866e729ea73661508d4c7ff6b2b5f2af.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Internet Advertising & Promotional Communication Class 8 Ad Placement / Media Planning/Buying Issues
Internet Advertising & Promotional Communication Class 8 Ad Placement / Media Planning/Buying Issues
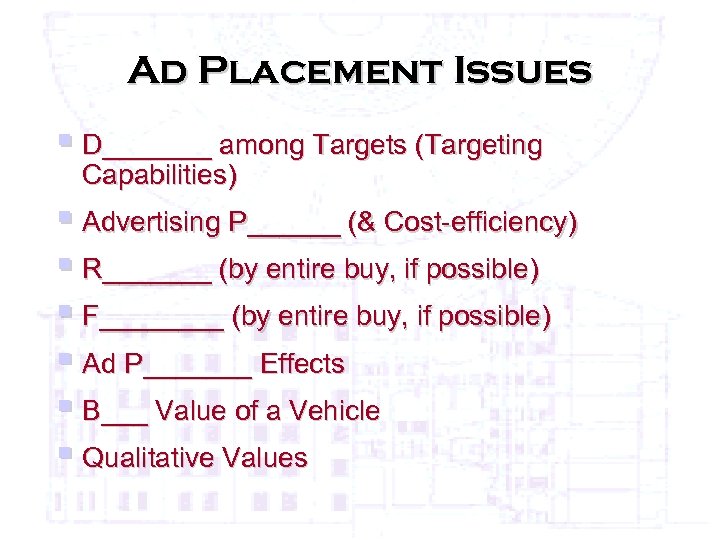 Ad Placement Issues § D_______ among Targets (Targeting Capabilities) § Advertising P______ (& Cost-efficiency) § R_______ (by entire buy, if possible) § F____ (by entire buy, if possible) § Ad P_______ Effects § B___ Value of a Vehicle § Qualitative Values
Ad Placement Issues § D_______ among Targets (Targeting Capabilities) § Advertising P______ (& Cost-efficiency) § R_______ (by entire buy, if possible) § F____ (by entire buy, if possible) § Ad P_______ Effects § B___ Value of a Vehicle § Qualitative Values
 Delivery Among Targets § Content F___ § based on analysis of consumer characteristics, interest, values & lifestyle, etc. § S____ of Delivery (target i______, when possible): § % delivery breakdown by consumer groups – demographic, geographic, usage, etc. § Site Reach & T_____ Reach § ______ reach: total unique users of the site § _______ reach: target unique users as % of total unique users
Delivery Among Targets § Content F___ § based on analysis of consumer characteristics, interest, values & lifestyle, etc. § S____ of Delivery (target i______, when possible): § % delivery breakdown by consumer groups – demographic, geographic, usage, etc. § Site Reach & T_____ Reach § ______ reach: total unique users of the site § _______ reach: target unique users as % of total unique users
 Delivery Among Targets § Site F____ § frequency control capabilities § T_____ Capabilities § geodemographics, behavioral, any desired option, etc.
Delivery Among Targets § Site F____ § frequency control capabilities § T_____ Capabilities § geodemographics, behavioral, any desired option, etc.
 Ad Pricing § Sources for Web Advertising Sites & Rates § Who sells ad space on the Net? § How much does it cost? § Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency § How is ad priced and its cost-efficiency determined? § Tactics of Buying & Selling Ad Space
Ad Pricing § Sources for Web Advertising Sites & Rates § Who sells ad space on the Net? § How much does it cost? § Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency § How is ad priced and its cost-efficiency determined? § Tactics of Buying & Selling Ad Space
 Ad Pricing Sources for Web Ad Sites & Rates • _______ – general source – covers the largest number of sites • PSA Banner Ads -- PSA only • ______ Double. Click (www. doubleclick. net) 24/7 Media (www. 247 media. com) Link Exchange (www. bcentral. com) • Ad Auction (www. adauction. com)
Ad Pricing Sources for Web Ad Sites & Rates • _______ – general source – covers the largest number of sites • PSA Banner Ads -- PSA only • ______ Double. Click (www. doubleclick. net) 24/7 Media (www. 247 media. com) Link Exchange (www. bcentral. com) • Ad Auction (www. adauction. com)
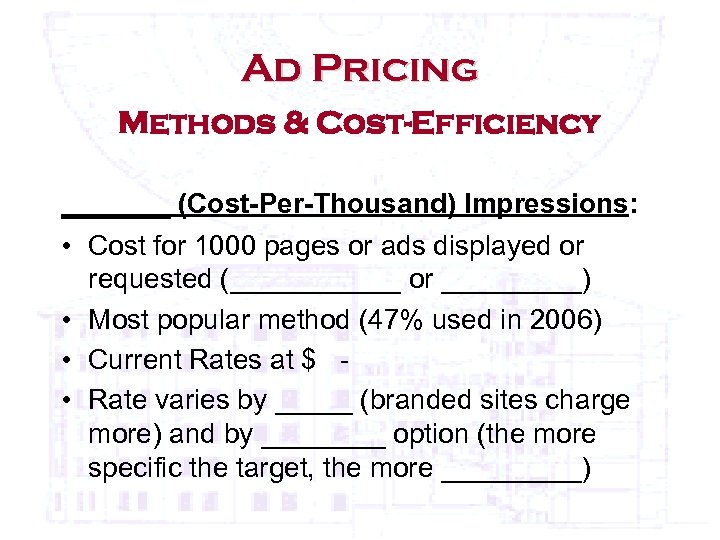 Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency _______ (Cost-Per-Thousand) Impressions: • Cost for 1000 pages or ads displayed or requested (______ or _____) • Most popular method (47% used in 2006) • Current Rates at $ • Rate varies by _____ (branded sites charge more) and by ____ option (the more specific the target, the more _____)
Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency _______ (Cost-Per-Thousand) Impressions: • Cost for 1000 pages or ads displayed or requested (______ or _____) • Most popular method (47% used in 2006) • Current Rates at $ • Rate varies by _____ (branded sites charge more) and by ____ option (the more specific the target, the more _____)
 Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency CPC (Click-Through) • Paying only for the number of ______ made (those who clicked the given ad and linked to the destination page – mini-page in the current site or advertiser’s site) • Demanded by ______ advertisers, though its use or popularity is decreasing • Rates are ____ than CPM • Popular for search buys
Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency CPC (Click-Through) • Paying only for the number of ______ made (those who clicked the given ad and linked to the destination page – mini-page in the current site or advertiser’s site) • Demanded by ______ advertisers, though its use or popularity is decreasing • Rates are ____ than CPM • Popular for search buys
 Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency _______ • Paying only for the completed sales transaction (in terms of so much $ or % of the sale, which varies on the value of the item sold) ________ • Paying for other desired actions leading to sales (store visits, leaving info for contact, testdrive, etc. )
Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency _______ • Paying only for the completed sales transaction (in terms of so much $ or % of the sale, which varies on the value of the item sold) ________ • Paying for other desired actions leading to sales (store visits, leaving info for contact, testdrive, etc. )
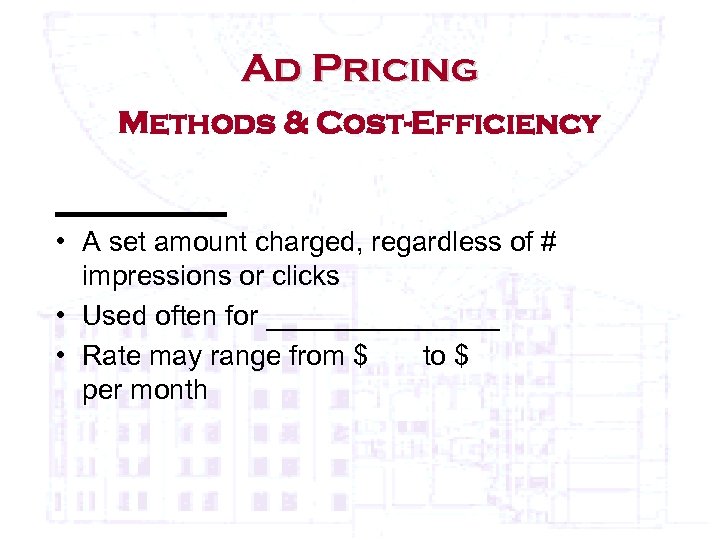 Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency ______ • A set amount charged, regardless of # impressions or clicks • Used often for ________ • Rate may range from $ to $ per month
Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency ______ • A set amount charged, regardless of # impressions or clicks • Used often for ________ • Rate may range from $ to $ per month
 Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency CPVT (Cost per View-Through) • Number of those who are exposed to the ad and take action within 30 days of the exposure • New approach, getting popular for _____ marketers
Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency CPVT (Cost per View-Through) • Number of those who are exposed to the ad and take action within 30 days of the exposure • New approach, getting popular for _____ marketers
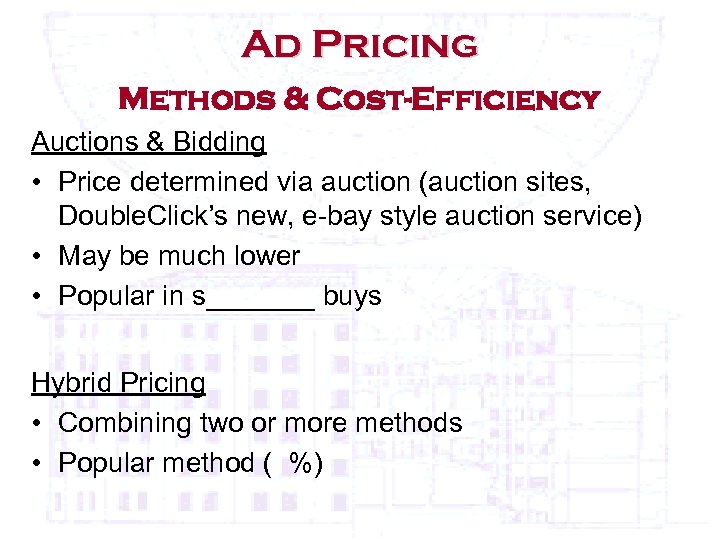 Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency Auctions & Bidding • Price determined via auction (auction sites, Double. Click’s new, e-bay style auction service) • May be much lower • Popular in s_______ buys Hybrid Pricing • Combining two or more methods • Popular method ( %)
Ad Pricing Methods & Cost-Efficiency Auctions & Bidding • Price determined via auction (auction sites, Double. Click’s new, e-bay style auction service) • May be much lower • Popular in s_______ buys Hybrid Pricing • Combining two or more methods • Popular method ( %)
 Tactics of Buying and Selling Ad Space § Study Competitive Pricing § Be Open to Negotiation § Flexibility is the Key
Tactics of Buying and Selling Ad Space § Study Competitive Pricing § Be Open to Negotiation § Flexibility is the Key
 Reach • Unduplicated audience = ______ expressed in number or % of total online population • Reported by week, month, quarter • Tactics of building reach (in general): – Use ________ categories; use _______ sites within a category (thru ______); use ____ sites in unique users (costly); and/or buy ____ at search engines
Reach • Unduplicated audience = ______ expressed in number or % of total online population • Reported by week, month, quarter • Tactics of building reach (in general): – Use ________ categories; use _______ sites within a category (thru ______); use ____ sites in unique users (costly); and/or buy ____ at search engines
 Frequency § Average # of times the target is exposed to ad § Issue: How much is optimal? § Limit ad frequency to avoid burnout? Or the more the better? – see reading list § How much is too much? -- depends on the goal (direct response vs. branding), and many other factors. § 3 exposures in a purchasing cycle? § Tactics of Building Frequency: § Use ____ content categories; use _______ in each category § Develop and rote _______ within the same site
Frequency § Average # of times the target is exposed to ad § Issue: How much is optimal? § Limit ad frequency to avoid burnout? Or the more the better? – see reading list § How much is too much? -- depends on the goal (direct response vs. branding), and many other factors. § 3 exposures in a purchasing cycle? § Tactics of Building Frequency: § Use ____ content categories; use _______ in each category § Develop and rote _______ within the same site
 Ad Timing/Scheduling § When is the best time to run ads? § Any day of the week? Any time of the day? Seasonal effects? § Least developed, increasingly important area – how ad timing is related to the desired response § Advertising will be most effective when delivered right before one is about to make a purchase decision or when he searches for the relevant information § Traditional tactics may apply (e. g. , double-spots, roadblocks, etc. )
Ad Timing/Scheduling § When is the best time to run ads? § Any day of the week? Any time of the day? Seasonal effects? § Least developed, increasingly important area – how ad timing is related to the desired response § Advertising will be most effective when delivered right before one is about to make a purchase decision or when he searches for the relevant information § Traditional tactics may apply (e. g. , double-spots, roadblocks, etc. )
 Ad Positions within a Site § Keep the Message Close to Page Content § (Place at the Top and/or Bottom of Page? ? ) § Place a Third Way Down Close to the Scroll Bar
Ad Positions within a Site § Keep the Message Close to Page Content § (Place at the Top and/or Bottom of Page? ? ) § Place a Third Way Down Close to the Scroll Bar
 BPI Value Assessment § Most useful for direct response marketers § Net. Score by com. Score Network Inc. – see table in reading list § BPI overall vs. BPI by Product Category (ROI or cost-efficiency indicator) § 100 = ____________; <100 = above average; >100 = below average; the larger the BPI, the more ______ (______) the buy § Example: a site with overall BPI of 120 (site visitors are 20% more likely than an average Internet user to purchase anything); a site with BPI of 120 for Travel (site visitors are 20% more likely than an average Internet user to travel)
BPI Value Assessment § Most useful for direct response marketers § Net. Score by com. Score Network Inc. – see table in reading list § BPI overall vs. BPI by Product Category (ROI or cost-efficiency indicator) § 100 = ____________; <100 = above average; >100 = below average; the larger the BPI, the more ______ (______) the buy § Example: a site with overall BPI of 120 (site visitors are 20% more likely than an average Internet user to purchase anything); a site with BPI of 120 for Travel (site visitors are 20% more likely than an average Internet user to travel)
 BPI Value Assessment § Other Valuable Information (see the table in Journal Exercises) § Unique User weighed by BPI: § Indicates the relative ________ to be generated by site; the larger this number, the larger the _____
BPI Value Assessment § Other Valuable Information (see the table in Journal Exercises) § Unique User weighed by BPI: § Indicates the relative ________ to be generated by site; the larger this number, the larger the _____
 Qualitative Values § content match/fit § ad clutter (article in reading list) § audience loyalty/site stickiness (article in reading list) § ad inventory availability § category exclusivity
Qualitative Values § content match/fit § ad clutter (article in reading list) § audience loyalty/site stickiness (article in reading list) § ad inventory availability § category exclusivity
 Qualitative Values § any added value (special deals & discount) § image and reputation § Read Zeff & Aronson book for others (reporting quality & frequency, performance guarantees, etc. )
Qualitative Values § any added value (special deals & discount) § image and reputation § Read Zeff & Aronson book for others (reporting quality & frequency, performance guarantees, etc. )


