963801175af81432cbd454ee1a72fc04.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62
 Intro to Animals (EUMETAZOA) Image from: http: //animaldiversity. ummz. umich. edu/index. html
Intro to Animals (EUMETAZOA) Image from: http: //animaldiversity. ummz. umich. edu/index. html
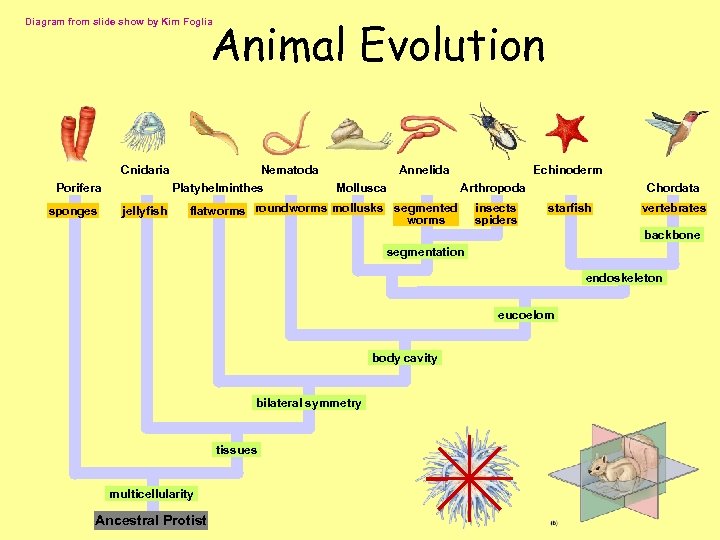 Animal Evolution Diagram from slide show by Kim Foglia Cnidaria Porifera sponges jellyfish Nematoda Platyhelminthes Annelida Mollusca Echinoderm Arthropoda flatworms roundworms mollusks segmented worms insects spiders Chordata starfish vertebrates backbone segmentation endoskeleton eucoelom body cavity bilateral symmetry tissues multicellularity Ancestral Protist
Animal Evolution Diagram from slide show by Kim Foglia Cnidaria Porifera sponges jellyfish Nematoda Platyhelminthes Annelida Mollusca Echinoderm Arthropoda flatworms roundworms mollusks segmented worms insects spiders Chordata starfish vertebrates backbone segmentation endoskeleton eucoelom body cavity bilateral symmetry tissues multicellularity Ancestral Protist
 Animals Invertebrates (animals without a backbone) Porifera Cnidaria Worms Mollusks Echinoderms Arthropods
Animals Invertebrates (animals without a backbone) Porifera Cnidaria Worms Mollusks Echinoderms Arthropods
 Animals Vertebrates. Animals with backbones Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals
Animals Vertebrates. Animals with backbones Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals
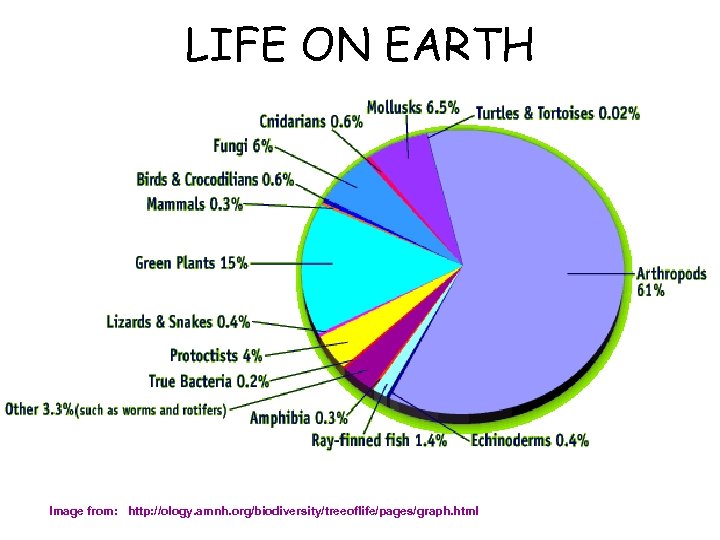 LIFE ON EARTH Image from: http: //ology. amnh. org/biodiversity/treeoflife/pages/graph. html
LIFE ON EARTH Image from: http: //ology. amnh. org/biodiversity/treeoflife/pages/graph. html
 Characteristics of ALL Animals: 1. Eukaryotic 2. Heterotrophic 3. Multicellular/differentiated cells 4. Cells have NO cell walls 5. Movement 6. Reproduction (Most sexual)
Characteristics of ALL Animals: 1. Eukaryotic 2. Heterotrophic 3. Multicellular/differentiated cells 4. Cells have NO cell walls 5. Movement 6. Reproduction (Most sexual)
 Body Systems : ___________ INTEGUMENTARY OUTSIDE BODY COVERING (fur, skin, scales, feathers) Covers and protects, ID, prevents heat & water loss Orangutan image from: http: //www. biologycorner. com/webquests. php Fish image from: http: //www. woodburning. com/fish/ Frog image from: http: //gladstone. uoregon. edu/~mmorley/rainbow/green%20 frog. jpg Cardinal image from: http: //www. nps. gov/fopu/pulaskione/GRAPHIC/IMAGES/birds/Northern%20 Cardinal. jpg
Body Systems : ___________ INTEGUMENTARY OUTSIDE BODY COVERING (fur, skin, scales, feathers) Covers and protects, ID, prevents heat & water loss Orangutan image from: http: //www. biologycorner. com/webquests. php Fish image from: http: //www. woodburning. com/fish/ Frog image from: http: //gladstone. uoregon. edu/~mmorley/rainbow/green%20 frog. jpg Cardinal image from: http: //www. nps. gov/fopu/pulaskione/GRAPHIC/IMAGES/birds/Northern%20 Cardinal. jpg
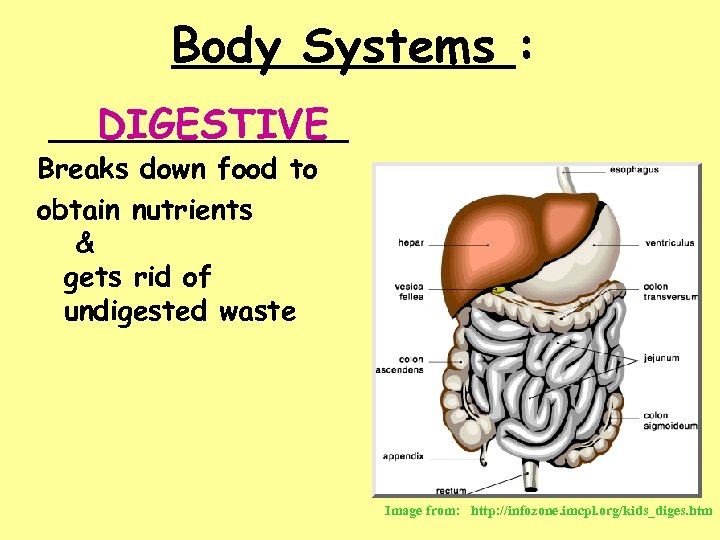 Body Systems : _________ DIGESTIVE Breaks down food to obtain nutrients & gets rid of undigested waste Image from: http: //infozone. imcpl. org/kids_diges. htm
Body Systems : _________ DIGESTIVE Breaks down food to obtain nutrients & gets rid of undigested waste Image from: http: //infozone. imcpl. org/kids_diges. htm
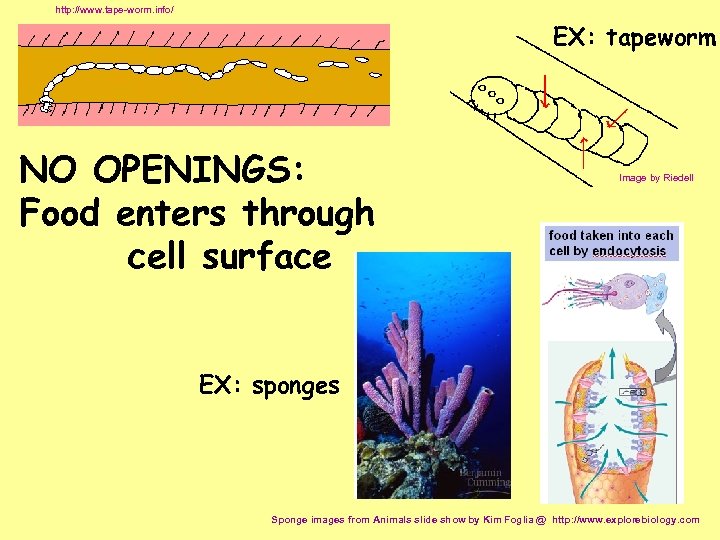 http: //www. tape-worm. info/ EX: tapeworm NO OPENINGS: Food enters through cell surface Image by Riedell EX: sponges Sponge images from Animals slide show by Kim Foglia @ http: //www. explorebiology. com
http: //www. tape-worm. info/ EX: tapeworm NO OPENINGS: Food enters through cell surface Image by Riedell EX: sponges Sponge images from Animals slide show by Kim Foglia @ http: //www. explorebiology. com
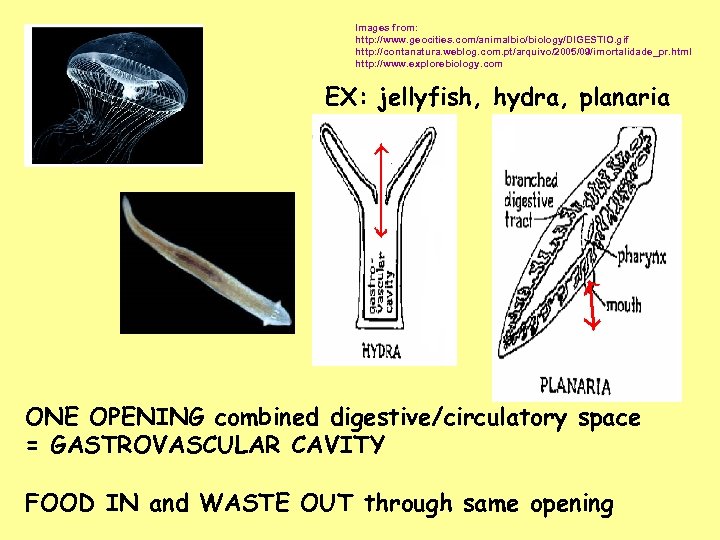 Images from: http: //www. geocities. com/animalbio/biology/DIGESTIO. gif http: //contanatura. weblog. com. pt/arquivo/2005/09/imortalidade_pr. html http: //www. explorebiology. com EX: jellyfish, hydra, planaria ONE OPENING combined digestive/circulatory space = GASTROVASCULAR CAVITY FOOD IN and WASTE OUT through same opening
Images from: http: //www. geocities. com/animalbio/biology/DIGESTIO. gif http: //contanatura. weblog. com. pt/arquivo/2005/09/imortalidade_pr. html http: //www. explorebiology. com EX: jellyfish, hydra, planaria ONE OPENING combined digestive/circulatory space = GASTROVASCULAR CAVITY FOOD IN and WASTE OUT through same opening
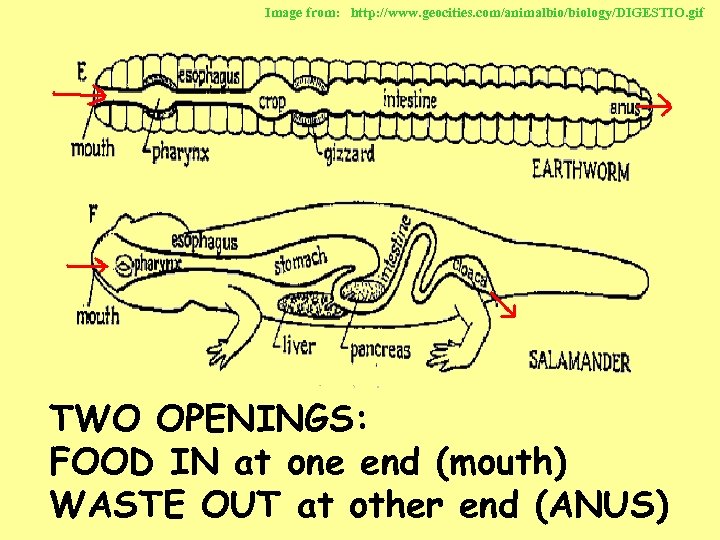 Image from: http: //www. geocities. com/animalbio/biology/DIGESTIO. gif TWO OPENINGS: FOOD IN at one end (mouth) WASTE OUT at other end (ANUS)
Image from: http: //www. geocities. com/animalbio/biology/DIGESTIO. gif TWO OPENINGS: FOOD IN at one end (mouth) WASTE OUT at other end (ANUS)
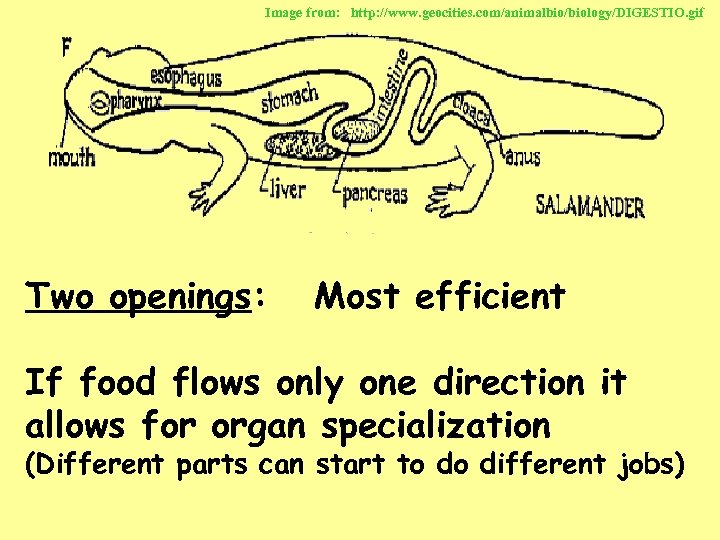 Image from: http: //www. geocities. com/animalbio/biology/DIGESTIO. gif Two openings: Most efficient If food flows only one direction it allows for organ specialization (Different parts can start to do different jobs)
Image from: http: //www. geocities. com/animalbio/biology/DIGESTIO. gif Two openings: Most efficient If food flows only one direction it allows for organ specialization (Different parts can start to do different jobs)
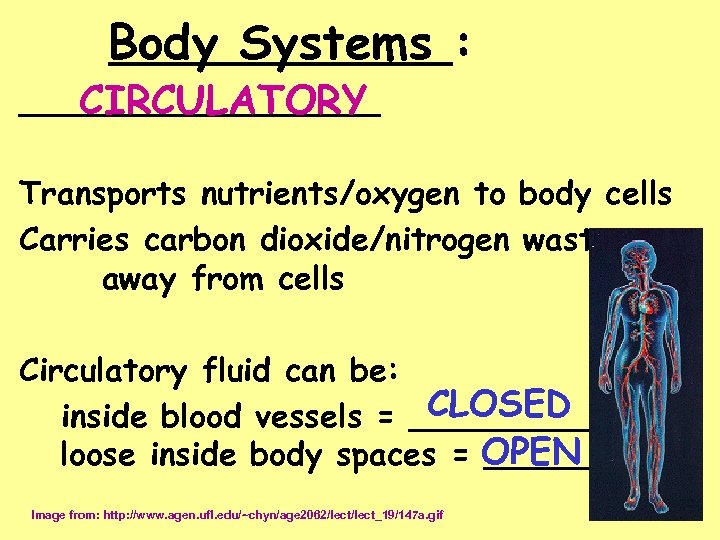 Body Systems : _________ CIRCULATORY Transports nutrients/oxygen to body cells Carries carbon dioxide/nitrogen waste away from cells Circulatory fluid can be: CLOSED inside blood vessels = _____ loose inside body spaces = OPEN _______ Image from: http: //www. agen. ufl. edu/~chyn/age 2062/lect_19/147 a. gif
Body Systems : _________ CIRCULATORY Transports nutrients/oxygen to body cells Carries carbon dioxide/nitrogen waste away from cells Circulatory fluid can be: CLOSED inside blood vessels = _____ loose inside body spaces = OPEN _______ Image from: http: //www. agen. ufl. edu/~chyn/age 2062/lect_19/147 a. gif
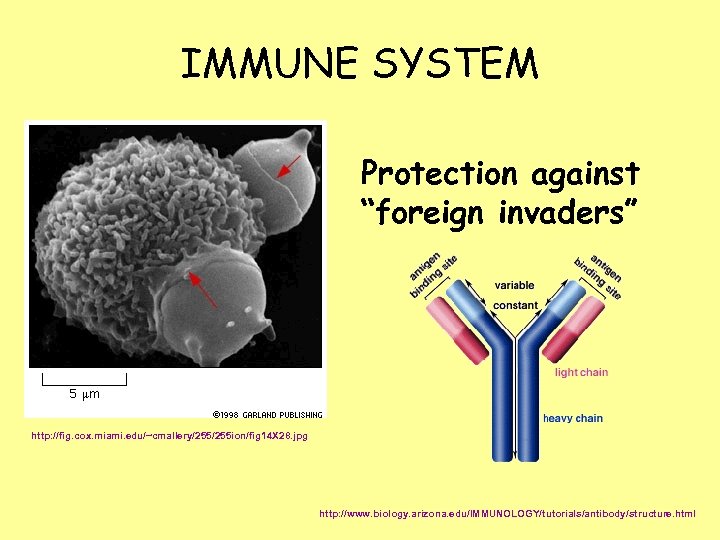 IMMUNE SYSTEM Protection against “foreign invaders” http: //fig. cox. miami. edu/~cmallery/255 ion/fig 14 X 28. jpg http: //www. biology. arizona. edu/IMMUNOLOGY/tutorials/antibody/structure. html
IMMUNE SYSTEM Protection against “foreign invaders” http: //fig. cox. miami. edu/~cmallery/255 ion/fig 14 X 28. jpg http: //www. biology. arizona. edu/IMMUNOLOGY/tutorials/antibody/structure. html
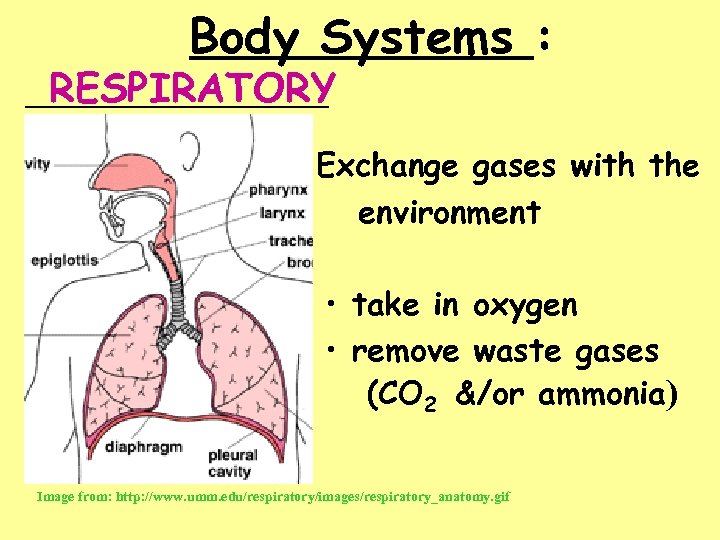 Body Systems : __________ RESPIRATORY Exchange gases with the environment • take in oxygen • remove waste gases (CO 2 &/or ammonia) Image from: http: //www. umm. edu/respiratory/images/respiratory_anatomy. gif
Body Systems : __________ RESPIRATORY Exchange gases with the environment • take in oxygen • remove waste gases (CO 2 &/or ammonia) Image from: http: //www. umm. edu/respiratory/images/respiratory_anatomy. gif
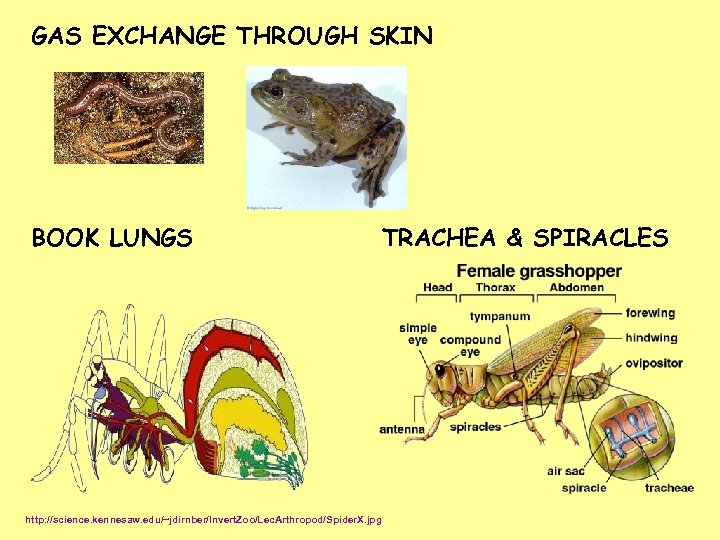 GAS EXCHANGE THROUGH SKIN BOOK LUNGS TRACHEA & SPIRACLES http: //science. kennesaw. edu/~jdirnber/Invert. Zoo/Lec. Arthropod/Spider. X. jpg
GAS EXCHANGE THROUGH SKIN BOOK LUNGS TRACHEA & SPIRACLES http: //science. kennesaw. edu/~jdirnber/Invert. Zoo/Lec. Arthropod/Spider. X. jpg
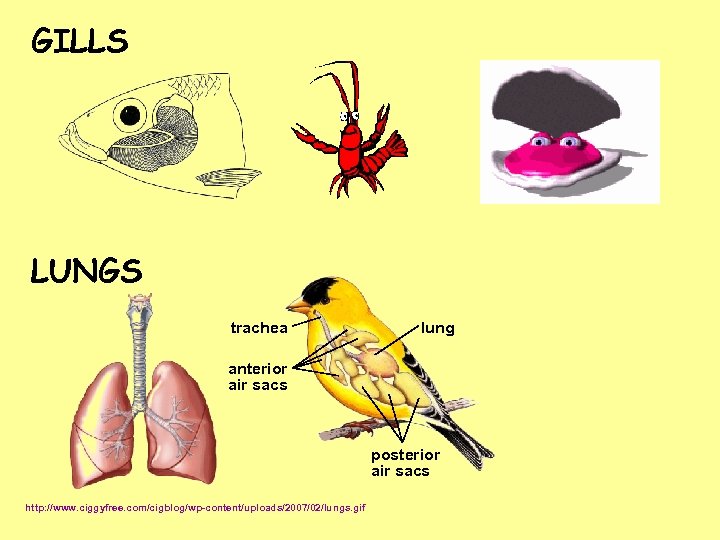 GILLS LUNGS trachea lung anterior air sacs posterior air sacs http: //www. ciggyfree. com/cigblog/wp-content/uploads/2007/02/lungs. gif
GILLS LUNGS trachea lung anterior air sacs posterior air sacs http: //www. ciggyfree. com/cigblog/wp-content/uploads/2007/02/lungs. gif
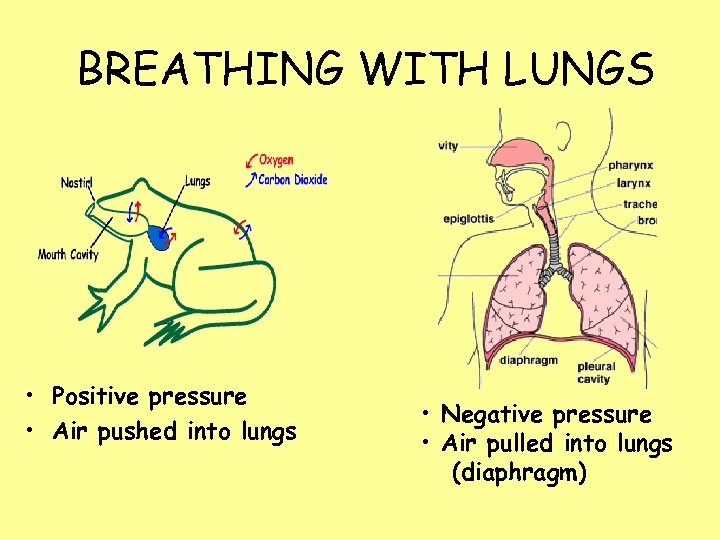 BREATHING WITH LUNGS • Positive pressure • Air pushed into lungs • Negative pressure • Air pulled into lungs (diaphragm)
BREATHING WITH LUNGS • Positive pressure • Air pushed into lungs • Negative pressure • Air pulled into lungs (diaphragm)
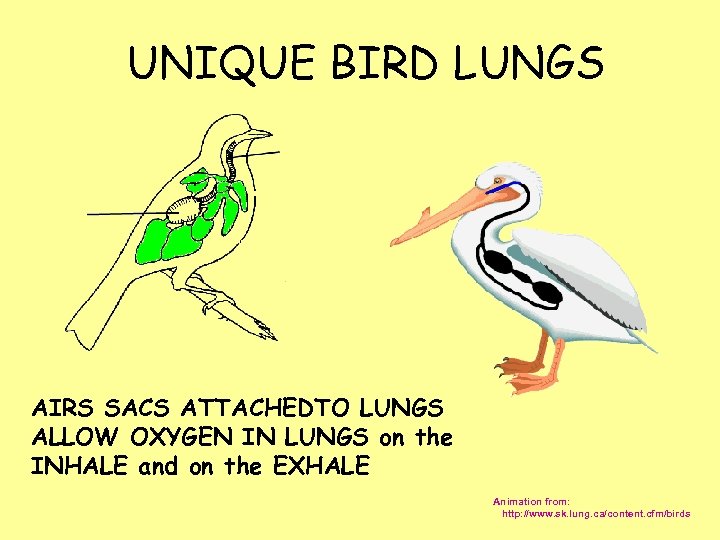 UNIQUE BIRD LUNGS AIRS SACS ATTACHEDTO LUNGS ALLOW OXYGEN IN LUNGS on the INHALE and on the EXHALE Animation from: http: //www. sk. lung. ca/content. cfm/birds
UNIQUE BIRD LUNGS AIRS SACS ATTACHEDTO LUNGS ALLOW OXYGEN IN LUNGS on the INHALE and on the EXHALE Animation from: http: //www. sk. lung. ca/content. cfm/birds
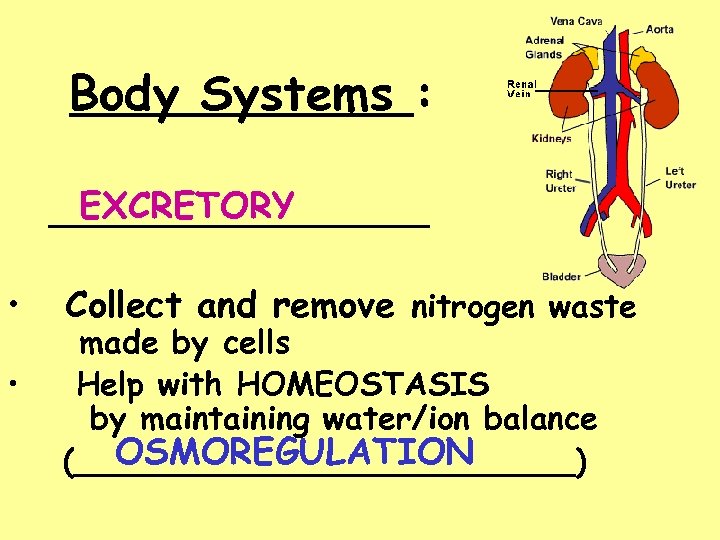 Body Systems : EXCRETORY __________ • • Collect and remove nitrogen waste made by cells Help with HOMEOSTASIS by maintaining water/ion balance OSMOREGULATION (_____________)
Body Systems : EXCRETORY __________ • • Collect and remove nitrogen waste made by cells Help with HOMEOSTASIS by maintaining water/ion balance OSMOREGULATION (_____________)
 NITROGEN WASTE : AMMONIA Most TOXIC _________ Must be removed QUICKLY Needs MOST water to dilute UREA _______ Made from ammonia by liver Less toxic than ammonia Can be stored if diluted with water (Needs less water to dilute than ammonia) URIC ACID _______ LEAST TOXIC Can be stored if diluted with water (Needs LEAST amount of water to dilute)
NITROGEN WASTE : AMMONIA Most TOXIC _________ Must be removed QUICKLY Needs MOST water to dilute UREA _______ Made from ammonia by liver Less toxic than ammonia Can be stored if diluted with water (Needs less water to dilute than ammonia) URIC ACID _______ LEAST TOXIC Can be stored if diluted with water (Needs LEAST amount of water to dilute)
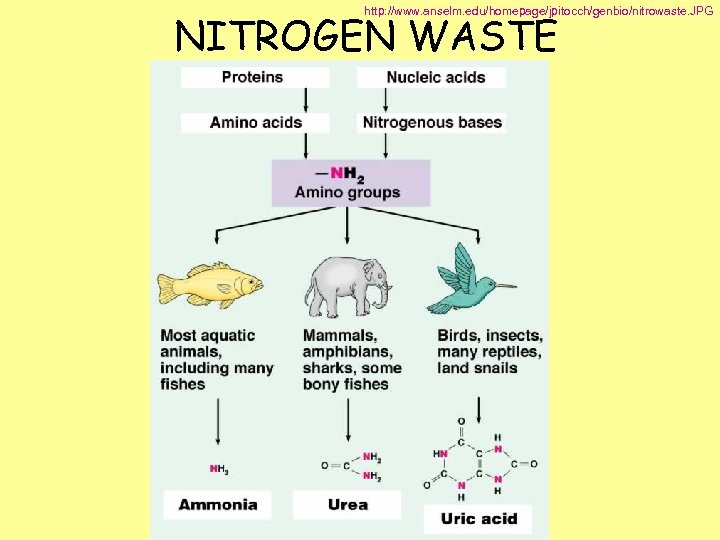 http: //www. anselm. edu/homepage/jpitocch/genbio/nitrowaste. JPG NITROGEN WASTE
http: //www. anselm. edu/homepage/jpitocch/genbio/nitrowaste. JPG NITROGEN WASTE
 ALL WASTE is NOT THE SAME! DIGESTIVE WASTE WHERE IT’S MADE? Body system used? In what form? NITROGEN WASTE made by cells left over from break undigested food down of proteins & nucleic acids Handled by digestive system Feces (poop) Handled by excretory system ammonia, urea, or uric acid (waste + water = urine)
ALL WASTE is NOT THE SAME! DIGESTIVE WASTE WHERE IT’S MADE? Body system used? In what form? NITROGEN WASTE made by cells left over from break undigested food down of proteins & nucleic acids Handled by digestive system Feces (poop) Handled by excretory system ammonia, urea, or uric acid (waste + water = urine)
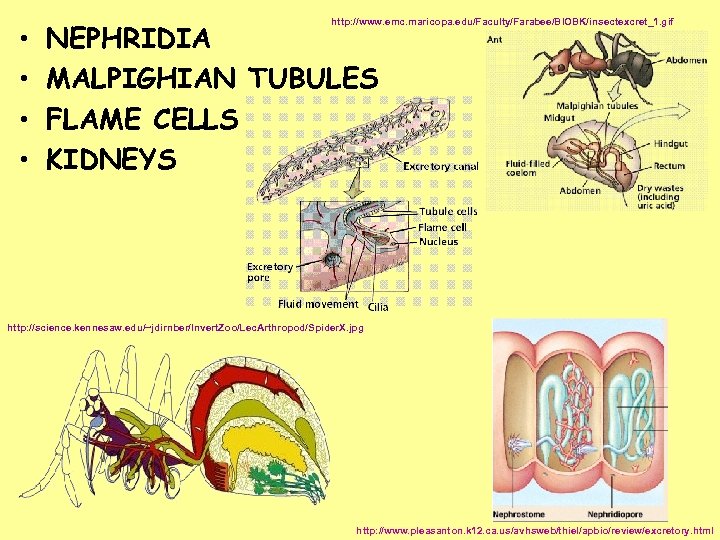 • • http: //www. emc. maricopa. edu/Faculty/Farabee/BIOBK/insectexcret_1. gif NEPHRIDIA MALPIGHIAN TUBULES FLAME CELLS KIDNEYS http: //science. kennesaw. edu/~jdirnber/Invert. Zoo/Lec. Arthropod/Spider. X. jpg http: //www. pleasanton. k 12. ca. us/avhsweb/thiel/apbio/review/excretory. html
• • http: //www. emc. maricopa. edu/Faculty/Farabee/BIOBK/insectexcret_1. gif NEPHRIDIA MALPIGHIAN TUBULES FLAME CELLS KIDNEYS http: //science. kennesaw. edu/~jdirnber/Invert. Zoo/Lec. Arthropod/Spider. X. jpg http: //www. pleasanton. k 12. ca. us/avhsweb/thiel/apbio/review/excretory. html
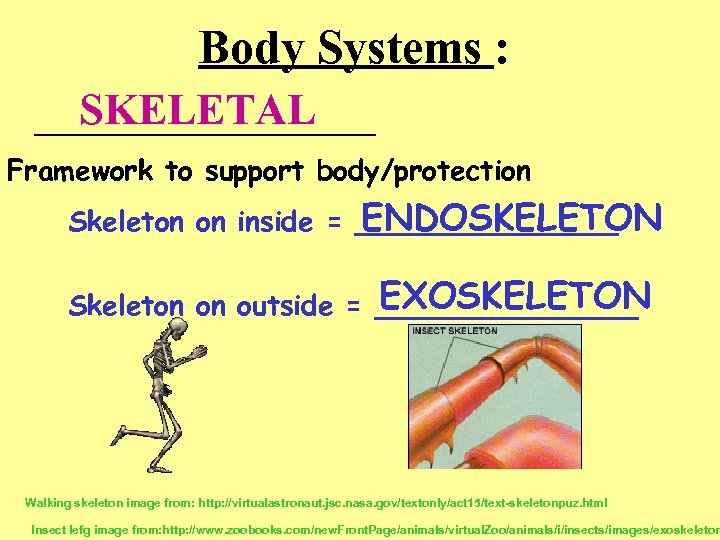 Body Systems : SKELETAL __________ Framework to support body/protection ENDOSKELETON Skeleton on inside = ________ EXOSKELETON Skeleton on outside = ________ Walking skeleton image from: http: //virtualastronaut. jsc. nasa. gov/textonly/act 15/text-skeletonpuz. html Insect lefg image from: http: //www. zoobooks. com/new. Front. Page/animals/virtual. Zoo/animals/i/insects/images/exoskeleton
Body Systems : SKELETAL __________ Framework to support body/protection ENDOSKELETON Skeleton on inside = ________ EXOSKELETON Skeleton on outside = ________ Walking skeleton image from: http: //virtualastronaut. jsc. nasa. gov/textonly/act 15/text-skeletonpuz. html Insect lefg image from: http: //www. zoobooks. com/new. Front. Page/animals/virtual. Zoo/animals/i/insects/images/exoskeleton
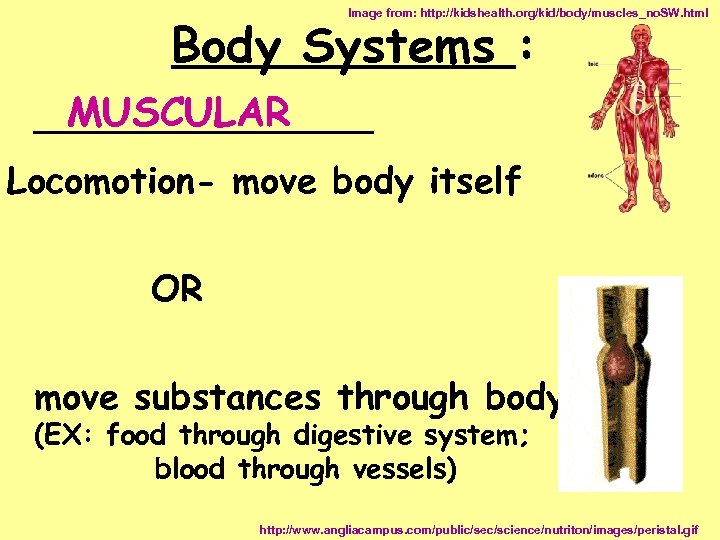 Image from: http: //kidshealth. org/kid/body/muscles_no. SW. html Body Systems : MUSCULAR ________ Locomotion- move body itself OR move substances through body (EX: food through digestive system; blood through vessels) http: //www. angliacampus. com/public/sec/science/nutriton/images/peristal. gif
Image from: http: //kidshealth. org/kid/body/muscles_no. SW. html Body Systems : MUSCULAR ________ Locomotion- move body itself OR move substances through body (EX: food through digestive system; blood through vessels) http: //www. angliacampus. com/public/sec/science/nutriton/images/peristal. gif
 Body Systems : REPRODUCTIVE ___________ - Produce offspring by combining genetic material from 2 parents SEXUAL REPRODUCTION = _____________ Produce offspring using genetic material from only 1 parent ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION =____________ Family image from: http: //babyhearing. org/Parenet 2 Parent/index. asp Planaria animation: http: //www. t 3. rim. or. jp/~hylas/planaria/title. htm
Body Systems : REPRODUCTIVE ___________ - Produce offspring by combining genetic material from 2 parents SEXUAL REPRODUCTION = _____________ Produce offspring using genetic material from only 1 parent ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION =____________ Family image from: http: //babyhearing. org/Parenet 2 Parent/index. asp Planaria animation: http: //www. t 3. rim. or. jp/~hylas/planaria/title. htm
 REPRODUCTIVE INDIRECT _______ DEVELOPMENT immature LARVA looks different than adult Metamorphosis image from: http: //www. lincoln. midcoast. com/~del/butterfly Frog image from: http: //www. animationlibrary. co DIRECT _____ DEVELOPMENT young are smaller versions on adults Image from: http: //www. bcps. org/offices/lis/models/life/images/grow. JPG
REPRODUCTIVE INDIRECT _______ DEVELOPMENT immature LARVA looks different than adult Metamorphosis image from: http: //www. lincoln. midcoast. com/~del/butterfly Frog image from: http: //www. animationlibrary. co DIRECT _____ DEVELOPMENT young are smaller versions on adults Image from: http: //www. bcps. org/offices/lis/models/life/images/grow. JPG
 Sperm and egg join External fertilization outside female’s body = __________ Sperm and egg join Internal fertilization inside female’s body = __________ Animation from: http: //discover. edventures. com/images/termlib/f/fertilization/support. gif
Sperm and egg join External fertilization outside female’s body = __________ Sperm and egg join Internal fertilization inside female’s body = __________ Animation from: http: //discover. edventures. com/images/termlib/f/fertilization/support. gif
 __________ NERVOUS Receive sensory info about environment & send response signals http: //www. roadhunter. com/~ceph/gallery/anatomy 07. jpg
__________ NERVOUS Receive sensory info about environment & send response signals http: //www. roadhunter. com/~ceph/gallery/anatomy 07. jpg
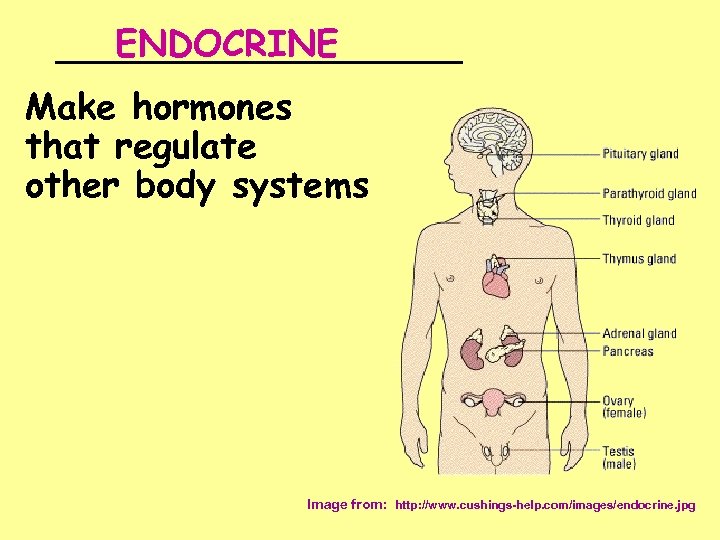 ENDOCRINE _________ Make hormones that regulate other body systems Image from: http: //www. cushings-help. com/images/endocrine. jpg
ENDOCRINE _________ Make hormones that regulate other body systems Image from: http: //www. cushings-help. com/images/endocrine. jpg
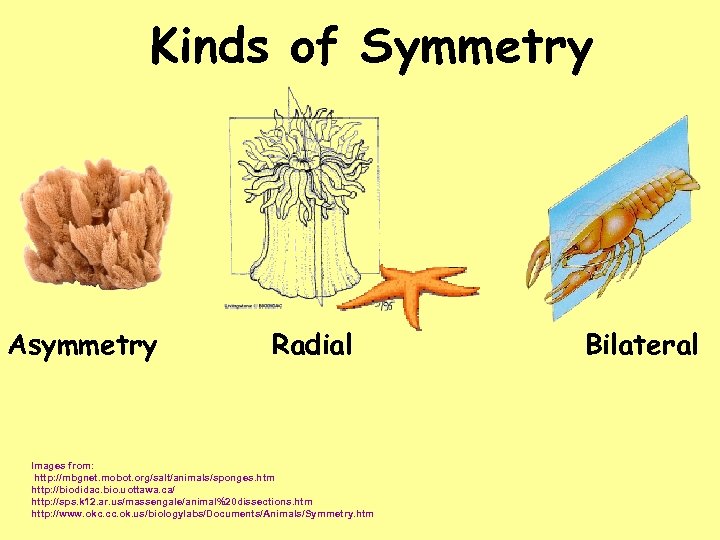 Kinds of Symmetry Asymmetry Radial Images from: http: //mbgnet. mobot. org/salt/animals/sponges. htm http: //biodidac. bio. uottawa. ca/ http: //sps. k 12. ar. us/massengale/animal%20 dissections. htm http: //www. okc. cc. ok. us/biologylabs/Documents/Animals/Symmetry. htm Bilateral
Kinds of Symmetry Asymmetry Radial Images from: http: //mbgnet. mobot. org/salt/animals/sponges. htm http: //biodidac. bio. uottawa. ca/ http: //sps. k 12. ar. us/massengale/animal%20 dissections. htm http: //www. okc. cc. ok. us/biologylabs/Documents/Animals/Symmetry. htm Bilateral
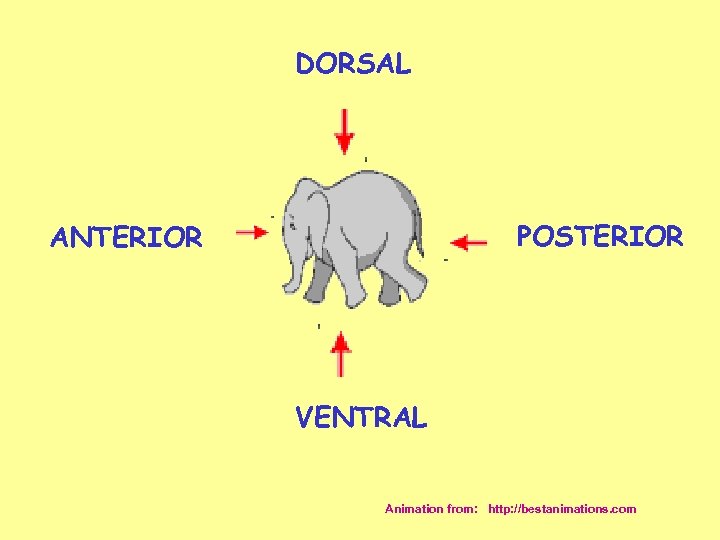 DORSAL POSTERIOR ANTERIOR VENTRAL Animation from: http: //bestanimations. com
DORSAL POSTERIOR ANTERIOR VENTRAL Animation from: http: //bestanimations. com
 CEPHALIZATION ________ Concentration of nervous tissue and sensory organs in anterior end of an organism (head area) • • First seen in Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Associated with bilateral symmetry Efficient response to stimulus Sense organs encounter environment first
CEPHALIZATION ________ Concentration of nervous tissue and sensory organs in anterior end of an organism (head area) • • First seen in Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Associated with bilateral symmetry Efficient response to stimulus Sense organs encounter environment first
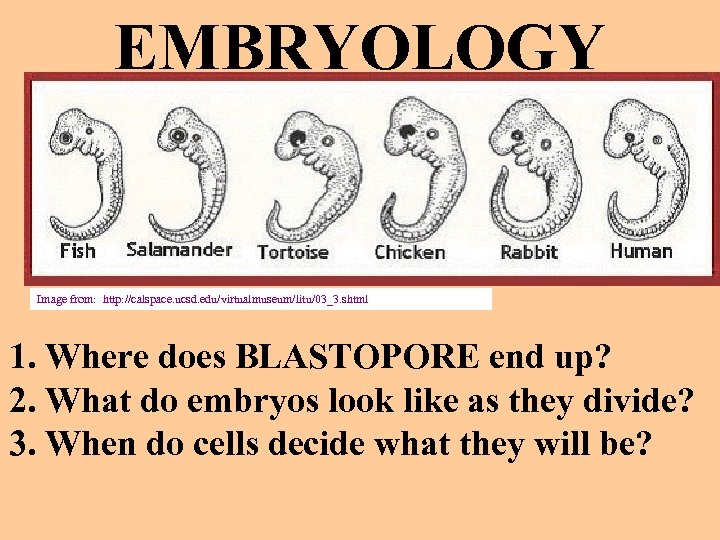 EMBRYOLOGY Image from: http: //calspace. ucsd. edu/virtualmuseum/litu/03_3. shtml 1. Where does BLASTOPORE end up? 2. What do embryos look like as they divide? 3. When do cells decide what they will be?
EMBRYOLOGY Image from: http: //calspace. ucsd. edu/virtualmuseum/litu/03_3. shtml 1. Where does BLASTOPORE end up? 2. What do embryos look like as they divide? 3. When do cells decide what they will be?
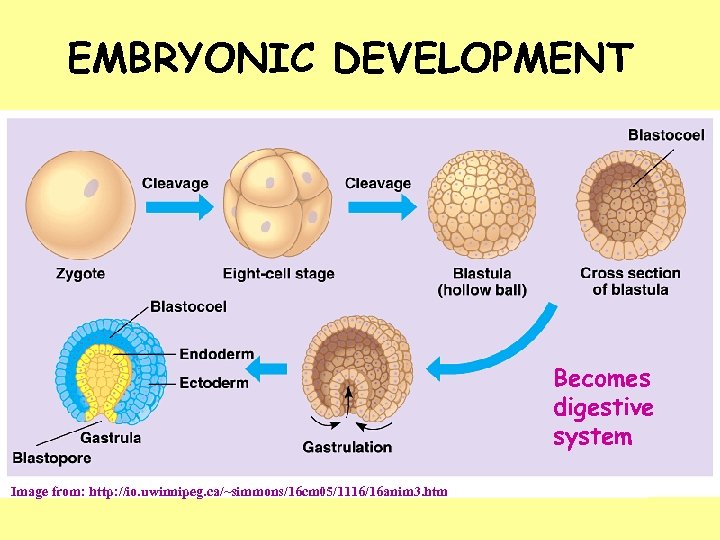 EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT Becomes digestive system Image from: http: //io. uwinnipeg. ca/~simmons/16 cm 05/1116/16 anim 3. htm
EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT Becomes digestive system Image from: http: //io. uwinnipeg. ca/~simmons/16 cm 05/1116/16 anim 3. htm
 1. Where does BLASTOPORE end up? Images modified from: http: //io. uwinnipeg. ca/~simmons/16 cm 05/1116/16 anim 3. htm
1. Where does BLASTOPORE end up? Images modified from: http: //io. uwinnipeg. ca/~simmons/16 cm 05/1116/16 anim 3. htm
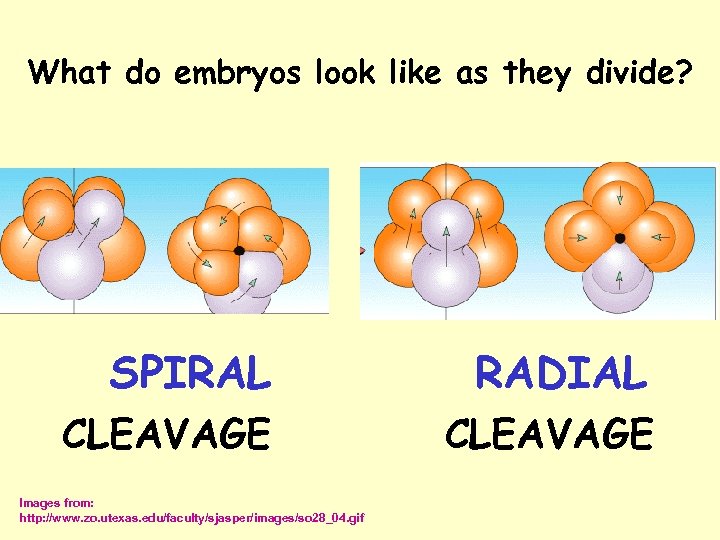 What do embryos look like as they divide? SPIRAL RADIAL CLEAVAGE Images from: http: //www. zo. utexas. edu/faculty/sjasper/images/so 28_04. gif
What do embryos look like as they divide? SPIRAL RADIAL CLEAVAGE Images from: http: //www. zo. utexas. edu/faculty/sjasper/images/so 28_04. gif
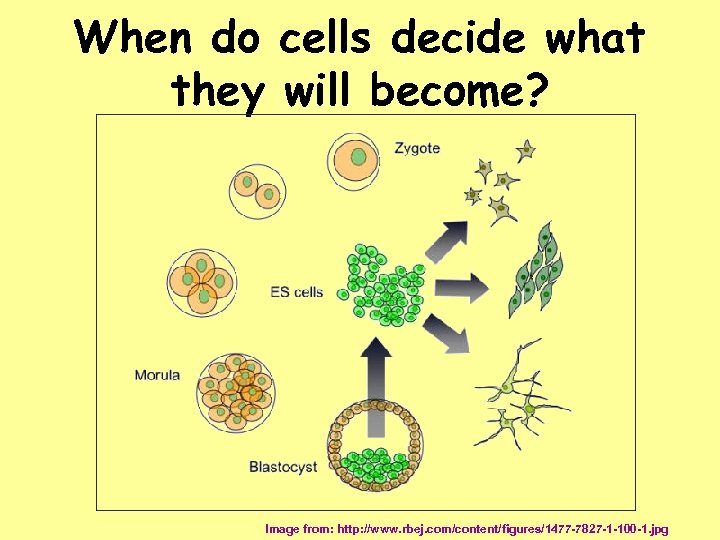 When do cells decide what they will become? Image from: http: //www. rbej. com/content/figures/1477 -7827 -1 -100 -1. jpg
When do cells decide what they will become? Image from: http: //www. rbej. com/content/figures/1477 -7827 -1 -100 -1. jpg
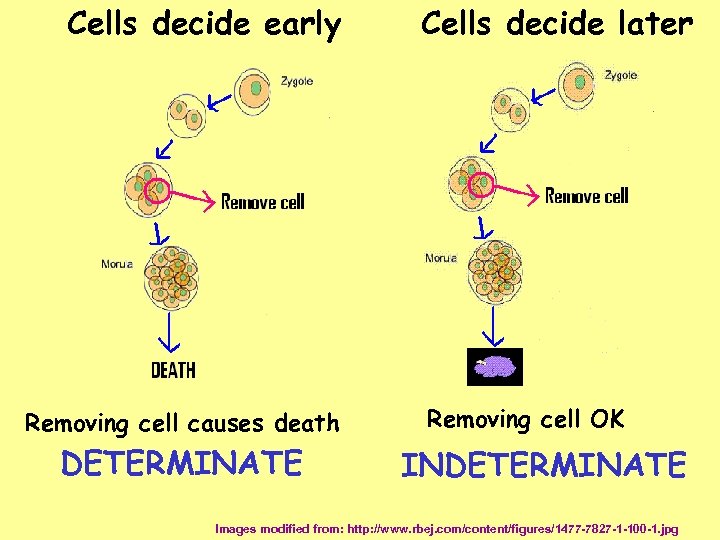 Cells decide early Removing cell causes death DETERMINATE Cells decide later Removing cell OK INDETERMINATE Images modified from: http: //www. rbej. com/content/figures/1477 -7827 -1 -100 -1. jpg
Cells decide early Removing cell causes death DETERMINATE Cells decide later Removing cell OK INDETERMINATE Images modified from: http: //www. rbej. com/content/figures/1477 -7827 -1 -100 -1. jpg
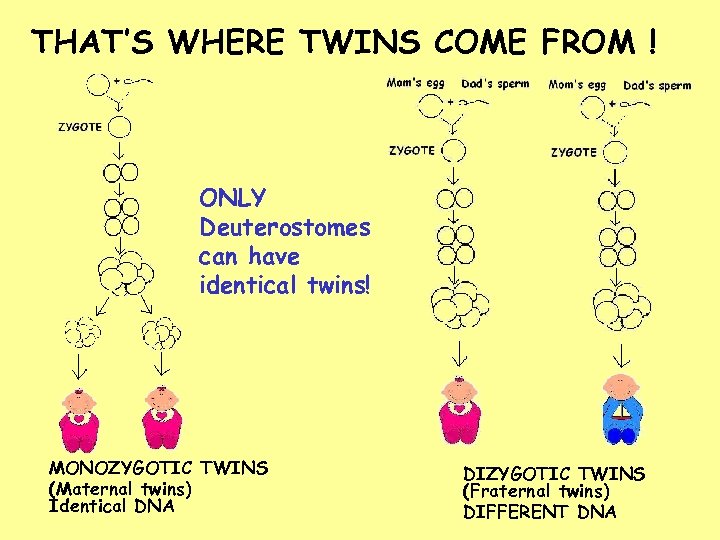 THAT’S WHERE TWINS COME FROM ! ONLY Deuterostomes can have identical twins! MONOZYGOTIC TWINS (Maternal twins) Identical DNA DIZYGOTIC TWINS (Fraternal twins) DIFFERENT DNA
THAT’S WHERE TWINS COME FROM ! ONLY Deuterostomes can have identical twins! MONOZYGOTIC TWINS (Maternal twins) Identical DNA DIZYGOTIC TWINS (Fraternal twins) DIFFERENT DNA
 ANIMALS (Triploblastic) PROTOSTOMES Blastopore becomes MOUTH Decide very early (DETERMINATE) SPIRAL cleavage MOST INVERTEBRATES except ECHINODERMS DEUTEROSTOMES Blastopore becomes ANUS Decide later (INDETERMINATE) RADIAL cleavage ALL VERTEBRATES (Fish, amphibians, birds, reptiles, mammals) plus ECHINODERMS
ANIMALS (Triploblastic) PROTOSTOMES Blastopore becomes MOUTH Decide very early (DETERMINATE) SPIRAL cleavage MOST INVERTEBRATES except ECHINODERMS DEUTEROSTOMES Blastopore becomes ANUS Decide later (INDETERMINATE) RADIAL cleavage ALL VERTEBRATES (Fish, amphibians, birds, reptiles, mammals) plus ECHINODERMS
 Image from: http: //www. bsac 21. freeserve. co. uk/images/Critters/Starfish%20 Bloody%20 Henry. JPG “Exception to the rule” ECHINODERMS ARE THE ONLY INVERTEBRATE DEUTEROSTOMES http: //my 3 boysandi. files. wordpress. com/2007/11/spongebob_1. jpg Porifera and Cnidarians have only TWO germ layers Not considered PROTOSTOMES http: //z. about. com/d/healing/1/0/Y/O/gtotem_jellyfish. jpg
Image from: http: //www. bsac 21. freeserve. co. uk/images/Critters/Starfish%20 Bloody%20 Henry. JPG “Exception to the rule” ECHINODERMS ARE THE ONLY INVERTEBRATE DEUTEROSTOMES http: //my 3 boysandi. files. wordpress. com/2007/11/spongebob_1. jpg Porifera and Cnidarians have only TWO germ layers Not considered PROTOSTOMES http: //z. about. com/d/healing/1/0/Y/O/gtotem_jellyfish. jpg
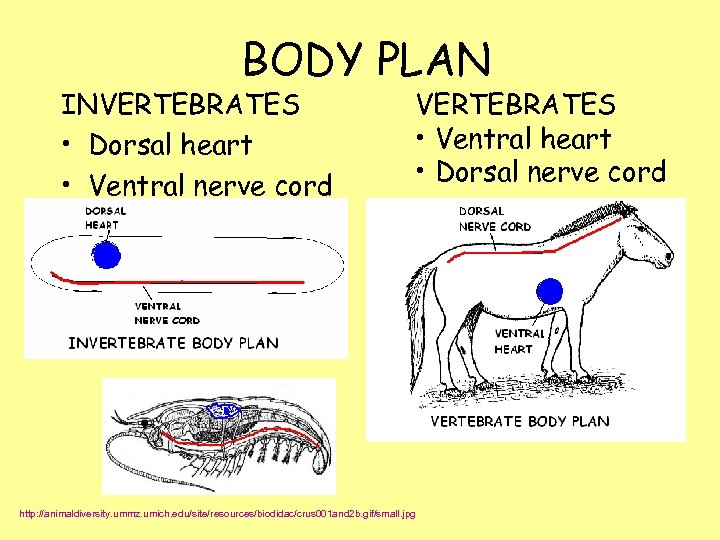 BODY PLAN INVERTEBRATES • Dorsal heart • Ventral nerve cord VERTEBRATES • Ventral heart • Dorsal nerve cord http: //animaldiversity. ummz. umich. edu/site/resources/biodidac/crus 001 and 2 b. gif/small. jpg
BODY PLAN INVERTEBRATES • Dorsal heart • Ventral nerve cord VERTEBRATES • Ventral heart • Dorsal nerve cord http: //animaldiversity. ummz. umich. edu/site/resources/biodidac/crus 001 and 2 b. gif/small. jpg
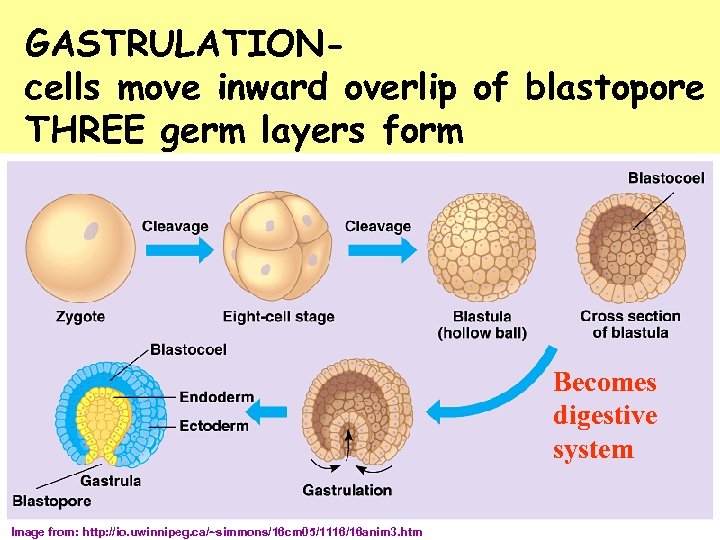 GASTRULATIONcells move inward overlip of blastopore THREE germ layers form Becomes digestive system Image from: http: //io. uwinnipeg. ca/~simmons/16 cm 05/1116/16 anim 3. htm
GASTRULATIONcells move inward overlip of blastopore THREE germ layers form Becomes digestive system Image from: http: //io. uwinnipeg. ca/~simmons/16 cm 05/1116/16 anim 3. htm
 All animals have 3 germ layers = TRIPLOBLASTIC Except: sponges, jellyfish, anemones = DIPLOBLASTIC Endoderm Digestive system, respiratory Mesoderm Muscle, excretory, bones, circulatory Ectoderm Outer skin, brain, nervous system
All animals have 3 germ layers = TRIPLOBLASTIC Except: sponges, jellyfish, anemones = DIPLOBLASTIC Endoderm Digestive system, respiratory Mesoderm Muscle, excretory, bones, circulatory Ectoderm Outer skin, brain, nervous system
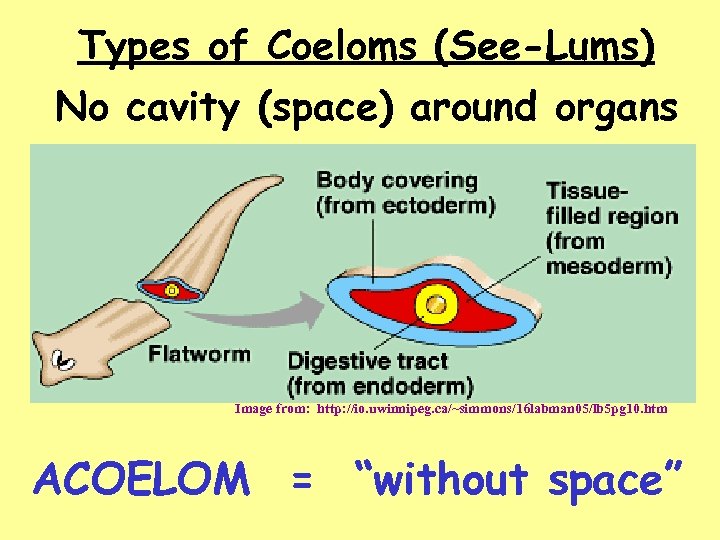 Types of Coeloms (See-Lums) No cavity (space) around organs Image from: http: //io. uwinnipeg. ca/~simmons/16 labman 05/lb 5 pg 10. htm ACOELOM = “without space”
Types of Coeloms (See-Lums) No cavity (space) around organs Image from: http: //io. uwinnipeg. ca/~simmons/16 labman 05/lb 5 pg 10. htm ACOELOM = “without space”
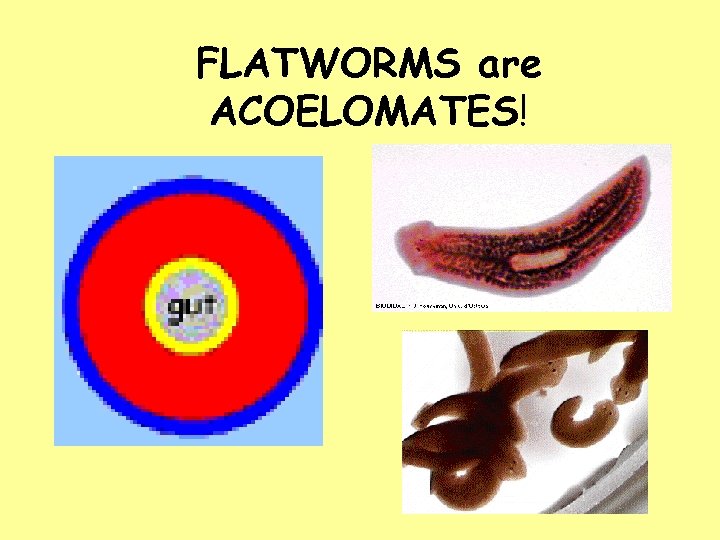 FLATWORMS are ACOELOMATES!
FLATWORMS are ACOELOMATES!
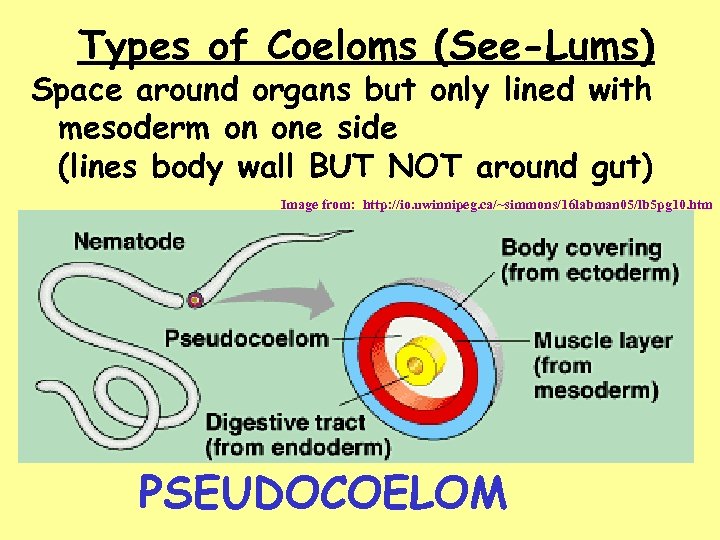 Types of Coeloms (See-Lums) Space around organs but only lined with mesoderm on one side (lines body wall BUT NOT around gut) Image from: http: //io. uwinnipeg. ca/~simmons/16 labman 05/lb 5 pg 10. htm PSEUDOCOELOM
Types of Coeloms (See-Lums) Space around organs but only lined with mesoderm on one side (lines body wall BUT NOT around gut) Image from: http: //io. uwinnipeg. ca/~simmons/16 labman 05/lb 5 pg 10. htm PSEUDOCOELOM
 ROUND WORMS are PSEUDOCOELOMATES!
ROUND WORMS are PSEUDOCOELOMATES!
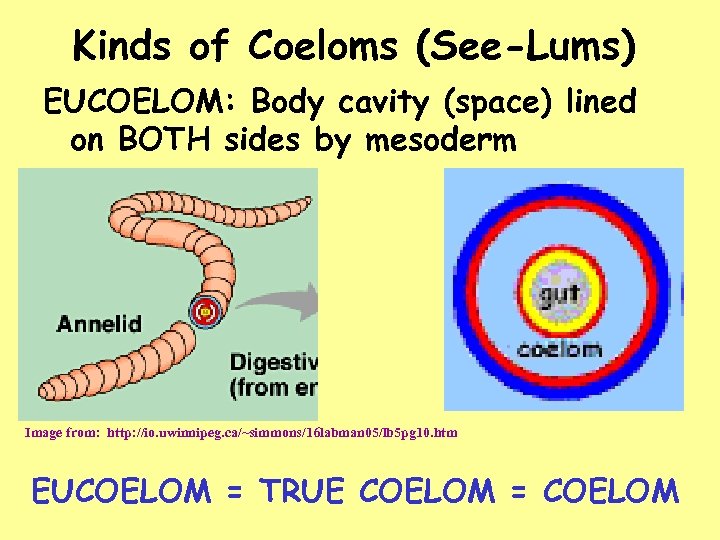 Kinds of Coeloms (See-Lums) EUCOELOM: Body cavity (space) lined on BOTH sides by mesoderm Image from: http: //io. uwinnipeg. ca/~simmons/16 labman 05/lb 5 pg 10. htm EUCOELOM = TRUE COELOM = COELOM
Kinds of Coeloms (See-Lums) EUCOELOM: Body cavity (space) lined on BOTH sides by mesoderm Image from: http: //io. uwinnipeg. ca/~simmons/16 labman 05/lb 5 pg 10. htm EUCOELOM = TRUE COELOM = COELOM
 EUCOELOMATES ALL VERTEBRATES & MOST INVERTEBRATES
EUCOELOMATES ALL VERTEBRATES & MOST INVERTEBRATES
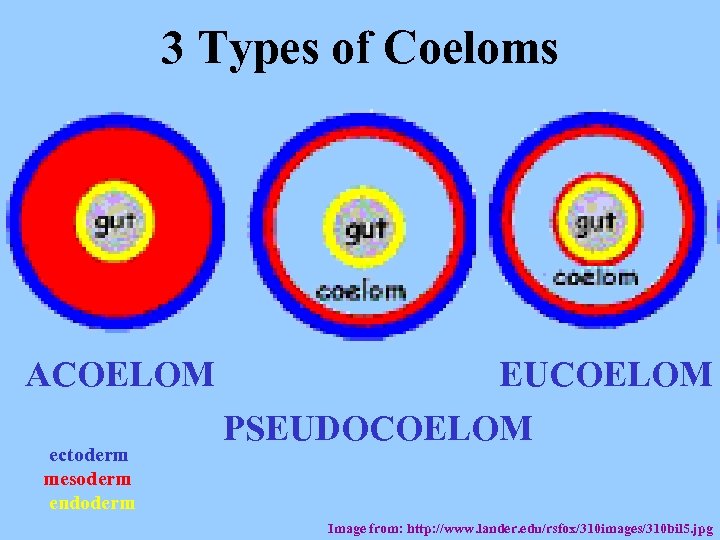 3 Types of Coeloms ACOELOM ectoderm mesoderm endoderm EUCOELOM PSEUDOCOELOM Image from: http: //www. lander. edu/rsfox/310 images/310 bil 5. jpg
3 Types of Coeloms ACOELOM ectoderm mesoderm endoderm EUCOELOM PSEUDOCOELOM Image from: http: //www. lander. edu/rsfox/310 images/310 bil 5. jpg
 FUNCTIONS of having a COELOM (body space): Provides space/cushion internal organs In animals without a skeleton. Fluid in coelom space can act as a HYDROSTATIC skeleton In animals without blood vessels. Fluid in coelom space can circulate nutrients and oxygen to cells
FUNCTIONS of having a COELOM (body space): Provides space/cushion internal organs In animals without a skeleton. Fluid in coelom space can act as a HYDROSTATIC skeleton In animals without blood vessels. Fluid in coelom space can circulate nutrients and oxygen to cells
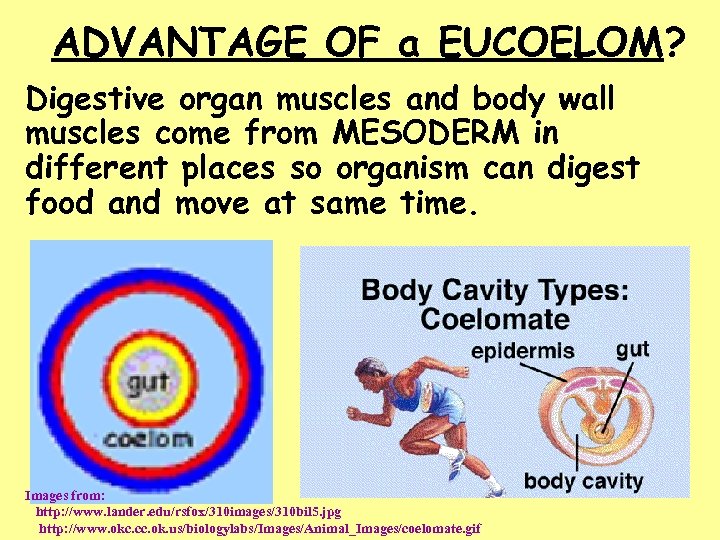 ADVANTAGE OF a EUCOELOM? Digestive organ muscles and body wall muscles come from MESODERM in different places so organism can digest food and move at same time. Images from: http: //www. lander. edu/rsfox/310 images/310 bil 5. jpg http: //www. okc. cc. ok. us/biologylabs/Images/Animal_Images/coelomate. gif
ADVANTAGE OF a EUCOELOM? Digestive organ muscles and body wall muscles come from MESODERM in different places so organism can digest food and move at same time. Images from: http: //www. lander. edu/rsfox/310 images/310 bil 5. jpg http: //www. okc. cc. ok. us/biologylabs/Images/Animal_Images/coelomate. gif
 ECTOTHERMIC ADVANTAGES: Slow metabolism means you can survive on 1/10 the food as a same size endotherm DISADVANTAGES: • Can’t to live in extremely cold places (NO reptiles in Arctic) • Can’t keep up max activity level for long
ECTOTHERMIC ADVANTAGES: Slow metabolism means you can survive on 1/10 the food as a same size endotherm DISADVANTAGES: • Can’t to live in extremely cold places (NO reptiles in Arctic) • Can’t keep up max activity level for long
 Endothermic “warm-blooded” • Create own body heat • FAST metabolism allows for: high activity for extended time ability to live in variety of environments • EX: Birds, Mammals
Endothermic “warm-blooded” • Create own body heat • FAST metabolism allows for: high activity for extended time ability to live in variety of environments • EX: Birds, Mammals
 SOURCES Anemone from: http: //www. oum. ox. ac. uk/children/animals/cnidaria. gif Snail from: http: //www. lucinda. net/surber/graphics/orlovsky. gif Crab from: http: //www. gifs. net Clam from: http: //sps. k 12. ar. us/massengale/animal%20 dissections. htm Ant from: http: //www. wildaboutbritain. co. uk
SOURCES Anemone from: http: //www. oum. ox. ac. uk/children/animals/cnidaria. gif Snail from: http: //www. lucinda. net/surber/graphics/orlovsky. gif Crab from: http: //www. gifs. net Clam from: http: //sps. k 12. ar. us/massengale/animal%20 dissections. htm Ant from: http: //www. wildaboutbritain. co. uk
 Millipede from: http: //atschool. eduweb. co. uk/sirrobhitch. suffolk/key/images/invertebrates/millipede. jpg Starfish from: http: //www. gifs. net Jellyfish from: http: //www. aloha. com/~lifeguards/jellie 75. jpg
Millipede from: http: //atschool. eduweb. co. uk/sirrobhitch. suffolk/key/images/invertebrates/millipede. jpg Starfish from: http: //www. gifs. net Jellyfish from: http: //www. aloha. com/~lifeguards/jellie 75. jpg
 Tree frog: http: //www. dynamicearth. co. uk/education/images/tree_frog. jpg Turtle: http: //www. 50 birds. com/images/endttboxturtle. jpg Bird: http: //people. eku. edu/ritchisong/homepage. htm Fish from: http: //www. chm. bris. ac. uk/motm/trimethylamine/fish. gif Orangutan: http: //www. biologycorner. com/webquests. php
Tree frog: http: //www. dynamicearth. co. uk/education/images/tree_frog. jpg Turtle: http: //www. 50 birds. com/images/endttboxturtle. jpg Bird: http: //people. eku. edu/ritchisong/homepage. htm Fish from: http: //www. chm. bris. ac. uk/motm/trimethylamine/fish. gif Orangutan: http: //www. biologycorner. com/webquests. php
 Earthworm : http: //www. york. ac. uk/org/ciec/Caringforthe. Environment. 29. 4. 03/Exxon/Food%20 Chain%20 images/Exxon. Pics. Large/Earthworms. jpg Starfish from: http: //www. gifs. net Snail from: http: //www. lucinda. net/surber/graphics/orlovsky. gif Crab from: http: //www. animation-station. com/fish/index. php? page=2
Earthworm : http: //www. york. ac. uk/org/ciec/Caringforthe. Environment. 29. 4. 03/Exxon/Food%20 Chain%20 images/Exxon. Pics. Large/Earthworms. jpg Starfish from: http: //www. gifs. net Snail from: http: //www. lucinda. net/surber/graphics/orlovsky. gif Crab from: http: //www. animation-station. com/fish/index. php? page=2
 All images on this page from: http: //www. seaworld. org/Animal. Bytes/animal_bytes. html
All images on this page from: http: //www. seaworld. org/Animal. Bytes/animal_bytes. html


