7f1d283a503f909738368d4604f3b713.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62
 INTERVENTION STRATEGIES & ACTIVITIES for PRESCHOOLERS with SPEECH SOUND DISORDERS Nancy Creaghead & Barbara Hodson ASHA Annual Convention—November 16, 2006 PART 1 --INTERVENTION for PRESCHOOLERS with HIGHLY UNINTELLIGIBLE SPEECH Barbara W. Hodson, Ph. D, CCC-SLP barbara. hodson@wichita. edu
INTERVENTION STRATEGIES & ACTIVITIES for PRESCHOOLERS with SPEECH SOUND DISORDERS Nancy Creaghead & Barbara Hodson ASHA Annual Convention—November 16, 2006 PART 1 --INTERVENTION for PRESCHOOLERS with HIGHLY UNINTELLIGIBLE SPEECH Barbara W. Hodson, Ph. D, CCC-SLP barbara. hodson@wichita. edu

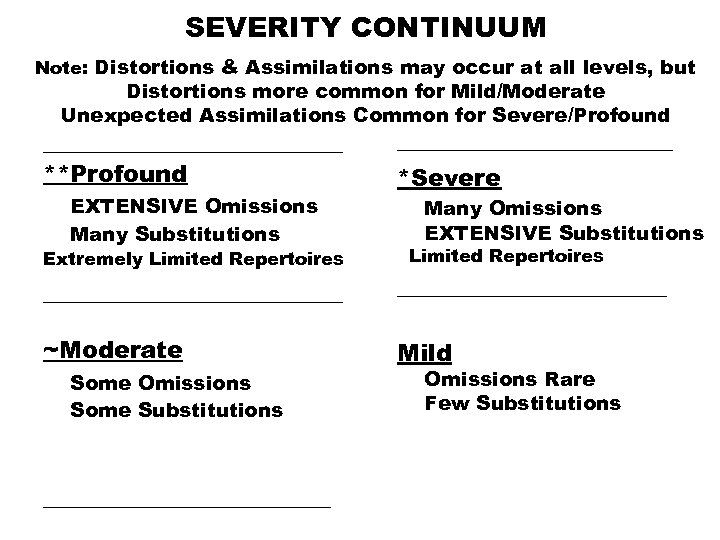 SEVERITY CONTINUUM Note: Distortions & Assimilations may occur at all levels, but Distortions more common for Mild/Moderate Unexpected Assimilations Common for Severe/Profound _____________ **Profound EXTENSIVE Omissions Many Substitutions Extremely Limited Repertoires ____________ *Severe Many Omissions EXTENSIVE Substitutions Limited Repertoires _______________ ~Moderate Mild Some Omissions Some Substitutions ________________ Omissions Rare Few Substitutions
SEVERITY CONTINUUM Note: Distortions & Assimilations may occur at all levels, but Distortions more common for Mild/Moderate Unexpected Assimilations Common for Severe/Profound _____________ **Profound EXTENSIVE Omissions Many Substitutions Extremely Limited Repertoires ____________ *Severe Many Omissions EXTENSIVE Substitutions Limited Repertoires _______________ ~Moderate Mild Some Omissions Some Substitutions ________________ Omissions Rare Few Substitutions

 MAJOR OPTIONS for TREATMENT
MAJOR OPTIONS for TREATMENT
 POTENTIAL OPTIMAL “PRIMARY” PHONOLOGICAL TARGET PATTERNS* for BEGINNING CYCLES
POTENTIAL OPTIMAL “PRIMARY” PHONOLOGICAL TARGET PATTERNS* for BEGINNING CYCLES

 GENERAL COMMENTS Regarding Targets
GENERAL COMMENTS Regarding Targets
 POTENTIAL “SECONDARY” TARGETS Target Any of the Following that are still Consistently Lacking/Deficient • Palatals • Singleton Stridents • Other Consonant Sequences • Vowel Contrasts • Voicing Contrasts • Assimilations • Any Remaining Idiosyncratic Patterns Minimal Pair Words especially useful for these
POTENTIAL “SECONDARY” TARGETS Target Any of the Following that are still Consistently Lacking/Deficient • Palatals • Singleton Stridents • Other Consonant Sequences • Vowel Contrasts • Voicing Contrasts • Assimilations • Any Remaining Idiosyncratic Patterns Minimal Pair Words especially useful for these
 INAPPROPRIATE TARGETS for PRESCHOOLERS
INAPPROPRIATE TARGETS for PRESCHOOLERS
 TREATMENT SESSION-BASIC STRUCTURE
TREATMENT SESSION-BASIC STRUCTURE



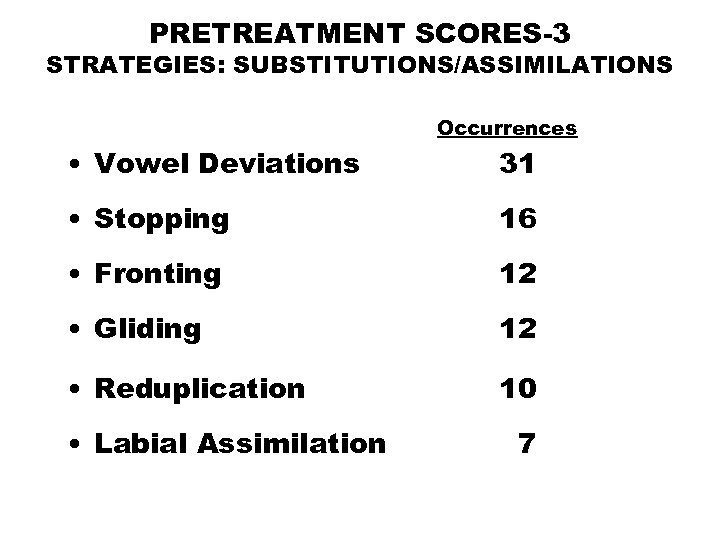 PRETREATMENT SCORES-3 STRATEGIES: SUBSTITUTIONS/ASSIMILATIONS Occurrences • Vowel Deviations 31 • Stopping 16 • Fronting 12 • Gliding 12 • Reduplication 10 • Labial Assimilation 7
PRETREATMENT SCORES-3 STRATEGIES: SUBSTITUTIONS/ASSIMILATIONS Occurrences • Vowel Deviations 31 • Stopping 16 • Fronting 12 • Gliding 12 • Reduplication 10 • Labial Assimilation 7
 PHONETIC & PHONOTACTIC INVENTORIES & PCC
PHONETIC & PHONOTACTIC INVENTORIES & PCC
 STIMULABILITY CONSIDERATIONS & GOAL STATEMENT
STIMULABILITY CONSIDERATIONS & GOAL STATEMENT
 CLIENT’S PHONOLOGICAL TARGETS for CYCLE-ONE
CLIENT’S PHONOLOGICAL TARGETS for CYCLE-ONE
 CYCLE-TWO TARGETS
CYCLE-TWO TARGETS
 CLIENT’S ADDITIONAL TARGETS for CYCLES THREE & FOUR
CLIENT’S ADDITIONAL TARGETS for CYCLES THREE & FOUR
 PRE-, INTERIM, & POST-TREATMENT DATA*/OUTCOMES
PRE-, INTERIM, & POST-TREATMENT DATA*/OUTCOMES
 PRODUCTIONS/TRANSCRIPTIONS OVER TIME
PRODUCTIONS/TRANSCRIPTIONS OVER TIME
![Total Occurrences of Major Phonological Deviations [TOMPD] Ages 3: 6 to 5: 7 Total Occurrences of Major Phonological Deviations [TOMPD] Ages 3: 6 to 5: 7](https://present5.com/presentation/7f1d283a503f909738368d4604f3b713/image-23.jpg) Total Occurrences of Major Phonological Deviations [TOMPD] Ages 3: 6 to 5: 7
Total Occurrences of Major Phonological Deviations [TOMPD] Ages 3: 6 to 5: 7
 MAJOR RECOMMENDATIONS Expressive Phonology
MAJOR RECOMMENDATIONS Expressive Phonology
 GENERAL RECOMMENDATIONS for CHILDREN with HIGHLY UNINTELLIGIBLE SPEECH • Early Intervention-Critical • Individualize Treatment • Evidence-based Practices/Documentation • Enhancement of PATTERNS
GENERAL RECOMMENDATIONS for CHILDREN with HIGHLY UNINTELLIGIBLE SPEECH • Early Intervention-Critical • Individualize Treatment • Evidence-based Practices/Documentation • Enhancement of PATTERNS
 ENHANCE PATTERNS PHONOLOGICAL & METAPHONOLOGICAL
ENHANCE PATTERNS PHONOLOGICAL & METAPHONOLOGICAL


 SOME SELECTED REFERENCES-Books/Special Issues ASHA Monograph (1994). Children’s phonology disorders: Pathways and patterns. Bernthal, J. , & Bankson, N. (2004). Articulation and phonological disorders. Bleile, K. (2004). Manual of articulation and phonological disorders. Gillon, G. (2004). Phonological awareness: From research to practice. Hodson, B. (Ed. ) (1994). From phonology to metaphonology: Issues, assessment, and intervention. Topics in Language Disorders. Hodson, B. (2007). Evaluating and enhancing children’s phonological systems: From research and theory to practice. Hodson, B. , & Edwards, M. (Eds. ) (1997). Perspectives in applied phonology. Hodson, B. , & Paden, E. (1983, 1991). Targeting intelligible speech: A phonological approach to remediation. Kent, R. (Ed. ) (2004). The MIT encyclopedia of communication disorders. Stackhouse, J. , & Wells, B. (1997, 2001, 2006). Children’s speech and literacy difficulties (I, II, & III).
SOME SELECTED REFERENCES-Books/Special Issues ASHA Monograph (1994). Children’s phonology disorders: Pathways and patterns. Bernthal, J. , & Bankson, N. (2004). Articulation and phonological disorders. Bleile, K. (2004). Manual of articulation and phonological disorders. Gillon, G. (2004). Phonological awareness: From research to practice. Hodson, B. (Ed. ) (1994). From phonology to metaphonology: Issues, assessment, and intervention. Topics in Language Disorders. Hodson, B. (2007). Evaluating and enhancing children’s phonological systems: From research and theory to practice. Hodson, B. , & Edwards, M. (Eds. ) (1997). Perspectives in applied phonology. Hodson, B. , & Paden, E. (1983, 1991). Targeting intelligible speech: A phonological approach to remediation. Kent, R. (Ed. ) (2004). The MIT encyclopedia of communication disorders. Stackhouse, J. , & Wells, B. (1997, 2001, 2006). Children’s speech and literacy difficulties (I, II, & III).
 SOME SELECTED REFERENCES-Articles/Chapters Forrest, K. (2002). Are oral-motor exercises useful in the treatment of phonological/articulatory disorders? Seminars in Speech and Language. Gordon-Brannan & Hodson (2000). Intelligibility/severity measurements of prekindergarten children’s speech. AJSLP. Hodson, B. (1994). Helping children become intelligible, literate, and articulate: The role of phonology. Topics in Language Disorders Hodson, B. (1997). Disordered phonologies: What have we learned about assessment and treatment? Perspectives in applied phonology. Hodson, Scherz, & Strattman (2002). Evaluating communicative abilities of a highly unintelligible preschooler. AJSLP. Hodson & Strattman (2004). Phonological awareness intervention for children with expressive phonological impairments. The MIT Encyclopedia of Communication Disorders. Nathan, Stackhouse, Goulandris, & Snowling (2004). The development of early literacy skills among children with speech difficulties. JSLHR. Porter & Hodson (2001). Collaborating to obtain phonological acquisition data for local schools. LSHSS.
SOME SELECTED REFERENCES-Articles/Chapters Forrest, K. (2002). Are oral-motor exercises useful in the treatment of phonological/articulatory disorders? Seminars in Speech and Language. Gordon-Brannan & Hodson (2000). Intelligibility/severity measurements of prekindergarten children’s speech. AJSLP. Hodson, B. (1994). Helping children become intelligible, literate, and articulate: The role of phonology. Topics in Language Disorders Hodson, B. (1997). Disordered phonologies: What have we learned about assessment and treatment? Perspectives in applied phonology. Hodson, Scherz, & Strattman (2002). Evaluating communicative abilities of a highly unintelligible preschooler. AJSLP. Hodson & Strattman (2004). Phonological awareness intervention for children with expressive phonological impairments. The MIT Encyclopedia of Communication Disorders. Nathan, Stackhouse, Goulandris, & Snowling (2004). The development of early literacy skills among children with speech difficulties. JSLHR. Porter & Hodson (2001). Collaborating to obtain phonological acquisition data for local schools. LSHSS.

 Questions to Consider
Questions to Consider
 Relationship between Language and Phonology
Relationship between Language and Phonology
 Assumptions about Intervention
Assumptions about Intervention
 Treatment Strategies
Treatment Strategies
 Implications for Treatment
Implications for Treatment




 Phonological Awareness and Reading Problems
Phonological Awareness and Reading Problems

 Implications regarding Phonological Awareness
Implications regarding Phonological Awareness
 Treatment Approaches for Speech Sound Disorders
Treatment Approaches for Speech Sound Disorders

 PRINCIPLES OF LANGUAGE LEARNING
PRINCIPLES OF LANGUAGE LEARNING
 PRINCIPLES FOR LANGUAGE "TEACHING"
PRINCIPLES FOR LANGUAGE "TEACHING"
 PRINCIPLES FOR LANGUAGE "TEACHING"
PRINCIPLES FOR LANGUAGE "TEACHING"
 Remediation Based on Normal Development
Remediation Based on Normal Development
 Implications for Serving Preschool Children
Implications for Serving Preschool Children



 Our Preschool Phonology Group
Our Preschool Phonology Group
 Our Preschool Phonology Group
Our Preschool Phonology Group
 Target: Fricatives Theme: At the Beach
Target: Fricatives Theme: At the Beach
 Including Phonology in the Preschool Classroom
Including Phonology in the Preschool Classroom


 Velar Opportunities for “Going on a Picnic”
Velar Opportunities for “Going on a Picnic”
 Phonologic Treatment in Preschool Settings
Phonologic Treatment in Preschool Settings
 References
References


