6d3f048574d722e27f9de0460797c663.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
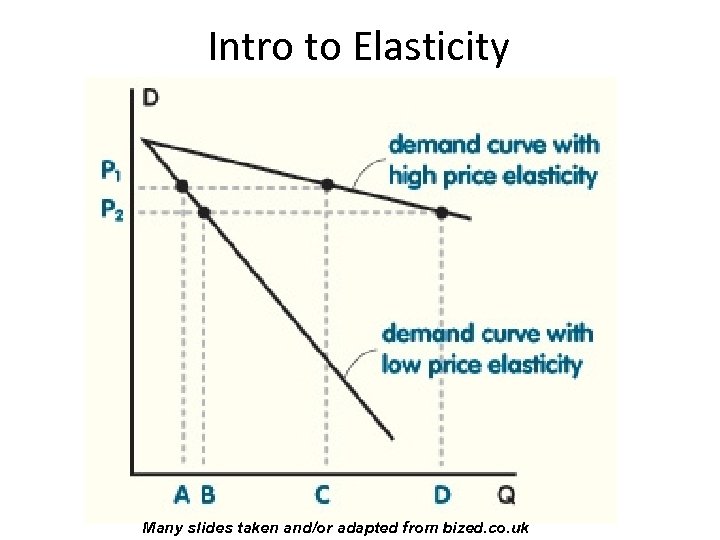 Intro to Elasticity Many slides taken and/or adapted from bized. co. uk
Intro to Elasticity Many slides taken and/or adapted from bized. co. uk
 Elasticity • The responsiveness of one variable to changes in another – Or…Responsiveness or sensitivity of consumers to a price change
Elasticity • The responsiveness of one variable to changes in another – Or…Responsiveness or sensitivity of consumers to a price change
 PED • Price Elasticity of Demand – DEFINITION: The responsiveness of demand to changes in price • PED helps us understand this: If the price rises by 10%, will demand decrease by more than, less than, or exactly 10%? – ELASTIC OR INELASTIC? : Where % change in demand is greater than % change in price – ELASTIC OR INELASTIC? Where % change in demand is less than % change in price
PED • Price Elasticity of Demand – DEFINITION: The responsiveness of demand to changes in price • PED helps us understand this: If the price rises by 10%, will demand decrease by more than, less than, or exactly 10%? – ELASTIC OR INELASTIC? : Where % change in demand is greater than % change in price – ELASTIC OR INELASTIC? Where % change in demand is less than % change in price
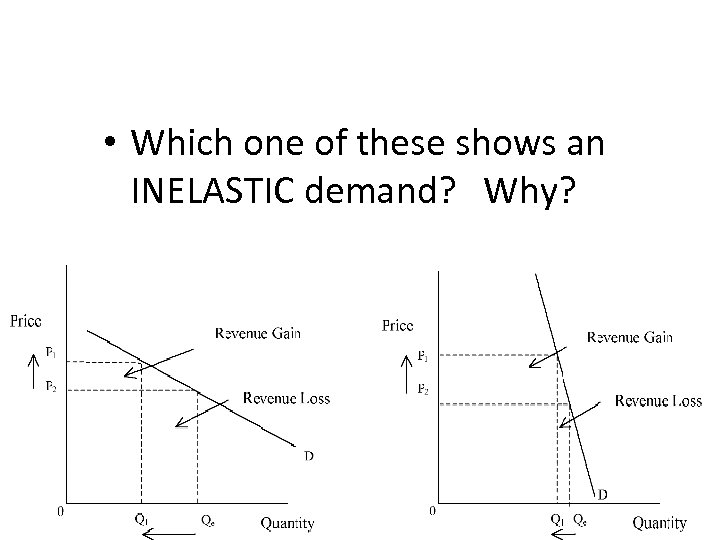 • Which one of these shows an INELASTIC demand? Why?
• Which one of these shows an INELASTIC demand? Why?
 Factors that Determine Demand Short-Term Elasticity • 1. Substitutability – Are there adequate substitutes available? • 2. Proportion of Income – Does the purchase use a large portion of income? • 3. Luxuries v. Necessities – Can the purchase be delayed? • (Long-Term Elasticity) -- Time – Have consumers had time to adjust to a change in prices? (Short term—people stuck w/their cars…long term—people buy what kind of
Factors that Determine Demand Short-Term Elasticity • 1. Substitutability – Are there adequate substitutes available? • 2. Proportion of Income – Does the purchase use a large portion of income? • 3. Luxuries v. Necessities – Can the purchase be delayed? • (Long-Term Elasticity) -- Time – Have consumers had time to adjust to a change in prices? (Short term—people stuck w/their cars…long term—people buy what kind of

 • • • • What type of elasticity do you think the following would have? Salt Orange juice Stamps Gasoline – In general – From a particular station Water Baby Food Tobacco Insulin butter Haircut Lawyer services Heart transplant Schooling at an international school in Guangzhou, China So, in an effort to make more profits a producer may want to raise prices. For which of the above would you advise this action?
• • • • What type of elasticity do you think the following would have? Salt Orange juice Stamps Gasoline – In general – From a particular station Water Baby Food Tobacco Insulin butter Haircut Lawyer services Heart transplant Schooling at an international school in Guangzhou, China So, in an effort to make more profits a producer may want to raise prices. For which of the above would you advise this action?
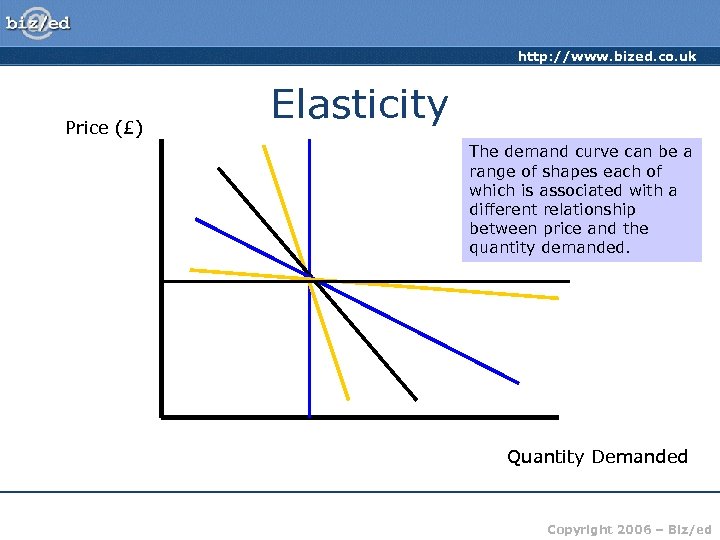 http: //www. bized. co. uk Price (£) Elasticity The demand curve can be a range of shapes each of which is associated with a different relationship between price and the quantity demanded. Quantity Demanded Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed
http: //www. bized. co. uk Price (£) Elasticity The demand curve can be a range of shapes each of which is associated with a different relationship between price and the quantity demanded. Quantity Demanded Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed
 Elasticity http: //www. bized. co. uk The Formula: In Other Words… If answer is between 0 and -1: the relationship is inelastic Each part of equation (New-original)/original) Exactly zero: perfectly inelastic; Exactly one: unit elastic Less than one: inelastic; More than one: elastic Note: The # is usually negative but is always expressed as a positive Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed
Elasticity http: //www. bized. co. uk The Formula: In Other Words… If answer is between 0 and -1: the relationship is inelastic Each part of equation (New-original)/original) Exactly zero: perfectly inelastic; Exactly one: unit elastic Less than one: inelastic; More than one: elastic Note: The # is usually negative but is always expressed as a positive Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed
 The Bigger the Number, the ____ MORE people respond to the price Over 1. 0 = Elastic Under 1. 0 =Inelastic Unit Elastic Exactly 1. 0 =
The Bigger the Number, the ____ MORE people respond to the price Over 1. 0 = Elastic Under 1. 0 =Inelastic Unit Elastic Exactly 1. 0 =
 Total Revenue • What is the definition for revenue? • What is the equation for Total Revenue? • In the example below, What is the total revenue if the quantity purchased is 90? 50? 20?
Total Revenue • What is the definition for revenue? • What is the equation for Total Revenue? • In the example below, What is the total revenue if the quantity purchased is 90? 50? 20?
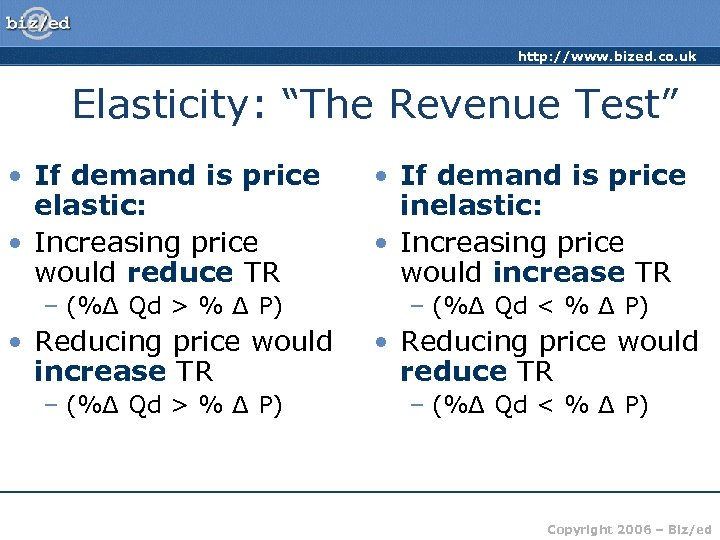 http: //www. bized. co. uk Elasticity: “The Revenue Test” • If demand is price elastic: • Increasing price would reduce TR • If demand is price inelastic: • Increasing price would increase TR – (%Δ Qd > % Δ P) – (%Δ Qd < % Δ P) • Reducing price would increase TR • Reducing price would reduce TR – (%Δ Qd > % Δ P) – (%Δ Qd < % Δ P) Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed
http: //www. bized. co. uk Elasticity: “The Revenue Test” • If demand is price elastic: • Increasing price would reduce TR • If demand is price inelastic: • Increasing price would increase TR – (%Δ Qd > % Δ P) – (%Δ Qd < % Δ P) • Reducing price would increase TR • Reducing price would reduce TR – (%Δ Qd > % Δ P) – (%Δ Qd < % Δ P) Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed
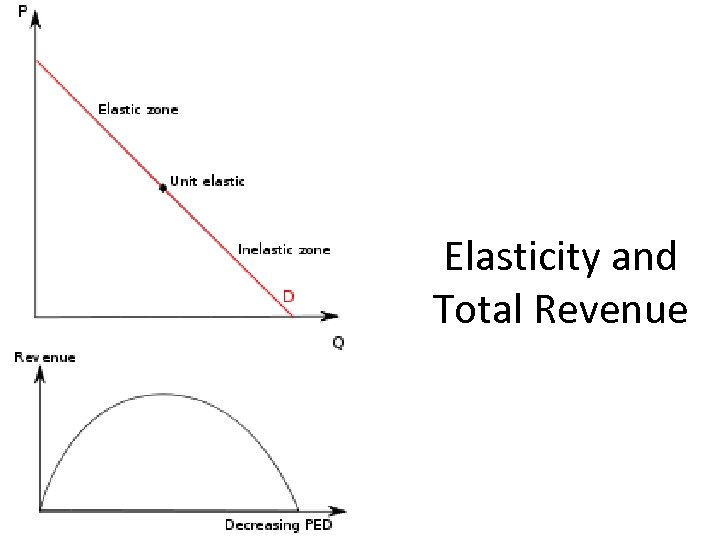 Elasticity and Total Revenue
Elasticity and Total Revenue
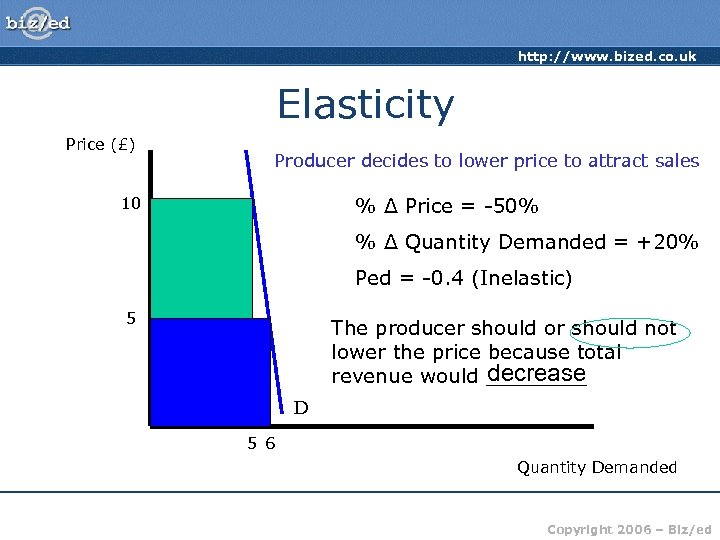 http: //www. bized. co. uk Elasticity Price (£) Producer decides to lower price to attract sales % Δ Price = -50% 10 % Δ Quantity Demanded = +20% Ped = -0. 4 (Inelastic) 5 The producer should or should not lower the price because total decrease revenue would ____ D 5 6 Quantity Demanded Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed
http: //www. bized. co. uk Elasticity Price (£) Producer decides to lower price to attract sales % Δ Price = -50% 10 % Δ Quantity Demanded = +20% Ped = -0. 4 (Inelastic) 5 The producer should or should not lower the price because total decrease revenue would ____ D 5 6 Quantity Demanded Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed
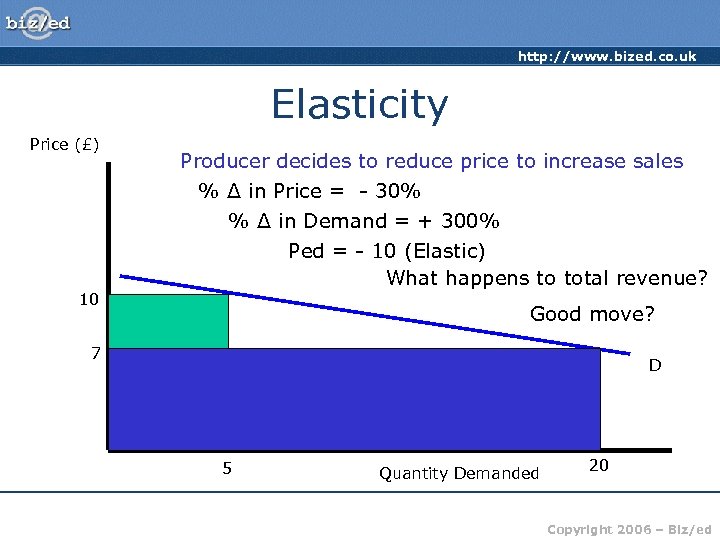 http: //www. bized. co. uk Elasticity Price (£) 10 Producer decides to reduce price to increase sales % Δ in Price = - 30% % Δ in Demand = + 300% Ped = - 10 (Elastic) What happens to total revenue? Good move? 7 D 5 Quantity Demanded 20 Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed
http: //www. bized. co. uk Elasticity Price (£) 10 Producer decides to reduce price to increase sales % Δ in Price = - 30% % Δ in Demand = + 300% Ped = - 10 (Elastic) What happens to total revenue? Good move? 7 D 5 Quantity Demanded 20 Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed
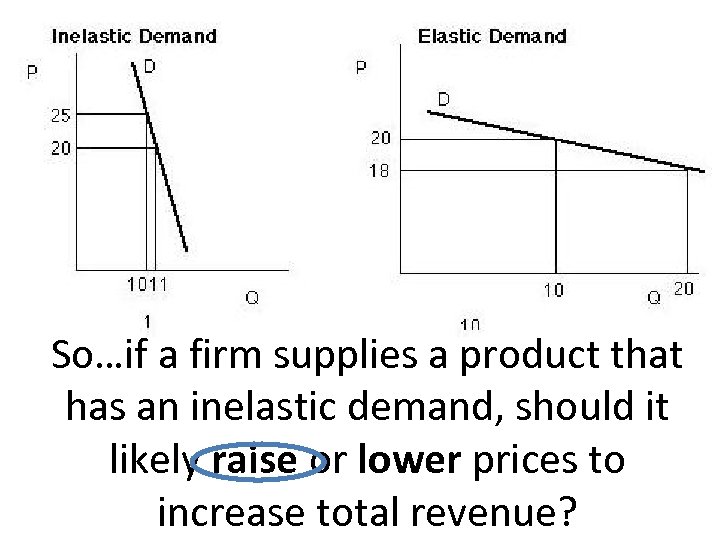 So…if a firm supplies a product that has an inelastic demand, should it likely raise or lower prices to increase total revenue?
So…if a firm supplies a product that has an inelastic demand, should it likely raise or lower prices to increase total revenue?
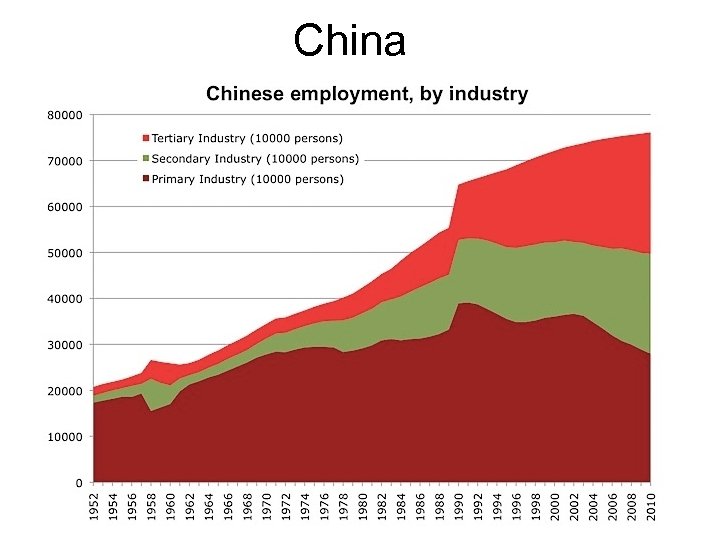
 Primary v. Secondary v. Tertiary: the 3 (Main) Sectors of the Economy • Characteristics? • Examples? • Why/When/How do countries move into different sectors?
Primary v. Secondary v. Tertiary: the 3 (Main) Sectors of the Economy • Characteristics? • Examples? • Why/When/How do countries move into different sectors?
 What is a ‘primary commodity? ’ • Wheat, oil, copper, rubber, metals, cotton, etc.
What is a ‘primary commodity? ’ • Wheat, oil, copper, rubber, metals, cotton, etc.
 Is the PED for… • Many primary commodities high or low? • Many manufactured products relatively high or low? .
Is the PED for… • Many primary commodities high or low? • Many manufactured products relatively high or low? .
 TIME PERMITTING…MORE PRIMARY/SECONDARY/TERTIARY INFO
TIME PERMITTING…MORE PRIMARY/SECONDARY/TERTIARY INFO
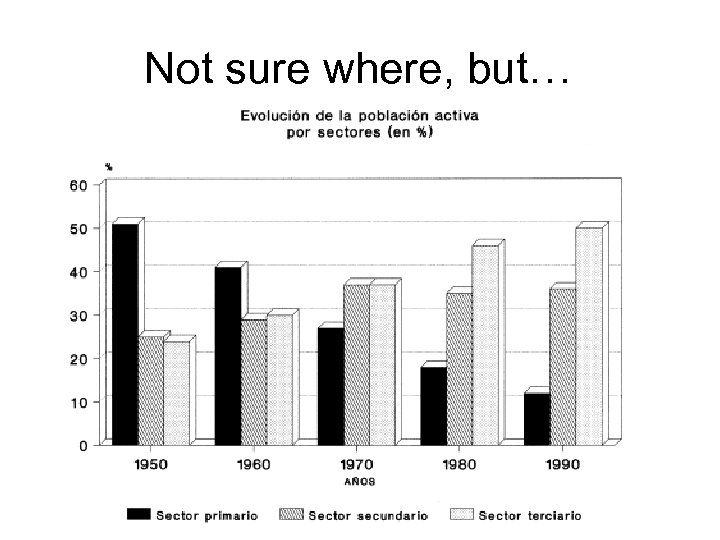 Not sure where, but…
Not sure where, but…
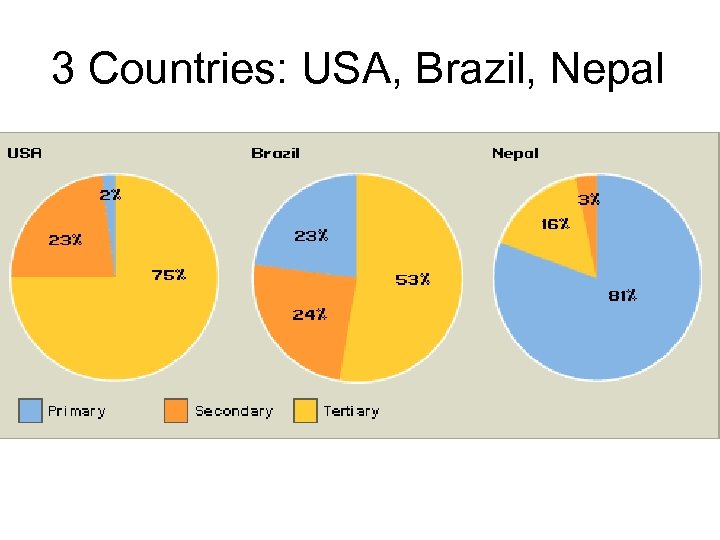 3 Countries: USA, Brazil, Nepal
3 Countries: USA, Brazil, Nepal
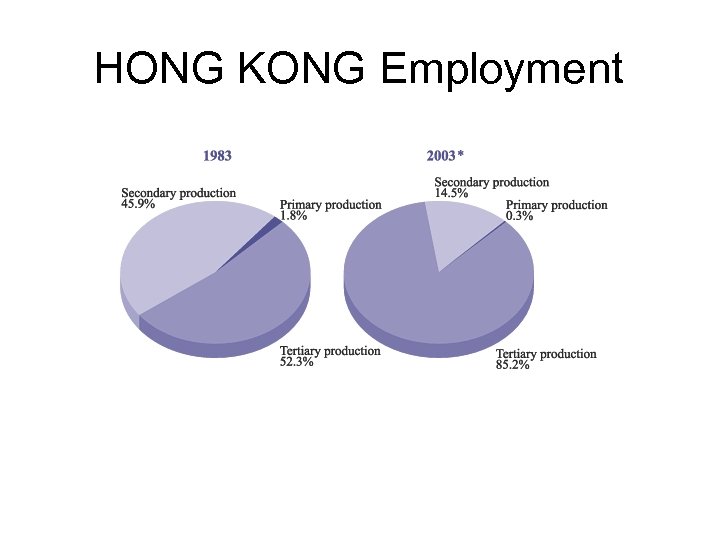 HONG KONG Employment
HONG KONG Employment
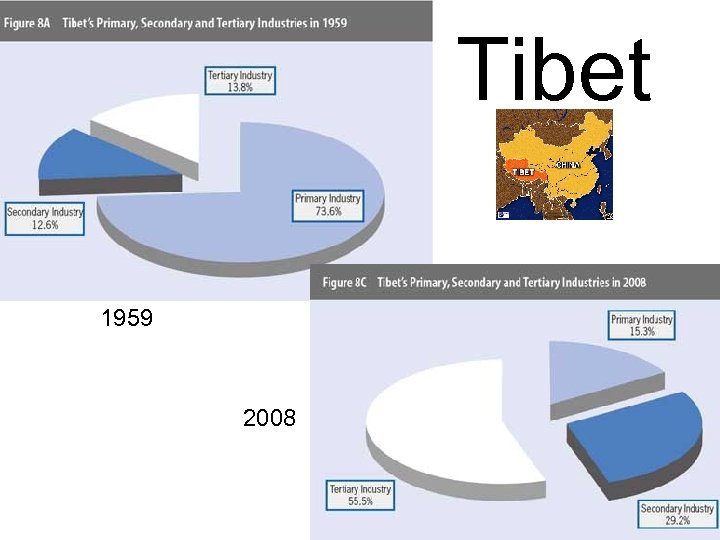 Tibet 1959 2008
Tibet 1959 2008
 China
China


