e54774b46c3ae1d0314b0bb731c594b6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62
 Internet Technologies The Resource Description Framework (RDF and RDFa) 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Internet Technologies The Resource Description Framework (RDF and RDFa) 95 -733 Internet Technologies
 RDF and RDFa Notes from two articles on course schedule: “What is RDF” by Tim Bray and Joshua Tauberer and the “RDFa Primer” from W 3 C 95 -733 Internet Technologies
RDF and RDFa Notes from two articles on course schedule: “What is RDF” by Tim Bray and Joshua Tauberer and the “RDFa Primer” from W 3 C 95 -733 Internet Technologies
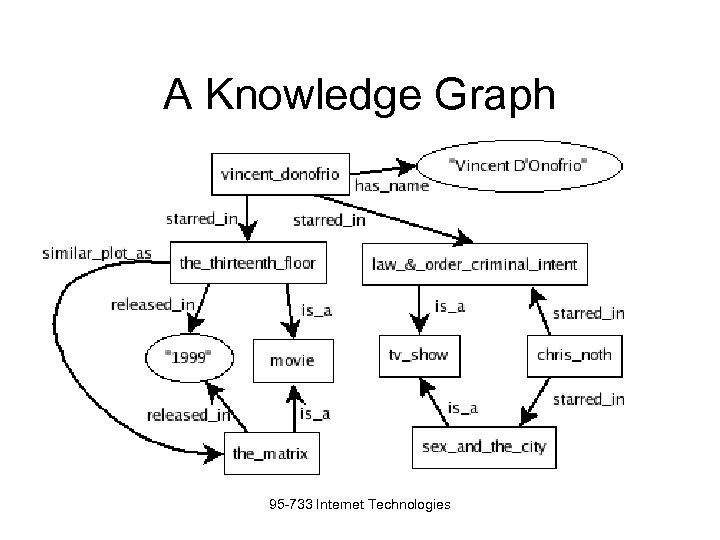 A Knowledge Graph 95 -733 Internet Technologies
A Knowledge Graph 95 -733 Internet Technologies
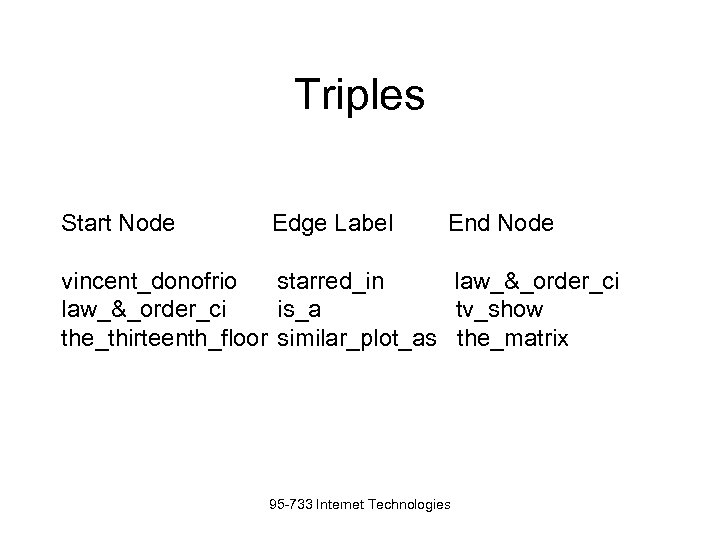 Triples Start Node Edge Label End Node vincent_donofrio starred_in law_&_order_ci is_a tv_show the_thirteenth_floor similar_plot_as the_matrix 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Triples Start Node Edge Label End Node vincent_donofrio starred_in law_&_order_ci is_a tv_show the_thirteenth_floor similar_plot_as the_matrix 95 -733 Internet Technologies
 Notation 3 (N 3) or Turtle Format @prefix rdf:
Notation 3 (N 3) or Turtle Format @prefix rdf:
 RDF/XML
RDF/XML
 Another RDF/XML
Another RDF/XML
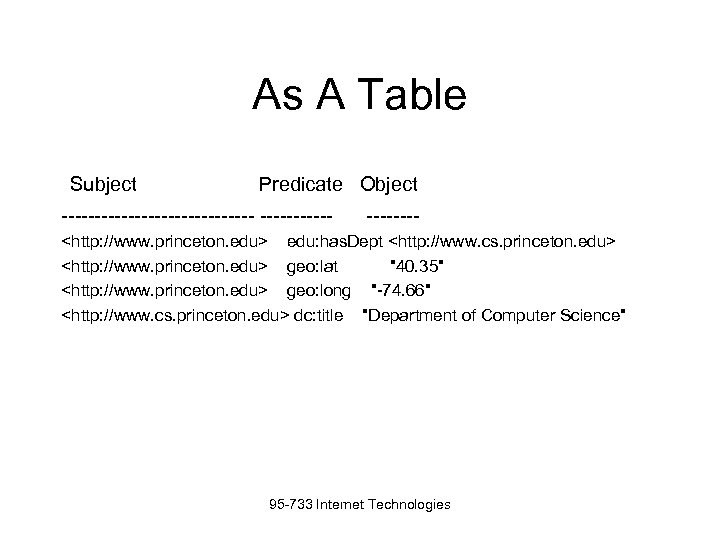 As A Table Subject Predicate Object --------------- ----
As A Table Subject Predicate Object --------------- ----
 Notation 3 @prefix rdf:
Notation 3 @prefix rdf:
 From the RDFa W 3 C Primer “When web data meant for humans is augmented with hints meant for computer programs, these programs become significantly more helpful. ” 95 -733 Internet Technologies
From the RDFa W 3 C Primer “When web data meant for humans is augmented with hints meant for computer programs, these programs become significantly more helpful. ” 95 -733 Internet Technologies
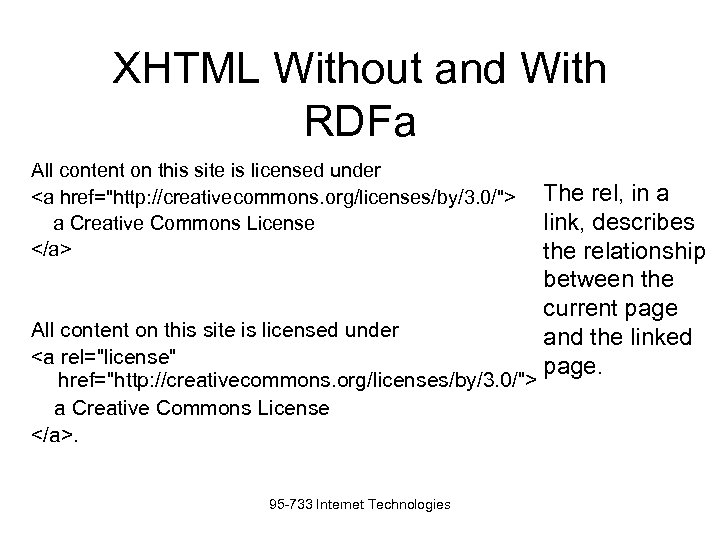 XHTML Without and With RDFa All content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons License All content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons License . 95 -733 Internet Technologies The rel, in a link, describes the relationship between the current page and the linked page.
XHTML Without and With RDFa All content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons License All content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons License . 95 -733 Internet Technologies The rel, in a link, describes the relationship between the current page and the linked page.
 A Link with a Flavor 95 -733 Internet Technologies
A Link with a Flavor 95 -733 Internet Technologies
 Labeling Title and Author
Labeling Title and Author
 In RDFa, all property names are, in fact, URLs. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
In RDFa, all property names are, in fact, URLs. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Alice Birpemswick Alice Birpemswick Email: The Dublin core has no vocabulary for describing friendships. But foaf does. The typeof is an alice@example. com RDFa attribute that is declare a new data Phone: +1 617. 555. 7332 a certain
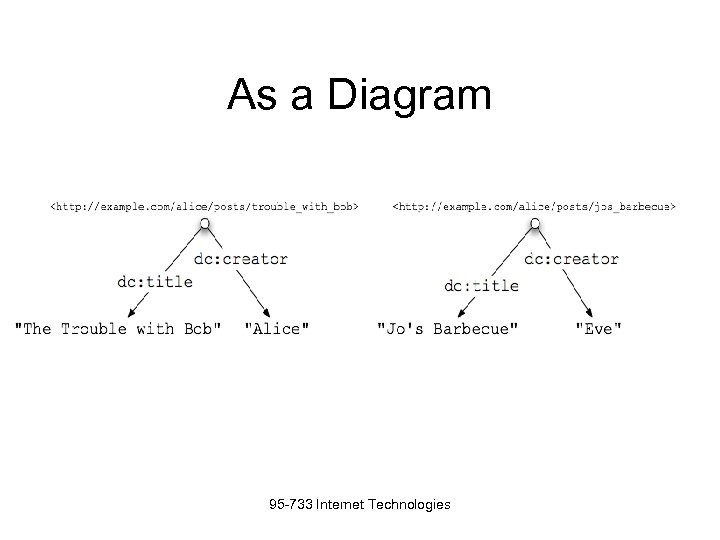 As a Diagram 95 -733 Internet Technologies
As a Diagram 95 -733 Internet Technologies

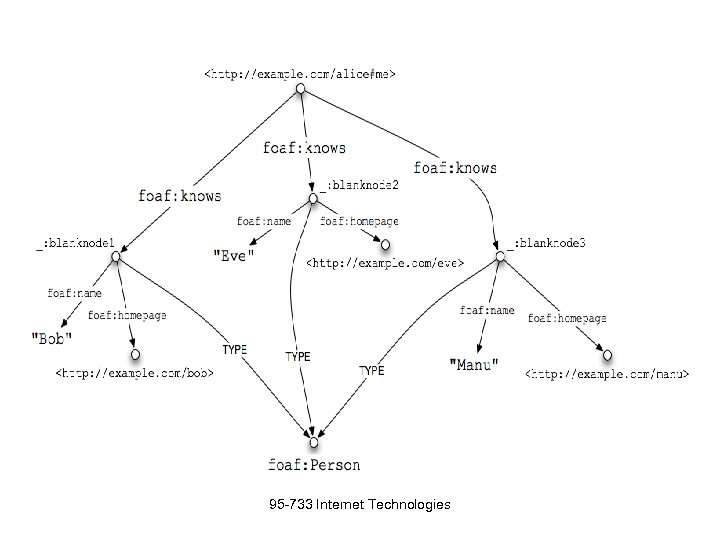
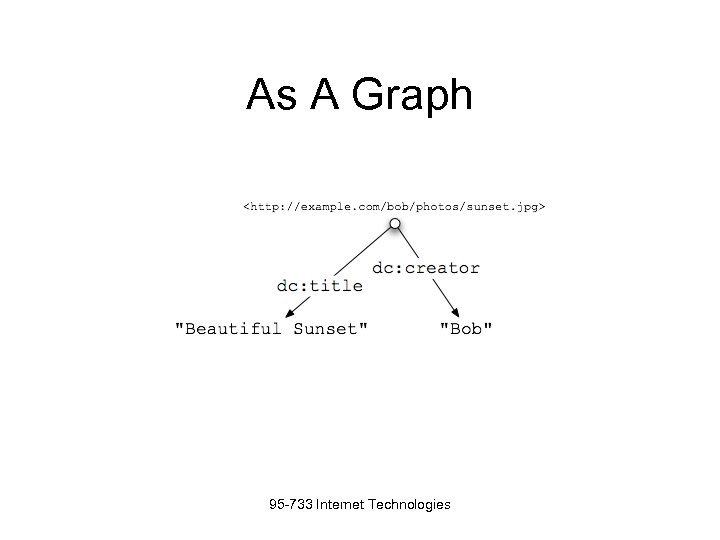 As A Graph 95 -733 Internet Technologies
As A Graph 95 -733 Internet Technologies alice@example." src="https://present5.com/presentation/e54774b46c3ae1d0314b0bb731c594b6/image-19.jpg" alt="Blog Contact Info
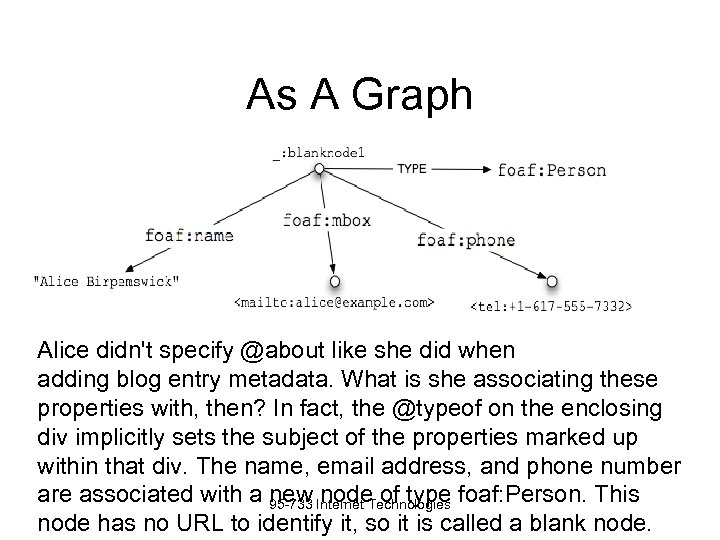 As A Graph Alice didn't specify @about like she did when adding blog entry metadata. What is she associating these properties with, then? In fact, the @typeof on the enclosing div implicitly sets the subject of the properties marked up within that div. The name, email address, and phone number are associated with a 95 -733 Internet Technologies foaf: Person. This new node of type node has no URL to identify it, so it is called a blank node.
As A Graph Alice didn't specify @about like she did when adding blog entry metadata. What is she associating these properties with, then? In fact, the @typeof on the enclosing div implicitly sets the subject of the properties marked up within that div. The name, email address, and phone number are associated with a 95 -733 Internet Technologies foaf: Person. This new node of type node has no URL to identify it, so it is called a blank node. Bob Eve" src="https://present5.com/presentation/e54774b46c3ae1d0314b0bb731c594b6/image-22.jpg" alt="Social Networks
" src="https://present5.com/presentation/e54774b46c3ae1d0314b0bb731c594b6/image-23.jpg" alt="Adding RDFa First, describe these as Persons.
" src="https://present5.com/presentation/e54774b46c3ae1d0314b0bb731c594b6/image-24.jpg" alt="Add Homepages Use rel for the link relationships.
 Claim in Primer “Alice is ecstatic that, with so little additional markup, she's able to fully express both a pleasant human-readable page and a machine-readable dataset. ” 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Claim in Primer “Alice is ecstatic that, with so little additional markup, she's able to fully express both a pleasant human-readable page and a machine-readable dataset. ” 95 -733 Internet Technologies
 95 -733 Internet Technologies
95 -733 Internet Technologies  Building Custom Vocabularies 1. Selecting a URL where the vocabulary will reside, e. g. http: //example. com/photos/vocab#. 2. Distributing an RDF document, at that URL, which defines the classes and properties that make up the vocabulary. For example, Alice may want to define classes Photo and Camera, as well as the property taken. With that relates a photo to the camera with which it was taken. 3. Using the vocabulary in XHTML+RDFa with the usual prefix declaration mechanism, e. g. xmlns: photo="http: //example. com/photos/vocab#", and typeof="photo: Camera". 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Building Custom Vocabularies 1. Selecting a URL where the vocabulary will reside, e. g. http: //example. com/photos/vocab#. 2. Distributing an RDF document, at that URL, which defines the classes and properties that make up the vocabulary. For example, Alice may want to define classes Photo and Camera, as well as the property taken. With that relates a photo to the camera with which it was taken. 3. Using the vocabulary in XHTML+RDFa with the usual prefix declaration mechanism, e. g. xmlns: photo="http: //example. com/photos/vocab#", and typeof="photo: Camera". 95 -733 Internet Technologies  Microformats Compete with RDFa h. Card Business card data XFN Friends and contacts h. Calendar Events h. Review movies, books, etc. . “When web data meant for humans is augmented with hints meant for computer programs, these programs become significantly more helpful. ” But, perhaps we will use microformats rather than RDFa. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Microformats Compete with RDFa h. Card Business card data XFN Friends and contacts h. Calendar Events h. Review movies, books, etc. . “When web data meant for humans is augmented with hints meant for computer programs, these programs become significantly more helpful. ” But, perhaps we will use microformats rather than RDFa. 95 -733 Internet Technologies  Microformats Compete with RDFa As an exercise, visit http: //microformats. org and build an h. Card an h. Calendar. Use h. Card creator and h. Calendar creator. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Microformats Compete with RDFa As an exercise, visit http: //microformats. org and build an h. Card an h. Calendar. Use h. Card creator and h. Calendar creator. 95 -733 Internet Technologies  RDF On Its Own • RDFa is RDF in XHTML. • The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a W 3 C recommendation for an XML encoding of metadata. • A standard for encoding metadata is important for finding and describing resources. A “resource” is anything with a URI. This would include people, books, devices and so on. • Card catalogs, for example, have been used for years to record metadata about the collection of materials in libraries. Is Google the card catalogue for the web? Are we done? 95 -733 Internet Technologies
RDF On Its Own • RDFa is RDF in XHTML. • The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a W 3 C recommendation for an XML encoding of metadata. • A standard for encoding metadata is important for finding and describing resources. A “resource” is anything with a URI. This would include people, books, devices and so on. • Card catalogs, for example, have been used for years to record metadata about the collection of materials in libraries. Is Google the card catalogue for the web? Are we done? 95 -733 Internet Technologies  • RDF Is All About Making Statements An RDF Document contains Statements. • A statement can be thought of as an ordered triple composed of three items: (resource, property-type, property-value) • A Resource is anything that can be identified. • A Predicate is a property name that has a URI. The Predicate may or may not actually be resolvable. • A Value is another Resource or a literal • Statements may be represented in RDF XML, abbreviated RDF XML, NTriples or graphs. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
• RDF Is All About Making Statements An RDF Document contains Statements. • A statement can be thought of as an ordered triple composed of three items: (resource, property-type, property-value) • A Resource is anything that can be identified. • A Predicate is a property name that has a URI. The Predicate may or may not actually be resolvable. • A Value is another Resource or a literal • Statements may be represented in RDF XML, abbreviated RDF XML, NTriples or graphs. 95 -733 Internet Technologies  RDF Triples It is required that each resource have a URI. http: //www. andrew. cmu. edu/~mm 6/my. xml#root(). child(1) mailto: mm 6@andrew. cmu. edu urn: isbn: 0764532367 (resource, property-type, property-value) A property is a specific characteristic, attribute or relationship of a resource. Each property has a specific meaning that can be identified by the property’s name and the associated schema. The schema must actually be pointed to by the property’s namespace. Using RDF Schema we can describe the property names, values and value ranges that are permitted for the property. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
RDF Triples It is required that each resource have a URI. http: //www. andrew. cmu. edu/~mm 6/my. xml#root(). child(1) mailto: mm 6@andrew. cmu. edu urn: isbn: 0764532367 (resource, property-type, property-value) A property is a specific characteristic, attribute or relationship of a resource. Each property has a specific meaning that can be identified by the property’s name and the associated schema. The schema must actually be pointed to by the property’s namespace. Using RDF Schema we can describe the property names, values and value ranges that are permitted for the property. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
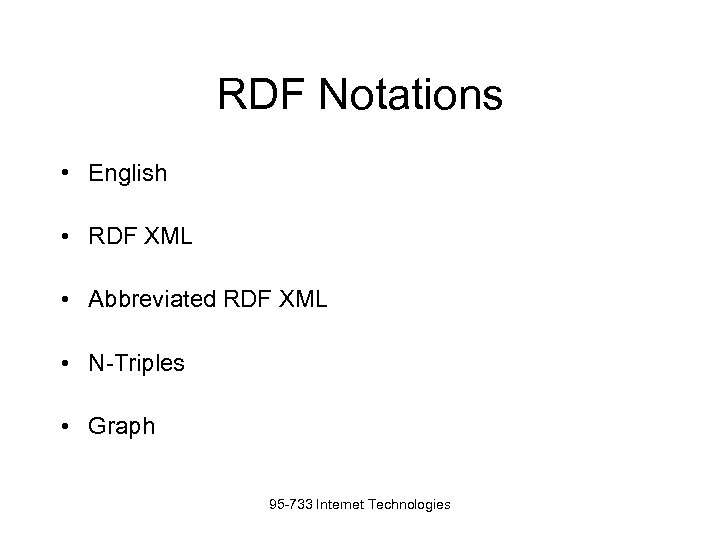 RDF Notations • English • RDF XML • Abbreviated RDF XML • N-Triples • Graph 95 -733 Internet Technologies
RDF Notations • English • RDF XML • Abbreviated RDF XML • N-Triples • Graph 95 -733 Internet Technologies  Another RDF Application Composite Capabilities/Preference Profiles • The CC/PP working group was formed in August 1999. • Its mission was to develop an RDF-based framework for the management of device profile information. • Now under W 3 C’s Ubiquitous Web Applications Working Group (UWAWG) 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Another RDF Application Composite Capabilities/Preference Profiles • The CC/PP working group was formed in August 1999. • Its mission was to develop an RDF-based framework for the management of device profile information. • Now under W 3 C’s Ubiquitous Web Applications Working Group (UWAWG) 95 -733 Internet Technologies  An RDF Application CC/PP A composite capability/preference profile is a collection of information which describes the capabilities, hardware, system software and applications used by someone accessing the web. Information might include: • Preferred language (Spanish, French, etc. ) • Sound (on/off) • Images (on/off) • Class of device (phone, PC, printer, etc. ) • Screen size • Available bandwidth • Version of HTML supported, and so on. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
An RDF Application CC/PP A composite capability/preference profile is a collection of information which describes the capabilities, hardware, system software and applications used by someone accessing the web. Information might include: • Preferred language (Spanish, French, etc. ) • Sound (on/off) • Images (on/off) • Class of device (phone, PC, printer, etc. ) • Screen size • Available bandwidth • Version of HTML supported, and so on. 95 -733 Internet Technologies 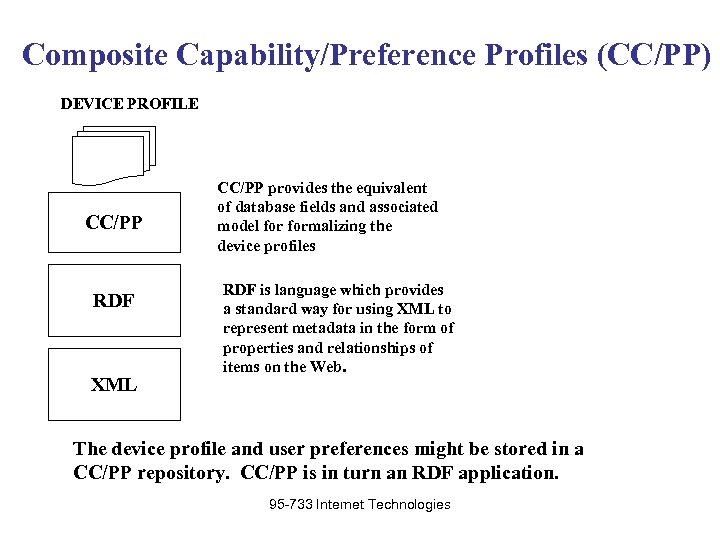 Composite Capability/Preference Profiles (CC/PP) DEVICE PROFILE CC/PP RDF XML CC/PP provides the equivalent of database fields and associated model formalizing the device profiles RDF is language which provides a standard way for using XML to represent metadata in the form of properties and relationships of items on the Web. The device profile and user preferences might be stored in a CC/PP repository. CC/PP is in turn an RDF application. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Composite Capability/Preference Profiles (CC/PP) DEVICE PROFILE CC/PP RDF XML CC/PP provides the equivalent of database fields and associated model formalizing the device profiles RDF is language which provides a standard way for using XML to represent metadata in the form of properties and relationships of items on the Web. The device profile and user preferences might be stored in a CC/PP repository. CC/PP is in turn an RDF application. 95 -733 Internet Technologies  Composite Capability/Preference Profiles (CC/PP) • The location of the device profile is sent with a request for a Web page. • The CC/PP data is accessed and on the basis of the profile, a Web server can choose the right content. This might be a certain XHTML file or perhaps a suitable document would be generated on the fly. • A document on the server may refer to its own document profile-describing the required capabilities of its client. • The server might match and send or generate and send. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Composite Capability/Preference Profiles (CC/PP) • The location of the device profile is sent with a request for a Web page. • The CC/PP data is accessed and on the basis of the profile, a Web server can choose the right content. This might be a certain XHTML file or perhaps a suitable document would be generated on the fly. • A document on the server may refer to its own document profile-describing the required capabilities of its client. • The server might match and send or generate and send. 95 -733 Internet Technologies 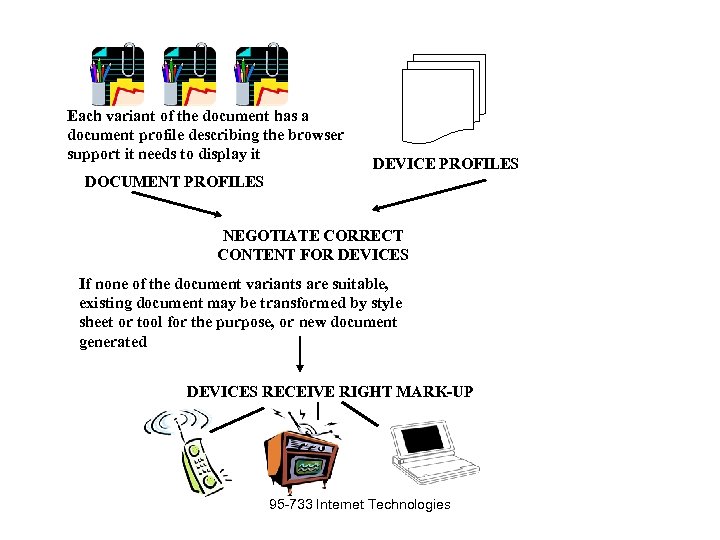 Each variant of the document has a document profile describing the browser support it needs to display it DEVICE PROFILES DOCUMENT PROFILES NEGOTIATE CORRECT CONTENT FOR DEVICES If none of the document variants are suitable, existing document may be transformed by style sheet or tool for the purpose, or new document generated DEVICES RECEIVE RIGHT MARK-UP 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Each variant of the document has a document profile describing the browser support it needs to display it DEVICE PROFILES DOCUMENT PROFILES NEGOTIATE CORRECT CONTENT FOR DEVICES If none of the document variants are suitable, existing document may be transformed by style sheet or tool for the purpose, or new document generated DEVICES RECEIVE RIGHT MARK-UP 95 -733 Internet Technologies  Processing RDF in Java • • • XSLT? DOM? SAX? St. AX? Open source Jena from HP Research provides another approach 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Processing RDF in Java • • • XSLT? DOM? SAX? St. AX? Open source Jena from HP Research provides another approach 95 -733 Internet Technologies  Jena Example 1 // Modified from HP's Jena Tutorial // ~/mm 6/www/95 -733/examples/Jena import com. hpl. jena. rdf. model. *; import com. hpl. jena. vocabulary. *; public class Tutorial 01 extends Object { // some definitions static String person. URI static String full. Name = "http: //somewhere/John. Smith"; = "John Smith"; 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Jena Example 1 // Modified from HP's Jena Tutorial // ~/mm 6/www/95 -733/examples/Jena import com. hpl. jena. rdf. model. *; import com. hpl. jena. vocabulary. *; public class Tutorial 01 extends Object { // some definitions static String person. URI static String full. Name = "http: //somewhere/John. Smith"; = "John Smith"; 95 -733 Internet Technologies ![public static void main (String args[]) { // create an empty model (An empty public static void main (String args[]) { // create an empty model (An empty](https://present5.com/presentation/e54774b46c3ae1d0314b0bb731c594b6/image-50.jpg) public static void main (String args[]) { // create an empty model (An empty RDF graph) Model model = Model. Factory. create. Default. Model(); // create the resource Resource john. Smith = model. create. Resource(person. URI); // add the property john. Smith. add. Property(VCARD. FN, full. Name); model. write(System. out); } } 95 -733 Internet Technologies
public static void main (String args[]) { // create an empty model (An empty RDF graph) Model model = Model. Factory. create. Default. Model(); // create the resource Resource john. Smith = model. create. Resource(person. URI); // add the property john. Smith. add. Property(VCARD. FN, full. Name); model. write(System. out); } } 95 -733 Internet Technologies  D: Mc. Carthywww95 -733examplesJena>java Tutorial 01
D: Mc. Carthywww95 -733examplesJena>java Tutorial 01  A Resource Valued Predicate // Modified from HP's Jena Tutorial import com. hpl. jena. rdf. model. *; import com. hpl. jena. vocabulary. *; public class Tutorial 03 extends Object { public static void main (String args[]) { String person. URI = "http: //somewhere/John. Smith"; String given. Name = "John"; String family. Name = "Smith"; String full. Name = given. Name + " " + family. Name; // create an empty model Model model = Model. Factory. create. Default. Model(); 95 -733 Internet Technologies
A Resource Valued Predicate // Modified from HP's Jena Tutorial import com. hpl. jena. rdf. model. *; import com. hpl. jena. vocabulary. *; public class Tutorial 03 extends Object { public static void main (String args[]) { String person. URI = "http: //somewhere/John. Smith"; String given. Name = "John"; String family. Name = "Smith"; String full. Name = given. Name + " " + family. Name; // create an empty model Model model = Model. Factory. create. Default. Model(); 95 -733 Internet Technologies  // create the resource // and add the properties cascading style Resource john. Smith = model. create. Resource(person. URI). add. Property(VCARD. FN, full. Name). add. Property(VCARD. N, model. create. Resource(). add. Property(VCARD. Given, given. Name). add. Property(VCARD. Family, family. Name)) 95 -733 Internet Technologies
// create the resource // and add the properties cascading style Resource john. Smith = model. create. Resource(person. URI). add. Property(VCARD. FN, full. Name). add. Property(VCARD. N, model. create. Resource(). add. Property(VCARD. Given, given. Name). add. Property(VCARD. Family, family. Name)) 95 -733 Internet Technologies  // list the statements in the graph Stmt. Iterator iter = model. list. Statements(); // print out the predicate, subject and object of each statement while (iter. has. Next()) { Statement stmt = iter. next. Statement(); // get next statement Resource subject = stmt. get. Subject(); // get the subject Property predicate = stmt. get. Predicate(); // get the predicate RDFNode object = stmt. get. Object(); // get the object System. out. print(subject. to. String()); System. out. print(" " + predicate. to. String() + " "); 95 -733 Internet Technologies
// list the statements in the graph Stmt. Iterator iter = model. list. Statements(); // print out the predicate, subject and object of each statement while (iter. has. Next()) { Statement stmt = iter. next. Statement(); // get next statement Resource subject = stmt. get. Subject(); // get the subject Property predicate = stmt. get. Predicate(); // get the predicate RDFNode object = stmt. get. Object(); // get the object System. out. print(subject. to. String()); System. out. print(" " + predicate. to. String() + " "); 95 -733 Internet Technologies 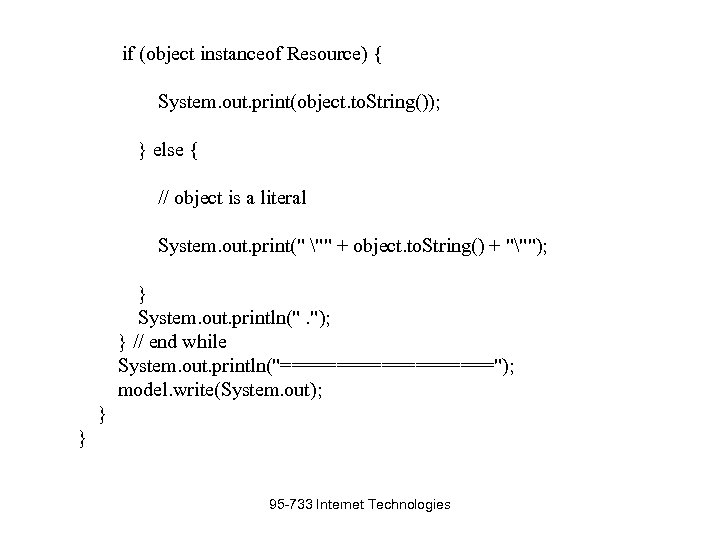 if (object instanceof Resource) { System. out. print(object. to. String()); } else { // object is a literal System. out. print(" "" + object. to. String() + """); } System. out. println(". "); } // end while System. out. println("=========="); model. write(System. out); } } 95 -733 Internet Technologies
if (object instanceof Resource) { System. out. print(object. to. String()); } else { // object is a literal System. out. print(" "" + object. to. String() + """); } System. out. println(". "); } // end while System. out. println("=========="); model. write(System. out); } } 95 -733 Internet Technologies  D: Mc. Carthywww95 -733examplesJena>java Tutorial 03 16 fa 474: fd 074695 f 6: -8000 http: //www. w 3. org/2001/vcard-rdf/3. 0#Given "John". http: //somewhere/John. Smith http: //www. w 3. org/2001/vcard-rdf/3. 0#FN "John Smith". 16 fa 474: fd 074695 f 6: -8000 http: //www. w 3. org/2001/vcard-rdf/3. 0#Family "Smith". http: //somewhere/John. Smith http: //www. w 3. org/2001/vcard-rdf/3. 0#N 16 fa 474: fd 074695 f 6: -8000. ==========
D: Mc. Carthywww95 -733examplesJena>java Tutorial 03 16 fa 474: fd 074695 f 6: -8000 http: //www. w 3. org/2001/vcard-rdf/3. 0#Given "John". http: //somewhere/John. Smith http: //www. w 3. org/2001/vcard-rdf/3. 0#FN "John Smith". 16 fa 474: fd 074695 f 6: -8000 http: //www. w 3. org/2001/vcard-rdf/3. 0#Family "Smith". http: //somewhere/John. Smith http: //www. w 3. org/2001/vcard-rdf/3. 0#N 16 fa 474: fd 074695 f 6: -8000. ==========  Reading OWL with Jena import com. hpl. jena. rdf. model. *; import com. hpl. jena. ontology. *; import java. io. *; import java. net. *; public class Read. Wine. Ontology extends Object { public static void main (String args[]) throws Exception { // create an empty model Ont. Model model = Model. Factory. create. Ontology. Model(); 95 -733 Internet Technologies
Reading OWL with Jena import com. hpl. jena. rdf. model. *; import com. hpl. jena. ontology. *; import java. io. *; import java. net. *; public class Read. Wine. Ontology extends Object { public static void main (String args[]) throws Exception { // create an empty model Ont. Model model = Model. Factory. create. Ontology. Model(); 95 -733 Internet Technologies  // read the wine. xml file either way model. read("file: D: /Mc. Carthy/www/95 -733/examples/Jena/wine. xml"); //model. read("http: //www. andrew. cmu. edu/user/mm 6/ontology/wine. xml"); // write it to standard out model. write(System. out); } } The next step is to use Jena to make or verify deductions. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
// read the wine. xml file either way model. read("file: D: /Mc. Carthy/www/95 -733/examples/Jena/wine. xml"); //model. read("http: //www. andrew. cmu. edu/user/mm 6/ontology/wine. xml"); // write it to standard out model. write(System. out); } } The next step is to use Jena to make or verify deductions. 95 -733 Internet Technologies  The Semantic Web These notes are from an article entitled “The Semantic Web” by Tim Berners-Lee, James Hendler and Ora Lassila appearing in Scientific American, May 2001 By augmenting web pages with data directed at computers and by adding documents solely for computers, we will transform the web into the Semantic Web. Intuitive software will be developed that will allow anyone to create Semantic Web Pages. For the semantic web to function, computers must have access to structured collections of information and sets of inference rules that can be used to conduct automated reasoning. XML has no built-in mechanism to convey the meaning of the user’s new tags to other users. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
The Semantic Web These notes are from an article entitled “The Semantic Web” by Tim Berners-Lee, James Hendler and Ora Lassila appearing in Scientific American, May 2001 By augmenting web pages with data directed at computers and by adding documents solely for computers, we will transform the web into the Semantic Web. Intuitive software will be developed that will allow anyone to create Semantic Web Pages. For the semantic web to function, computers must have access to structured collections of information and sets of inference rules that can be used to conduct automated reasoning. XML has no built-in mechanism to convey the meaning of the user’s new tags to other users. 95 -733 Internet Technologies  The Semantic Web The challenge of the Semantic Web is to provide a language that expresses both data and rules for reasoning about the data and that allows rules from an existing knowledge-representation system to be exported unto the Web. Ontologies: Collections of statements written in a language such as RDF that define the relations between concepts and specify logical rules for reasoning about them. Computers will “understand” the meaning of semantic data on a web page by following links to specified ontologies. Consider the statement “a hex-head bolt is a type of machine bolt”. We could encode this in RDF. When writing code against traditional XML data, the programmer must know what the document author uses each tag for. Meaning is expressed by RDF, which encodes it in a set of triples. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
The Semantic Web The challenge of the Semantic Web is to provide a language that expresses both data and rules for reasoning about the data and that allows rules from an existing knowledge-representation system to be exported unto the Web. Ontologies: Collections of statements written in a language such as RDF that define the relations between concepts and specify logical rules for reasoning about them. Computers will “understand” the meaning of semantic data on a web page by following links to specified ontologies. Consider the statement “a hex-head bolt is a type of machine bolt”. We could encode this in RDF. When writing code against traditional XML data, the programmer must know what the document author uses each tag for. Meaning is expressed by RDF, which encodes it in a set of triples. 95 -733 Internet Technologies  The Semantic Web An RDF document makes assertions that particular things (people, web pages, or whatever) have properties (such as “is sister of”, “is the author of”) with certain values (another person, another Web page). We can remove ambiguity by associating each of the three parts with a URI. For example: “(filed 5 in database A) (is a field of type) (zip code)” could be replaced with three URI’s. An ontology is a document or file that formally defines the relations among terms. An ontology may express a rule “If a city code is associated with a state code, and an address uses that city code, then that address has the associated state code. ” A program can then draw conclusions. The meaning of terms or XML codes can be defined by pointers from the page to an ontology. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
The Semantic Web An RDF document makes assertions that particular things (people, web pages, or whatever) have properties (such as “is sister of”, “is the author of”) with certain values (another person, another Web page). We can remove ambiguity by associating each of the three parts with a URI. For example: “(filed 5 in database A) (is a field of type) (zip code)” could be replaced with three URI’s. An ontology is a document or file that formally defines the relations among terms. An ontology may express a rule “If a city code is associated with a state code, and an address uses that city code, then that address has the associated state code. ” A program can then draw conclusions. The meaning of terms or XML codes can be defined by pointers from the page to an ontology. 95 -733 Internet Technologies  The Semantic Web Many automated web based services already exist without semantics, but other programs such as agents have no way to locate one that will perform a specific function. Service Discovery will happen only when there is a common language to describe a service in a way that lets other agents “understand” both the function offered and how to take advantage of it. Services can advertise their functions in directories analogous to the Yellow Pages. Devices can advertise their abilities with RDF. 95 -733 Internet Technologies
The Semantic Web Many automated web based services already exist without semantics, but other programs such as agents have no way to locate one that will perform a specific function. Service Discovery will happen only when there is a common language to describe a service in a way that lets other agents “understand” both the function offered and how to take advantage of it. Services can advertise their functions in directories analogous to the Yellow Pages. Devices can advertise their abilities with RDF. 95 -733 Internet Technologies


