271c5d7d6c5aac065d134078d313f097.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 INTODUCTION TO OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
INTODUCTION TO OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
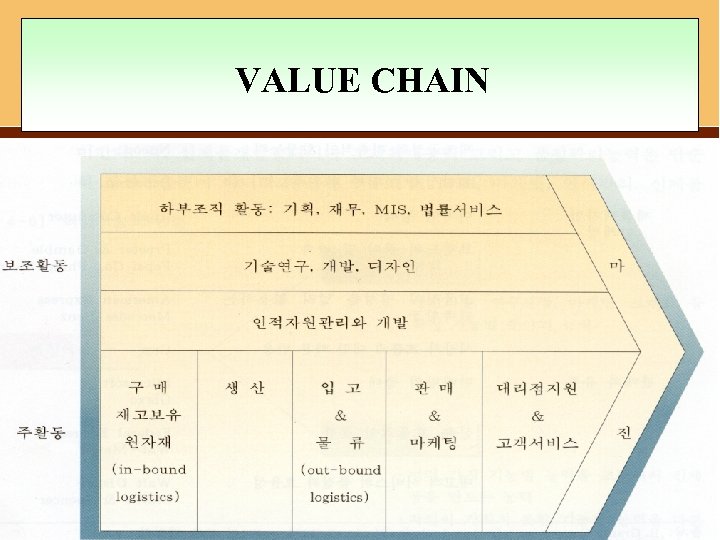 VALUE CHAIN 2
VALUE CHAIN 2
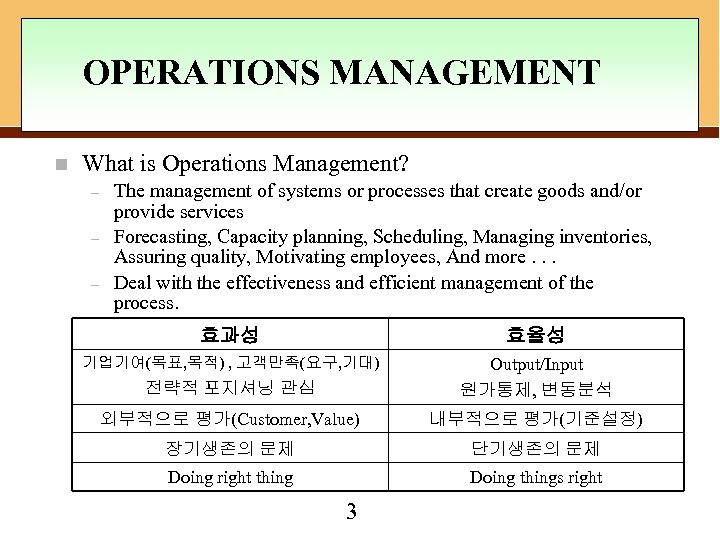 OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT n What is Operations Management? – – – The management of systems or processes that create goods and/or provide services Forecasting, Capacity planning, Scheduling, Managing inventories, Assuring quality, Motivating employees, And more. . . Deal with the effectiveness and efficient management of the process. 효과성 효율성 기업기여(목표, 목적) , 고객만족(요구, 기대) 전략적 포지셔닝 관심 Output/Input 원가통제, 변동분석 외부적으로 평가(Customer, Value) 내부적으로 평가(기준설정) 장기생존의 문제 단기생존의 문제 Doing right thing Doing things right 3
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT n What is Operations Management? – – – The management of systems or processes that create goods and/or provide services Forecasting, Capacity planning, Scheduling, Managing inventories, Assuring quality, Motivating employees, And more. . . Deal with the effectiveness and efficient management of the process. 효과성 효율성 기업기여(목표, 목적) , 고객만족(요구, 기대) 전략적 포지셔닝 관심 Output/Input 원가통제, 변동분석 외부적으로 평가(Customer, Value) 내부적으로 평가(기준설정) 장기생존의 문제 단기생존의 문제 Doing right thing Doing things right 3
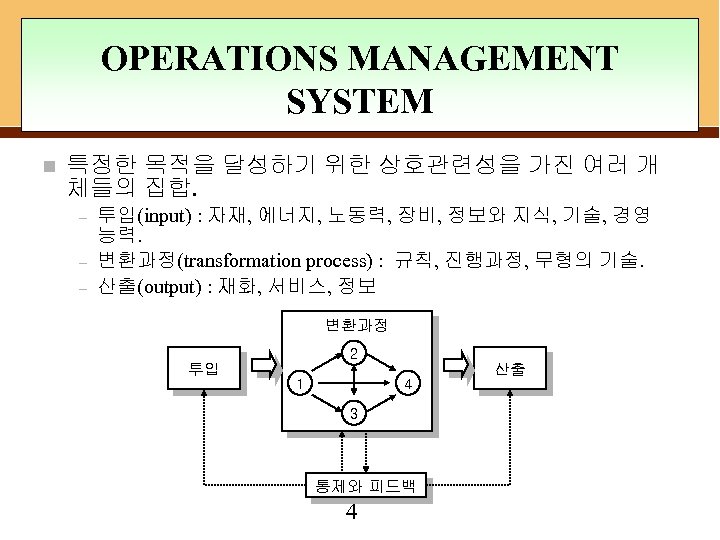 OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT SYSTEM n 특정한 목적을 달성하기 위한 상호관련성을 가진 여러 개 체들의 집합. – – – 투입(input) : 자재, 에너지, 노동력, 장비, 정보와 지식, 기술, 경영 능력. 변환과정(transformation process) : 규칙, 진행과정, 무형의 기술. 산출(output) : 재화, 서비스, 정보 변환과정 2 투입 1 4 3 통제와 피드백 4 산출
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT SYSTEM n 특정한 목적을 달성하기 위한 상호관련성을 가진 여러 개 체들의 집합. – – – 투입(input) : 자재, 에너지, 노동력, 장비, 정보와 지식, 기술, 경영 능력. 변환과정(transformation process) : 규칙, 진행과정, 무형의 기술. 산출(output) : 재화, 서비스, 정보 변환과정 2 투입 1 4 3 통제와 피드백 4 산출
 THE FOUNDATIONS OF THE OM SYSTEM: CUSTOMER, PROCESS & CAPACITY n 고객(Customer) – – n 생산관리 시스템의 출발점이자 종착점 Order losers , Order qualifiers & Order winners Internal &I External(Intermediate & Final) : A chain of customer Current & Potential (New market segment) Stakeholder – – 생산관리시스템 이나 기업의 기능과 이익에 관심 Financial(ROI), Resource(Physical: labor, materials, equipment), Community, Societal & Government(regulator or evaluator: criteria) stakeholder 5
THE FOUNDATIONS OF THE OM SYSTEM: CUSTOMER, PROCESS & CAPACITY n 고객(Customer) – – n 생산관리 시스템의 출발점이자 종착점 Order losers , Order qualifiers & Order winners Internal &I External(Intermediate & Final) : A chain of customer Current & Potential (New market segment) Stakeholder – – 생산관리시스템 이나 기업의 기능과 이익에 관심 Financial(ROI), Resource(Physical: labor, materials, equipment), Community, Societal & Government(regulator or evaluator: criteria) stakeholder 5
 THE FOUNDATIONS OF THE OM SYSTEM: CUSTOMER, PROCESS & CAPACITY n n A process is sequence and organization of all activities needed to convert inputs into outputs. Convert, transport & move, store, check & inspect The design of a process should reflect what the customer wants and be flexible enough change when customer preferences change. 제품(Product) = 재화(Good) + Service(서비스) 6
THE FOUNDATIONS OF THE OM SYSTEM: CUSTOMER, PROCESS & CAPACITY n n A process is sequence and organization of all activities needed to convert inputs into outputs. Convert, transport & move, store, check & inspect The design of a process should reflect what the customer wants and be flexible enough change when customer preferences change. 제품(Product) = 재화(Good) + Service(서비스) 6
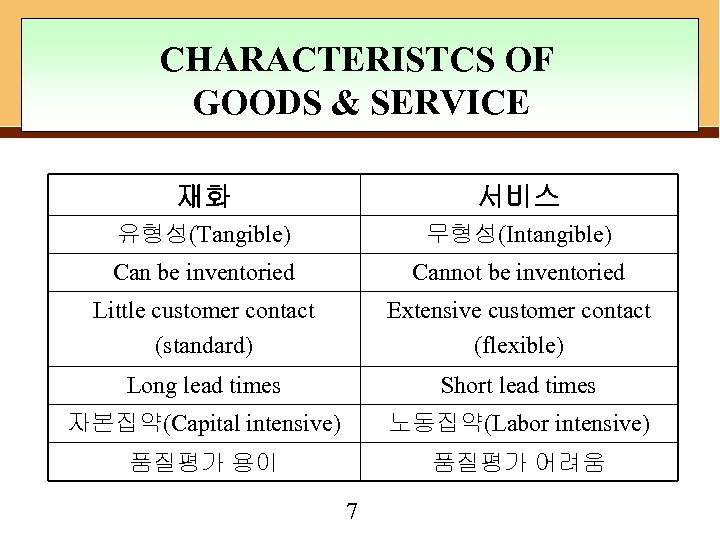 CHARACTERISTCS OF GOODS & SERVICE 재화 서비스 유형성(Tangible) 무형성(Intangible) Can be inventoried Cannot be inventoried Little customer contact (standard) Extensive customer contact (flexible) Long lead times Short lead times 자본집약(Capital intensive) 노동집약(Labor intensive) 품질평가 용이 품질평가 어려움 7
CHARACTERISTCS OF GOODS & SERVICE 재화 서비스 유형성(Tangible) 무형성(Intangible) Can be inventoried Cannot be inventoried Little customer contact (standard) Extensive customer contact (flexible) Long lead times Short lead times 자본집약(Capital intensive) 노동집약(Labor intensive) 품질평가 용이 품질평가 어려움 7
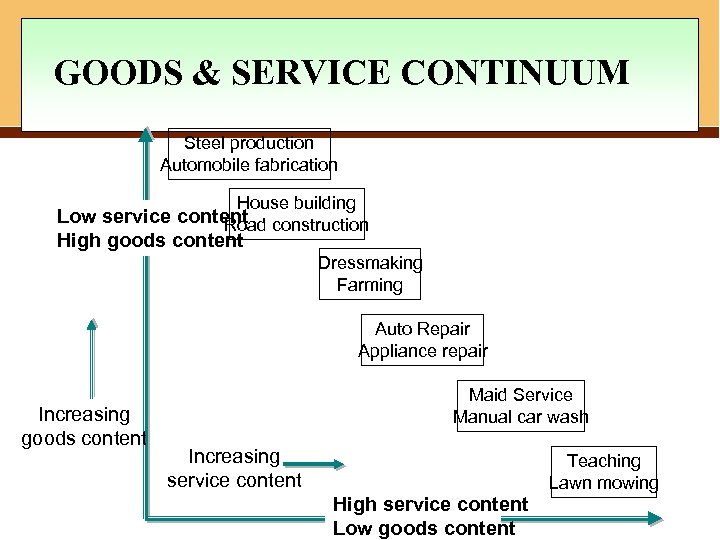 GOODS & SERVICE CONTINUUM Steel production Automobile fabrication House building Low service content construction Road High goods content Dressmaking Farming Auto Repair Appliance repair Increasing goods content Maid Service Manual car wash Increasing service content Teaching Lawn mowing High service content 8 Low goods content
GOODS & SERVICE CONTINUUM Steel production Automobile fabrication House building Low service content construction Road High goods content Dressmaking Farming Auto Repair Appliance repair Increasing goods content Maid Service Manual car wash Increasing service content Teaching Lawn mowing High service content 8 Low goods content
 THE FOUNDATIONS OF THE OM SYSTEM: CUSTOMER, PROCESS & CAPACITY n CAPACITY(생산능력) determines how much output a process can produce. – – Not comprehensive : type of capacity – n Capacity usually is measured in units of output per unit of time, i. e. , cars per hour. 예) Mc. Donald : grill, Burger king : flame-broiling The type of process and the type and amount of capacity must support needs of customers 9
THE FOUNDATIONS OF THE OM SYSTEM: CUSTOMER, PROCESS & CAPACITY n CAPACITY(생산능력) determines how much output a process can produce. – – Not comprehensive : type of capacity – n Capacity usually is measured in units of output per unit of time, i. e. , cars per hour. 예) Mc. Donald : grill, Burger king : flame-broiling The type of process and the type and amount of capacity must support needs of customers 9
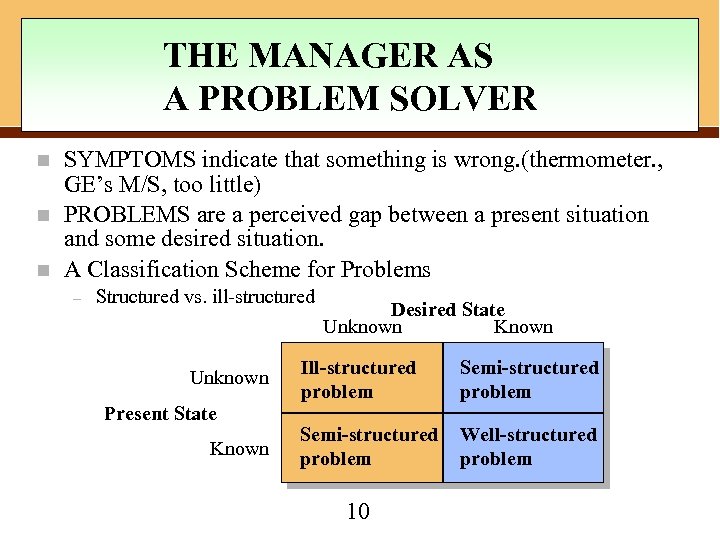 THE MANAGER AS A PROBLEM SOLVER n n n SYMPTOMS indicate that something is wrong. (thermometer. , GE’s M/S, too little) PROBLEMS are a perceived gap between a present situation and some desired situation. A Classification Scheme for Problems – Structured vs. ill-structured Unknown Present State Known Desired State Unknown Known Ill-structured problem Semi-structured problem Well-structured problem 10
THE MANAGER AS A PROBLEM SOLVER n n n SYMPTOMS indicate that something is wrong. (thermometer. , GE’s M/S, too little) PROBLEMS are a perceived gap between a present situation and some desired situation. A Classification Scheme for Problems – Structured vs. ill-structured Unknown Present State Known Desired State Unknown Known Ill-structured problem Semi-structured problem Well-structured problem 10
 PROBLEM, CAUSE & SOLUTION – – – Strategic versus Operational Orientation(time) Urgency of a Problem(crises vs. opportunity) Activity Focus(행위의 유형: trade-off 평가) n n n n n Routing(Machine & site) Replacement(tool 교체) Competition(pricing or bidding) Search(sampling & inspection) Cause – n Queuing(Service Center) Allocation(Job) Inventory(재고유지비) Sequencing(Job & Machine) Anything that creates or contributes to a gap b/w current and desired future situation( A source of observed symptoms) Solution – A set of actions designed to close the gap b/w the current and desired future situations by changing the conditions 11
PROBLEM, CAUSE & SOLUTION – – – Strategic versus Operational Orientation(time) Urgency of a Problem(crises vs. opportunity) Activity Focus(행위의 유형: trade-off 평가) n n n n n Routing(Machine & site) Replacement(tool 교체) Competition(pricing or bidding) Search(sampling & inspection) Cause – n Queuing(Service Center) Allocation(Job) Inventory(재고유지비) Sequencing(Job & Machine) Anything that creates or contributes to a gap b/w current and desired future situation( A source of observed symptoms) Solution – A set of actions designed to close the gap b/w the current and desired future situations by changing the conditions 11
 PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS n Size-up/Description : gathering information – – n 불분명한 문제 규명, 올바른 문제 파악, 해결되어야 할 문제 파악, 새 로운 문제 발견 Tool : Observation, Participation, Questionnaires. Interview, Written document, Process mapping, Check sheet, Benchmarking Problem Statement/Diagnostics-critical agreement Identify controllable vs. Uncontrollable variables, Constraints & desired outcomes n Analysis : 현재상황 개발, Tool: model n Prescription/Alternatives : 대안제시 및 평가 n Implementation : 해결책 선정 후 실행-작업자 영향고려 12 –
PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS n Size-up/Description : gathering information – – n 불분명한 문제 규명, 올바른 문제 파악, 해결되어야 할 문제 파악, 새 로운 문제 발견 Tool : Observation, Participation, Questionnaires. Interview, Written document, Process mapping, Check sheet, Benchmarking Problem Statement/Diagnostics-critical agreement Identify controllable vs. Uncontrollable variables, Constraints & desired outcomes n Analysis : 현재상황 개발, Tool: model n Prescription/Alternatives : 대안제시 및 평가 n Implementation : 해결책 선정 후 실행-작업자 영향고려 12 –
 MODEL n n A model is an abstract representation of reality that simplifies actual events and situations. Models are designed to answer: – n Physical Model – n What (identify important element), How(Relationships), Why (Reason), Under what conditions(specify condition) Iconic model(형상-모형 비행기) , Analog model(상사-속도계) Mathematical model – – descriptive model(서술적 모형) : 시스템의 행태(시뮬레이션) normative model(규범적 모형) or optimization model(최적화 모형) : 목적달성위한 행동지침 산출 13
MODEL n n A model is an abstract representation of reality that simplifies actual events and situations. Models are designed to answer: – n Physical Model – n What (identify important element), How(Relationships), Why (Reason), Under what conditions(specify condition) Iconic model(형상-모형 비행기) , Analog model(상사-속도계) Mathematical model – – descriptive model(서술적 모형) : 시스템의 행태(시뮬레이션) normative model(규범적 모형) or optimization model(최적화 모형) : 목적달성위한 행동지침 산출 13
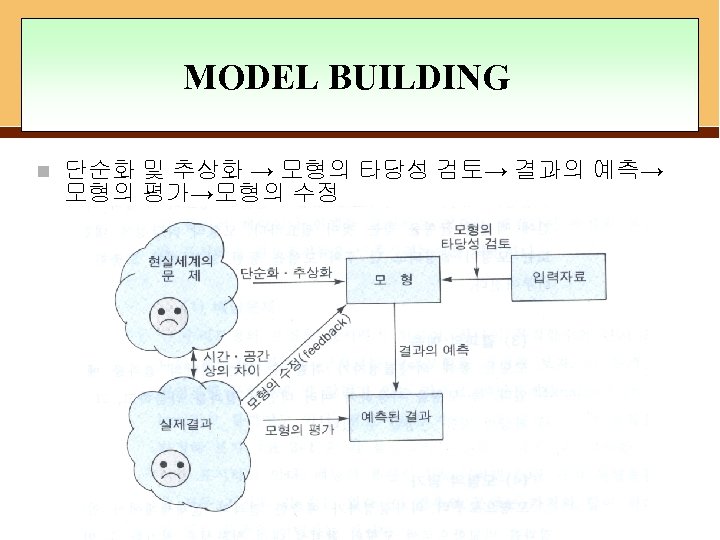 MODEL BUILDING n 단순화 및 추상화 → 모형의 타당성 검토→ 결과의 예측→ 모형의 평가→모형의 수정 14
MODEL BUILDING n 단순화 및 추상화 → 모형의 타당성 검토→ 결과의 예측→ 모형의 평가→모형의 수정 14
 RESPONSIBILITIES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Planning – – – – Capacity Location Products & services Make or buy Layout Projects Scheduling Organizing – Degree of centralization – Subcontracting Staffing – Hiring/laying off – Use of Overtime Directing – Incentive plans – Issuance of work orders – Job assignments Controlling – Inventory – Quality 15
RESPONSIBILITIES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Planning – – – – Capacity Location Products & services Make or buy Layout Projects Scheduling Organizing – Degree of centralization – Subcontracting Staffing – Hiring/laying off – Use of Overtime Directing – Incentive plans – Issuance of work orders – Job assignments Controlling – Inventory – Quality 15
 TRENDS n Resent Trends – – – n Internet E-business Supply Chain Management Continuing Trends – – – 16 Quality and process innovation Technology Globalization Operation Strategy Environment Issue
TRENDS n Resent Trends – – – n Internet E-business Supply Chain Management Continuing Trends – – – 16 Quality and process innovation Technology Globalization Operation Strategy Environment Issue


