 Interpersonal Communication Perceptions and Listening
Interpersonal Communication Perceptions and Listening
 Can you do it? FINISHED FILES ARE THE RESULT OF YEARS OF SCIENTIFIC STUDY COMBINED WITH THE EXPERIENCE OF MANY YEARS OF EXPERTS
Can you do it? FINISHED FILES ARE THE RESULT OF YEARS OF SCIENTIFIC STUDY COMBINED WITH THE EXPERIENCE OF MANY YEARS OF EXPERTS
 Can you do it?
Can you do it?
 The Process of Perceiving • Selective exposure • Selective attention • Selective interpretation • Selective retention
The Process of Perceiving • Selective exposure • Selective attention • Selective interpretation • Selective retention
 Frames of Reference • Closure – we combine pieces of data to create a whole picture • Assimilation – we change what we perceive to fit our frame of reference • Accommodation – we create new perceptions and change our existing frame of reference
Frames of Reference • Closure – we combine pieces of data to create a whole picture • Assimilation – we change what we perceive to fit our frame of reference • Accommodation – we create new perceptions and change our existing frame of reference
 Levels of Perception Perceiving occurs on many levels: • Direct perspective – “I think he is cute” • Meta-perspective – “I think you think he is cute” • Meta-meta perspective – “I think you think I think he is cute”
Levels of Perception Perceiving occurs on many levels: • Direct perspective – “I think he is cute” • Meta-perspective – “I think you think he is cute” • Meta-meta perspective – “I think you think I think he is cute”
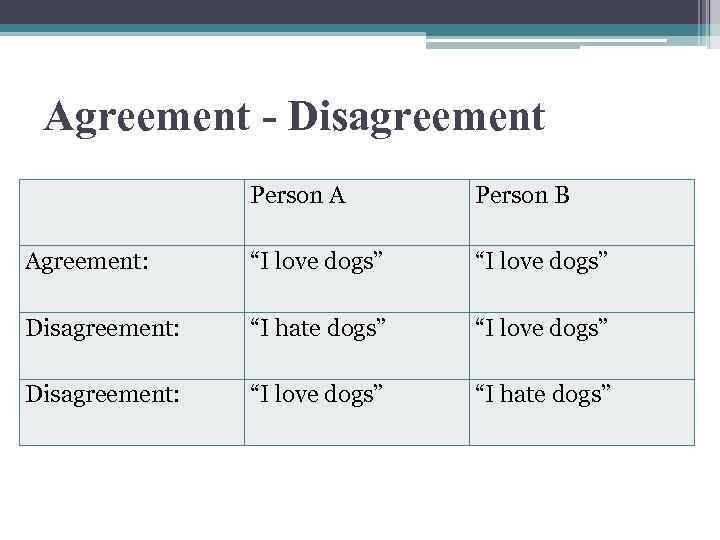 Agreement - Disagreement Person A Person B Agreement: “I love dogs” Disagreement: “I hate dogs” “I love dogs” Disagreement: “I love dogs” “I hate dogs”
Agreement - Disagreement Person A Person B Agreement: “I love dogs” Disagreement: “I hate dogs” “I love dogs” Disagreement: “I love dogs” “I hate dogs”
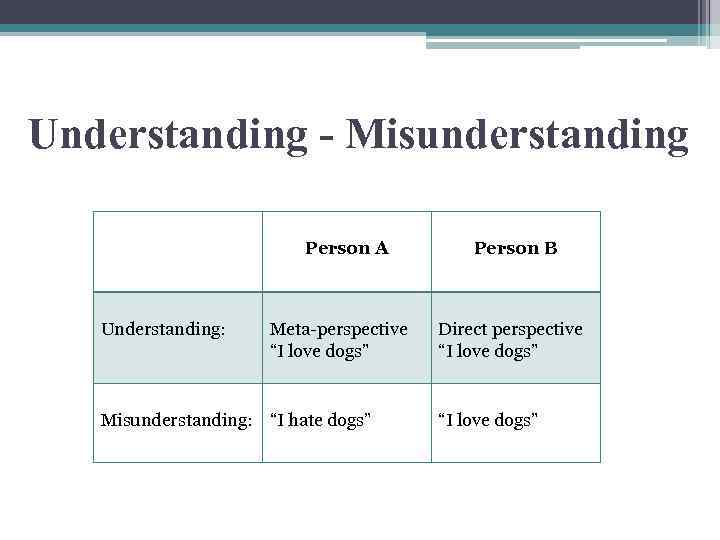 Understanding - Misunderstanding Person A Understanding: Meta-perspective “I love dogs” Misunderstanding: “I hate dogs” Person B Direct perspective “I love dogs”
Understanding - Misunderstanding Person A Understanding: Meta-perspective “I love dogs” Misunderstanding: “I hate dogs” Person B Direct perspective “I love dogs”
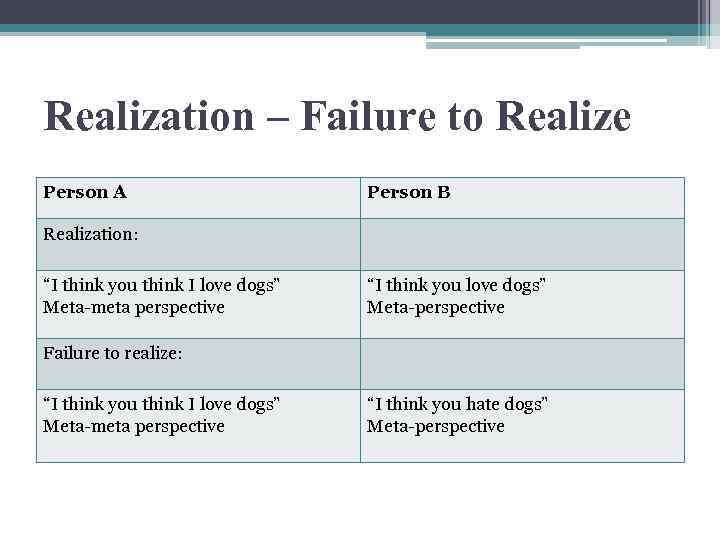 Realization – Failure to Realize Person A Person B Realization: “I think you think I love dogs” Meta-meta perspective “I think you love dogs” Meta-perspective Failure to realize: “I think you think I love dogs” Meta-meta perspective “I think you hate dogs” Meta-perspective
Realization – Failure to Realize Person A Person B Realization: “I think you think I love dogs” Meta-meta perspective “I think you love dogs” Meta-perspective Failure to realize: “I think you think I love dogs” Meta-meta perspective “I think you hate dogs” Meta-perspective
 Listening Process • Motivation • Selective exposure • Selective attention (concentration) • Selective interpretation • Feedback
Listening Process • Motivation • Selective exposure • Selective attention (concentration) • Selective interpretation • Feedback
 Deterrents to Effective Listening • Assuming in advance that the subject is uninteresting or unimportant • Mentally criticizing the speakers’ delivery • Listening only for facts • Pretending to be attentive • Rehearsing a response • Daydreaming
Deterrents to Effective Listening • Assuming in advance that the subject is uninteresting or unimportant • Mentally criticizing the speakers’ delivery • Listening only for facts • Pretending to be attentive • Rehearsing a response • Daydreaming