a46400eea1e6c16f81532f07e5270887.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Intro to Info Tech Networks This presentation can be viewed on line at: http: //web. fscj. edu/janson/cgs 1060/wk 10. Networks. ppt Copyright 2003 by Janson Industries 1
Intro to Info Tech Networks This presentation can be viewed on line at: http: //web. fscj. edu/janson/cgs 1060/wk 10. Networks. ppt Copyright 2003 by Janson Industries 1
 Objectives n Explain u Components u Type of a network of networks u Network providers 2 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Objectives n Explain u Components u Type of a network of networks u Network providers 2 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Networks n n Enable communication Don't have to be computer networks u. Phone u. TV u. Radio u. Cable 3 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Networks n n Enable communication Don't have to be computer networks u. Phone u. TV u. Radio u. Cable 3 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Networks n n The Rothchild's network Today, high frequency traders rely on getting trade information before others u So they can go to other exchanges and make trades based on the info u Called front running F Ie. short a stock if you know the price is going to go down Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries 4
Networks n n The Rothchild's network Today, high frequency traders rely on getting trade information before others u So they can go to other exchanges and make trades based on the info u Called front running F Ie. short a stock if you know the price is going to go down Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries 4
 Networks n How much sooner do they need the information u All they need is a 500 microsecond (ms) advantage u What's a ms: one millionth of a second 5 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Networks n How much sooner do they need the information u All they need is a 500 microsecond (ms) advantage u What's a ms: one millionth of a second 5 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Networks n 1, 000 ms (1 second) u Time for a single human heartbeat at rest n 100, 000 ms u n One fast blink of a human eye 1000 ms u One beat of a tsetse fly’s wings u 150 separate trades of a stock can occur 6 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Networks n 1, 000 ms (1 second) u Time for a single human heartbeat at rest n 100, 000 ms u n One fast blink of a human eye 1000 ms u One beat of a tsetse fly’s wings u 150 separate trades of a stock can occur 6 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Networks n How do/did the high freq traders get the advantage u Building faster networks F Squeezing out nanosecond (billionth of a second) improvements u Pay to place their computers closer to the stock exchanges u Pay banks/funds to execute their stock trades (called a rebate for order flow) 7 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Networks n How do/did the high freq traders get the advantage u Building faster networks F Squeezing out nanosecond (billionth of a second) improvements u Pay to place their computers closer to the stock exchanges u Pay banks/funds to execute their stock trades (called a rebate for order flow) 7 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Networks n n Estimated that they made $160, 000 a day If you're interested in more info, great article based on the book "Flash Boys: A Wall Street Revolt" u http: //www. nytimes. com/2014/04/ 06/magazine/flash-boys-michaellewis. html? hp&_r=0 8 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Networks n n Estimated that they made $160, 000 a day If you're interested in more info, great article based on the book "Flash Boys: A Wall Street Revolt" u http: //www. nytimes. com/2014/04/ 06/magazine/flash-boys-michaellewis. html? hp&_r=0 8 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Networks n Modern networks all have u Some device(s) /node(s) that humans interact with that F Either receives and/or sends u Some device(s) to manage/direct the communication u Some transmission medium 9 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Networks n Modern networks all have u Some device(s) /node(s) that humans interact with that F Either receives and/or sends u Some device(s) to manage/direct the communication u Some transmission medium 9 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Computer Networks n Communication does not have to be between people u EDI (electronic data interchange) u Download n files When it does, a "computer" acts as the human interface device u GPS u PDA Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries device (Palm, Blackberry) u Smart Phone 10
Computer Networks n Communication does not have to be between people u EDI (electronic data interchange) u Download n files When it does, a "computer" acts as the human interface device u GPS u PDA Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries device (Palm, Blackberry) u Smart Phone 10
 Network Classifications n Amount of area covered n Architecture n Topology n Wireless vs. physical lines 11 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Network Classifications n Amount of area covered n Architecture n Topology n Wireless vs. physical lines 11 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Networks n LAN – Local Area Network u Limited area FA room, a home, a building, a small group of bldgs u Shared n resources – printer MAN – Metropolitan Area Network u High speed network that connects LANS u Usually larger area F Town, u Ex. Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries city, county Comcast's cable based network 12
Networks n LAN – Local Area Network u Limited area FA room, a home, a building, a small group of bldgs u Shared n resources – printer MAN – Metropolitan Area Network u High speed network that connects LANS u Usually larger area F Town, u Ex. Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries city, county Comcast's cable based network 12
 Networks n WAN – Wide Area Network u Largest F State, geographic area country, world u Can be a bunch of LANS/MANS tied together F The u Or Internet can be a single high speed network F Satellite phone network 13 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Networks n WAN – Wide Area Network u Largest F State, geographic area country, world u Can be a bunch of LANS/MANS tied together F The u Or Internet can be a single high speed network F Satellite phone network 13 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
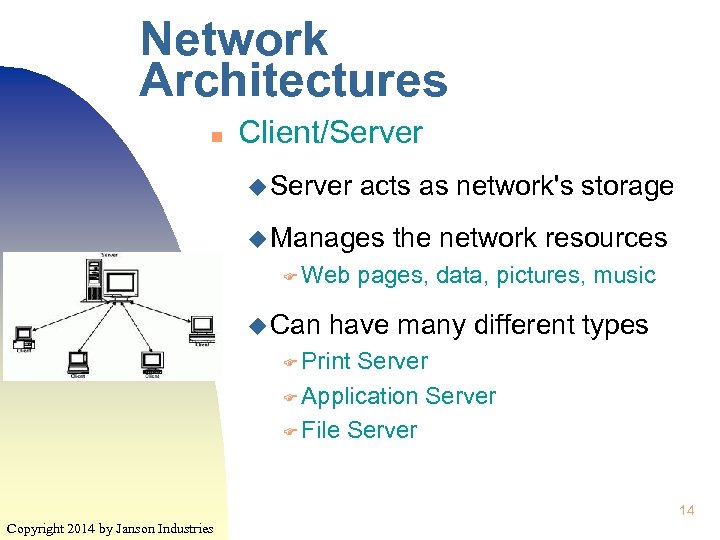 Network Architectures n Client/Server u Server acts as network's storage u Manages F Web u Can the network resources pages, data, pictures, music have many different types F Print Server F Application Server F File Server 14 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Network Architectures n Client/Server u Server acts as network's storage u Manages F Web u Can the network resources pages, data, pictures, music have many different types F Print Server F Application Server F File Server 14 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
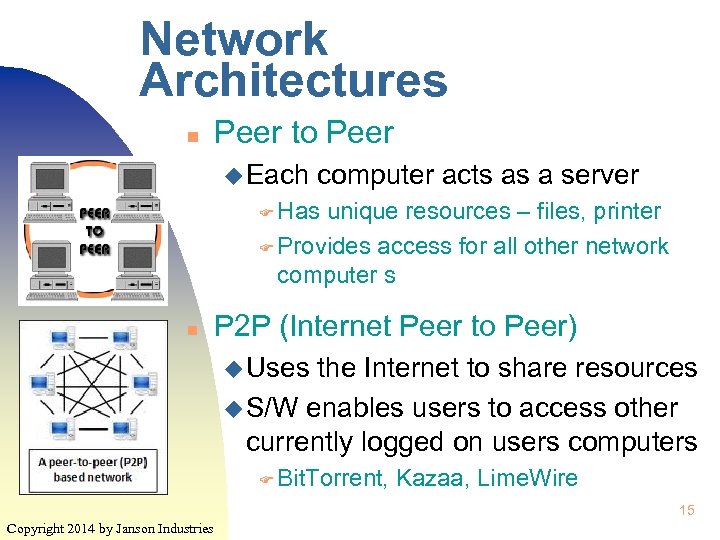 Network Architectures n Peer to Peer u Each computer acts as a server F Has unique resources – files, printer F Provides access for all other network computer s n P 2 P (Internet Peer to Peer) u Uses the Internet to share resources u S/W enables users to access other currently logged on users computers F Bit. Torrent, Kazaa, Lime. Wire 15 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Network Architectures n Peer to Peer u Each computer acts as a server F Has unique resources – files, printer F Provides access for all other network computer s n P 2 P (Internet Peer to Peer) u Uses the Internet to share resources u S/W enables users to access other currently logged on users computers F Bit. Torrent, Kazaa, Lime. Wire 15 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
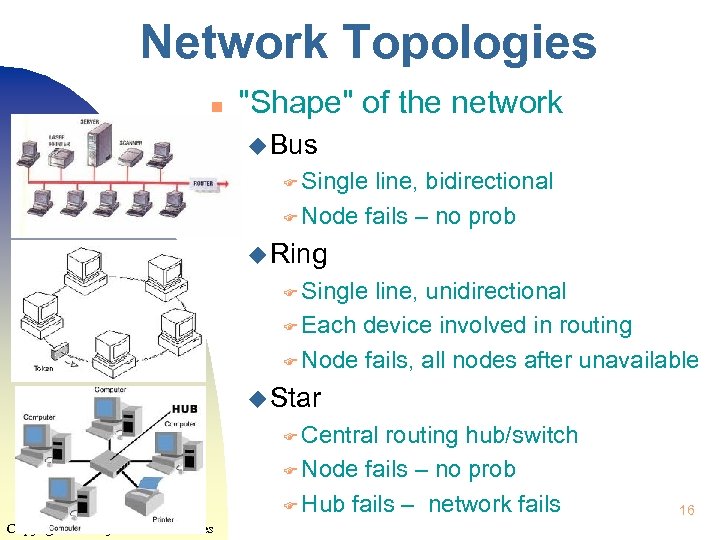 Network Topologies n "Shape" of the network u Bus F Single line, bidirectional F Node fails – no prob u Ring F Single line, unidirectional F Each device involved in routing F Node fails, all nodes after unavailable u Star F Central routing hub/switch F Node fails – no prob F Hub fails – network fails Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries 16
Network Topologies n "Shape" of the network u Bus F Single line, bidirectional F Node fails – no prob u Ring F Single line, unidirectional F Each device involved in routing F Node fails, all nodes after unavailable u Star F Central routing hub/switch F Node fails – no prob F Hub fails – network fails Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries 16
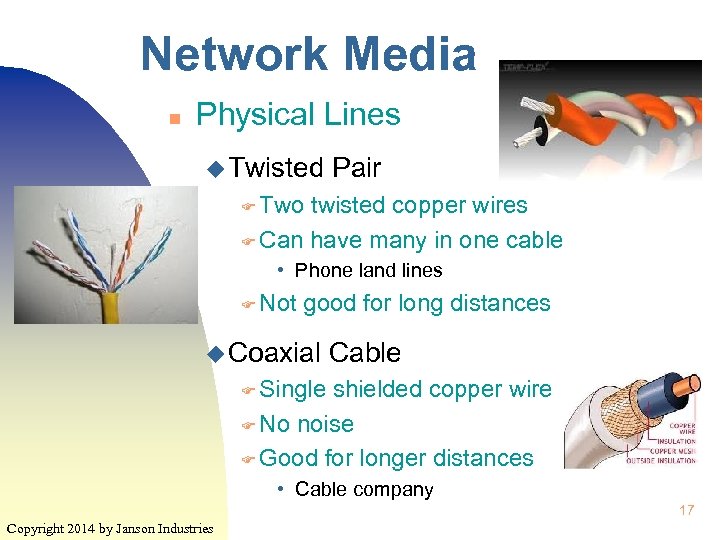 Network Media n Physical Lines u Twisted Pair F Two twisted copper wires F Can have many in one cable • Phone land lines F Not good for long distances u Coaxial Cable F Single shielded copper wire F No noise F Good for longer distances • Cable company 17 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Network Media n Physical Lines u Twisted Pair F Two twisted copper wires F Can have many in one cable • Phone land lines F Not good for long distances u Coaxial Cable F Single shielded copper wire F No noise F Good for longer distances • Cable company 17 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Network Media n Physical Lines u Fiber Optic F Many shielded glass/plastic lines F Transmit F Vs. light copper wires • No interference from other electrical devices • Smaller, lighter and faster • More expensive and harder to install and modify 18 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Network Media n Physical Lines u Fiber Optic F Many shielded glass/plastic lines F Transmit F Vs. light copper wires • No interference from other electrical devices • Smaller, lighter and faster • More expensive and harder to install and modify 18 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Network Media n Wireless u Infrared F Often used by peripherals (wireless mouse, keyboard, printer) F Need line of sight u Broadcast Radio F Good for broad area transmissions F Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 19 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Network Media n Wireless u Infrared F Often used by peripherals (wireless mouse, keyboard, printer) F Need line of sight u Broadcast Radio F Good for broad area transmissions F Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 19 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Network Media n Wireless u Cellular F High Radio frequency radio waves F Uses network of towers to relay signal F Popular with mobile devices u Microwave F Ultrahigh frequency radio waves F Called fixed wireless because transmitted from dish to dish F Line Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries of sight needed • On top of buildings: Empire State Bldg 20
Network Media n Wireless u Cellular F High Radio frequency radio waves F Uses network of towers to relay signal F Popular with mobile devices u Microwave F Ultrahigh frequency radio waves F Called fixed wireless because transmitted from dish to dish F Line Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries of sight needed • On top of buildings: Empire State Bldg 20
 Network Media n Wireless How many satellites are there? u Satellite F Receives transmissions from earth based station F Relays to other earth based station F Often microwave F Vs. terrestrial wireless • Wide range – half the Earth • Less interference • Less real estate needed - no towers, relay stations, wires, etc. • Satellites are expensive • Difficult to repair 21 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Network Media n Wireless How many satellites are there? u Satellite F Receives transmissions from earth based station F Relays to other earth based station F Often microwave F Vs. terrestrial wireless • Wide range – half the Earth • Less interference • Less real estate needed - no towers, relay stations, wires, etc. • Satellites are expensive • Difficult to repair 21 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Network Providers n Do it yourself u Lay your copper wire u Get a router F Hotels, n schools, businesses Common Carriers u Regulated by gov't u Must provide access to anyone F Phone n Value Added Network u Provide Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries company, cable company a service over common carrier line (1 -800 -Big-Date) 22
Network Providers n Do it yourself u Lay your copper wire u Get a router F Hotels, n schools, businesses Common Carriers u Regulated by gov't u Must provide access to anyone F Phone n Value Added Network u Provide Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries company, cable company a service over common carrier line (1 -800 -Big-Date) 22
 Phone Company Services n Switched vs. Dedicated Lines u Switched uses standard telephone lines u Dedicated connects two points F Provides u Advs n constant connection and Disadvs? Dial up connection u Use the telephones switched network u Temporary analog connection u Problem: computers are digital 23 u Need a modem Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Phone Company Services n Switched vs. Dedicated Lines u Switched uses standard telephone lines u Dedicated connects two points F Provides u Advs n constant connection and Disadvs? Dial up connection u Use the telephones switched network u Temporary analog connection u Problem: computers are digital 23 u Need a modem Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Phone Company Services n ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) u Digital over copper (faster than dial up) u Need ISDN modem u Distance limitation – 3. 5 miles n DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) u Digital over copper (faster than ISDN) u Need DSL modem and network card u Distance limitation – 3. 5 miles 24 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Phone Company Services n ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) u Digital over copper (faster than dial up) u Need ISDN modem u Distance limitation – 3. 5 miles n DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) u Digital over copper (faster than ISDN) u Need DSL modem and network card u Distance limitation – 3. 5 miles 24 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Phone Company Services n FTTH/FTTB –Fiber to the Home/Business u The last quarter mile problem u Very fast u Distance limitation – 3. 5 miles n T Lines (T 1, T 2, T 3, etc. ) u High speed lines u Usually make up the backbone of a network 25 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Phone Company Services n FTTH/FTTB –Fiber to the Home/Business u The last quarter mile problem u Very fast u Distance limitation – 3. 5 miles n T Lines (T 1, T 2, T 3, etc. ) u High speed lines u Usually make up the backbone of a network 25 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Network Equipment n With cable need cable modem n Wireless modem n Router u Manages transmissions over the network u Home routers enable multiple computers to share Internet connection 26 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Network Equipment n With cable need cable modem n Wireless modem n Router u Manages transmissions over the network u Home routers enable multiple computers to share Internet connection 26 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Network Standards n n Protocols dictate how two devices communicate over the network Network standards dictate h/w u Connectors u Medium u Cabling u Plug types u Speed 27 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Network Standards n n Protocols dictate how two devices communicate over the network Network standards dictate h/w u Connectors u Medium u Cabling u Plug types u Speed 27 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Network Standards n Ethernet is most popular for LANS u Easy to install and cheap u No central controlling device u Two computers trying to send at same time cause a "collision" n Token Ring u Token passes around network u Only one token so only one computer can communicate at a time u No collisions 28 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Network Standards n Ethernet is most popular for LANS u Easy to install and cheap u No central controlling device u Two computers trying to send at same time cause a "collision" n Token Ring u Token passes around network u Only one token so only one computer can communicate at a time u No collisions 28 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Wireless Network Standards n n Wi. Fi (Wireless Fidelity) similar to Ethernet for radio wave communication UWB (Ultra Wideband) u Short range, high speed, radio wave communication F Video n and image transfers Ir. DA: infrared communications u Must be line of sight 29 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Wireless Network Standards n n Wi. Fi (Wireless Fidelity) similar to Ethernet for radio wave communication UWB (Ultra Wideband) u Short range, high speed, radio wave communication F Video n and image transfers Ir. DA: infrared communications u Must be line of sight 29 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Wireless Network Standards n RFID: radio communication between a reader and a tag u Tag consists of at least an antenna and memory n Near Field Communication (NFC) u AKA u. A Beaming subset of RFID u Dictates how devices communicate at short distances 4 cm (1½ inches) 30 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
Wireless Network Standards n RFID: radio communication between a reader and a tag u Tag consists of at least an antenna and memory n Near Field Communication (NFC) u AKA u. A Beaming subset of RFID u Dictates how devices communicate at short distances 4 cm (1½ inches) 30 Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries
 Wireless Network Standards n Sprint’s Wi. MAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) MW communication over a WAN u Dictates how devices talk to towers, towers communicate to Internet or other towers u Like n Wi. Fi with a bigger hotspot Verizon’s LTE (Long Term Evolution) u Same as Sprint’s Wi. MAX: MW communication over a WAN Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries 31
Wireless Network Standards n Sprint’s Wi. MAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) MW communication over a WAN u Dictates how devices talk to towers, towers communicate to Internet or other towers u Like n Wi. Fi with a bigger hotspot Verizon’s LTE (Long Term Evolution) u Same as Sprint’s Wi. MAX: MW communication over a WAN Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries 31
 Protocols n n TCP/IP dictates how Internet communications work Bluetooth how short range radio communication work u Include non-computer devices like F Headsets, n fax machines, cameras WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) u How smaller devices display Internet resources F Web Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries page on a phone F Email to blackberry 32
Protocols n n TCP/IP dictates how Internet communications work Bluetooth how short range radio communication work u Include non-computer devices like F Headsets, n fax machines, cameras WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) u How smaller devices display Internet resources F Web Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries page on a phone F Email to blackberry 32
 Points to Remember n n n Communication networks require both h/w and software Standards dictate h/w, protocols dictate s/w Computer networks have at least: u User node u Medium u Communication Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries management device 33
Points to Remember n n n Communication networks require both h/w and software Standards dictate h/w, protocols dictate s/w Computer networks have at least: u User node u Medium u Communication Copyright 2014 by Janson Industries management device 33


