374b12bef640dd14b59af546ac0ada5b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63
 Internet dan Jaringan Komputer The Internet and Network Security Dr. Tb. Maulana Kusuma mkusuma@staff. gunadarma. ac. id http: //staffsite. gunadarma. ac. id/mkusuma Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 0
Internet dan Jaringan Komputer The Internet and Network Security Dr. Tb. Maulana Kusuma mkusuma@staff. gunadarma. ac. id http: //staffsite. gunadarma. ac. id/mkusuma Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 0
 An Overview of Telecommunications and Networks Telecommunications: the electronic transmission of signals for communications Telecommunications medium: anything that carries an electronic signal and interfaces between a sending device and a receiving device Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 1
An Overview of Telecommunications and Networks Telecommunications: the electronic transmission of signals for communications Telecommunications medium: anything that carries an electronic signal and interfaces between a sending device and a receiving device Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 1
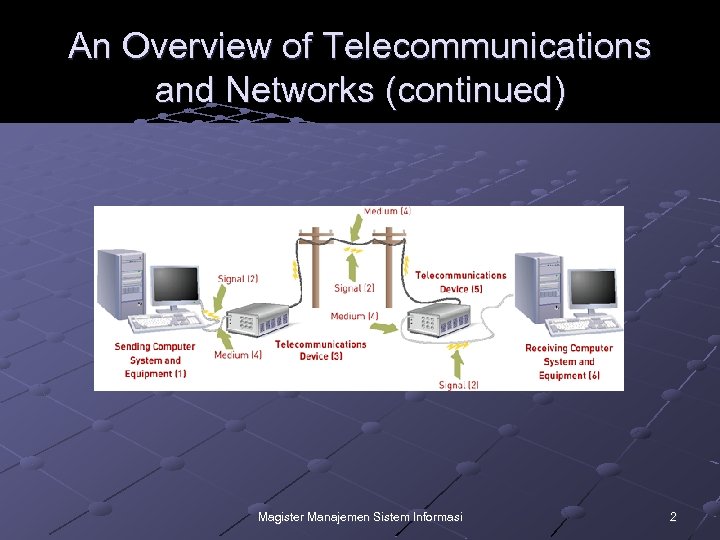 An Overview of Telecommunications and Networks (continued) Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 2
An Overview of Telecommunications and Networks (continued) Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 2
 Use and Functioning of the Internet: a collection of interconnected networks, all freely exchanging information ARPANET n n The ancestor of the Internet A project started by the U. S. Department of Defense (Do. D) in 1969 Internet Protocol (IP): communication standard that enables traffic to be routed from one network to another as needed Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 3
Use and Functioning of the Internet: a collection of interconnected networks, all freely exchanging information ARPANET n n The ancestor of the Internet A project started by the U. S. Department of Defense (Do. D) in 1969 Internet Protocol (IP): communication standard that enables traffic to be routed from one network to another as needed Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 3
 How the Internet Works The Internet transmits data from one computer (called a host) to another If the receiving computer is on a network to which the first computer is directly connected, it can send the message directly If the receiving computer is not on a network to which the sending computer is connected, the sending computer relays the message to another computer that can forward it Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 4
How the Internet Works The Internet transmits data from one computer (called a host) to another If the receiving computer is on a network to which the first computer is directly connected, it can send the message directly If the receiving computer is not on a network to which the sending computer is connected, the sending computer relays the message to another computer that can forward it Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 4
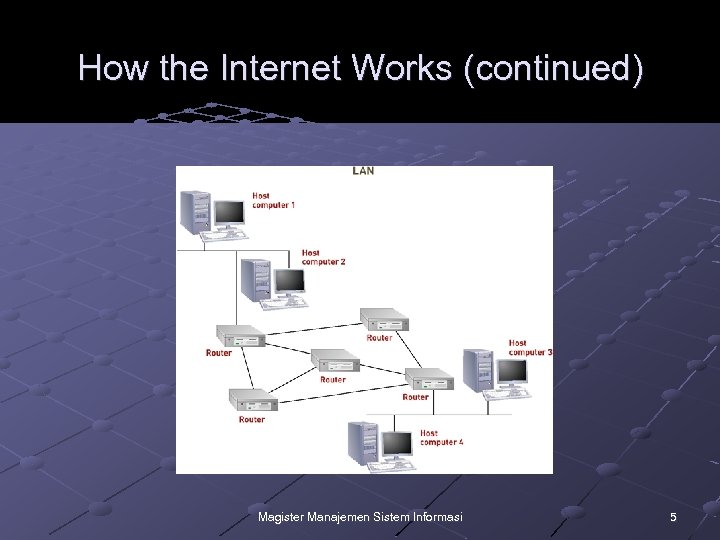 How the Internet Works (continued) Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 5
How the Internet Works (continued) Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 5
 How the Internet Works (continued) Data is passed in chunks called packets Internet Protocol (IP): communications standard that enables traffic to be routed from one network to another as needed Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): widely used transport-layer protocol that is used in combination with IP by most Internet applications Uniform Resource Locator (URL): an assigned address on the Internet for each computer Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 6
How the Internet Works (continued) Data is passed in chunks called packets Internet Protocol (IP): communications standard that enables traffic to be routed from one network to another as needed Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): widely used transport-layer protocol that is used in combination with IP by most Internet applications Uniform Resource Locator (URL): an assigned address on the Internet for each computer Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 6
 Accessing the Internet Connect via a LAN server Connect via Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP)/Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Connect via an online service Other ways to connect Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 7
Accessing the Internet Connect via a LAN server Connect via Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP)/Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Connect via an online service Other ways to connect Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 7
 Accessing the Internet (continued) Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 8
Accessing the Internet (continued) Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 8
 Internet and Telecommunications Services E-mail and instant messaging n Instant messaging: a method that allows two or more individuals to communicate online, using the Internet cell phones and handheld computers Career information and job searching Web log (blog): a Web site that people can create and use to write about their observations, experiences, and feelings on a wide range of topics Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 9
Internet and Telecommunications Services E-mail and instant messaging n Instant messaging: a method that allows two or more individuals to communicate online, using the Internet cell phones and handheld computers Career information and job searching Web log (blog): a Web site that people can create and use to write about their observations, experiences, and feelings on a wide range of topics Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 9
 Internet and Telecommunications Services (continued) Chat rooms: enable two or more people to engage in interactive “conversations” over the Internet phone and videoconferencing services Content streaming: a method for transferring multimedia files over the Internet so that the data stream of voice and pictures plays more or less continuously without a break, or very few of them Shopping on the Web Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 10
Internet and Telecommunications Services (continued) Chat rooms: enable two or more people to engage in interactive “conversations” over the Internet phone and videoconferencing services Content streaming: a method for transferring multimedia files over the Internet so that the data stream of voice and pictures plays more or less continuously without a break, or very few of them Shopping on the Web Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 10
 Internet and Telecommunications Services (continued) Web auctions Music, radio, and video on the Internet Other Internet services and applications Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 11
Internet and Telecommunications Services (continued) Web auctions Music, radio, and video on the Internet Other Internet services and applications Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 11
 Intranets and Extranets Intranet n n n Internal corporate network built using Internet and World Wide Web standards and products Used by employees to gain access to corporate information Slashes the need for paper Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 12
Intranets and Extranets Intranet n n n Internal corporate network built using Internet and World Wide Web standards and products Used by employees to gain access to corporate information Slashes the need for paper Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 12
 Intranets and Extranets (continued) Extranet n A network based on Web technologies that links selected resources of a company’s intranet with its customers, suppliers, or other business partners Virtual private network (VPN): a secure connection between two points across the Internet Tunneling: the process by which VPNs transfer information by encapsulating traffic in IP packets over the Internet Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 13
Intranets and Extranets (continued) Extranet n A network based on Web technologies that links selected resources of a company’s intranet with its customers, suppliers, or other business partners Virtual private network (VPN): a secure connection between two points across the Internet Tunneling: the process by which VPNs transfer information by encapsulating traffic in IP packets over the Internet Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 13
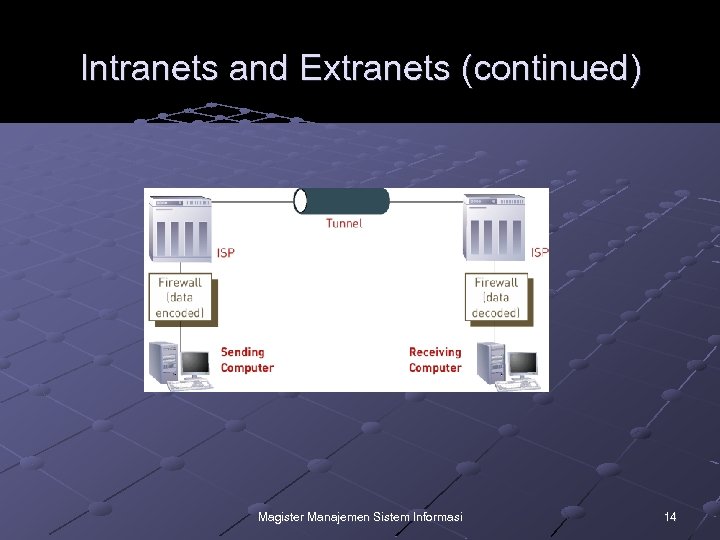 Intranets and Extranets (continued) Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 14
Intranets and Extranets (continued) Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 14
 Net Issues Management issues n No centralized governing body controls the Internet Service and speed issues n Web server computers can be overwhelmed by the amount of “hits” (requests for pages) n More and more Web sites have video, audio clips, or other features that require faster Internet speeds Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 15
Net Issues Management issues n No centralized governing body controls the Internet Service and speed issues n Web server computers can be overwhelmed by the amount of “hits” (requests for pages) n More and more Web sites have video, audio clips, or other features that require faster Internet speeds Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 15
 Net Issues (continued) Privacy n Spyware: hidden files and information trackers that install themselves secretly when you visit some Internet sites n Cookie: a text file that an Internet company can place on the hard disk of a computer system Fraud n Phishing Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 16
Net Issues (continued) Privacy n Spyware: hidden files and information trackers that install themselves secretly when you visit some Internet sites n Cookie: a text file that an Internet company can place on the hard disk of a computer system Fraud n Phishing Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 16
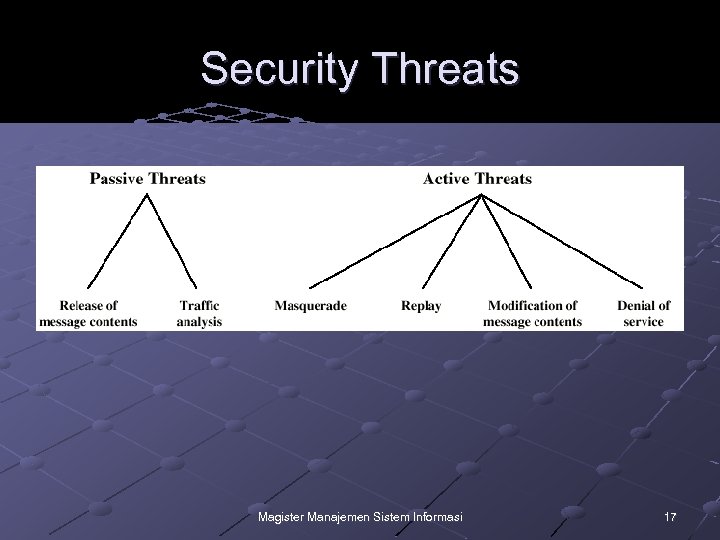 Security Threats Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 17
Security Threats Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 17
 Passive Attacks Eavesdropping on transmissions To obtain information Release of message contents n Outsider learns content of transmission Traffic analysis n By monitoring frequency and length of messages, even encrypted, nature of communication may be guessed Difficult to detect Can be prevented Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 18
Passive Attacks Eavesdropping on transmissions To obtain information Release of message contents n Outsider learns content of transmission Traffic analysis n By monitoring frequency and length of messages, even encrypted, nature of communication may be guessed Difficult to detect Can be prevented Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 18
 Active Attacks Masquerade n Pretending to be a different entity Replay Modification of messages Denial of service Easy to detect n Detection may lead to deterrent Hard to prevent Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 19
Active Attacks Masquerade n Pretending to be a different entity Replay Modification of messages Denial of service Easy to detect n Detection may lead to deterrent Hard to prevent Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 19
 Net Issues (continued) Security with encryption and firewalls n Cryptography: converting a message into a secret code and changing the encoded message back to regular text n Digital signature: encryption technique used to verify the identity of a message sender for processing online financial transactions n Firewall: a device that sits between an internal network and the Internet, limiting access into and out of a network based on access policies Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 20
Net Issues (continued) Security with encryption and firewalls n Cryptography: converting a message into a secret code and changing the encoded message back to regular text n Digital signature: encryption technique used to verify the identity of a message sender for processing online financial transactions n Firewall: a device that sits between an internal network and the Internet, limiting access into and out of a network based on access policies Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 20
 Net Issues (continued) Cryptography is the process of converting a message into a secret code and changing the encoded message back into regular text. Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 21
Net Issues (continued) Cryptography is the process of converting a message into a secret code and changing the encoded message back into regular text. Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 21
 An Introduction To PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE Tb. Maulana Kusuma mkusuma@staff. gunadarma. ac. id Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 22
An Introduction To PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE Tb. Maulana Kusuma mkusuma@staff. gunadarma. ac. id Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 22
 Outline Introduction How to build the trust ? Basic Cryptography One way hashing Digital Signature Certification Authority CA Component Future Technology Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 23
Outline Introduction How to build the trust ? Basic Cryptography One way hashing Digital Signature Certification Authority CA Component Future Technology Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 23
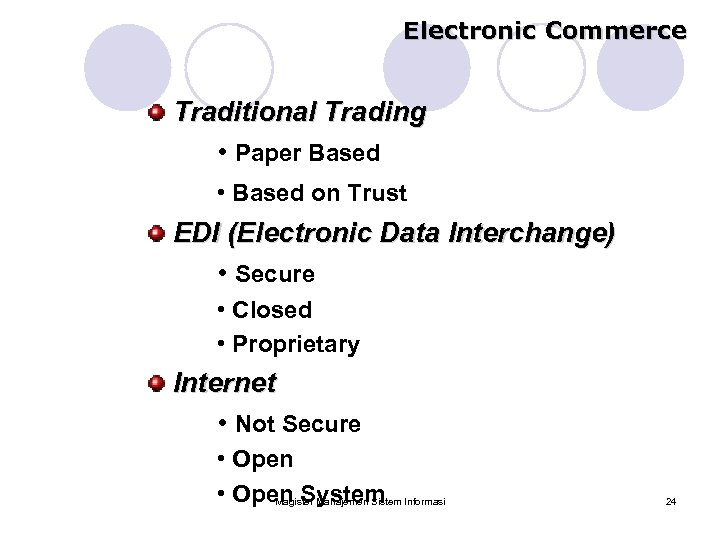 Electronic Commerce Traditional Trading • Paper Based • Based on Trust EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) • Secure • Closed • Proprietary Internet • Not Secure • Open System Informasi Magister Manajemen Sistem 24
Electronic Commerce Traditional Trading • Paper Based • Based on Trust EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) • Secure • Closed • Proprietary Internet • Not Secure • Open System Informasi Magister Manajemen Sistem 24
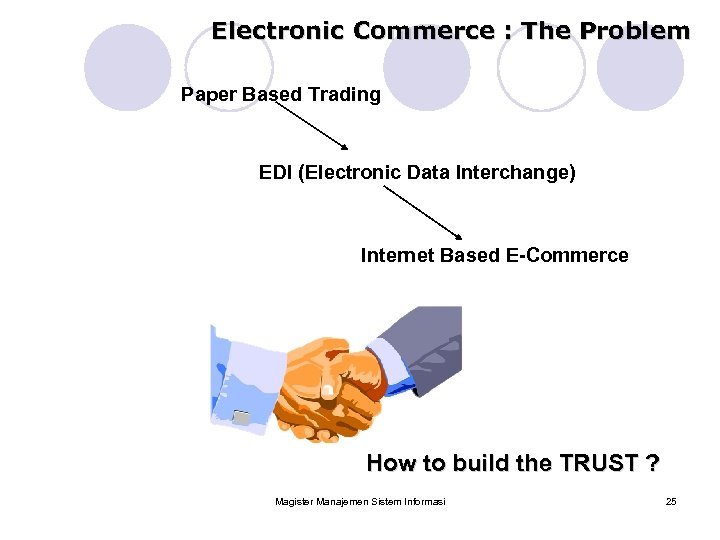 Electronic Commerce : The Problem Paper Based Trading EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) Internet Based E-Commerce How to build the TRUST ? Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 25
Electronic Commerce : The Problem Paper Based Trading EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) Internet Based E-Commerce How to build the TRUST ? Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 25
 The Problem (cont’d) Information over the Internet is Free, Available, Unencrypted, and Untrusted. Not desirable for many Applications ü Electronic Commerce ü Software Products ü Financial Services ü Corporate Data ü Healthcare ü Subscriptions ü Legal Information Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 26
The Problem (cont’d) Information over the Internet is Free, Available, Unencrypted, and Untrusted. Not desirable for many Applications ü Electronic Commerce ü Software Products ü Financial Services ü Corporate Data ü Healthcare ü Subscriptions ü Legal Information Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 26
 Another Problem Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 27
Another Problem Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 27
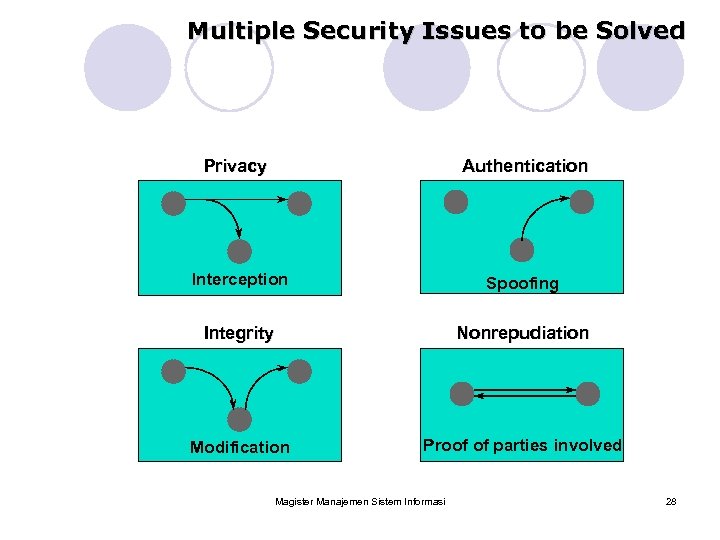 Multiple Security Issues to be Solved Privacy Authentication Interception Spoofing Integrity Nonrepudiation Modification Proof of parties involved Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 28
Multiple Security Issues to be Solved Privacy Authentication Interception Spoofing Integrity Nonrepudiation Modification Proof of parties involved Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 28
 Trust in conducting e-commerce AUTHENTICATION to identify the parties involved CONFIDENTIALITY to keep the information private INTEGRITY to prevent the manipulation of information NON-REPUDIATION to prevent the denial of information by the owner Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 29
Trust in conducting e-commerce AUTHENTICATION to identify the parties involved CONFIDENTIALITY to keep the information private INTEGRITY to prevent the manipulation of information NON-REPUDIATION to prevent the denial of information by the owner Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 29
 Trust in paper based commerce AUTHENTICATION wrote a letter and sign CONFIDENTIALITY put the letter in envelope and seal it INTEGRITY send it by certified mail, make a copy and send it twice NON-REPUDIATION have a witness verified that our signature was authentic Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 30
Trust in paper based commerce AUTHENTICATION wrote a letter and sign CONFIDENTIALITY put the letter in envelope and seal it INTEGRITY send it by certified mail, make a copy and send it twice NON-REPUDIATION have a witness verified that our signature was authentic Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 30
 Technology Outline Basic Cryptography • Symmetric Cryptography • Asymmetric Cryptography One Way Hashing Digital Signature C. A. & Digital Certificate Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 31
Technology Outline Basic Cryptography • Symmetric Cryptography • Asymmetric Cryptography One Way Hashing Digital Signature C. A. & Digital Certificate Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 31
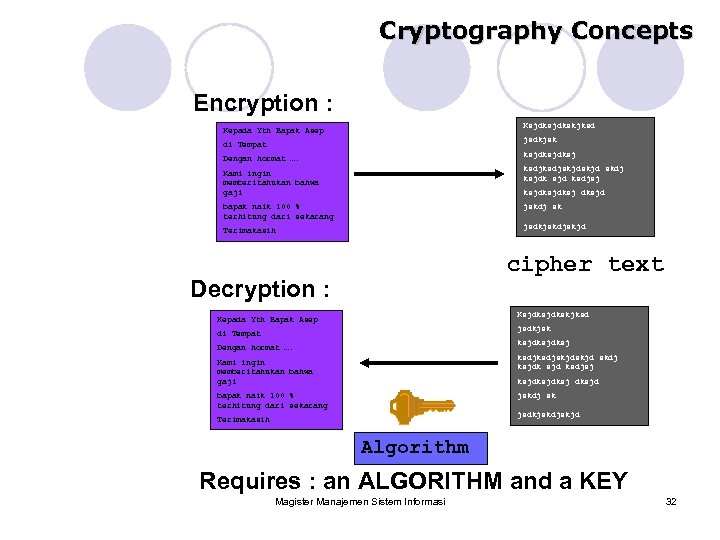 Cryptography Concepts Encryption : Ksjdkskjksd Kepada Yth Bapak Asep jsdkjsk di Tempat ksjdksj Dengan hormat …. ksdjskjd skdj ksjdk sjd ksdjsj Kami ingin memberitahukan bahwa gaji ksjdksjd jskdj sk bapak naik 100 % terhitung dari sekarang jsdkjskdjskjd Terimakasih cipher text Decryption : Ksjdkskjksd Kepada Yth Bapak Asep jsdkjsk di Tempat ksjdksj Dengan hormat …. ksdjskjd skdj ksjdk sjd ksdjsj Kami ingin memberitahukan bahwa gaji ksjdksjd jskdj sk bapak naik 100 % terhitung dari sekarang jsdkjskdjskjd Terimakasih Algorithm Requires : an ALGORITHM and a KEY Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 32
Cryptography Concepts Encryption : Ksjdkskjksd Kepada Yth Bapak Asep jsdkjsk di Tempat ksjdksj Dengan hormat …. ksdjskjd skdj ksjdk sjd ksdjsj Kami ingin memberitahukan bahwa gaji ksjdksjd jskdj sk bapak naik 100 % terhitung dari sekarang jsdkjskdjskjd Terimakasih cipher text Decryption : Ksjdkskjksd Kepada Yth Bapak Asep jsdkjsk di Tempat ksjdksj Dengan hormat …. ksdjskjd skdj ksjdk sjd ksdjsj Kami ingin memberitahukan bahwa gaji ksjdksjd jskdj sk bapak naik 100 % terhitung dari sekarang jsdkjskdjskjd Terimakasih Algorithm Requires : an ALGORITHM and a KEY Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 32
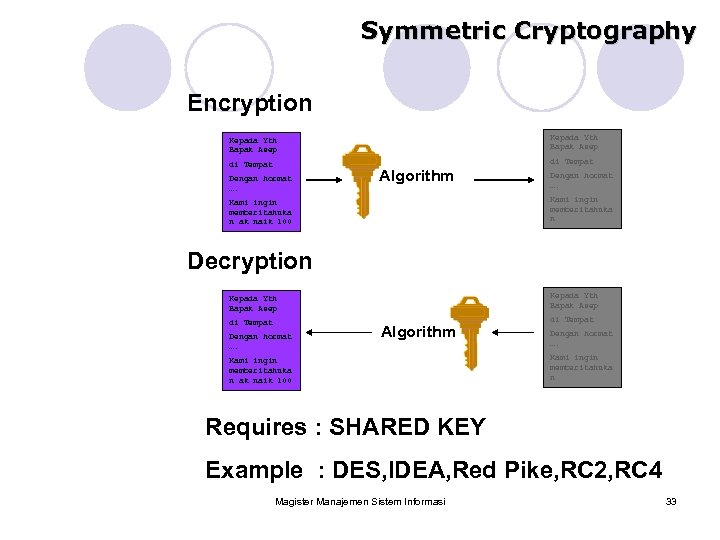 Symmetric Cryptography Encryption Kepada Yth Bapak Asep di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Algorithm Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 Decryption Kepada Yth Bapak Asep di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Algorithm Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n Requires : SHARED KEY Example : DES, IDEA, Red Pike, RC 2, RC 4 Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 33
Symmetric Cryptography Encryption Kepada Yth Bapak Asep di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Algorithm Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 Decryption Kepada Yth Bapak Asep di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Algorithm Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n Requires : SHARED KEY Example : DES, IDEA, Red Pike, RC 2, RC 4 Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 33
 Symmetric Cryptography (cont’d) Characteristic : • High Performance • Useful for Fast Encryption / Decryption • Key management is not practical Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 34
Symmetric Cryptography (cont’d) Characteristic : • High Performance • Useful for Fast Encryption / Decryption • Key management is not practical Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 34
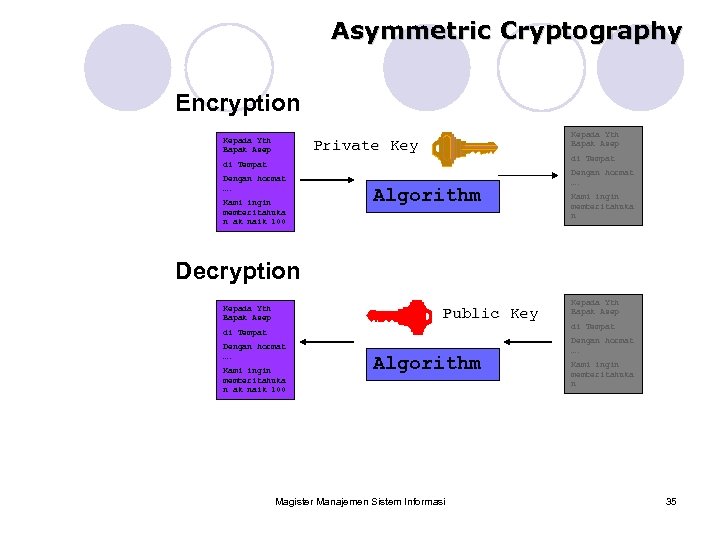 Asymmetric Cryptography Encryption Kepada Yth Bapak Asep Private Key di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 Algorithm Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n Decryption Kepada Yth Bapak Asep Public Key di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 Algorithm Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi Kepada Yth Bapak Asep di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n 35
Asymmetric Cryptography Encryption Kepada Yth Bapak Asep Private Key di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 Algorithm Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n Decryption Kepada Yth Bapak Asep Public Key di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 Algorithm Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi Kepada Yth Bapak Asep di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n 35
 Asymmetric Cryptography (cont’d) Also known as Public Key Cryptography • Public Key is distributed to public • Private Key is kept private • IF Private Key is used to encrypt then ONLY Public Key can decrypt • IF Public Key is used to encrypt then ONLY Private Key can decrypt Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 36
Asymmetric Cryptography (cont’d) Also known as Public Key Cryptography • Public Key is distributed to public • Private Key is kept private • IF Private Key is used to encrypt then ONLY Public Key can decrypt • IF Public Key is used to encrypt then ONLY Private Key can decrypt Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 36
 Asymmetric Cryptography (cont’d) Public Key & Private Key : • Generated as a pair of keys • Derived from very large prime number • It’s impossible to determine one knowing each other • Strength of Key : 512 bit, 1024 bit, 2048 bit …… • Example : RSA, ECC, DSA Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 37
Asymmetric Cryptography (cont’d) Public Key & Private Key : • Generated as a pair of keys • Derived from very large prime number • It’s impossible to determine one knowing each other • Strength of Key : 512 bit, 1024 bit, 2048 bit …… • Example : RSA, ECC, DSA Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 37
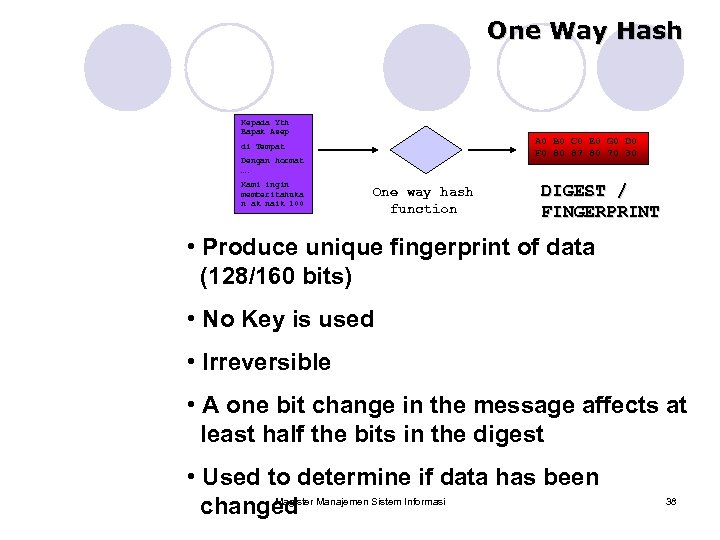 One Way Hash Kepada Yth Bapak Asep A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 G 0 D 0 F 0 80 87 80 70 30 di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 One way hash function DIGEST / FINGERPRINT • Produce unique fingerprint of data (128/160 bits) • No Key is used • Irreversible • A one bit change in the message affects at least half the bits in the digest • Used to determine if data has been Magister changed Manajemen Sistem Informasi 38
One Way Hash Kepada Yth Bapak Asep A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 G 0 D 0 F 0 80 87 80 70 30 di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 One way hash function DIGEST / FINGERPRINT • Produce unique fingerprint of data (128/160 bits) • No Key is used • Irreversible • A one bit change in the message affects at least half the bits in the digest • Used to determine if data has been Magister changed Manajemen Sistem Informasi 38
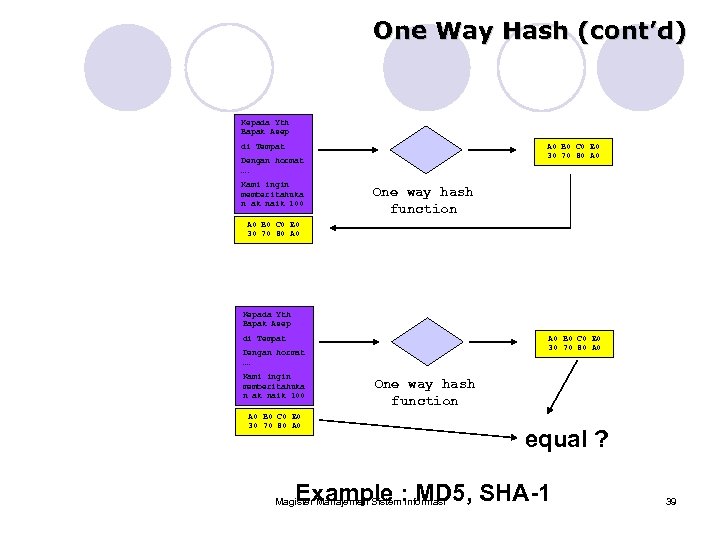 One Way Hash (cont’d) Kepada Yth Bapak Asep di Tempat A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 One way hash function A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 Kepada Yth Bapak Asep A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 One way hash function A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 equal ? Example : MD 5, SHA-1 Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 39
One Way Hash (cont’d) Kepada Yth Bapak Asep di Tempat A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 One way hash function A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 Kepada Yth Bapak Asep A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 One way hash function A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 equal ? Example : MD 5, SHA-1 Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 39
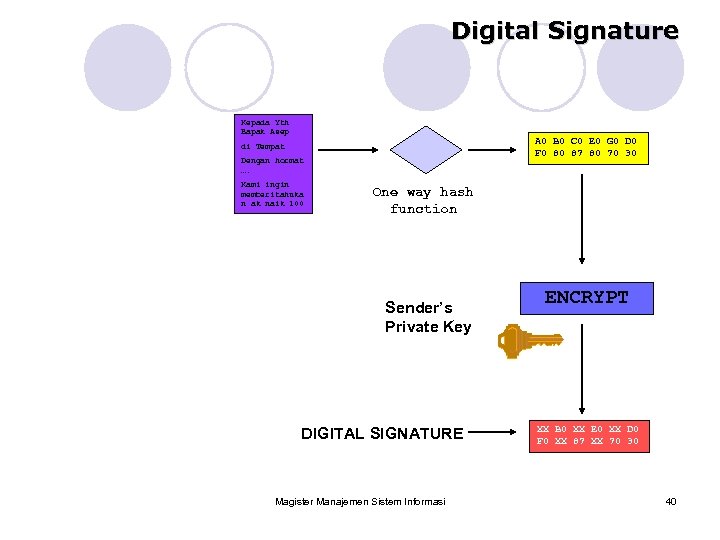 Digital Signature Kepada Yth Bapak Asep A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 G 0 D 0 F 0 80 87 80 70 30 di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 One way hash function Sender’s Private Key DIGITAL SIGNATURE Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi ENCRYPT XX B 0 XX E 0 XX D 0 F 0 XX 87 XX 70 30 40
Digital Signature Kepada Yth Bapak Asep A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 G 0 D 0 F 0 80 87 80 70 30 di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 One way hash function Sender’s Private Key DIGITAL SIGNATURE Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi ENCRYPT XX B 0 XX E 0 XX D 0 F 0 XX 87 XX 70 30 40
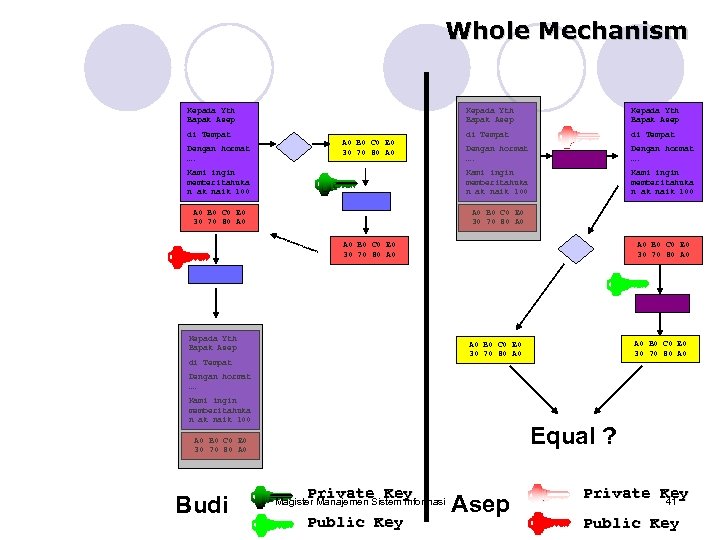 Whole Mechanism Kepada Yth Bapak Asep di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 Kepada Yth Bapak Asep di Tempat Dengan hormat …. A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 Kepada Yth Bapak Asep A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 Equal ? A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 Budi Private Key Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi Public Key Asep Private Key 41 Public Key
Whole Mechanism Kepada Yth Bapak Asep di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 Kepada Yth Bapak Asep di Tempat Dengan hormat …. A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 Kepada Yth Bapak Asep A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 di Tempat Dengan hormat …. Kami ingin memberitahuka n ak naik 100 Equal ? A 0 B 0 C 0 E 0 30 70 80 A 0 Budi Private Key Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi Public Key Asep Private Key 41 Public Key
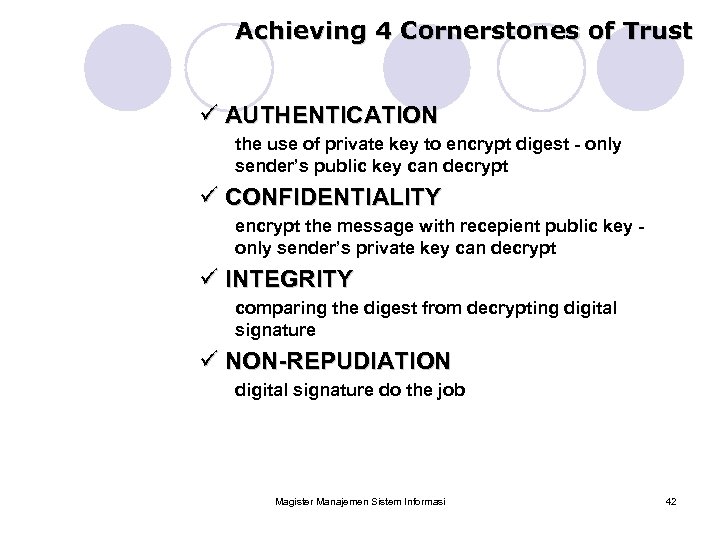 Achieving 4 Cornerstones of Trust ü AUTHENTICATION the use of private key to encrypt digest - only sender’s public key can decrypt ü CONFIDENTIALITY encrypt the message with recepient public key only sender’s private key can decrypt ü INTEGRITY comparing the digest from decrypting digital signature ü NON-REPUDIATION digital signature do the job Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 42
Achieving 4 Cornerstones of Trust ü AUTHENTICATION the use of private key to encrypt digest - only sender’s public key can decrypt ü CONFIDENTIALITY encrypt the message with recepient public key only sender’s private key can decrypt ü INTEGRITY comparing the digest from decrypting digital signature ü NON-REPUDIATION digital signature do the job Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 42
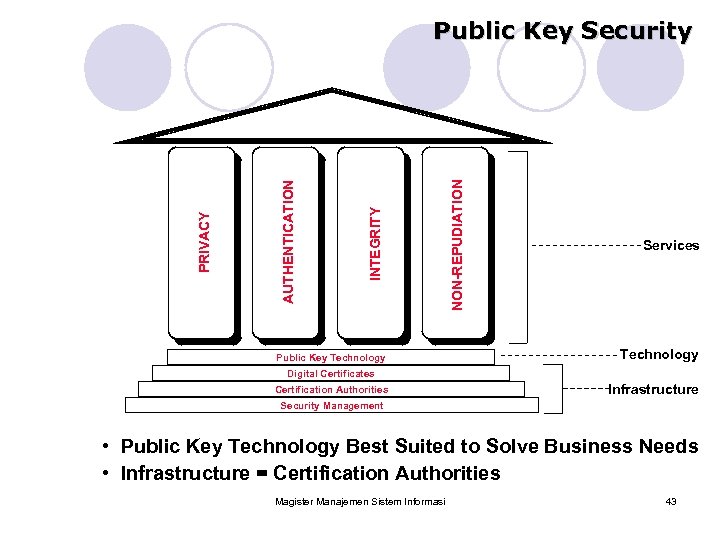 Public Key Technology NON-REPUDIATION INTEGRITY AUTHENTICATION PRIVACY Public Key Security Services Technology Digital Certificates Certification Authorities Infrastructure Security Management • Public Key Technology Best Suited to Solve Business Needs • Infrastructure = Certification Authorities Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 43
Public Key Technology NON-REPUDIATION INTEGRITY AUTHENTICATION PRIVACY Public Key Security Services Technology Digital Certificates Certification Authorities Infrastructure Security Management • Public Key Technology Best Suited to Solve Business Needs • Infrastructure = Certification Authorities Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 43
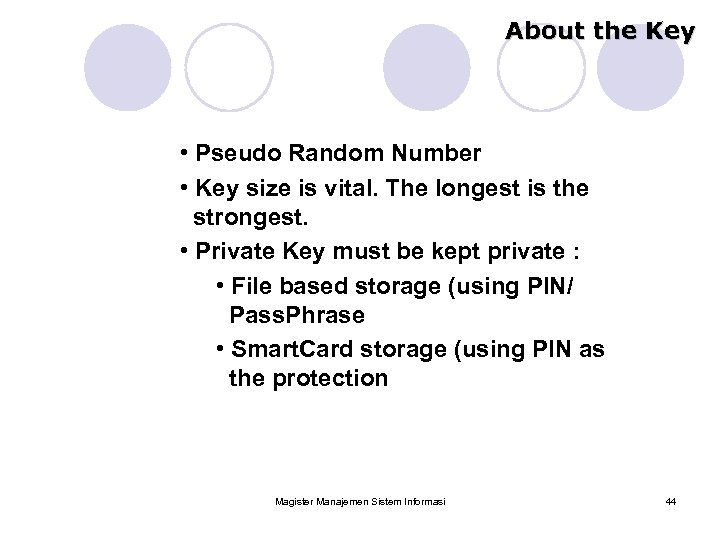 About the Key • Pseudo Random Number • Key size is vital. The longest is the strongest. • Private Key must be kept private : • File based storage (using PIN/ Pass. Phrase • Smart. Card storage (using PIN as the protection Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 44
About the Key • Pseudo Random Number • Key size is vital. The longest is the strongest. • Private Key must be kept private : • File based storage (using PIN/ Pass. Phrase • Smart. Card storage (using PIN as the protection Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 44
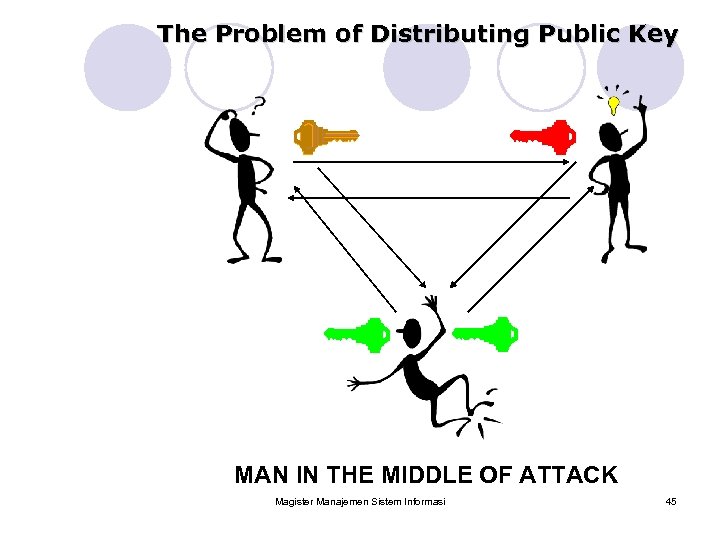 The Problem of Distributing Public Key MAN IN THE MIDDLE OF ATTACK Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 45
The Problem of Distributing Public Key MAN IN THE MIDDLE OF ATTACK Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 45
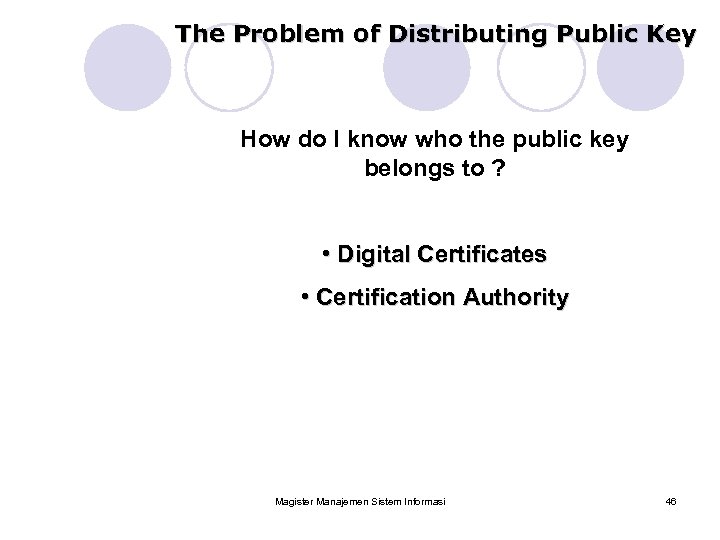 The Problem of Distributing Public Key How do I know who the public key belongs to ? • Digital Certificates • Certification Authority Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 46
The Problem of Distributing Public Key How do I know who the public key belongs to ? • Digital Certificates • Certification Authority Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 46
 Digital Certificate • A certificate binds a public key to an owner • It is the envelope to distribute public key • The trusted CA digitally sign the certificate to verify the ownership of the key itself Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 47
Digital Certificate • A certificate binds a public key to an owner • It is the envelope to distribute public key • The trusted CA digitally sign the certificate to verify the ownership of the key itself Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 47
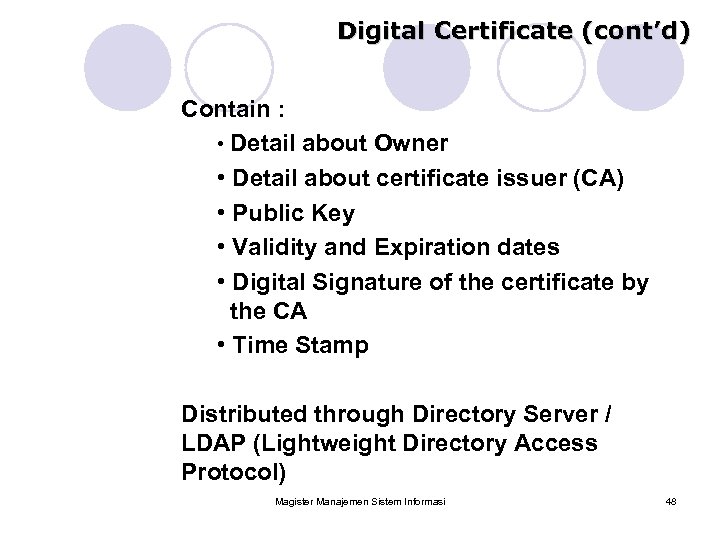 Digital Certificate (cont’d) Contain : • Detail about Owner • Detail about certificate issuer (CA) • Public Key • Validity and Expiration dates • Digital Signature of the certificate by the CA • Time Stamp Distributed through Directory Server / LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 48
Digital Certificate (cont’d) Contain : • Detail about Owner • Detail about certificate issuer (CA) • Public Key • Validity and Expiration dates • Digital Signature of the certificate by the CA • Time Stamp Distributed through Directory Server / LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 48
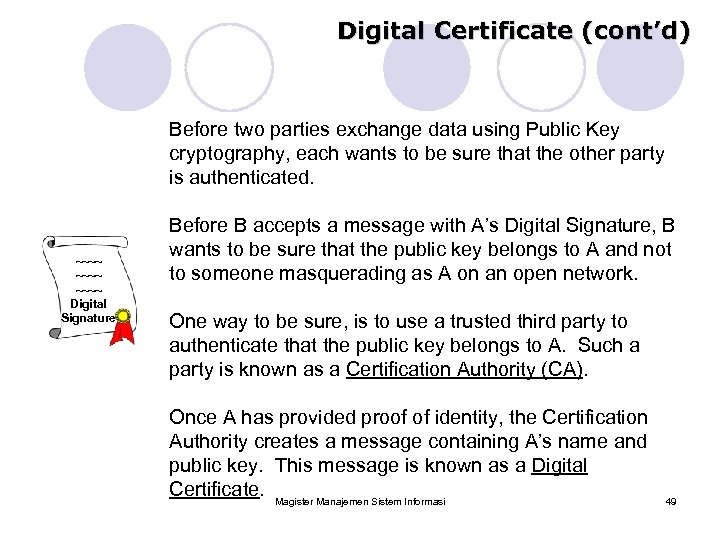 Digital Certificate (cont’d) Before two parties exchange data using Public Key cryptography, each wants to be sure that the other party is authenticated. ~~~~ Digital Signature Before B accepts a message with A’s Digital Signature, B wants to be sure that the public key belongs to A and not to someone masquerading as A on an open network. One way to be sure, is to use a trusted third party to authenticate that the public key belongs to A. Such a party is known as a Certification Authority (CA). Once A has provided proof of identity, the Certification Authority creates a message containing A’s name and public key. This message is known as a Digital Certificate. Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 49
Digital Certificate (cont’d) Before two parties exchange data using Public Key cryptography, each wants to be sure that the other party is authenticated. ~~~~ Digital Signature Before B accepts a message with A’s Digital Signature, B wants to be sure that the public key belongs to A and not to someone masquerading as A on an open network. One way to be sure, is to use a trusted third party to authenticate that the public key belongs to A. Such a party is known as a Certification Authority (CA). Once A has provided proof of identity, the Certification Authority creates a message containing A’s name and public key. This message is known as a Digital Certificate. Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 49
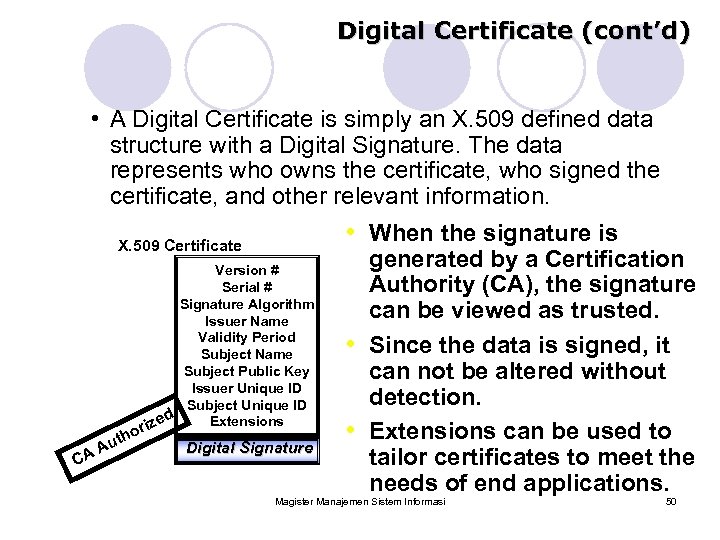 Digital Certificate (cont’d) • A Digital Certificate is simply an X. 509 defined data structure with a Digital Signature. The data represents who owns the certificate, who signed the certificate, and other relevant information. • When the signature is X. 509 Certificate generated by a Certification Version # Serial # Authority (CA), the signature Signature Algorithm can be viewed as trusted. Issuer Name Validity Period • Since the data is signed, it Subject Name Subject Public Key can not be altered without Issuer Unique ID detection. Subject Unique ID ed Extensions riz o • Extensions can be used to uth Digital Signature A tailor certificates to meet the CA needs of end applications. Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 50
Digital Certificate (cont’d) • A Digital Certificate is simply an X. 509 defined data structure with a Digital Signature. The data represents who owns the certificate, who signed the certificate, and other relevant information. • When the signature is X. 509 Certificate generated by a Certification Version # Serial # Authority (CA), the signature Signature Algorithm can be viewed as trusted. Issuer Name Validity Period • Since the data is signed, it Subject Name Subject Public Key can not be altered without Issuer Unique ID detection. Subject Unique ID ed Extensions riz o • Extensions can be used to uth Digital Signature A tailor certificates to meet the CA needs of end applications. Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 50
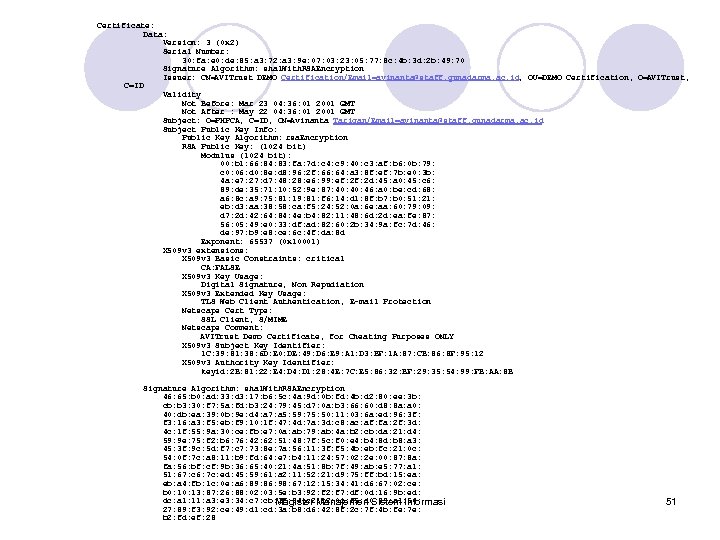 Certificate: Data: Version: 3 (0 x 2) Serial Number: 30: fa: e 0: de: 85: a 3: 72: a 3: 9 e: 07: 03: 23: 05: 77: 8 c: 4 b: 3 d: 2 b: 49: 70 Signature Algorithm: sha 1 With. RSAEncryption Issuer: CN=AVITrust DEMO Certification/Email=avinanta@staff. gunadarma. ac. id, OU=DEMO Certification, O=AVITrust, C=ID Validity Not Before: Mar 23 04: 36: 01 2001 GMT Not After : May 22 04: 36: 01 2001 GMT Subject: O=PHPCA, C=ID, CN= Avinanta Tarigan/Email=avinanta@staff. gunadarma. ac. id Subject Public Key Info: Public Key Algorithm: rsa. Encryption RSA Public Key: (1024 bit) Modulus (1024 bit): 00: b 1: 66: 84: 83: fa: 7 d: c 4: c 9: 40: c 3: af: b 6: 0 b: 79: c 0: 06: d 0: 8 e: d 8: 96: 2 f: 66: 64: a 3: 8 f: ef: 7 b: e 0: 3 b: 4 a: e 7: 27: d 7: 48: 28: e 6: 99: ef: 2 d: 45: a 0: 45: c 6: 89: de: 35: 71: 10: 52: 9 e: 87: 40: 46: a 0: be: cd: 68: a 6: 8 c: a 9: 75: 81: 19: 81: f 6: 14: d 1: 8 f: b 7: b 0: 51: 21: eb: d 3: aa: 38: 58: ca: f 5: 24: 52: 0 a: 6 e: aa: 60: 79: 09: d 7: 2 d: 42: 64: 84: 4 e: b 4: 82: 11: 48: 6 d: 2 d: ea: fe: 87: 56: 05: 49: e 0: 33: df: ad: 82: 60: 2 b: 34: 9 a: fc: 7 d: 46: de: 97: b 9: e 8: ce: 6 c: 4 f: da: 8 d Exponent: 65537 (0 x 10001) X 509 v 3 extensions: X 509 v 3 Basic Constraints: critical CA: FALSE X 509 v 3 Key Usage: Digital Signature, Non Repudiation X 509 v 3 Extended Key Usage: TLS Web Client Authentication, E-mail Protection Netscape Cert Type: SSL Client, S/MIME Netscape Comment: AVITrust Demo Certificate, for Cheating Purposes ONLY X 509 v 3 Subject Key Identifier: 1 C: 39: 81: 38: 6 D: E 0: DE: 49: D 6: E 9: A 1: D 3: BF: 1 A: 87: CB: 86: 8 F: 95: 12 X 509 v 3 Authority Key Identifier: keyid: 2 B: 81: 22: E 4: D 1: 28: 4 E: 7 C: E 5: 86: 32: BF: 29: 35: 54: 99: FB: AA: 8 B Signature Algorithm: sha 1 With. RSAEncryption 46: 65: b 0: ad: 33: d 3: 17: b 6: 5 c: 4 a: 9 d: 0 b: fd: 4 b: d 2: 80: ee: 3 b: cb: b 3: 30: f 7: 5 a: fd: b 3: 24: 79: 45: d 7: 0 a: b 3: 66: 60: d 8: 8 a: a 0: 40: db: ea: 39: 0 b: 9 e: d 4: a 7: a 5: 59: 75: 50: 11: 03: 6 a: ed: 96: 3 f: f 3: 16: a 3: f 5: eb: f 9: 10: 1 f: 47: 4 d: 7 a: 3 d: c 8: ac: af: fa: 2 f: 3 d: 4 c: 1 f: 55: 9 a: 30: ce: fb: e 7: 0 a: ab: 79: ab: 4 a: b 2: cb: da: 21: d 4: 59: 9 e: 75: f 2: b 6: 76: 42: 62: 51: 48: 7 f: 5 c: f 0: e 4: b 4: 8 d: b 8: a 3: 45: 3 f: 9 c: 5 d: f 7: c 7: 73: 8 e: 7 a: 56: 11: 3 f: f 5: 4 b: eb: fc: 21: 0 c: 54: 0 f: 7 c: a 8: 11: b 9: fd: 64: e 7: b 4: 11: 24: 57: 02: 2 e: 00: 87: 8 a: fa: 56: bf: cf: 9 b: 36: 65: 40: 21: 4 a: 51: 8 b: 7 f: 49: ab: e 5: 77: a 1: 51: 67: c 6: 7 c: ed: 45: 59: 61: a 2: 11: 52: 21: d 9: 75: ff: bd: 15: ea: eb: a 4: fb: 1 c: 0 e: a 6: 89: 86: 98: 67: 12: 15: 34: 41: d 6: 67: 02: ce: b 0: 13: 87: 26: 88: 02: 03: 5 e: b 3: 92: f 7: df: 0 d: 16: 9 b: ed: dc: a 1: 11: a 3: e 3: 34: c 7: cb: 1 f: 94: c 2: b 2: 0 c: f 5: d 0: 89: a 1: 50: Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 27: 89: f 3: 92: ce: 49: d 1: cd: 3 a: b 8: d 6: 42: 8 f: 2 c: 7 f: 4 b: fe: 7 e: b 2: fd: ef: 28 51
Certificate: Data: Version: 3 (0 x 2) Serial Number: 30: fa: e 0: de: 85: a 3: 72: a 3: 9 e: 07: 03: 23: 05: 77: 8 c: 4 b: 3 d: 2 b: 49: 70 Signature Algorithm: sha 1 With. RSAEncryption Issuer: CN=AVITrust DEMO Certification/Email=avinanta@staff. gunadarma. ac. id, OU=DEMO Certification, O=AVITrust, C=ID Validity Not Before: Mar 23 04: 36: 01 2001 GMT Not After : May 22 04: 36: 01 2001 GMT Subject: O=PHPCA, C=ID, CN= Avinanta Tarigan/Email=avinanta@staff. gunadarma. ac. id Subject Public Key Info: Public Key Algorithm: rsa. Encryption RSA Public Key: (1024 bit) Modulus (1024 bit): 00: b 1: 66: 84: 83: fa: 7 d: c 4: c 9: 40: c 3: af: b 6: 0 b: 79: c 0: 06: d 0: 8 e: d 8: 96: 2 f: 66: 64: a 3: 8 f: ef: 7 b: e 0: 3 b: 4 a: e 7: 27: d 7: 48: 28: e 6: 99: ef: 2 d: 45: a 0: 45: c 6: 89: de: 35: 71: 10: 52: 9 e: 87: 40: 46: a 0: be: cd: 68: a 6: 8 c: a 9: 75: 81: 19: 81: f 6: 14: d 1: 8 f: b 7: b 0: 51: 21: eb: d 3: aa: 38: 58: ca: f 5: 24: 52: 0 a: 6 e: aa: 60: 79: 09: d 7: 2 d: 42: 64: 84: 4 e: b 4: 82: 11: 48: 6 d: 2 d: ea: fe: 87: 56: 05: 49: e 0: 33: df: ad: 82: 60: 2 b: 34: 9 a: fc: 7 d: 46: de: 97: b 9: e 8: ce: 6 c: 4 f: da: 8 d Exponent: 65537 (0 x 10001) X 509 v 3 extensions: X 509 v 3 Basic Constraints: critical CA: FALSE X 509 v 3 Key Usage: Digital Signature, Non Repudiation X 509 v 3 Extended Key Usage: TLS Web Client Authentication, E-mail Protection Netscape Cert Type: SSL Client, S/MIME Netscape Comment: AVITrust Demo Certificate, for Cheating Purposes ONLY X 509 v 3 Subject Key Identifier: 1 C: 39: 81: 38: 6 D: E 0: DE: 49: D 6: E 9: A 1: D 3: BF: 1 A: 87: CB: 86: 8 F: 95: 12 X 509 v 3 Authority Key Identifier: keyid: 2 B: 81: 22: E 4: D 1: 28: 4 E: 7 C: E 5: 86: 32: BF: 29: 35: 54: 99: FB: AA: 8 B Signature Algorithm: sha 1 With. RSAEncryption 46: 65: b 0: ad: 33: d 3: 17: b 6: 5 c: 4 a: 9 d: 0 b: fd: 4 b: d 2: 80: ee: 3 b: cb: b 3: 30: f 7: 5 a: fd: b 3: 24: 79: 45: d 7: 0 a: b 3: 66: 60: d 8: 8 a: a 0: 40: db: ea: 39: 0 b: 9 e: d 4: a 7: a 5: 59: 75: 50: 11: 03: 6 a: ed: 96: 3 f: f 3: 16: a 3: f 5: eb: f 9: 10: 1 f: 47: 4 d: 7 a: 3 d: c 8: ac: af: fa: 2 f: 3 d: 4 c: 1 f: 55: 9 a: 30: ce: fb: e 7: 0 a: ab: 79: ab: 4 a: b 2: cb: da: 21: d 4: 59: 9 e: 75: f 2: b 6: 76: 42: 62: 51: 48: 7 f: 5 c: f 0: e 4: b 4: 8 d: b 8: a 3: 45: 3 f: 9 c: 5 d: f 7: c 7: 73: 8 e: 7 a: 56: 11: 3 f: f 5: 4 b: eb: fc: 21: 0 c: 54: 0 f: 7 c: a 8: 11: b 9: fd: 64: e 7: b 4: 11: 24: 57: 02: 2 e: 00: 87: 8 a: fa: 56: bf: cf: 9 b: 36: 65: 40: 21: 4 a: 51: 8 b: 7 f: 49: ab: e 5: 77: a 1: 51: 67: c 6: 7 c: ed: 45: 59: 61: a 2: 11: 52: 21: d 9: 75: ff: bd: 15: ea: eb: a 4: fb: 1 c: 0 e: a 6: 89: 86: 98: 67: 12: 15: 34: 41: d 6: 67: 02: ce: b 0: 13: 87: 26: 88: 02: 03: 5 e: b 3: 92: f 7: df: 0 d: 16: 9 b: ed: dc: a 1: 11: a 3: e 3: 34: c 7: cb: 1 f: 94: c 2: b 2: 0 c: f 5: d 0: 89: a 1: 50: Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 27: 89: f 3: 92: ce: 49: d 1: cd: 3 a: b 8: d 6: 42: 8 f: 2 c: 7 f: 4 b: fe: 7 e: b 2: fd: ef: 28 51
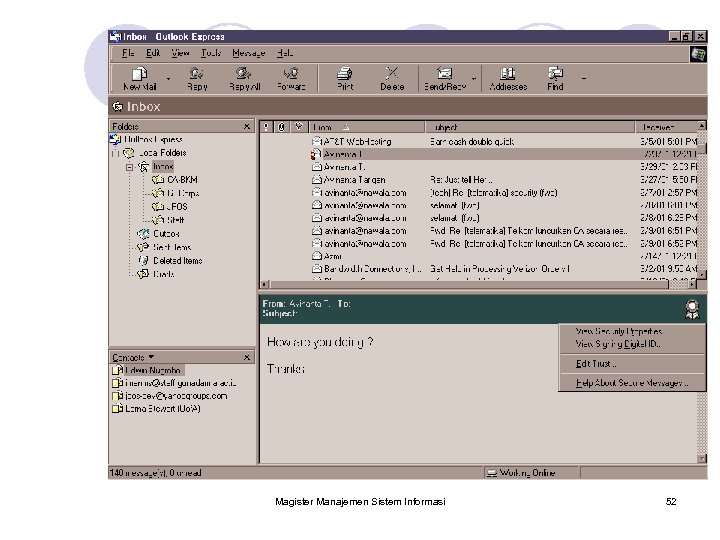 Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 52
Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 52
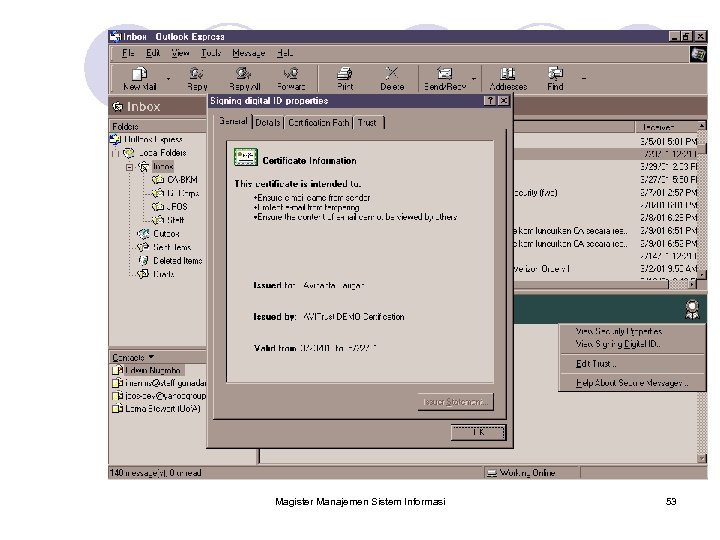 Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 53
Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 53
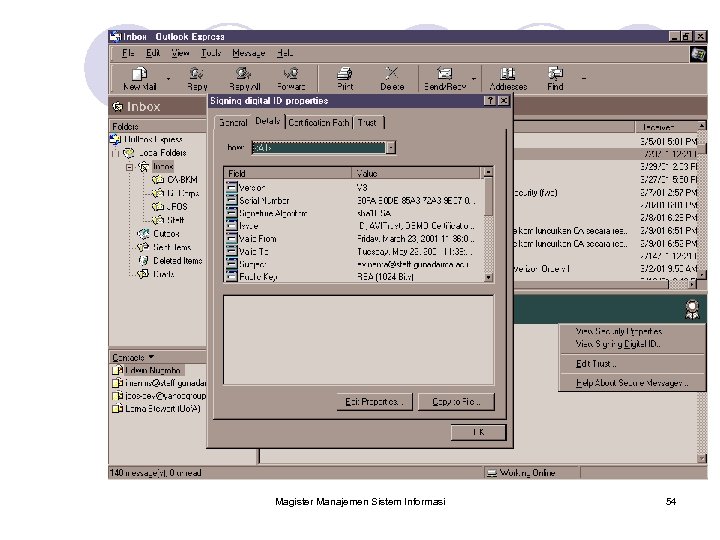 Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 54
Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 54
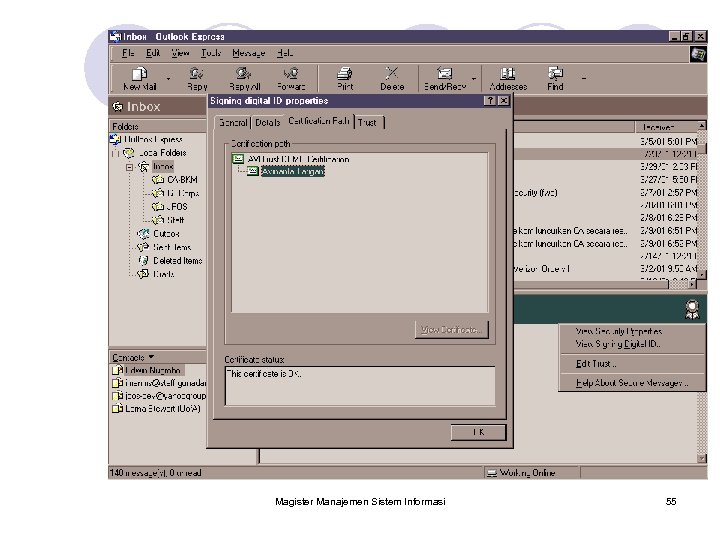 Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 55
Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 55
 What is a Certification Authority? Certification Authority • Trusted (Third) Party • Enrolls and Validates What’s Important • Operational Experience • High Assurance Security Subscribers Architecture • Issues and Manages Certificates • Manages Revocation and Renewal of Certificates • Establishes Policies & Procedures • • • Scalability Flexibility / Tailorability Interoperability Outsource vs. Inhouse Trustworthiness Certification Authority = Basis of Trust Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 56
What is a Certification Authority? Certification Authority • Trusted (Third) Party • Enrolls and Validates What’s Important • Operational Experience • High Assurance Security Subscribers Architecture • Issues and Manages Certificates • Manages Revocation and Renewal of Certificates • Establishes Policies & Procedures • • • Scalability Flexibility / Tailorability Interoperability Outsource vs. Inhouse Trustworthiness Certification Authority = Basis of Trust Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 56
 Certification Authority (cont’d) • Authoring the Certificates • Responsible in validating the owner of the public key • Distribute the Certificates in CA’s Directory Server • Create CRL (Certification Revocation List) • Usually Government Institution or National Chamber of Commerce Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 57
Certification Authority (cont’d) • Authoring the Certificates • Responsible in validating the owner of the public key • Distribute the Certificates in CA’s Directory Server • Create CRL (Certification Revocation List) • Usually Government Institution or National Chamber of Commerce Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 57
 Trusted CA’s • When someone receives a certificate, why should they trust the signature? ~~~~ Digital Signature ? • Trusted CAs are required in order to verify a signature. If you Trust the CA that signed the certificate, you can trust the certificate. • Many Companies are embedding Trusted CA Certificates in their Certificate Enabled products – Netscape Navigator (Options, Security Preferences, Site Cert) – Microsoft Internet Explorer (Tool, Internet Options, Content, Cert) • Some products refer to Trusted CAs as Trusted Site Certificates. Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 58
Trusted CA’s • When someone receives a certificate, why should they trust the signature? ~~~~ Digital Signature ? • Trusted CAs are required in order to verify a signature. If you Trust the CA that signed the certificate, you can trust the certificate. • Many Companies are embedding Trusted CA Certificates in their Certificate Enabled products – Netscape Navigator (Options, Security Preferences, Site Cert) – Microsoft Internet Explorer (Tool, Internet Options, Content, Cert) • Some products refer to Trusted CAs as Trusted Site Certificates. Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 58
 Public Key Infrastructure Typically consist of : • Certification Authorities • Registration Authorities • Directories • PKI-Enabled Applications • Policies & Procedures Usually : • 20 % technology • 80 % policy Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 59
Public Key Infrastructure Typically consist of : • Certification Authorities • Registration Authorities • Directories • PKI-Enabled Applications • Policies & Procedures Usually : • 20 % technology • 80 % policy Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 59
 Future Enhancement Stronger Non-Repudiation : • What do you have ? The use of smartcard to store private key • What do you know ? Protecting the smartcard with PIN • When The use of global timestamp server • Who you are ? Biometrics Validation to activate Smart. Card : • Fingerprint Scan • Retina Scan, Voice Recognition • DNA Validation, etc. Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 60
Future Enhancement Stronger Non-Repudiation : • What do you have ? The use of smartcard to store private key • What do you know ? Protecting the smartcard with PIN • When The use of global timestamp server • Who you are ? Biometrics Validation to activate Smart. Card : • Fingerprint Scan • Retina Scan, Voice Recognition • DNA Validation, etc. Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 60
 Conclusion PKI brings 4 basic principle in building the trust from paper based The CA is needed to verify public key by envelope it in Digital Certificate PKI : 20% technology, 80% policy Stronger Non-Repudiation is supported PKI is an umbrella for E-Commerce Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 61
Conclusion PKI brings 4 basic principle in building the trust from paper based The CA is needed to verify public key by envelope it in Digital Certificate PKI : 20% technology, 80% policy Stronger Non-Repudiation is supported PKI is an umbrella for E-Commerce Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 61
 Conclusion (cont’d) Symmetric Key vs. Public Key Encryption - Public key is easier to manage than symmetric key. Easier to recover when compromised. Digital Signature - Provides a digital seal indicating who signed the data. Can be used in many applications. Digital Certificate - Identity data signed by a Certification Authority. Provides a Trusted source of identification. Authentication/Access Control - Digital Certificates can be used to identify users and limit access to information, systems, etc. on Open Networks. Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 62
Conclusion (cont’d) Symmetric Key vs. Public Key Encryption - Public key is easier to manage than symmetric key. Easier to recover when compromised. Digital Signature - Provides a digital seal indicating who signed the data. Can be used in many applications. Digital Certificate - Identity data signed by a Certification Authority. Provides a Trusted source of identification. Authentication/Access Control - Digital Certificates can be used to identify users and limit access to information, systems, etc. on Open Networks. Magister Manajemen Sistem Informasi 62


