25efbc065e83b45a31788b49984ae19d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Into which column does each of the technologies below go? Alarm Clock – communicates the time (with a sound) to a human. Thermostat – measures the temperature and turns the furnace on or off. Telephone – a human speaks in one side, a human hears it on the other. T. V. Remote – a human pushes a button, a signal is send to the television.
Into which column does each of the technologies below go? Alarm Clock – communicates the time (with a sound) to a human. Thermostat – measures the temperature and turns the furnace on or off. Telephone – a human speaks in one side, a human hears it on the other. T. V. Remote – a human pushes a button, a signal is send to the television.
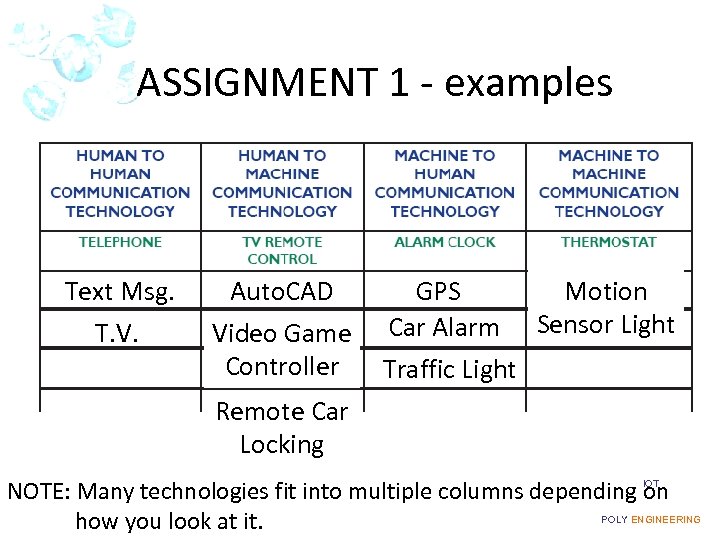 ASSIGNMENT 1 - examples Text Msg. T. V. Auto. CAD Video Game Controller GPS Motion Car Alarm Sensor Light Traffic Light Remote Car Locking NOTE: Many technologies fit into multiple columns depending on how you look at it. IOT POLY ENGINEERING
ASSIGNMENT 1 - examples Text Msg. T. V. Auto. CAD Video Game Controller GPS Motion Car Alarm Sensor Light Traffic Light Remote Car Locking NOTE: Many technologies fit into multiple columns depending on how you look at it. IOT POLY ENGINEERING
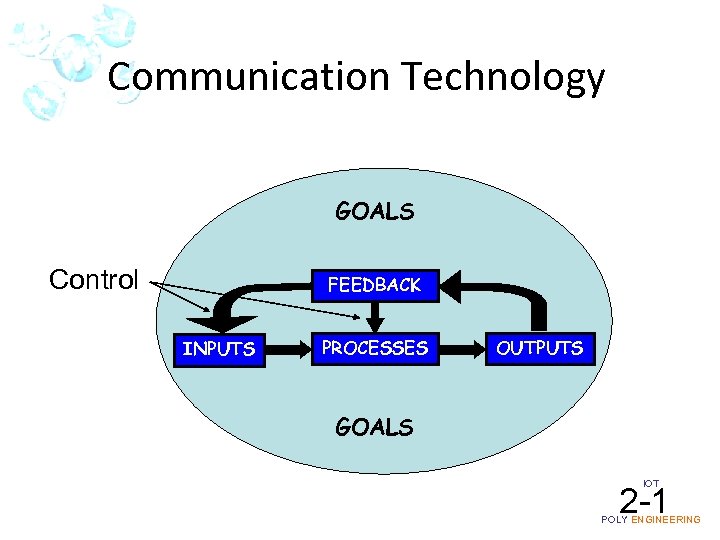 Communication Technology GOALS Control FEEDBACK INPUTS PROCESSES OUTPUTS GOALS IOT 2 -1 POLY ENGINEERING
Communication Technology GOALS Control FEEDBACK INPUTS PROCESSES OUTPUTS GOALS IOT 2 -1 POLY ENGINEERING
 Communication Technology – Goals Inform Persuade Entertain Control Manage Educate – Inputs Source of Communication – Processes (in this order) Encoder Transmitter Receiver Decoder Storage Retrieval – Outputs Message to the destination Not always – Feedback and Control Reversing the communication line IOT 2 -1 POLY ENGINEERING
Communication Technology – Goals Inform Persuade Entertain Control Manage Educate – Inputs Source of Communication – Processes (in this order) Encoder Transmitter Receiver Decoder Storage Retrieval – Outputs Message to the destination Not always – Feedback and Control Reversing the communication line IOT 2 -1 POLY ENGINEERING
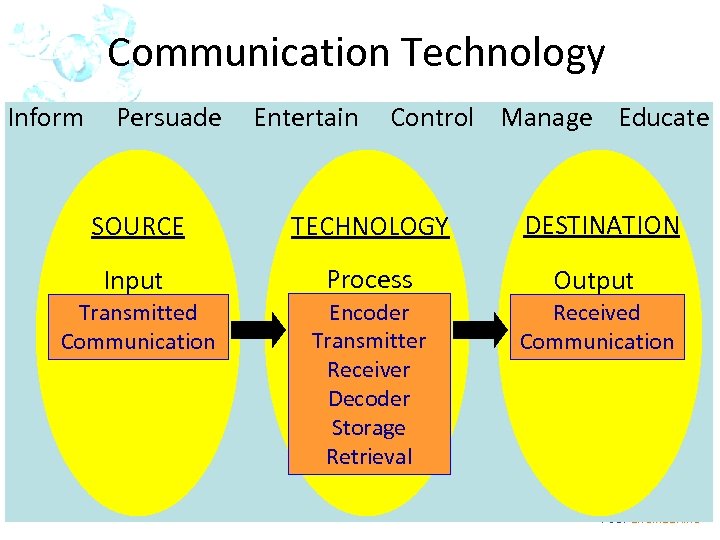 Communication Technology Inform Persuade Entertain Control Manage Educate SOURCE TECHNOLOGY DESTINATION Input Process Output Transmitted Communication Encoder Transmitter Receiver Decoder Storage Retrieval Received Communication IOT 2 -1 POLY ENGINEERING
Communication Technology Inform Persuade Entertain Control Manage Educate SOURCE TECHNOLOGY DESTINATION Input Process Output Transmitted Communication Encoder Transmitter Receiver Decoder Storage Retrieval Received Communication IOT 2 -1 POLY ENGINEERING
 Radio: Goal: Inform Persuade Entertain Source: Sounds and Information Educate Control Manage Encoder: Devices convert sound and info into modulated sine waves Transmitter: Antennas radiate the radio waves into air (medium) Receiver: Antennas capture the radio waves from air Decoder: Devices convert radio waves back into sounds and data [Storage: Recording devices store sounds and data for playback] [Retrieval: Stored data can be accessed and played] Destination: Consumers’ ears and eyes IOT 2 -2 POLY ENGINEERING
Radio: Goal: Inform Persuade Entertain Source: Sounds and Information Educate Control Manage Encoder: Devices convert sound and info into modulated sine waves Transmitter: Antennas radiate the radio waves into air (medium) Receiver: Antennas capture the radio waves from air Decoder: Devices convert radio waves back into sounds and data [Storage: Recording devices store sounds and data for playback] [Retrieval: Stored data can be accessed and played] Destination: Consumers’ ears and eyes IOT 2 -2 POLY ENGINEERING
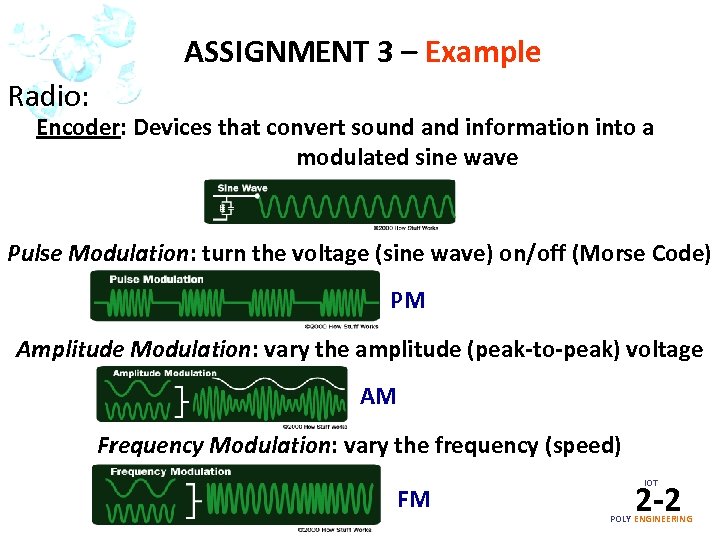 ASSIGNMENT 3 – Example Radio: Encoder: Devices that convert sound and information into a modulated sine wave Pulse Modulation: turn the voltage (sine wave) on/off (Morse Code) PM Amplitude Modulation: vary the amplitude (peak-to-peak) voltage AM Frequency Modulation: vary the frequency (speed) FM IOT 2 -2 POLY ENGINEERING
ASSIGNMENT 3 – Example Radio: Encoder: Devices that convert sound and information into a modulated sine wave Pulse Modulation: turn the voltage (sine wave) on/off (Morse Code) PM Amplitude Modulation: vary the amplitude (peak-to-peak) voltage AM Frequency Modulation: vary the frequency (speed) FM IOT 2 -2 POLY ENGINEERING
 Classes of Communication Technology DEFINITIONS: – Print Graphic Communication Visual, lingual messages that include printed media – Photographic Communication Using photographs, slides, or motion pictures to communicate a message – Telecommunications Communicating over a distance – Technical Graphic Communication Specific information about a product or its parts Size and shape, how to install, adjust, operate, maintain, or assemble a device IOT 2 -4 POLY ENGINEERING
Classes of Communication Technology DEFINITIONS: – Print Graphic Communication Visual, lingual messages that include printed media – Photographic Communication Using photographs, slides, or motion pictures to communicate a message – Telecommunications Communicating over a distance – Technical Graphic Communication Specific information about a product or its parts Size and shape, how to install, adjust, operate, maintain, or assemble a device IOT 2 -4 POLY ENGINEERING
 Matching Classes 1. 2. 3. 4. Print Graphic Communication Photographic Communication Telecommunications Technical Graphic Communication 3 1 2, 3 1 2 1 Telephone Book Videotape DVD Magazine Photograph Newspaper 3 3 3 2 2 1, 2 Headphones Computer Remote Control Painting Camera Comic Strip 2 -4 Billboard IOT POLY ENGINEERING
Matching Classes 1. 2. 3. 4. Print Graphic Communication Photographic Communication Telecommunications Technical Graphic Communication 3 1 2, 3 1 2 1 Telephone Book Videotape DVD Magazine Photograph Newspaper 3 3 3 2 2 1, 2 Headphones Computer Remote Control Painting Camera Comic Strip 2 -4 Billboard IOT POLY ENGINEERING
 Print Graphic Communication Technology – Major Processes: • Relief 2. The plate is covered in ink Intaglio – A modeled work that is raised (or lowered) from a flat background. By 593 A. D. , the first printing press was invented in (in-tal-yo) by the Sumerians ~6000 years ago. – Cuneiform China, and the first printed. Excess ink is removedavailable 3. newspaper was from surface – Wood block printing ~200 C. E. in Beijing in 700 A. D. It was a woodblock printing. And – Movable type printing ~1040 C. E. (Gutenberg ~1450) the Diamond Sutra, the earliest known complete – Intaglio (in-tal-yo) woodblock printed book~1430 illustrationsplaced on plate and with 4. Paper was printed – in 868 A. D. And Chinese printer Bi Sheng in China. Rotary printing press ~1843 compressed • Lithography (offset printing) ~1796 invented movable type in 1041 A. D. in China. – The source and destination are not on raised surfaces 5. Paper is removed and – cut into 1. Depressions. Relief and water do not readily mix ink has been transferred Low. Grease Cuneiform IOT printing plate – A chemical process High Relief POLY ENGINEERING – Most modern books and newspapers 2 -4
Print Graphic Communication Technology – Major Processes: • Relief 2. The plate is covered in ink Intaglio – A modeled work that is raised (or lowered) from a flat background. By 593 A. D. , the first printing press was invented in (in-tal-yo) by the Sumerians ~6000 years ago. – Cuneiform China, and the first printed. Excess ink is removedavailable 3. newspaper was from surface – Wood block printing ~200 C. E. in Beijing in 700 A. D. It was a woodblock printing. And – Movable type printing ~1040 C. E. (Gutenberg ~1450) the Diamond Sutra, the earliest known complete – Intaglio (in-tal-yo) woodblock printed book~1430 illustrationsplaced on plate and with 4. Paper was printed – in 868 A. D. And Chinese printer Bi Sheng in China. Rotary printing press ~1843 compressed • Lithography (offset printing) ~1796 invented movable type in 1041 A. D. in China. – The source and destination are not on raised surfaces 5. Paper is removed and – cut into 1. Depressions. Relief and water do not readily mix ink has been transferred Low. Grease Cuneiform IOT printing plate – A chemical process High Relief POLY ENGINEERING – Most modern books and newspapers 2 -4
 Communication Technology Print Graphic Communication • Screen Printing (~1000 C. E. , China; 1907 England) – Mainly billboards, package labels, fabric designs – Uses a woven mesh (a screen) to support an ink blocking stencil. – The stencil forms open areas of mesh that transfer ink as a sharp-edged image onto a substrate. – A roller or squeegee is moved across the screen stencil forcing or pumping ink past the threads of the woven mesh in the open areas. • Electrostatic (1938 / 1960 s) – Photocopier, Laser Printer – Opposite charges attract • Ink Jet (1980 s) IOT 2 -4 – Use a series of nozzles to spray ink directly on POLY ENGINEERING paper
Communication Technology Print Graphic Communication • Screen Printing (~1000 C. E. , China; 1907 England) – Mainly billboards, package labels, fabric designs – Uses a woven mesh (a screen) to support an ink blocking stencil. – The stencil forms open areas of mesh that transfer ink as a sharp-edged image onto a substrate. – A roller or squeegee is moved across the screen stencil forcing or pumping ink past the threads of the woven mesh in the open areas. • Electrostatic (1938 / 1960 s) – Photocopier, Laser Printer – Opposite charges attract • Ink Jet (1980 s) IOT 2 -4 – Use a series of nozzles to spray ink directly on POLY ENGINEERING paper
 Communication Technology • Telecommunications – Communicating over a distance Tele – Greek, “far off” Communicare – Latin, “to share” – Rely on the principles of electricity and magnetism – 2 types: • Hardwired systems (telephone, cable, fiber-optic) • Broadcast systems (radio and t. v. , mobile phones) – Point-to-point: • One transmitter and one receiver – Broadcast: • One powerful transmitter to numerous receivers IOT 2 -4 POLY ENGINEERING
Communication Technology • Telecommunications – Communicating over a distance Tele – Greek, “far off” Communicare – Latin, “to share” – Rely on the principles of electricity and magnetism – 2 types: • Hardwired systems (telephone, cable, fiber-optic) • Broadcast systems (radio and t. v. , mobile phones) – Point-to-point: • One transmitter and one receiver – Broadcast: • One powerful transmitter to numerous receivers IOT 2 -4 POLY ENGINEERING
 Communication Technology Telecommunications – Telegraph (mid 1830 s) • First instrument used to send messages by means of wires and electric current • A device interrupts the flow of a current through a wire • Uses shorter and longer bursts of current to represent letters • Device at receiving end converted electrical signal into clicks • Operator/mechanical printer converted clicks into words • Telegram – wires over land • Cable – wires under water – Telephone (1876 – Bell and Gray) • Greek: tele – far, phone – sound IOT 2 -4 POLY ENGINEERING
Communication Technology Telecommunications – Telegraph (mid 1830 s) • First instrument used to send messages by means of wires and electric current • A device interrupts the flow of a current through a wire • Uses shorter and longer bursts of current to represent letters • Device at receiving end converted electrical signal into clicks • Operator/mechanical printer converted clicks into words • Telegram – wires over land • Cable – wires under water – Telephone (1876 – Bell and Gray) • Greek: tele – far, phone – sound IOT 2 -4 POLY ENGINEERING
 Communication Technology Telecommunications – Broadcast • Radio (1893 – Tesla, 1901 – Marconi) • Television (1925) – Greek: tele – far, Latin: visio – seeing – 4 main parts (cathode ray tube) – Electron gun fires 3 beams – Steering coils move electron beam across screen – Phosphorus screen has over 200, 000 pixels – Glass tube holds it all together – Signals are broadcasted like radio signals IOT 2 -4 POLY ENGINEERING
Communication Technology Telecommunications – Broadcast • Radio (1893 – Tesla, 1901 – Marconi) • Television (1925) – Greek: tele – far, Latin: visio – seeing – 4 main parts (cathode ray tube) – Electron gun fires 3 beams – Steering coils move electron beam across screen – Phosphorus screen has over 200, 000 pixels – Glass tube holds it all together – Signals are broadcasted like radio signals IOT 2 -4 POLY ENGINEERING
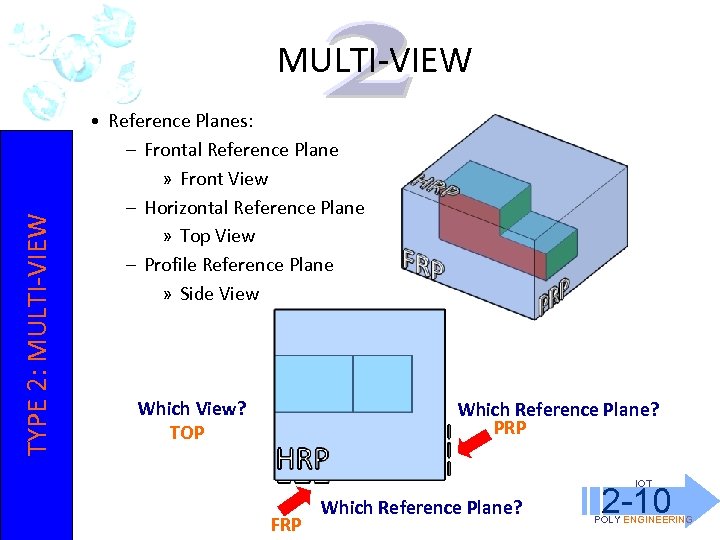 TYPE 2: MULTI-VIEW • Reference Planes: – Frontal Reference Plane » Front View – Horizontal Reference Plane » Top View – Profile Reference Plane » Side View Which View? TOP Which Reference Plane? PRP IOT FRP Which Reference Plane? 2 -10 POLY ENGINEERING
TYPE 2: MULTI-VIEW • Reference Planes: – Frontal Reference Plane » Front View – Horizontal Reference Plane » Top View – Profile Reference Plane » Side View Which View? TOP Which Reference Plane? PRP IOT FRP Which Reference Plane? 2 -10 POLY ENGINEERING
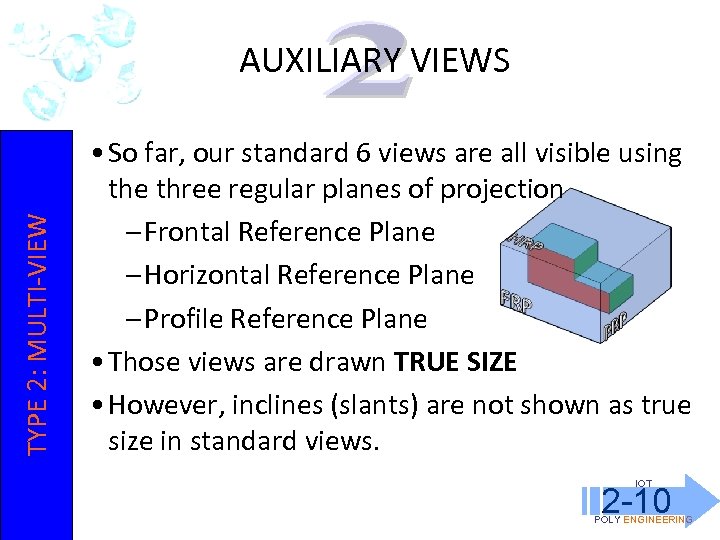 TYPE 2: MULTI-VIEW AUXILIARY VIEWS • So far, our standard 6 views are all visible using the three regular planes of projection – Frontal Reference Plane – Horizontal Reference Plane – Profile Reference Plane • Those views are drawn TRUE SIZE • However, inclines (slants) are not shown as true size in standard views. IOT 2 -10 POLY ENGINEERING
TYPE 2: MULTI-VIEW AUXILIARY VIEWS • So far, our standard 6 views are all visible using the three regular planes of projection – Frontal Reference Plane – Horizontal Reference Plane – Profile Reference Plane • Those views are drawn TRUE SIZE • However, inclines (slants) are not shown as true size in standard views. IOT 2 -10 POLY ENGINEERING
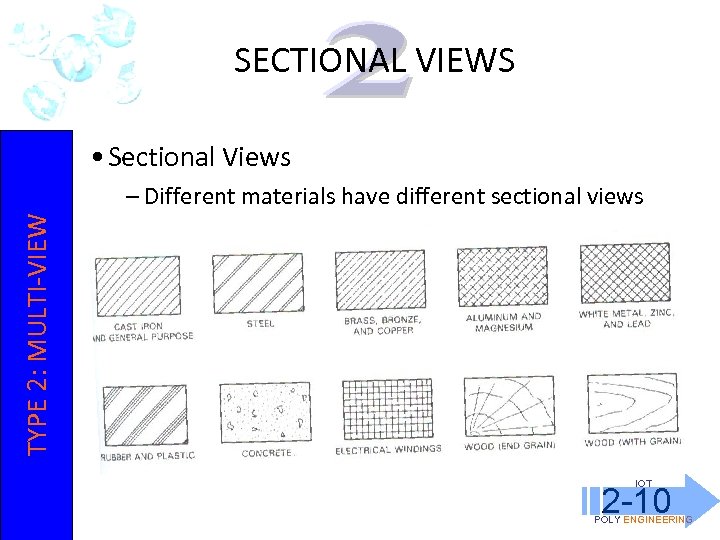 SECTIONAL VIEWS • Sectional Views TYPE 2: MULTI-VIEW – Different materials have different sectional views IOT 2 -10 POLY ENGINEERING
SECTIONAL VIEWS • Sectional Views TYPE 2: MULTI-VIEW – Different materials have different sectional views IOT 2 -10 POLY ENGINEERING
 Communication Technology October 13, 2008 DRILL • Turn in your 3 -view assignment (include NAME) • Match the type of Technical Graphics below with its type: B C A E B C F G D A Isometric Section Standard View Development Perspective Oblique D Cut-away Pictorial E F G IOT 2 -11 POLY ENGINEERING
Communication Technology October 13, 2008 DRILL • Turn in your 3 -view assignment (include NAME) • Match the type of Technical Graphics below with its type: B C A E B C F G D A Isometric Section Standard View Development Perspective Oblique D Cut-away Pictorial E F G IOT 2 -11 POLY ENGINEERING
![Technical Graphic Communication [REVIEW] MULTI-VIEW DRAWINGS Standard Views Sectional Views Auxiliary Views Developments Working Technical Graphic Communication [REVIEW] MULTI-VIEW DRAWINGS Standard Views Sectional Views Auxiliary Views Developments Working](https://present5.com/presentation/25efbc065e83b45a31788b49984ae19d/image-19.jpg) Technical Graphic Communication [REVIEW] MULTI-VIEW DRAWINGS Standard Views Sectional Views Auxiliary Views Developments Working Drawings IOT 2 -11 POLY ENGINEERING
Technical Graphic Communication [REVIEW] MULTI-VIEW DRAWINGS Standard Views Sectional Views Auxiliary Views Developments Working Drawings IOT 2 -11 POLY ENGINEERING
![Technical Graphic Communication [REVIEW] PICTORIAL DRAWINGS Show a likeness of an object as viewed Technical Graphic Communication [REVIEW] PICTORIAL DRAWINGS Show a likeness of an object as viewed](https://present5.com/presentation/25efbc065e83b45a31788b49984ae19d/image-20.jpg) Technical Graphic Communication [REVIEW] PICTORIAL DRAWINGS Show a likeness of an object as viewed by the eye Isometric Perspective as it is perceived by the eye. Oblique One face is true form Exploded Assembly IOT Cutaway Pictorial 2 -11 POLY ENGINEERING
Technical Graphic Communication [REVIEW] PICTORIAL DRAWINGS Show a likeness of an object as viewed by the eye Isometric Perspective as it is perceived by the eye. Oblique One face is true form Exploded Assembly IOT Cutaway Pictorial 2 -11 POLY ENGINEERING


