▀ Syntax checkers Debugging utilities Visual editors Test environments Examples ♦ ♦ ♦ MS: . NET (Visual Studio) Oracle: Net. Beans IBM: Web. Sphere (Rational Application Developer) 114 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
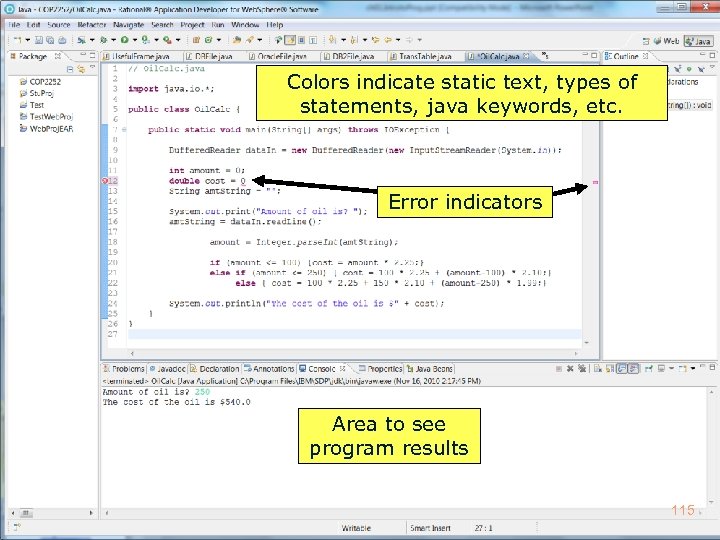 Colors indicate static text, types of statements, java keywords, etc. Error indicators Area to see program results 115 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
Colors indicate static text, types of statements, java keywords, etc. Error indicators Area to see program results 115 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
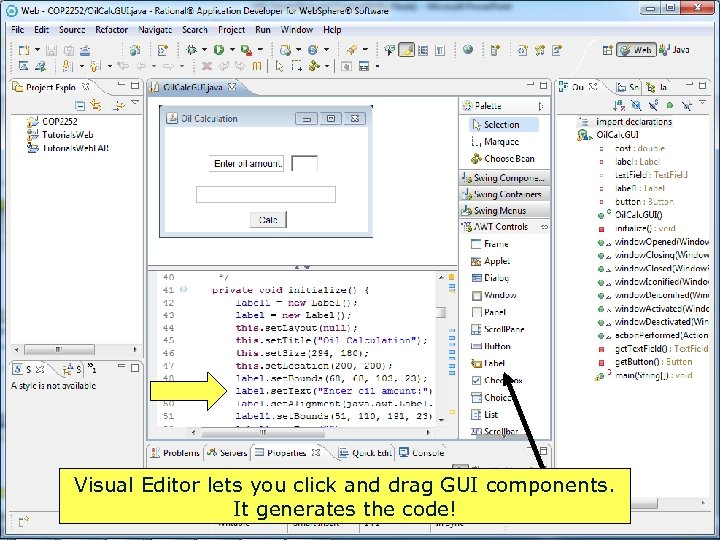 Visual Editor lets you click and drag GUI components. It generates the code! Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 116
Visual Editor lets you click and drag GUI components. It generates the code! Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries 116
 App Development Tools ▀ Some claim there are new 4 GLs ▀ Application generators ♦ You specify: ►What the output should look like ►Where the input is ♦ Application generator produces the program 117 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
App Development Tools ▀ Some claim there are new 4 GLs ▀ Application generators ♦ You specify: ►What the output should look like ►Where the input is ♦ Application generator produces the program 117 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 App Development Tools ▀ Some claim that applications, like Access, are 4 GLs ♦ ♦ ▀ Doesn't it let you create queries Aren't they essentially little programs? What about forms? Aren't they little input programs? Many Apps allow you to create macros ♦ ♦ Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Multiple actions that can be saved and rerun Sounds like a program to me 118
App Development Tools ▀ Some claim that applications, like Access, are 4 GLs ♦ ♦ ▀ Doesn't it let you create queries Aren't they essentially little programs? What about forms? Aren't they little input programs? Many Apps allow you to create macros ♦ ♦ Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Multiple actions that can be saved and rerun Sounds like a program to me 118
 App Development Tools ▀ Besides programming languages ♦ Mark up languages – HTML, XML ► Define format of web pages, data, website structure, etc. ♦ Scripting languages – Java script, PHP, Perl ► Allow ♦ functions to be coded in a web page Web page/site generators – Flash, Expression Web, Dreamweaver ► Generate markup and scripting code 119 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
App Development Tools ▀ Besides programming languages ♦ Mark up languages – HTML, XML ► Define format of web pages, data, website structure, etc. ♦ Scripting languages – Java script, PHP, Perl ► Allow ♦ functions to be coded in a web page Web page/site generators – Flash, Expression Web, Dreamweaver ► Generate markup and scripting code 119 Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries
 Points to Remember ▀ System Development and Program Development follow a complex process ▀ There a variety of people/roles ▀ Many technologies involved ♦ ♦ Application Development Tools ♦ Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Programming, scripting, mark up languages DBMS, networking 120
Points to Remember ▀ System Development and Program Development follow a complex process ▀ There a variety of people/roles ▀ Many technologies involved ♦ ♦ Application Development Tools ♦ Copyright 2017 by Janson Industries Programming, scripting, mark up languages DBMS, networking 120


