E-business models.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Internet Business Models Hung, Chia-Linag 2006, Spring
Objectives • Internet commerce patterns • Business models • E-business models • Survival indicators

Internet commerce linkage • B 2 B – Business hub (exchange) for equipments, material, operation, maintenance, etc. , on the Internet • B 2 C – Direct sale to customer over Internet • C 2 C – Customer community for information/product exchange • C 2 B – Actively queried by demanders and response from business suppliers – Reverse auction, e. g. , priceline. com
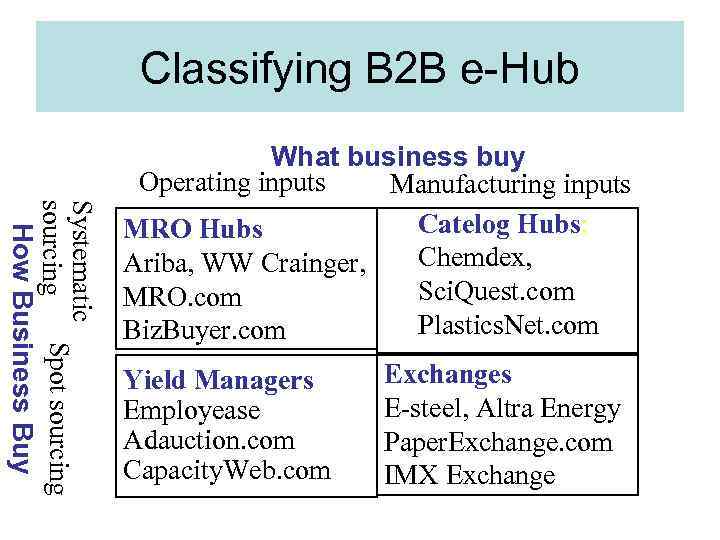
Classifying B 2 B e-Hub What business buy Operating inputs Manufacturing inputs Systematic Spot sourcing How Business Buy MRO Hubs Ariba, WW Crainger, MRO. com Biz. Buyer. com Yield Managers Employease Adauction. com Capacity. Web. com Catelog Hubs: Chemdex, Sci. Quest. com Plastics. Net. com Exchanges E-steel, Altra Energy Paper. Exchange. com IMX Exchange
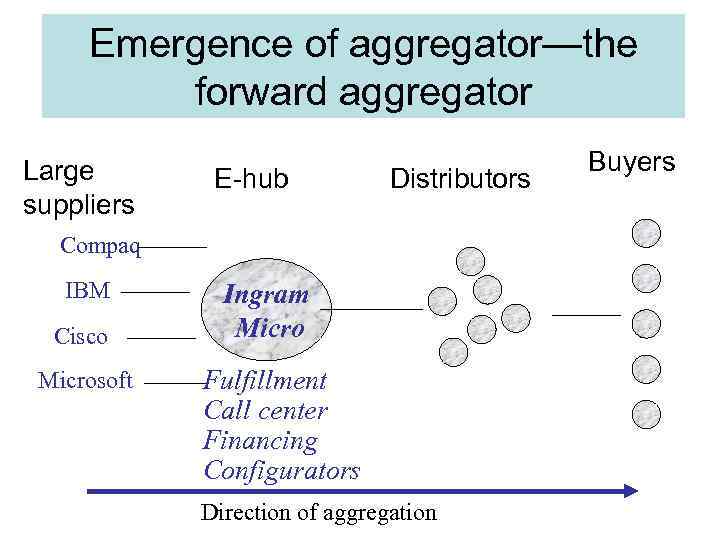
Emergence of aggregator—the forward aggregator Large suppliers E-hub Distributors Compaq IBM Cisco Microsoft Ingram Micro Fulfillment Call center Financing Configurators Direction of aggregation Buyers
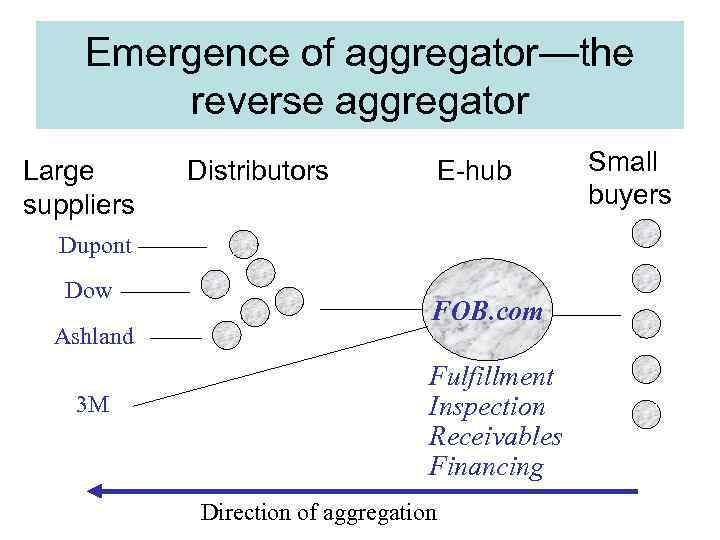
Emergence of aggregator—the reverse aggregator Large suppliers Distributors E-hub Dupont Dow Ashland 3 M FOB. com Fulfillment Inspection Receivables Financing Direction of aggregation Small buyers

B 2 C e-commerce • Internet direct sale – Migration from physical enterprise to virtual web—Dell – Pure virtual e-commerce—Amazon. com, • Cooperate with physical retailer • Internet intermediary – Information aggregator— 104. com

C 2 C e-commerce • Community – Information portal/exchange centers, pchome. com, Yahoo! – Interest clubs, i. Village. com, youthwant. com • Auction – Used product bazaar, e. Bay. com, u. Bid. com • P 2 P – Napster, Gnutella, etc.
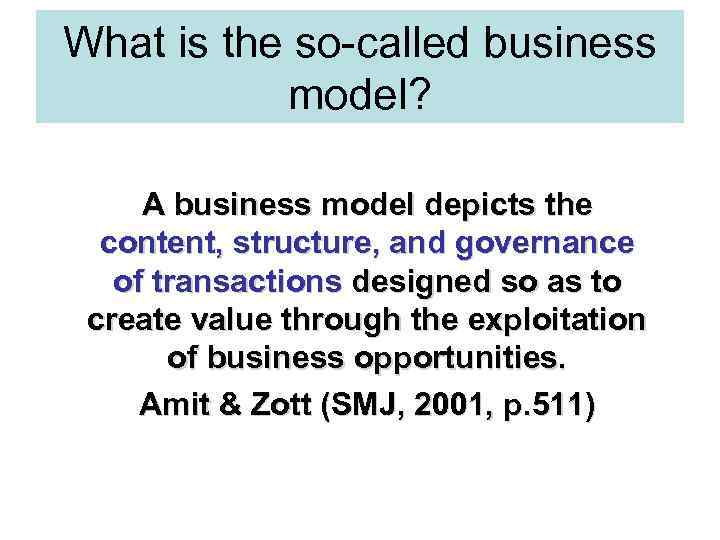
What is the so-called business model? A business model depicts the content, structure, and governance of transactions designed so as to create value through the exploitation of business opportunities. Amit & Zott (SMJ, 2001, p. 511)

The Content of Business Model • The good or information that are being exchanged • The resources and capabilities that are required to enable the exchange • E. g. , transparency of transaction, vertical & horizontal expansion of product/service, the degree of customization, technologies of transaction

The Structure of Business Model • The parties that participate in the exchange • The ways in which these parties are linked • The order process and the adopted exchange mechanism • E. g. , the providers of complementary assets, transaction speed, mode, simplicity, safety & reliability, integration of online & offline supply chains

The Governance of Business Model • The ways in which flows of information, resources, and goods are controlled by the relative parties • The incentives for the participants in transactions • E. g. , cooperative and shared incentive among allied partners, commitment and investment of co-specialized assets, loyalty maintenance
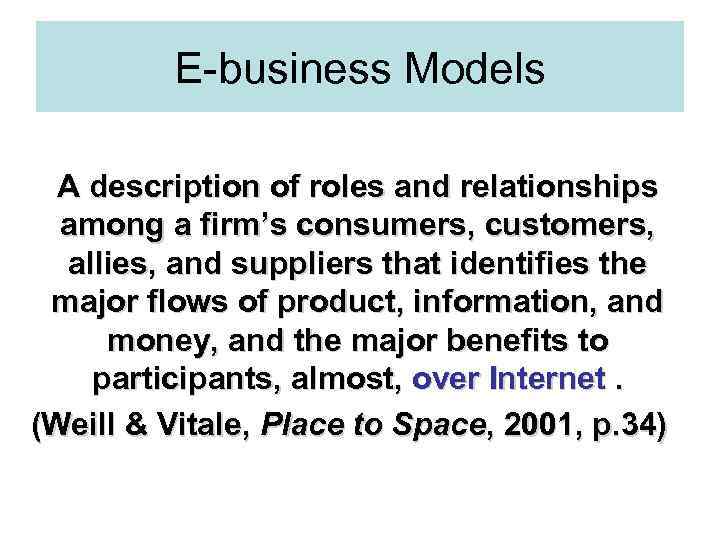
E-business Models A description of roles and relationships among a firm’s consumers, customers, allies, and suppliers that identifies the major flows of product, information, and money, and the major benefits to participants, almost, over Internet. (Weill & Vitale, Place to Space, 2001, p. 34)
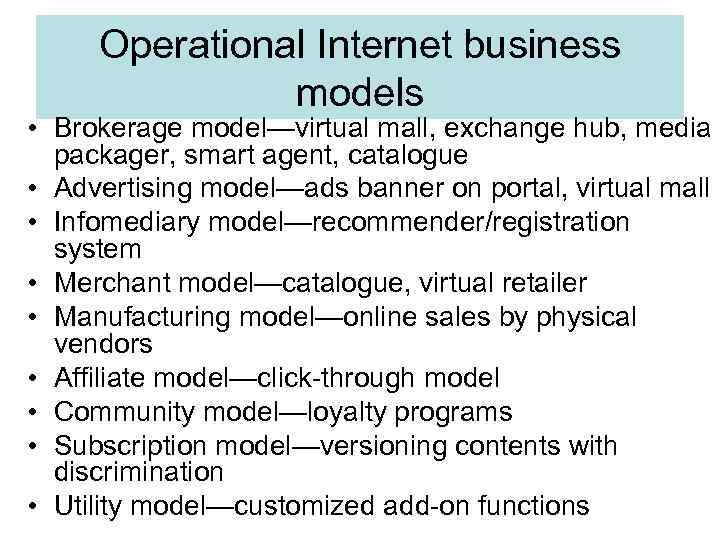
Operational Internet business models • Brokerage model—virtual mall, exchange hub, media packager, smart agent, catalogue • Advertising model—ads banner on portal, virtual mall • Infomediary model—recommender/registration system • Merchant model—catalogue, virtual retailer • Manufacturing model—online sales by physical vendors • Affiliate model—click-through model • Community model—loyalty programs • Subscription model—versioning contents with discrimination • Utility model—customized add-on functions

Indicators of survival business model • • Customer value—segmentation, value proposition Scope—core or by-products Pricing—attractive willingness-to-pay prices Revenue sources—exploitation & leverage of complements Connected activities—the complete value chain Construction—IT infrastructure, organization, and key champion Capability—acquisition of necessary competence Sustainability—setup firewall to prevent imitation
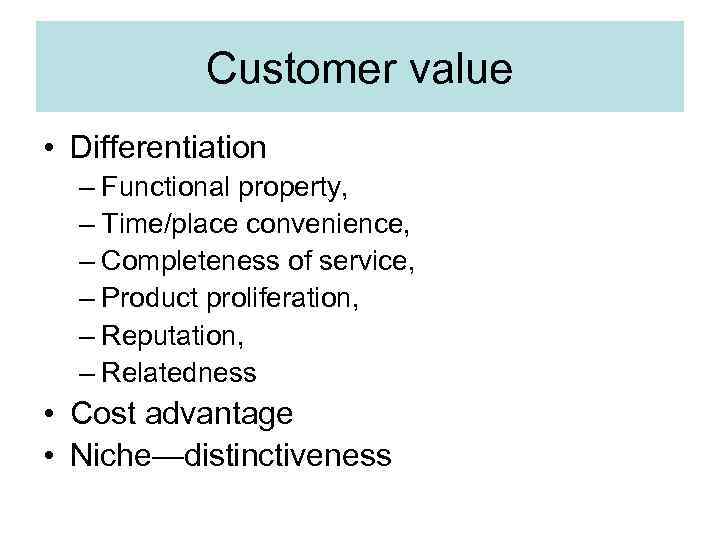
Customer value • Differentiation – Functional property, – Time/place convenience, – Completeness of service, – Product proliferation, – Reputation, – Relatedness • Cost advantage • Niche—distinctiveness
Scope • The profitable targeting – Geography – Demographics – Product lines – Segments – Diversification – Focus
Pricing • Calculate the average cost, marginal cost, fixed cost • Market share vs. profit margin vs. growth rate • Lock-in effects & switching costs • Menu price, 1 -1 bargaining, auction, reverse auction, barter

Revenue sources • Analysis of the whole process of service or product usage • Complements provision for utility enhancement • Enablers for facilitating transactions • Incentive mechanism for increasing demander exclusiveness & rivalry • Measurement criteria for profit evaluation
Connected activities • R&D, product design, manufacturing, testing, marketing, service, etc. , that is the value chain • Coherent objective • Mutual reinforcement • Cost-benefit analysis • Spill-over of core competence • Innovative arrangement for distinctiveness • Coordination of scheduling and deployment • Life cycle management

Construction • IT infrastructure—Internet & MIS • Functional organization structure—work, task, job, and project • System—information flow/gatekeeper, decision delegation, incentive/motivation mechanism • Context & culture—innovation climate, e. g. , Sony’s “neyaka”, an optimistic guy with open mind and broad interests, a generalist not a specialist

Capability • Resources—tangible, intangible, and human assets • Competencies—monopolistic, scalability • Competitive advantage—irreversibility, the case of path dependence, the case of specificity

Sustainability • Block/deterrence strategy – Private/public court protection • Run strategy – Pioneer, leadership • Team-up strategy – Embrace and extend – Co-option & co-optition – Leverage between co-specialized assets

Further thinking • Why does AOL want to merger Time. Warner? • Why does Amazon install her own warehouse and logistics? • Why had Yahoo! transform from a search engine into a media portal? • Why does Disney still survive in the Internet era?
Dis-integration & reconfiguration of electronic channels • Open Internet platform – Decreasing switching cost – Shifting lock-in value layers – Emerging digital channel—substitution or supplements? • E-Stamp—online stamp printing from personal printers • Vstore. com—online selling personal preferences as a new business • Where is the sticky value? – ISPs or ICPs – The sources of appropriability – The valuable content generators
The evolution of Yahoo! Business model • • • Searching engine website Content packager website Sticky/personal content website Communication portal website Commerce portal website Media convergence website

Clicks & bricks • Internet extension – Merrill Lynch, Charles Schwab, Toys ‘R’ Us, Wal-Mart, B&N bookstore, etc. • Amazon + Toys ‘R’ Us—combination into the whole product, & complete service • Integration between virtual clicks and supporting bricks – Dinners by parcel post? – E. g. , Webvan, Home. Grocer • Survivability? Sustainability?

Digital information products • The impact of digitalized content delivered through Internet – Bypassing the traditional channels – Versioning the digital products – Bundling & unbundling products – E. g. , MP 3. com • The emerging P 2 P business model – Direct interaction among customer communities – Napster. com
The emerging services of information flow management • Akamai—Internet flow management – Optimizing response and continuous accessibility – Necessary decentralized proxy servers • Inktomi—fast cache management – Decreasing redundancy – Increasing response • Exodus—outsourcing management – Server housing and sharing – Enhancing the web reliability
E-business models.ppt