b7437574ba23801662c720c71f91b5c3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 CHAPTER 19 Savings and Investment Strategies 19 -1 19 -2 19 -3 19 -4 19 -5 Saving and investment planning Stock investments Bonds and mutual funds Real estate investments Other investments © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 1

Intro to Business, 7 e 19 -1 Saving and Investment Planning Chapter 19 Goals l Explain the basics of saving and investing. l Identify types of savings and investments. l Discuss factors to consider when evaluating savings and investment alternatives. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 2

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Key Terms l saving l investing l yield l liquidity © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 3

Intro to Business, 7 e SAVING AND INVESTMENT BASICS Chapter 19 l Savings and investment activities l Determine investment goals l The growth of savings l Interest l Compound interest © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 4
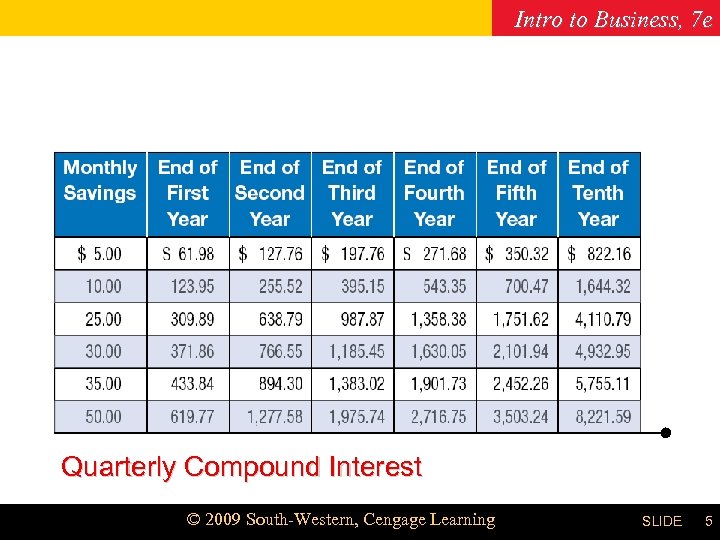
Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Quarterly Compound Interest © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 5

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> How does saving influence economic activity? Answer l Saving benefits the economy by making more money available for borrowing by individuals, businesses, and governments. l When this money is spent, demand for goods and services increases, resulting in more jobs and more spending by workers. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 6

Intro to Business, 7 e SAVING AND INVESTMENT CHOICES Chapter 19 l Savings plans l Savings account l Certificate of deposit l Money market account l Securities l Stock investments l Bond investments l Mutual funds © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 7

Intro to Business, 7 e SAVING AND INVESTMENT CHOICES Chapter 19 (continued) l Alternative investments l Real estate l Commodities l Collectibles © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 8

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> What are the nine main categories of saving and investment alternatives? Answer l Savings accounts l Certificates of deposit l Money market accounts l Stock investments l Bond investments l l Mutual funds Real estate Commodities Collectibles © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 9

Intro to Business, 7 e EVALUATING SAVINGS AND INVESTMENTS Chapter 19 l Safety and risk l Potential return l Liquidity l Taxes © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 10
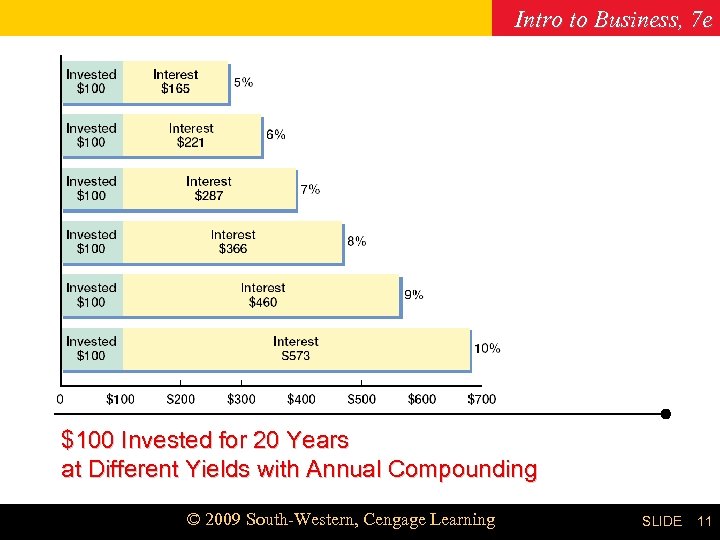
Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 $100 Invested for 20 Years at Different Yields with Annual Compounding © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 11
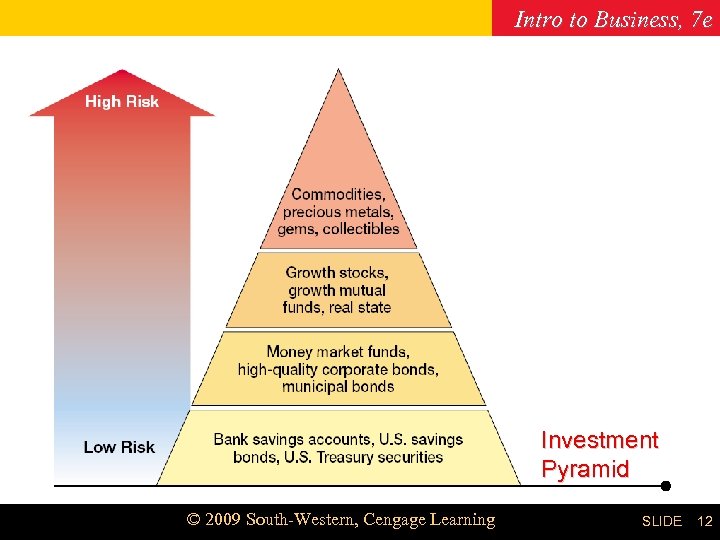
Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Investment Pyramid © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 12

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> What are four factors to consider when selecting an investment? Answer l Safety l Return l Liquidity l Taxes © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 13

Intro to Business, 7 e 19 -2 Stock Investments Chapter 19 Goals l Compare the two major types of stock. l Describe the activities involved with buying or selling stock. l Identify factors that affect the value of a stock. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 14

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Key Terms l preferred stock l common stock l stockbroker l stock exchange l market value © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 15

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 TYPES OF STOCK l Preferred stock l Common stock © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 16

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> How does preferred stock differ from common stock? Answer l Preferred stock has priority over common stock in the payment of dividends. l Investing in preferred stock is less risky than common stock, but preferred stockholders generally have no voting rights within the corporation. l Common stock represents general ownership in a corporation and a right to share in its profits. l Common stockholders are entitled to one vote per share. l Although preferred stockholders are paid first, their dividends usually are limited to a set rate. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 17

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 STOCK TRANSACTIONS l Using a stockbroker l Online investing l Stock exchanges l Changing stock values © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 18
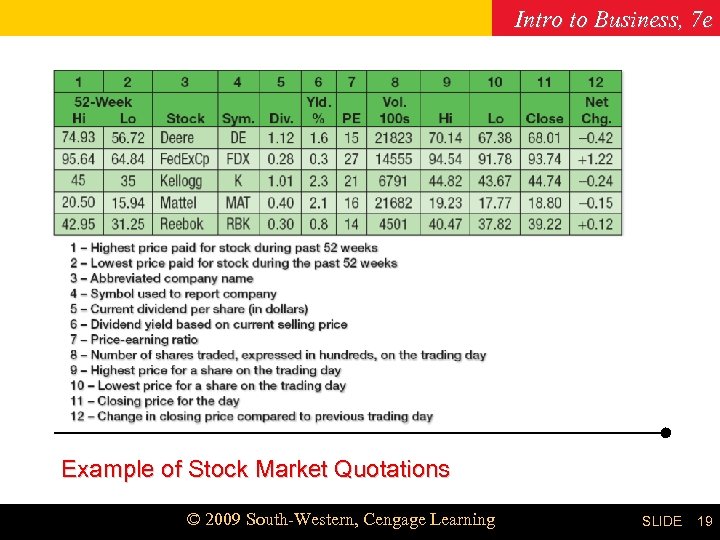
Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Example of Stock Market Quotations © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 19

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> What is the purpose of a stock exchange? Answer l The purpose of a stock exchange is to accommodate the buying and selling of securities. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 20

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 STOCK SELECTION l Stock information sources l Economic factors l l Inflation Interest rates Consumer spending Employment l Company factors © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 21

Intro to Business, 7 e PROCESS FOR DECIDING STOCK PURCHASES Chapter 19 1. Observe and analyze economic and social trends. 2. Determine industries that will be affected. 3. Identify companies in those industries. 4. Decide whether to buy, sell, or hold the stock of those companies. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 22

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> How do various economic factors affect stock prices? Answer l Inflation affects stock prices by causing lower spending by consumers, reducing company profits out of which dividends are paid. l Falling or rising interest rates can also increase or decrease company profits as the cost of money changes. l The employment rate also affects stock prices; when more people are employed, they spend more money on a company’s products and stock prices rise. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 23

Intro to Business, 7 e 19 -3 Bonds and Mutual Funds Chapter 19 Goals l List types of government bonds. l Describe features of corporate bonds. l Describe various types of mutual funds. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 24

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Key Terms l municipal bond l corporate bond l mutual fund © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 25

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 GOVERNMENT BONDS l Municipal bonds l U. S. savings bonds l Other federal securities l Federal notes (T-notes) l Treasury bills (T-bills) l Treasury bonds (T-bonds) © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 26

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> List the types of bonds issued by the federal government of the United States. Answer l The types of U. S. savings bonds issued by the federal government are Series EE bonds, Series HH bonds, and I bonds. l The federal government also issues Treasury bills and Treasury notes. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 27

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 CORPORATE BONDS l Bond components l Bond values © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 28
Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> What affects the value of a bond? Answer l The value of a bond is affected by changing interest rates. l If the bond’s stated rate is lower than interest rates on similar bonds, investors will want to buy the bond for less than its face value. l If the bond’s stated interest rate is higher than interest rates on similar bonds, the seller of the bond will want to receive more than its face value. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 29

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 MUTUAL FUNDS l A mutual fund is an investment fund set up and managed by companies that receive money from many investors. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 30

Intro to Business, 7 e TYPES OF MUTUAL FUNDS Chapter 19 l Aggressive-growth stock funds l Income funds l International funds l Sector funds l Bond funds l Balanced funds © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 31

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 MUTUAL FUND VALUES l Shares of the mutual fund l Value of each share l Net asset value (NAV) l Operating expenses l Earnings © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 32

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> l What are the main types of mutual funds? Answer l The main types of mutual funds are aggressive-growth stock funds, income funds, international funds, sector funds, bond funds, and balanced funds. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 33

Intro to Business, 7 e 19 -4 Real Estate Investments Chapter 19 Goals l Describe home buying activities. l Explain the benefits of home ownership. l Discuss the costs of home ownership. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 34

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Key Terms l real estate l mortgage l equity l assessed value © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 35

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 SELECTING HOUSING l Renting your residence l Owning a mobile home l Buying a home l Services of real estate agents l Other real estate professionals l Buying a condominium © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 36

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> What are four available housing alternatives? Answer l Renting l Owning a mobile home l Buying a traditional home l Buying a condominium © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 37

Intro to Business, 7 e BENEFITS OF HOME OWNERSHIP Chapter 19 l Tax benefits l Increased equity l Pride of ownership © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 38

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> What are the main benefits of home ownership? Answer l Tax benefits l Increased equity l Pride of ownership © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 39

Intro to Business, 7 e COSTS OF HOME OWNERSHIP Chapter 19 l Property taxes l Interest payments l Property insurance l Maintenance © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 40

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> What are common costs of home ownership? Answer l Common costs of home ownership are property taxes, interest payments, property insurance, and maintenance. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 41

Intro to Business, 7 e 19 -5 Other Investments Chapter 19 Goals l Discuss types of commodity investments. l Explain the use of collectibles as an investment. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 42

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Key Terms l commodities l futures contract l collectibles © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 43

Intro to Business, 7 e COMMODITIES AND FUTURES Chapter 19 l Commodity exchanges l Agricultural commodities l Gold, silver, and precious metals l Currency and financial instruments © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 44

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> What types of commodities are commonly used with futures contracts? Answer l Types of commodities commonly used with futures contracts are agricultural commodities, such as grain and livestock, and precious metals. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 45

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 COLLECTIBLES l Types of collectibles l Collectible values © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 46

Intro to Business, 7 e Chapter 19 Checkpoint >> What are common types of collectibles? Answer l Common types of collectibles are stamps, coins, sport trading cards, and antiques, as well as unusual items purchased as investments. © 2009 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 47
b7437574ba23801662c720c71f91b5c3.ppt