96d1b4d2ea35ec397d992142617bc83e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Internet POPs, Telecom Hotels, and Internet Data Centers CS 294 -3 – The Converged Network Spring 2002 George Porter Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Internet POPs, Telecom Hotels, and Internet Data Centers CS 294 -3 – The Converged Network Spring 2002 George Porter Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Internet: collection of networks • This talk is about connectivity and computation – How do the networks in the Internet communicate with each other? – What do transit providers do with their traffic? – Motivation for computation in the network (Internet Data Centers) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Internet: collection of networks • This talk is about connectivity and computation – How do the networks in the Internet communicate with each other? – What do transit providers do with their traffic? – Motivation for computation in the network (Internet Data Centers) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
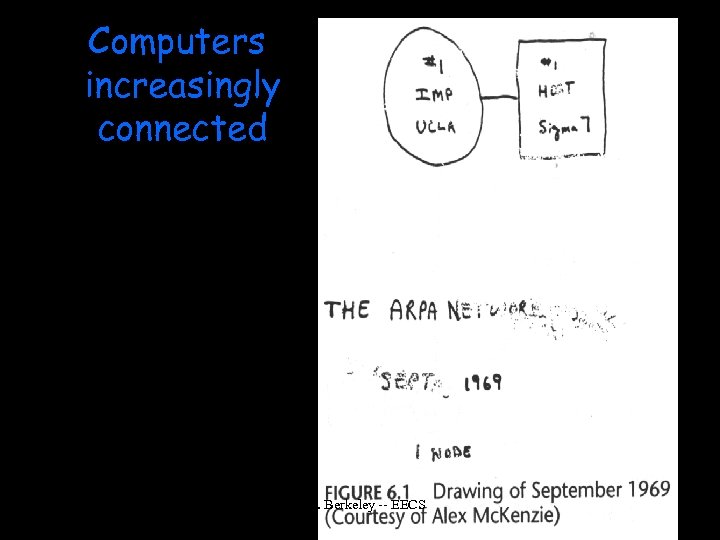 Computers increasingly connected Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Computers increasingly connected Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
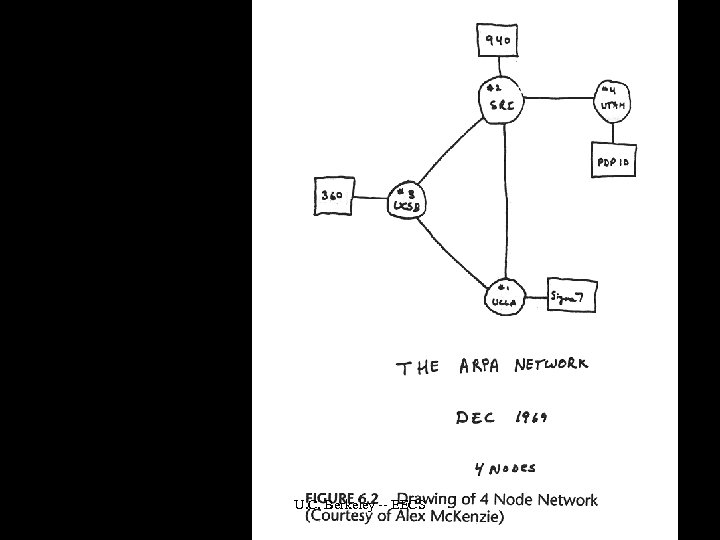 Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
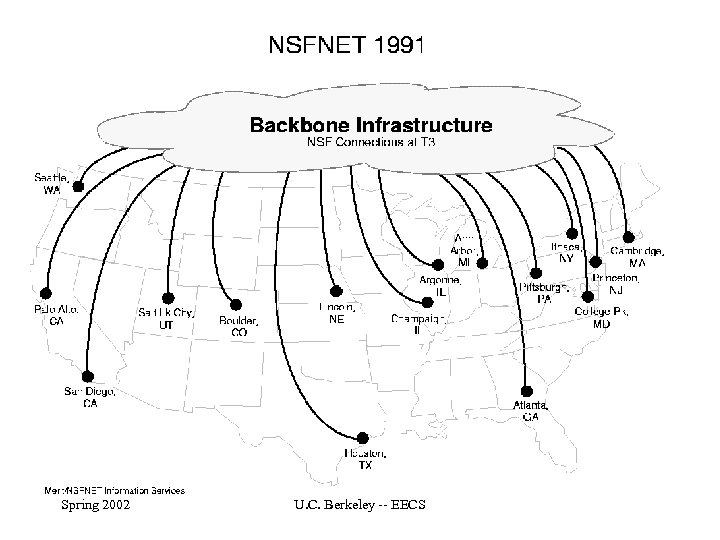
 NSFnet • 1987 -1995 • Managed by Merit – ANS, IBM, MCI, State of Michigan • Consisted of T-1 connections • In 1992, moved to T-3 links run by Advanced Network & Services (ANSnet) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
NSFnet • 1987 -1995 • Managed by Merit – ANS, IBM, MCI, State of Michigan • Consisted of T-1 connections • In 1992, moved to T-3 links run by Advanced Network & Services (ANSnet) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Post NFSnet • v. BNS (very high-speed backbone network services) run by MCI • Additional NAPs (Network Access Points) – – MAE-East, D. C. – MFS Datanet (now MCI Worldcom) Ameritech, Chicago – Ameritech Pac. Bell, San Jose – Pac. Bell Sprint, Pennsauken, NJ - Sprint Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Post NFSnet • v. BNS (very high-speed backbone network services) run by MCI • Additional NAPs (Network Access Points) – – MAE-East, D. C. – MFS Datanet (now MCI Worldcom) Ameritech, Chicago – Ameritech Pac. Bell, San Jose – Pac. Bell Sprint, Pennsauken, NJ - Sprint Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Many new Commercial NAPs • ATLnap (Atlanta) • Bellcore Multimedia exchange • NY 6 i. X – New York IPv 6 • MAE-LA • Seattle IX • MAE-Houston Spring 2002 • • • PAIX Equinix e. Xchange Linx (London) Free. IX (France) AMS-IX (Amsterdam) • etc U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Many new Commercial NAPs • ATLnap (Atlanta) • Bellcore Multimedia exchange • NY 6 i. X – New York IPv 6 • MAE-LA • Seattle IX • MAE-Houston Spring 2002 • • • PAIX Equinix e. Xchange Linx (London) Free. IX (France) AMS-IX (Amsterdam) • etc U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
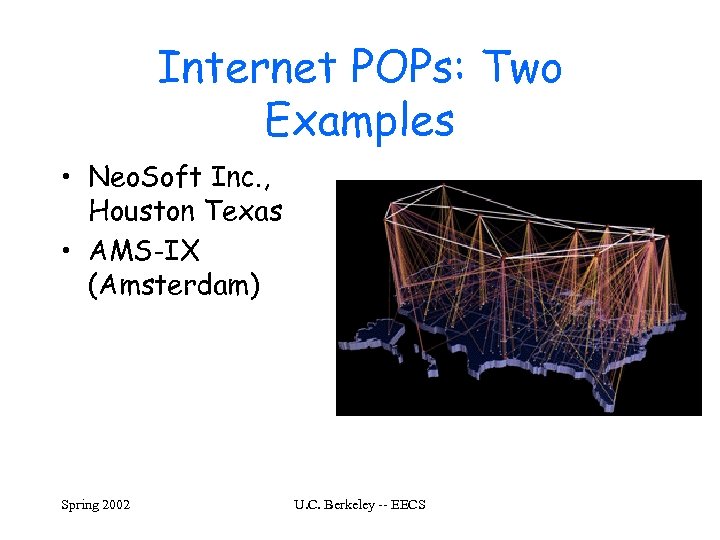 Internet POPs: Two Examples • Neo. Soft Inc. , Houston Texas • AMS-IX (Amsterdam) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Internet POPs: Two Examples • Neo. Soft Inc. , Houston Texas • AMS-IX (Amsterdam) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
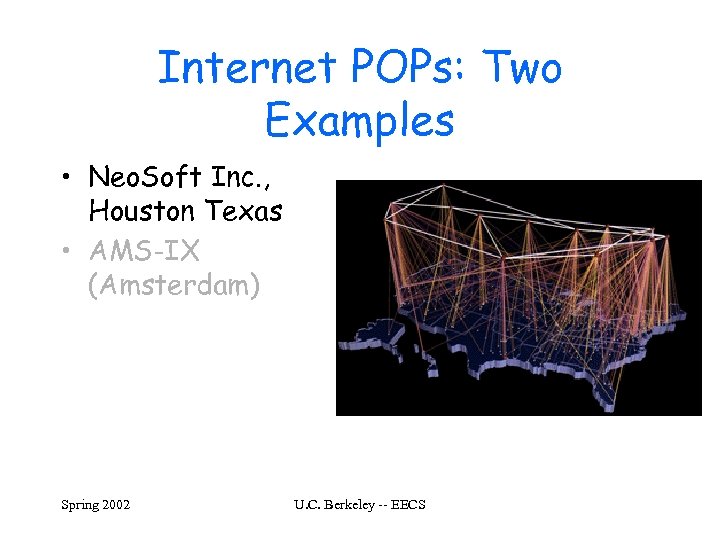 Internet POPs: Two Examples • Neo. Soft Inc. , Houston Texas • AMS-IX (Amsterdam) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Internet POPs: Two Examples • Neo. Soft Inc. , Houston Texas • AMS-IX (Amsterdam) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 • BBS in 1989, became an ISP in 1992 • Founder Karl Lehenbauer (Left) • I worked there from 1994 -1999 Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
• BBS in 1989, became an ISP in 1992 • Founder Karl Lehenbauer (Left) • I worked there from 1994 -1999 Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Initial Connectivity • Originally, Neo. Soft connected to NSFnet via Sesquinet @ Rice • T 1 cost $14 k up front, $2 k/month • Cisco router IGS $10 k • 198. ? ? . xx. yy from Sesquinet’s address space Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Initial Connectivity • Originally, Neo. Soft connected to NSFnet via Sesquinet @ Rice • T 1 cost $14 k up front, $2 k/month • Cisco router IGS $10 k • 198. ? ? . xx. yy from Sesquinet’s address space Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 New Connectivity • Eventually bought fractional DS 3 from MCI (Sprint wouldn’t route less than /20 due to problems) • On own CIDR block (128 class C’s: 206. 109) • BGP-4 running on Cisco 7513 Router • $15 k/month Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
New Connectivity • Eventually bought fractional DS 3 from MCI (Sprint wouldn’t route less than /20 due to problems) • On own CIDR block (128 class C’s: 206. 109) • BGP-4 running on Cisco 7513 Router • $15 k/month Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Peering • Peered with UUnet for 2 months – Neo. Soft had a large webserver, and served out much more traffic than inbound • Became member of MAE/Houston • MAGE (Metro Area Gigabit Ethernet) via Phonoscope ($4 k/month!) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Peering • Peered with UUnet for 2 months – Neo. Soft had a large webserver, and served out much more traffic than inbound • Became member of MAE/Houston • MAGE (Metro Area Gigabit Ethernet) via Phonoscope ($4 k/month!) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Experiences in Peering • Many other local providers didn’t have a clue! – INSYNC misconfigured their routes, and traffic would be outbound through MAGE, inbound through random other routes – Often advertised incorrect BGP updates • PSInet: Advertised Dial-up ISDN Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Experiences in Peering • Many other local providers didn’t have a clue! – INSYNC misconfigured their routes, and traffic would be outbound through MAGE, inbound through random other routes – Often advertised incorrect BGP updates • PSInet: Advertised Dial-up ISDN Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Hops, Multihoming • In 1994, the Sprint and MCI handoff was in Chicago – 20 hops to next door neighbor – Eventually exchanged in Dallas • Experimented with Multihoming (DS 3 and T 1 to Cable & wireless) – Not too good, BGP administration – Plan was for recovery Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Hops, Multihoming • In 1994, the Sprint and MCI handoff was in Chicago – 20 hops to next door neighbor – Eventually exchanged in Dallas • Experimented with Multihoming (DS 3 and T 1 to Cable & wireless) – Not too good, BGP administration – Plan was for recovery Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Neo. Soft Internet America • In 1999, Internet America buys Neo. Soft for $8 M • Houston office closes • I get laid off Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Neo. Soft Internet America • In 1999, Internet America buys Neo. Soft for $8 M • Houston office closes • I get laid off Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
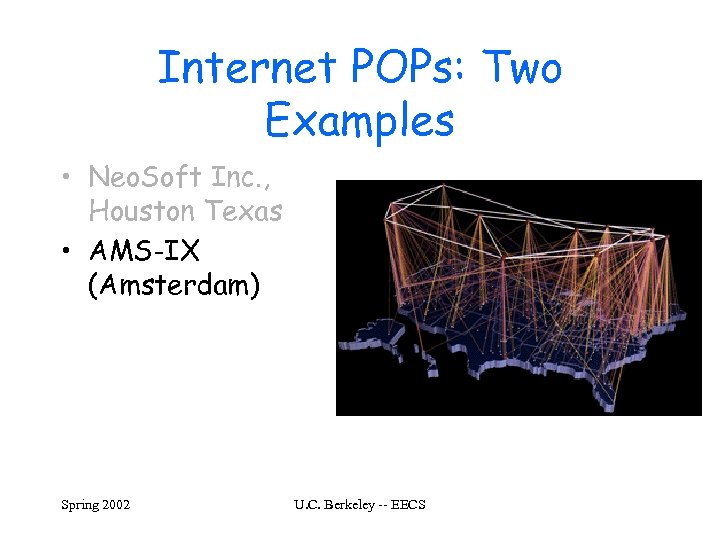 Internet POPs: Two Examples • Neo. Soft Inc. , Houston Texas • AMS-IX (Amsterdam) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Internet POPs: Two Examples • Neo. Soft Inc. , Houston Texas • AMS-IX (Amsterdam) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
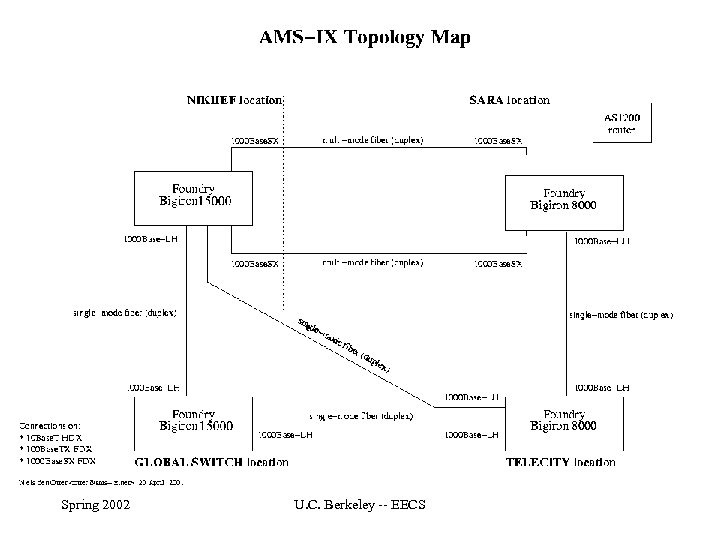
 AMS-IX • • • Carrier-neutral peering point Founded in 1994 100+ members 565 Tbytes/month AT&T, Akamai, Dynegy, Digital Island, Deutsche Telecom, France Telecom, Global Crossing, UUnet NL, etc Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
AMS-IX • • • Carrier-neutral peering point Founded in 1994 100+ members 565 Tbytes/month AT&T, Akamai, Dynegy, Digital Island, Deutsche Telecom, France Telecom, Global Crossing, UUnet NL, etc Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
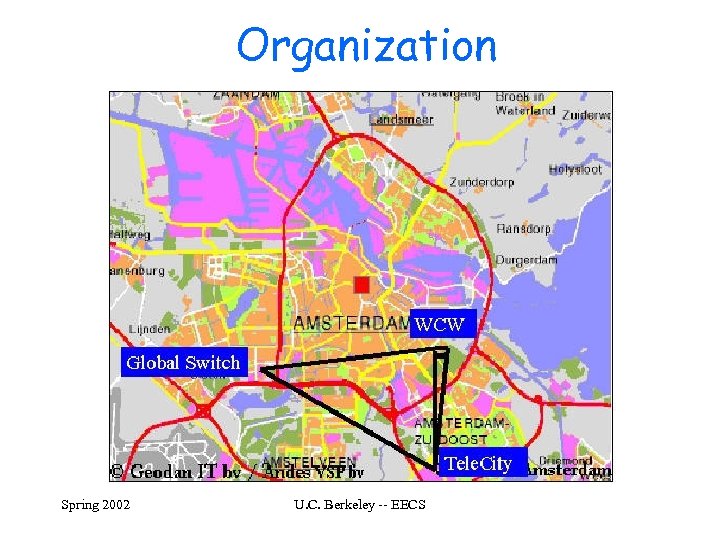 Organization Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Organization Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 How to Join • Companies apply for membership after agreeing to numerous policies (sometimes voting is involved) • Cost – 10 base. T = 500, 00 euro/month – 100 base. T = 850, 00 euro/month – 1000 base T = 1200, 00 euro/month • 1 euro = 0. 87 USD (12/26/2002) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
How to Join • Companies apply for membership after agreeing to numerous policies (sometimes voting is involved) • Cost – 10 base. T = 500, 00 euro/month – 100 base. T = 850, 00 euro/month – 1000 base T = 1200, 00 euro/month • 1 euro = 0. 87 USD (12/26/2002) Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Computation in the network • It makes sense to move servers and content to places of high connectivity • By the economics of scale it is cheaper to provide connectivity, power, management, etc to many customers at a central site Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Computation in the network • It makes sense to move servers and content to places of high connectivity • By the economics of scale it is cheaper to provide connectivity, power, management, etc to many customers at a central site Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Example: e. Xchange • Paul Ave location in SF: 350 K sq. ft • People can rent cabinets, racks, cages • In addition to being a data center, also a huge connectivity point Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Example: e. Xchange • Paul Ave location in SF: 350 K sq. ft • People can rent cabinets, racks, cages • In addition to being a data center, also a huge connectivity point Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Services • • UPS + generator Office space Climate Control “Meet me” room with carriers and other service providers • Professional monitoring • Security (hand scanners, guards) • Fire control Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Services • • UPS + generator Office space Climate Control “Meet me” room with carriers and other service providers • Professional monitoring • Security (hand scanners, guards) • Fire control Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 wave. Exchange • Unique facility located across the street from e. Xchange • 20+ carriers • Near fiber routes/loops • Carriers can meet in “meet me rooms” • Service between ASPs, ISPs, CDNs… • Opened Nov 2, 2001 Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
wave. Exchange • Unique facility located across the street from e. Xchange • 20+ carriers • Near fiber routes/loops • Carriers can meet in “meet me rooms” • Service between ASPs, ISPs, CDNs… • Opened Nov 2, 2001 Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Tenants of wave. Exchange • AT&T, Cogent, Enron, Level 3, Pac. Bell, Qwest, Sigma, Worldcom, Williams Communications, Xo, PAIX, others • Network effect • Huge connectivity + Highly available services Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Tenants of wave. Exchange • AT&T, Cogent, Enron, Level 3, Pac. Bell, Qwest, Sigma, Worldcom, Williams Communications, Xo, PAIX, others • Network effect • Huge connectivity + Highly available services Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
 Summary • Progression from leased lines to NAPs to peering points gives ISPs options • I haven’t even mentioned private peering arrangements • Putting computation in the network at the points of connectivity enables new services that can meet demand Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS
Summary • Progression from leased lines to NAPs to peering points gives ISPs options • I haven’t even mentioned private peering arrangements • Putting computation in the network at the points of connectivity enables new services that can meet demand Spring 2002 U. C. Berkeley -- EECS


