bc4b3979035083ab8a2ad56b0ec3da8f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 84
 Internet Addiction Jonathan Kandell, Ph. D. Assistant Director University of Maryland Counseling Center Presentation at the 10 th Annual C 3 Conference University of Maryland, College Park 10/7/11
Internet Addiction Jonathan Kandell, Ph. D. Assistant Director University of Maryland Counseling Center Presentation at the 10 th Annual C 3 Conference University of Maryland, College Park 10/7/11
 Overview What is Internet Addiction? Vulnerability of College Students Nature of Technology Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Patterns and Suggestions Treatment of Internet Addiction
Overview What is Internet Addiction? Vulnerability of College Students Nature of Technology Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Patterns and Suggestions Treatment of Internet Addiction

 What is Internet Addiction?
What is Internet Addiction?
 What is Internet Addiction? How would you define it?
What is Internet Addiction? How would you define it?
 What is Internet Addiction? How would you define it? Term coined in the mid-90 s by a New York psychiatrist, Dr. Ivan Goldberg n n He devised a list of symptoms (taken from those for pathological gambling) and created “Internet Addiction Disorder” Also created online Internet Addiction Support Group
What is Internet Addiction? How would you define it? Term coined in the mid-90 s by a New York psychiatrist, Dr. Ivan Goldberg n n He devised a list of symptoms (taken from those for pathological gambling) and created “Internet Addiction Disorder” Also created online Internet Addiction Support Group
 What is Internet Addiction? How would you define it? Term coined in the mid-90 s by a New York psychiatrist, Dr. Ivan Goldberg n n n He devised a list of symptoms (taken from those for pathological gambling) and created “Internet Addiction Disorder” Also created online Internet Addiction Support Group Did it as a joke!
What is Internet Addiction? How would you define it? Term coined in the mid-90 s by a New York psychiatrist, Dr. Ivan Goldberg n n n He devised a list of symptoms (taken from those for pathological gambling) and created “Internet Addiction Disorder” Also created online Internet Addiction Support Group Did it as a joke!
 What is Internet Addiction? How would you define it? Term coined in the mid-90 s by a New York psychiatrist, Dr. Ivan Goldberg n n He devised a list of symptoms (taken from those for pathological gambling) and created “Internet Addiction Disorder” Also created online Internet Addiction Support Group Did it as a joke! The joke was on him!!
What is Internet Addiction? How would you define it? Term coined in the mid-90 s by a New York psychiatrist, Dr. Ivan Goldberg n n He devised a list of symptoms (taken from those for pathological gambling) and created “Internet Addiction Disorder” Also created online Internet Addiction Support Group Did it as a joke! The joke was on him!!
 What is Internet Addiction? “Process Addiction” – disorder of behavior, not abuse of a substance
What is Internet Addiction? “Process Addiction” – disorder of behavior, not abuse of a substance
 What is Internet Addiction? “Process Addiction” – disorder of behavior, not abuse of a substance “Pathological Internet Use” (PIU) n n Term coined by Kimberly Young, Ph. D. - Psychologist, U. Pitt-Bradford – COLA Many liken IAD/PIU to pathological gambling (e. g. , Goldberg and Young), using symptoms from those disorders
What is Internet Addiction? “Process Addiction” – disorder of behavior, not abuse of a substance “Pathological Internet Use” (PIU) n n Term coined by Kimberly Young, Ph. D. - Psychologist, U. Pitt-Bradford – COLA Many liken IAD/PIU to pathological gambling (e. g. , Goldberg and Young), using symptoms from those disorders
 What is Internet Addiction? “Pathological Internet Use” (PIU) Given the usefulness/necessity of the Internet – more like compulsive exercise
What is Internet Addiction? “Pathological Internet Use” (PIU) Given the usefulness/necessity of the Internet – more like compulsive exercise
 What is Internet Addiction? Symptoms n n n n Increasing preoccupation with, and investment of resources (e. g. , time, money, energy) on Internet-related activities Unpleasant feelings (e. g. , depression, anxiety, loneliness, emptiness) when not online Negative impact on work/school performance Problems develop in existing relationships Difficulty in forming new offline relationships Tolerance can develop Denial
What is Internet Addiction? Symptoms n n n n Increasing preoccupation with, and investment of resources (e. g. , time, money, energy) on Internet-related activities Unpleasant feelings (e. g. , depression, anxiety, loneliness, emptiness) when not online Negative impact on work/school performance Problems develop in existing relationships Difficulty in forming new offline relationships Tolerance can develop Denial
 What is Internet Addiction? Research Findings – Literature 5 -12% of Those Surveyed have PIU
What is Internet Addiction? Research Findings – Literature 5 -12% of Those Surveyed have PIU
 What is Internet Addiction? Research Findings – Literature n Personality Characteristics Low self-esteem Intellectualization Self-reliance Strong preference for solitary activities Restricted social outlets Less socially conforming More emotionally reactive to others (Van. Gelder, 2003)
What is Internet Addiction? Research Findings – Literature n Personality Characteristics Low self-esteem Intellectualization Self-reliance Strong preference for solitary activities Restricted social outlets Less socially conforming More emotionally reactive to others (Van. Gelder, 2003)
 What is Internet Addiction? UM Counseling Service Data (2006 -07) Full Entire Helpseeker Population (N=1125) PIU Clients responding “Terribly” or “Poorly” to “How have you been getting along in the following areas of your life over the last two weeks? ” – Spending too much time on the computer/Internet (N=170)
What is Internet Addiction? UM Counseling Service Data (2006 -07) Full Entire Helpseeker Population (N=1125) PIU Clients responding “Terribly” or “Poorly” to “How have you been getting along in the following areas of your life over the last two weeks? ” – Spending too much time on the computer/Internet (N=170)
 What is Internet Addiction? UM Counseling Service Data (2006 -07) Out of 66 items on the four scales n n 60 showed an increase in endorsement 6 showed a decrease
What is Internet Addiction? UM Counseling Service Data (2006 -07) Out of 66 items on the four scales n n 60 showed an increase in endorsement 6 showed a decrease
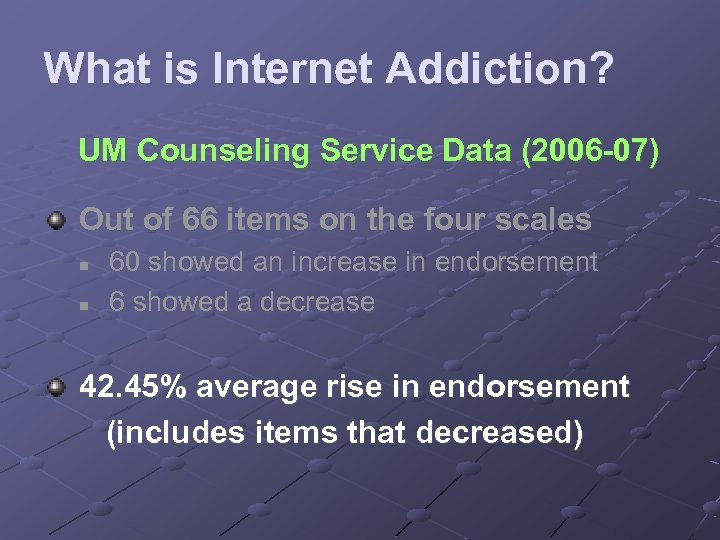 What is Internet Addiction? UM Counseling Service Data (2006 -07) Out of 66 items on the four scales n n 60 showed an increase in endorsement 6 showed a decrease 42. 45% average rise in endorsement (includes items that decreased)
What is Internet Addiction? UM Counseling Service Data (2006 -07) Out of 66 items on the four scales n n 60 showed an increase in endorsement 6 showed a decrease 42. 45% average rise in endorsement (includes items that decreased)
 What is Internet Addiction? UM Counseling Service Data (2006 -07) Item Repeated behaviors interfere w/ life Standing up for rights, express self School (performance, attendance) Studying effectively No energy, everything an effort Self management (plans, goals) Afraid of / avoiding normal situations Feeling hopeless about the future Eating problems Uncomfortable, shy, ill at ease FULL 26. 04% 15. 11 23. 72 38. 49 24. 53 39. 12 23. 29 25. 42 24. 44 19. 11 PIU 52. 35% 30. 00 45. 88 72. 94 46. 47 71. 18 42. 35 40. 00 31. 18
What is Internet Addiction? UM Counseling Service Data (2006 -07) Item Repeated behaviors interfere w/ life Standing up for rights, express self School (performance, attendance) Studying effectively No energy, everything an effort Self management (plans, goals) Afraid of / avoiding normal situations Feeling hopeless about the future Eating problems Uncomfortable, shy, ill at ease FULL 26. 04% 15. 11 23. 72 38. 49 24. 53 39. 12 23. 29 25. 42 24. 44 19. 11 PIU 52. 35% 30. 00 45. 88 72. 94 46. 47 71. 18 42. 35 40. 00 31. 18
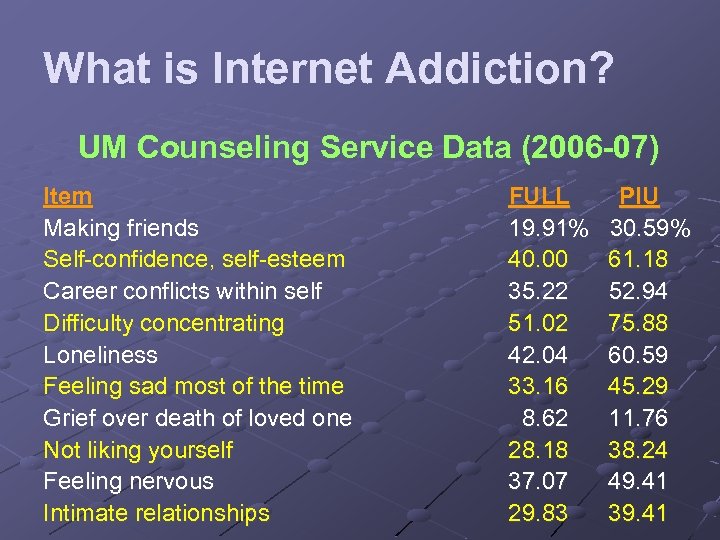 What is Internet Addiction? UM Counseling Service Data (2006 -07) Item Making friends Self-confidence, self-esteem Career conflicts within self Difficulty concentrating Loneliness Feeling sad most of the time Grief over death of loved one Not liking yourself Feeling nervous Intimate relationships FULL 19. 91% 40. 00 35. 22 51. 02 42. 04 33. 16 8. 62 28. 18 37. 07 29. 83 PIU 30. 59% 61. 18 52. 94 75. 88 60. 59 45. 29 11. 76 38. 24 49. 41 39. 41
What is Internet Addiction? UM Counseling Service Data (2006 -07) Item Making friends Self-confidence, self-esteem Career conflicts within self Difficulty concentrating Loneliness Feeling sad most of the time Grief over death of loved one Not liking yourself Feeling nervous Intimate relationships FULL 19. 91% 40. 00 35. 22 51. 02 42. 04 33. 16 8. 62 28. 18 37. 07 29. 83 PIU 30. 59% 61. 18 52. 94 75. 88 60. 59 45. 29 11. 76 38. 24 49. 41 39. 41
 What is Internet Addiction? UM Counseling Service Data (2006 -07) Item Rape or sexual assault Alc/drugs causing physical problems Pregnancy Getting into frequent arguments Alc/drugs interfering w/ job/school Sexual orientation issues FULL 3. 11% 2. 04 0. 71 11. 20 2. 31 4. 00 PIU 2. 94% 1. 76 0. 59 8. 82 1. 76 2. 94
What is Internet Addiction? UM Counseling Service Data (2006 -07) Item Rape or sexual assault Alc/drugs causing physical problems Pregnancy Getting into frequent arguments Alc/drugs interfering w/ job/school Sexual orientation issues FULL 3. 11% 2. 04 0. 71 11. 20 2. 31 4. 00 PIU 2. 94% 1. 76 0. 59 8. 82 1. 76 2. 94
 What is Internet Addiction? In my opinion, Pathological Internet Use is most often a condition secondary to a separate underlying psychological disorder. The compulsive internet behavior is functioning as a coping mechanism, a form of self-medication similar to other compulsive/addictive behaviors.
What is Internet Addiction? In my opinion, Pathological Internet Use is most often a condition secondary to a separate underlying psychological disorder. The compulsive internet behavior is functioning as a coping mechanism, a form of self-medication similar to other compulsive/addictive behaviors.
 Vulnerability of College Students
Vulnerability of College Students
 Vulnerability of College Students Societal Influences n n n Increasing pace of life and technological advancement – Toffler’s “Future Shock” Threats to safety (real and/or perceived) Environmental, political, financial worries
Vulnerability of College Students Societal Influences n n n Increasing pace of life and technological advancement – Toffler’s “Future Shock” Threats to safety (real and/or perceived) Environmental, political, financial worries
 Vulnerability of College Students Societal Influences n n n Increasing pace of life and technological advancement – Toffler’s “Future Shock” Threats to safety (real and/or perceived) Environmental, political, financial worries Familial Influences n n Usual dysfunction, financial issues, etc. “A Nation of Wimps” – Marano The Fragility Factor (“Helicopter Parents”) Cell Phone – “The Eternal Umbilicus”
Vulnerability of College Students Societal Influences n n n Increasing pace of life and technological advancement – Toffler’s “Future Shock” Threats to safety (real and/or perceived) Environmental, political, financial worries Familial Influences n n Usual dysfunction, financial issues, etc. “A Nation of Wimps” – Marano The Fragility Factor (“Helicopter Parents”) Cell Phone – “The Eternal Umbilicus”
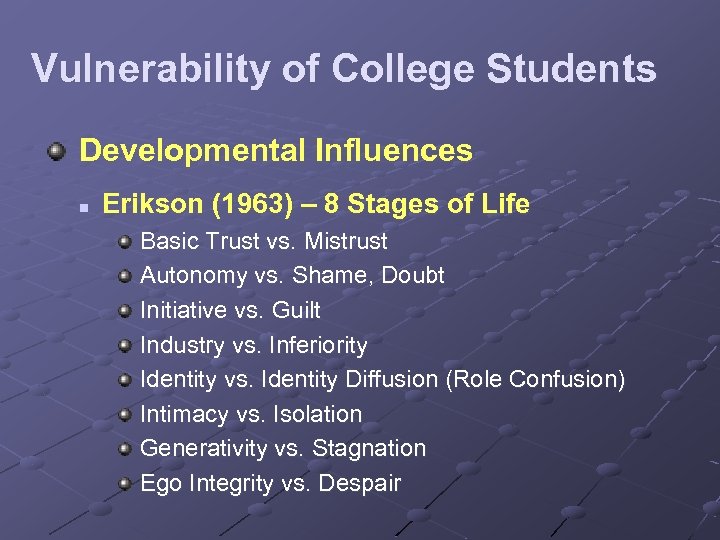 Vulnerability of College Students Developmental Influences n Erikson (1963) – 8 Stages of Life Basic Trust vs. Mistrust Autonomy vs. Shame, Doubt Initiative vs. Guilt Industry vs. Inferiority Identity vs. Identity Diffusion (Role Confusion) Intimacy vs. Isolation Generativity vs. Stagnation Ego Integrity vs. Despair
Vulnerability of College Students Developmental Influences n Erikson (1963) – 8 Stages of Life Basic Trust vs. Mistrust Autonomy vs. Shame, Doubt Initiative vs. Guilt Industry vs. Inferiority Identity vs. Identity Diffusion (Role Confusion) Intimacy vs. Isolation Generativity vs. Stagnation Ego Integrity vs. Despair
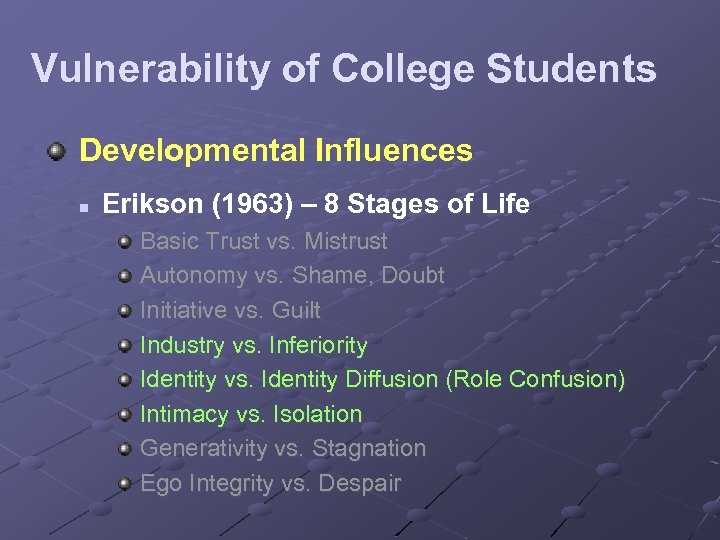 Vulnerability of College Students Developmental Influences n Erikson (1963) – 8 Stages of Life Basic Trust vs. Mistrust Autonomy vs. Shame, Doubt Initiative vs. Guilt Industry vs. Inferiority Identity vs. Identity Diffusion (Role Confusion) Intimacy vs. Isolation Generativity vs. Stagnation Ego Integrity vs. Despair
Vulnerability of College Students Developmental Influences n Erikson (1963) – 8 Stages of Life Basic Trust vs. Mistrust Autonomy vs. Shame, Doubt Initiative vs. Guilt Industry vs. Inferiority Identity vs. Identity Diffusion (Role Confusion) Intimacy vs. Isolation Generativity vs. Stagnation Ego Integrity vs. Despair
 Vulnerability of College Students Access / Expectancy n n n Most campuses replete with computers and internet connections Computer labs often open late, even 24/7 Many courses require (or strongly encourage) use of computer / internet Writing Papers Internet Research E-mail Instructors Online Discussions Blackboard / ELMS
Vulnerability of College Students Access / Expectancy n n n Most campuses replete with computers and internet connections Computer labs often open late, even 24/7 Many courses require (or strongly encourage) use of computer / internet Writing Papers Internet Research E-mail Instructors Online Discussions Blackboard / ELMS
 Vulnerability of College Students Access / Expectancy n It only takes a few keystrokes to go from writing a paper to checking your e-mail to: Facebook Blogging Chatting Gaming Online Porn etc.
Vulnerability of College Students Access / Expectancy n It only takes a few keystrokes to go from writing a paper to checking your e-mail to: Facebook Blogging Chatting Gaming Online Porn etc.
 Vulnerability of College Students Cumulative Impact n n Many strains on internal resources Various mechanisms used to reduce anxiety, depression, loneliness - Healthy? Substance abuse (alcohol/drugs – including legal) Compulsive Behaviors (Gambling, Exercise, TV, Internet, Cellphone, Gaming, Porn, etc. ) Eating Disorders Self-mutilation n What’s acceptable and available?
Vulnerability of College Students Cumulative Impact n n Many strains on internal resources Various mechanisms used to reduce anxiety, depression, loneliness - Healthy? Substance abuse (alcohol/drugs – including legal) Compulsive Behaviors (Gambling, Exercise, TV, Internet, Cellphone, Gaming, Porn, etc. ) Eating Disorders Self-mutilation n What’s acceptable and available?
 The Nature of Technology
The Nature of Technology
 The Nature of Technology “Good” or “Evil” - What do you think?
The Nature of Technology “Good” or “Evil” - What do you think?
 GOOD?
GOOD?
 EVIL?
EVIL?
 The Nature of Technology – Good or Evil? NEITHER! Technology is … a tool n Special kind of tool - amplifier n Depends on how it’s used n Creates change
The Nature of Technology – Good or Evil? NEITHER! Technology is … a tool n Special kind of tool - amplifier n Depends on how it’s used n Creates change
 Marshall Mc. Luhan
Marshall Mc. Luhan
 Mc. Luhan Marshall Mc. Luhan n “The medium is the message” We adapt to technology, not the other way around “Hot” vs. “Cool” media
Mc. Luhan Marshall Mc. Luhan n “The medium is the message” We adapt to technology, not the other way around “Hot” vs. “Cool” media
 Mc. Luhan “Hot” vs. “Cool” media n “A hot medium is one that extends one single sense in 'high definition. ' High definition is being well filled with data” - all the information is available; the person is passive n Cool media force the person to engage in the transmission process.
Mc. Luhan “Hot” vs. “Cool” media n “A hot medium is one that extends one single sense in 'high definition. ' High definition is being well filled with data” - all the information is available; the person is passive n Cool media force the person to engage in the transmission process.
 Mc. Luhan “Hot” vs. “Cool” media n Book vs. Newspaper Book Newspaper
Mc. Luhan “Hot” vs. “Cool” media n Book vs. Newspaper Book Newspaper
 Mc. Luhan “Hot” vs. “Cool” media n Film vs. Screen (TV / Computer / Internet) Film CRT/LCD
Mc. Luhan “Hot” vs. “Cool” media n Film vs. Screen (TV / Computer / Internet) Film CRT/LCD
 Control
Control
 Control Technology impacts people’s sense of control over their lives Positive Aspects n n Structure free time / Configure your life Easier to establish/maintain relationships Negative Aspects n n “Do more in less time” Privacy Issues / Identity Theft / “Phishing”
Control Technology impacts people’s sense of control over their lives Positive Aspects n n Structure free time / Configure your life Easier to establish/maintain relationships Negative Aspects n n “Do more in less time” Privacy Issues / Identity Theft / “Phishing”
 Internet Reinforcers
Internet Reinforcers
 Internet Reinforcers Van. Gelder, S. C. (2003). INTERNET ADDICTION: Is the Internet a “pathological agent” includable as a disorder separate from other psychiatric diagnoses? Journal of Addictive Disorders. Retrieved from http: //www. breining. edu n Reinforcers Specific to the Internet (e. g. , disinhibition, anonymity, intimacy, intensity, time distortion)
Internet Reinforcers Van. Gelder, S. C. (2003). INTERNET ADDICTION: Is the Internet a “pathological agent” includable as a disorder separate from other psychiatric diagnoses? Journal of Addictive Disorders. Retrieved from http: //www. breining. edu n Reinforcers Specific to the Internet (e. g. , disinhibition, anonymity, intimacy, intensity, time distortion)
 Internet Reinforcers Van. Gelder, S. C. (2003). INTERNET ADDICTION: Is the Internet a “pathological agent” includable as a disorder separate from other psychiatric diagnoses? Journal of Addictive Disorders. Retrieved from http: //www. breining. edu n Reinforcers Specific to the Internet (e. g. , disinhibition, anonymity, intimacy, intensity, time distortion) n Dissociative Aspects (paralanguage, body/image distortion, RL separation, identities)
Internet Reinforcers Van. Gelder, S. C. (2003). INTERNET ADDICTION: Is the Internet a “pathological agent” includable as a disorder separate from other psychiatric diagnoses? Journal of Addictive Disorders. Retrieved from http: //www. breining. edu n Reinforcers Specific to the Internet (e. g. , disinhibition, anonymity, intimacy, intensity, time distortion) n Dissociative Aspects (paralanguage, body/image distortion, RL separation, identities)
 The New Yorker -- July 5, 1993
The New Yorker -- July 5, 1993
 Internet Reinforcers Van. Gelder, S. C. (2003). INTERNET ADDICTION: Is the Internet a “pathological agent” includable as a disorder separate from other psychiatric diagnoses? Journal of Addictive Disorders. Retrieved from http: //www. breining. edu n Reinforcers Specific to the Internet (e. g. , disinhibition, anonymity, intimacy, intensity, time distortion) n Dissociative Aspects (paralanguage, body/image distortion, RL separation, identities) n Unconstrained Social Functioning (global home, boundlessness, realize sexual fantasies)
Internet Reinforcers Van. Gelder, S. C. (2003). INTERNET ADDICTION: Is the Internet a “pathological agent” includable as a disorder separate from other psychiatric diagnoses? Journal of Addictive Disorders. Retrieved from http: //www. breining. edu n Reinforcers Specific to the Internet (e. g. , disinhibition, anonymity, intimacy, intensity, time distortion) n Dissociative Aspects (paralanguage, body/image distortion, RL separation, identities) n Unconstrained Social Functioning (global home, boundlessness, realize sexual fantasies)
 Cutting Edge. . . or Cutting Off
Cutting Edge. . . or Cutting Off
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Technology can facilitate both meeting others and communicating with them n E-mail / Instant Messaging (IM) n Cell Phone / Texting / Twitter / Blog n Social Networking (e. g. , Facebook) n MMORPGs Massive Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games n n Gaming (e. g. , World of Warcraft, Halo) - FPS Second Life
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Technology can facilitate both meeting others and communicating with them n E-mail / Instant Messaging (IM) n Cell Phone / Texting / Twitter / Blog n Social Networking (e. g. , Facebook) n MMORPGs Massive Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games n n Gaming (e. g. , World of Warcraft, Halo) - FPS Second Life
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Technology can facilitate both meeting others and communicating with them n Positives Can help introverted people develop connections People can experiment with various identities You can learn to appreciate another without the distraction of looks You can practice social interchange without fear of significant reprisal or rejection Can raise an individual’s self-esteem
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Technology can facilitate both meeting others and communicating with them n Positives Can help introverted people develop connections People can experiment with various identities You can learn to appreciate another without the distraction of looks You can practice social interchange without fear of significant reprisal or rejection Can raise an individual’s self-esteem
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Technology can facilitate both meeting others and communicating with them But, … what is the nature and quality of these interactions?
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Technology can facilitate both meeting others and communicating with them But, … what is the nature and quality of these interactions?
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Online Interactions Conversations can seem the same … but there are some fundamental differences
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Online Interactions Conversations can seem the same … but there are some fundamental differences
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Online Interactions n n n Asynchronous Often just words on a screen Quality vs. Quantity Can be regressive (“flaming, ” graphic) “On the Internet, no one knows you’re a dog” Projection
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Online Interactions n n n Asynchronous Often just words on a screen Quality vs. Quantity Can be regressive (“flaming, ” graphic) “On the Internet, no one knows you’re a dog” Projection
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Online Interactions -- Impact n For those whose primary (or sole) mode of interaction is online, there is potential for loss of face-to-face relationship skills
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Online Interactions -- Impact n For those whose primary (or sole) mode of interaction is online, there is potential for loss of face-to-face relationship skills
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Online Interactions -- Impact n n For those whose primary (or sole) mode of interaction is online, there is potential for loss of face-to-face relationship skills For those who begin before learning face-to-face interaction skills, there is potential for lack of development of these skills
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Online Interactions -- Impact n n For those whose primary (or sole) mode of interaction is online, there is potential for loss of face-to-face relationship skills For those who begin before learning face-to-face interaction skills, there is potential for lack of development of these skills
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Cell Phone / Text Messaging n “Time On” vs. “Time Off” n Quantity vs. Quality n Can foster dependency (Marano) n Analysis/Sharing vs. Experience n “How do I look? ” n Sexting n Cell Phone/Texting while driving
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Cell Phone / Text Messaging n “Time On” vs. “Time Off” n Quantity vs. Quality n Can foster dependency (Marano) n Analysis/Sharing vs. Experience n “How do I look? ” n Sexting n Cell Phone/Texting while driving
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Facebook n Privacy vs. Exhibitionism n Do you want everyone to see your page? n How many friends are enough? n State of Relationship
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Facebook n Privacy vs. Exhibitionism n Do you want everyone to see your page? n How many friends are enough? n State of Relationship
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Online First Person Shooter Game Catharsis / Connection / Purpose
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Online First Person Shooter Game Catharsis / Connection / Purpose
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Second Life
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Second Life
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Second Life
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Second Life
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Second Life n Be who you want Your Avatar(s) – Create the “ideal” you!
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Second Life n Be who you want Your Avatar(s) – Create the “ideal” you!
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Second Life n Be who you want Your Avatar(s) – Create the “ideal” you! n Do what you want Buy land / build a house (for a fee) Eat, drink, sit on the beach, have sex
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Second Life n Be who you want Your Avatar(s) – Create the “ideal” you! n Do what you want Buy land / build a house (for a fee) Eat, drink, sit on the beach, have sex
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Second Life n Be who you want Your Avatar(s) – Create the “ideal” you! n Do what you want Buy land / build a house (for a fee) Eat, drink, sit on the beach, have sex n “Practice makes perfect!” Unpopular? – leave / resurface as new avatar Does it translate to the “non-virtual world? ” Can be highly compelling to loners
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Second Life n Be who you want Your Avatar(s) – Create the “ideal” you! n Do what you want Buy land / build a house (for a fee) Eat, drink, sit on the beach, have sex n “Practice makes perfect!” Unpopular? – leave / resurface as new avatar Does it translate to the “non-virtual world? ” Can be highly compelling to loners
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Blogging / Live. Journal n n Anyone can be a publisher or pundit Diary or something else? -- Hawthorne You. Tube n n Anyone can be a broadcaster The ultimate “reality” TV On Demand / Satellite Radio / i. Pod n Why wait? – What you want, when you want
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Blogging / Live. Journal n n Anyone can be a publisher or pundit Diary or something else? -- Hawthorne You. Tube n n Anyone can be a broadcaster The ultimate “reality” TV On Demand / Satellite Radio / i. Pod n Why wait? – What you want, when you want
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Smartphone / Tablet – The Ultimate! n n n n Your life in the palm of your hand!! Never disconnected!! (except for battery and coverage) Information – Internet / GPS Entertainment – Music / Video / Games Connection – Text / E-mail / Voice / Tweet Data - Why bother remembering? Who needs people?
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Smartphone / Tablet – The Ultimate! n n n n Your life in the palm of your hand!! Never disconnected!! (except for battery and coverage) Information – Internet / GPS Entertainment – Music / Video / Games Connection – Text / E-mail / Voice / Tweet Data - Why bother remembering? Who needs people?
 Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Smartphone / Tablet – The Ultimate! n Your life in the palm of your hand!! Never disconnected!! (except for battery and coverage) Information – Internet / GPS Entertainment – Music / Video / Games Connection – Text / E-mail / Voice / Tweet Data - Why bother remembering? Who needs people? n Technology Addiction! n n n
Cutting Edge … or Cutting Off? Smartphone / Tablet – The Ultimate! n Your life in the palm of your hand!! Never disconnected!! (except for battery and coverage) Information – Internet / GPS Entertainment – Music / Video / Games Connection – Text / E-mail / Voice / Tweet Data - Why bother remembering? Who needs people? n Technology Addiction! n n n
 Patterns and Suggestions
Patterns and Suggestions
 Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n Technology will continue to advance and is not going away, so you’d better learn to ride the wave (Luddites need not apply)
Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n Technology will continue to advance and is not going away, so you’d better learn to ride the wave (Luddites need not apply)
 Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n n Technology will continue to advance and is not going away, so you’d better learn to ride the wave (Luddites need not apply) As Mc. Luhan suggested, the increasing use of newer technologies is changing individual and societal behavior
Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n n Technology will continue to advance and is not going away, so you’d better learn to ride the wave (Luddites need not apply) As Mc. Luhan suggested, the increasing use of newer technologies is changing individual and societal behavior
 Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n A sense of connection, whether present or absent, seems to drive much of the behavior students (and others) exhibit when using advancing technology
Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n A sense of connection, whether present or absent, seems to drive much of the behavior students (and others) exhibit when using advancing technology
 Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n n A sense of connection, whether present or absent, seems to drive much of the behavior students (and others) exhibit when using advancing technology Students’ sense of what is private/public is changing, which likely will result in societal changes in this area
Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n n A sense of connection, whether present or absent, seems to drive much of the behavior students (and others) exhibit when using advancing technology Students’ sense of what is private/public is changing, which likely will result in societal changes in this area
 Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n We have only just started on some fundamental changes in the way people envision who they are and what they can be, the effects of which will likely not be known for at least a generation
Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n We have only just started on some fundamental changes in the way people envision who they are and what they can be, the effects of which will likely not be known for at least a generation
 Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n College students and teens have embraced technology “whole hog, ” and they’re not likely to go back
Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n College students and teens have embraced technology “whole hog, ” and they’re not likely to go back
 Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n n College students and teens have embraced technology “whole hog, ” and they’re not likely to go back More and more students want, and expect, life and other people to be as responsive to their needs/desires as their technology – lower frustration tolerance; can act much younger than age
Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n n College students and teens have embraced technology “whole hog, ” and they’re not likely to go back More and more students want, and expect, life and other people to be as responsive to their needs/desires as their technology – lower frustration tolerance; can act much younger than age
 Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n Adolescent / young adult psychological needs remain the same (mastery, affiliation, independence); means to fill them change
Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n Adolescent / young adult psychological needs remain the same (mastery, affiliation, independence); means to fill them change
 Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n n Adolescent / young adult psychological needs remain the same (mastery, affiliation, independence); means to fill them change While most people can successfully navigate the transition to these advancing technologies, some, especially those who are psychologically vulnerable, can develop compulsive behaviors
Patterns and Suggestions What can we learn from all this? n n Adolescent / young adult psychological needs remain the same (mastery, affiliation, independence); means to fill them change While most people can successfully navigate the transition to these advancing technologies, some, especially those who are psychologically vulnerable, can develop compulsive behaviors
 Patterns and Suggestions What can be done? n Meet the students where they are Find the best ways to get in contact with them Text Messaging / E-mail / Cell Phone Use Facebook, etc. to contact/organize
Patterns and Suggestions What can be done? n Meet the students where they are Find the best ways to get in contact with them Text Messaging / E-mail / Cell Phone Use Facebook, etc. to contact/organize
 Patterns and Suggestions What can be done? n Meet the students where they are Find the best ways to get in contact with them Text Messaging / E-mail / Cell Phone Use Facebook, etc. to contact/organize n Develop programming that fits your students’ interests Gaming tournament “Cult”-based watching parties
Patterns and Suggestions What can be done? n Meet the students where they are Find the best ways to get in contact with them Text Messaging / E-mail / Cell Phone Use Facebook, etc. to contact/organize n Develop programming that fits your students’ interests Gaming tournament “Cult”-based watching parties
 Patterns and Suggestions What can be done? n Learn about the technologies – try to “speak the language; ” get your students to teach you about what they do/think
Patterns and Suggestions What can be done? n Learn about the technologies – try to “speak the language; ” get your students to teach you about what they do/think
 Patterns and Suggestions What can be done? n n Learn about the technologies – try to “speak the language’” get your students to teach you about what they do/think Be aware of your students’ behaviors – learn and recognize what’s “normal” and what’s problematic; refer students for help when needed
Patterns and Suggestions What can be done? n n Learn about the technologies – try to “speak the language’” get your students to teach you about what they do/think Be aware of your students’ behaviors – learn and recognize what’s “normal” and what’s problematic; refer students for help when needed
 Treatment of Internet Addiction
Treatment of Internet Addiction
 Treatment of Internet Addiction Individual Clients – Five Prong Plan n n Establish a Working Relationship Break the Pattern Find Other Ways to Occupy Time Develop “Real Life” Relationships Explore and Treat Underlying Conditions
Treatment of Internet Addiction Individual Clients – Five Prong Plan n n Establish a Working Relationship Break the Pattern Find Other Ways to Occupy Time Develop “Real Life” Relationships Explore and Treat Underlying Conditions
 Treatment of Internet Addiction Individual Clients – Five Prong Plan n n Establish a Working Relationship Break the Pattern Find Other Ways to Occupy Time Develop “Real Life” Relationships Explore and Treat Underlying Conditions Internet Addiction Support Group n n n NOT ONLINE! – like AA meeting in a bar Can use Five Prong Plan with members Provides RL contact in safe setting
Treatment of Internet Addiction Individual Clients – Five Prong Plan n n Establish a Working Relationship Break the Pattern Find Other Ways to Occupy Time Develop “Real Life” Relationships Explore and Treat Underlying Conditions Internet Addiction Support Group n n n NOT ONLINE! – like AA meeting in a bar Can use Five Prong Plan with members Provides RL contact in safe setting
 References Erikson, E. H. (1963). Childhood and society (2 nd ed. ). New York: Norton. Kandell, J. J. (1998). Internet addiction on campus: The vulnerability of college students. Cyber. Psychology and Behavior, 1(1), 13 -24. (http: //www. counseling. umd. edu/Personal/~kandell/iacpbart. htm) Kraut R. , Patterson M. , Lundmark V. , et al. (1998). Internet paradox: A social technology that reduces social involvement and psychological well-being? American Psychologist, 53(9), 1017 -1031. Mc. Luhan, M. (1965). Understanding media: The extensions of man (rev. ed. ). New York: Mc. Graw-Hill. Mitra, A. , Willyard, J. , Platt, C. , & Parsons, M. (2005). Exploring web usage and selection criteria among male and female students. Journal of Computer Mediated Communication, 10 I(3), article 10. http: //jcmc. indiana. edu/vol 10/issue 3/mitra. html Van. Gelder, S. C. (2003). INTERNET ADDICTION: Is the Internet a “pathological agent” includable as a disorder separate from other psychiatric diagnoses? Journal of Addictive Disorders. Retrieved from http: //www. breining. edu
References Erikson, E. H. (1963). Childhood and society (2 nd ed. ). New York: Norton. Kandell, J. J. (1998). Internet addiction on campus: The vulnerability of college students. Cyber. Psychology and Behavior, 1(1), 13 -24. (http: //www. counseling. umd. edu/Personal/~kandell/iacpbart. htm) Kraut R. , Patterson M. , Lundmark V. , et al. (1998). Internet paradox: A social technology that reduces social involvement and psychological well-being? American Psychologist, 53(9), 1017 -1031. Mc. Luhan, M. (1965). Understanding media: The extensions of man (rev. ed. ). New York: Mc. Graw-Hill. Mitra, A. , Willyard, J. , Platt, C. , & Parsons, M. (2005). Exploring web usage and selection criteria among male and female students. Journal of Computer Mediated Communication, 10 I(3), article 10. http: //jcmc. indiana. edu/vol 10/issue 3/mitra. html Van. Gelder, S. C. (2003). INTERNET ADDICTION: Is the Internet a “pathological agent” includable as a disorder separate from other psychiatric diagnoses? Journal of Addictive Disorders. Retrieved from http: //www. breining. edu
 Questions ? ? ?
Questions ? ? ?


