63e085c1df2a6f74c869a508734647b6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 Internet 101 u. Technology u. Policy Framework 1
Internet 101 u. Technology u. Policy Framework 1
 Disclaimer! u This presentation is oversimplified u And incomplete for pedagogical reasons and because of time constraints! 2
Disclaimer! u This presentation is oversimplified u And incomplete for pedagogical reasons and because of time constraints! 2
 How does Internet work? 3
How does Internet work? 3
 Internet u The Internet is a network of networks interconnected by means of the Internet Protocol Suite. u It is an architecture for a system of computerbased applications. u Protocols are standard procedures, conventions and formats for inter-computer communication. u The Internet protocols are based on packet switching concepts. 4
Internet u The Internet is a network of networks interconnected by means of the Internet Protocol Suite. u It is an architecture for a system of computerbased applications. u Protocols are standard procedures, conventions and formats for inter-computer communication. u The Internet protocols are based on packet switching concepts. 4
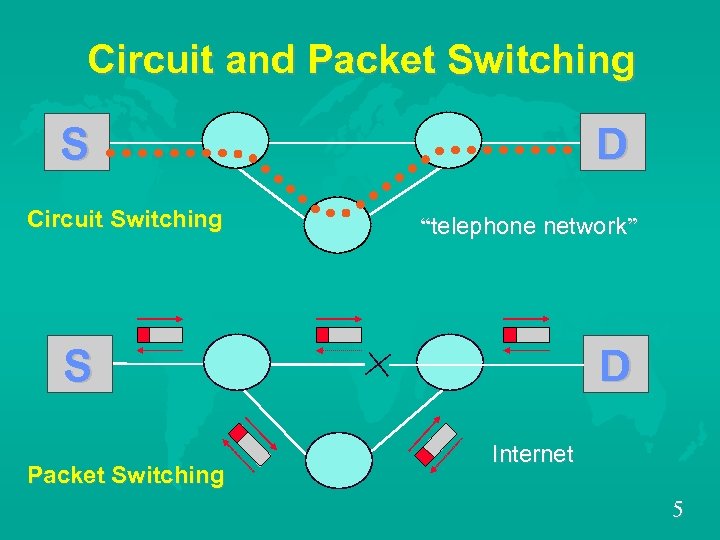 Circuit and Packet Switching S Circuit Switching D “telephone network” S Packet Switching D Internet 5
Circuit and Packet Switching S Circuit Switching D “telephone network” S Packet Switching D Internet 5
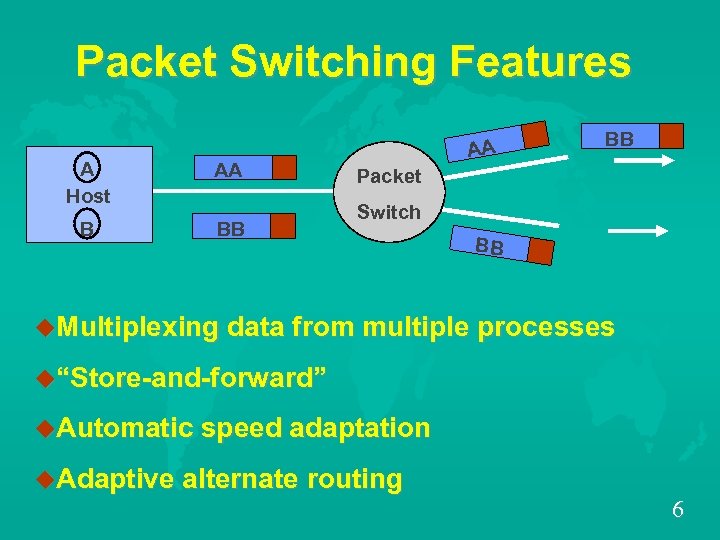 Packet Switching Features A Host AA B BB AA BB Packet Switch BB u. Multiplexing data from multiple processes u“Store-and-forward” u. Automatic speed adaptation u. Adaptive alternate routing 6
Packet Switching Features A Host AA B BB AA BB Packet Switch BB u. Multiplexing data from multiple processes u“Store-and-forward” u. Automatic speed adaptation u. Adaptive alternate routing 6
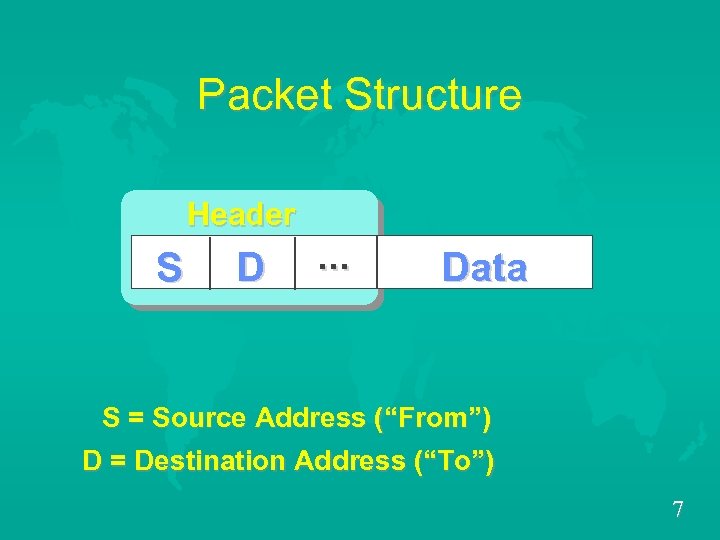 Packet Structure Header S S D . . . Data S = Source Address (“From”) D = Destination Address (“To”) 7
Packet Structure Header S S D . . . Data S = Source Address (“From”) D = Destination Address (“To”) 7
 Internet Addressing u IPv 4 - 32 bits (4. 3 billion addresses) u IPv 6 – 128 bits (1038 addresses) that’s 100 trillion … 8
Internet Addressing u IPv 4 - 32 bits (4. 3 billion addresses) u IPv 6 – 128 bits (1038 addresses) that’s 100 trillion … 8
 Internet Packet Formats “from” address 166. 45. 18. 99 “to” address Version number CONTENTS 204. 146. 165. 100 “ 4” “hello” An Internet Packet 9
Internet Packet Formats “from” address 166. 45. 18. 99 “to” address Version number CONTENTS 204. 146. 165. 100 “ 4” “hello” An Internet Packet 9
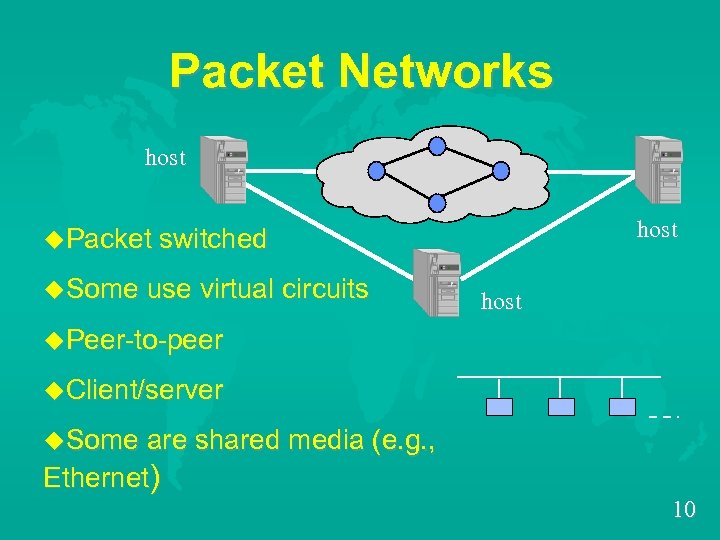 Packet Networks host u. Packet switched u. Some use virtual circuits host u. Peer-to-peer u. Client/server u. Some are shared media (e. g. , Ethernet) 10
Packet Networks host u. Packet switched u. Some use virtual circuits host u. Peer-to-peer u. Client/server u. Some are shared media (e. g. , Ethernet) 10
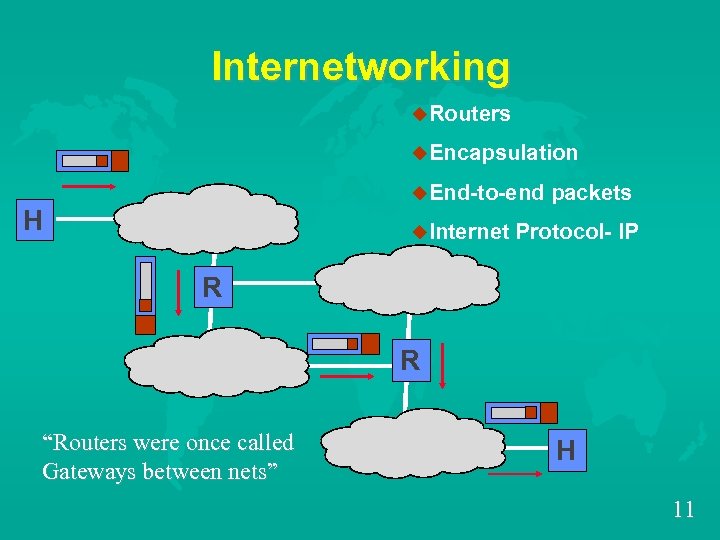 Internetworking u. Routers u. Encapsulation u. End-to-end H u. Internet packets Protocol- IP R R “Routers were once called Gateways between nets” H 11
Internetworking u. Routers u. Encapsulation u. End-to-end H u. Internet packets Protocol- IP R R “Routers were once called Gateways between nets” H 11
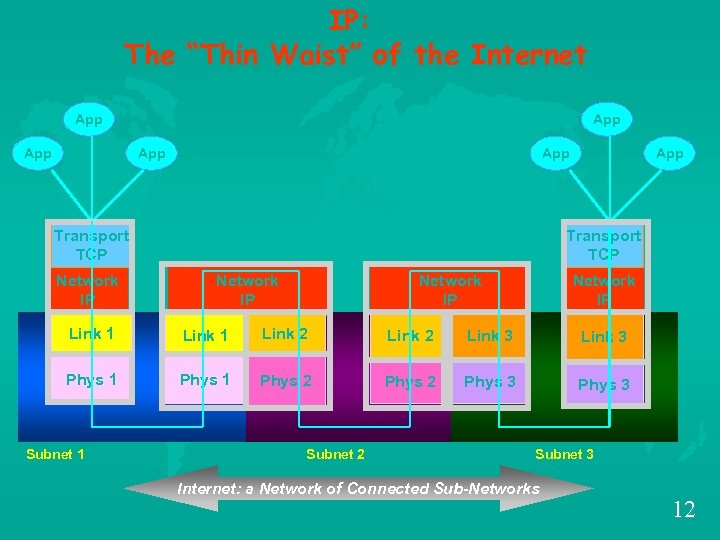 IP: The “Thin Waist” of the Internet App App App Transport TCP Network IP Link 1 Link 2 Link 3 Phys 1 Phys 2 Phys 3 Subnet 1 Subnet 2 Subnet 3 Internet: a Network of Connected Sub-Networks 12
IP: The “Thin Waist” of the Internet App App App Transport TCP Network IP Link 1 Link 2 Link 3 Phys 1 Phys 2 Phys 3 Subnet 1 Subnet 2 Subnet 3 Internet: a Network of Connected Sub-Networks 12
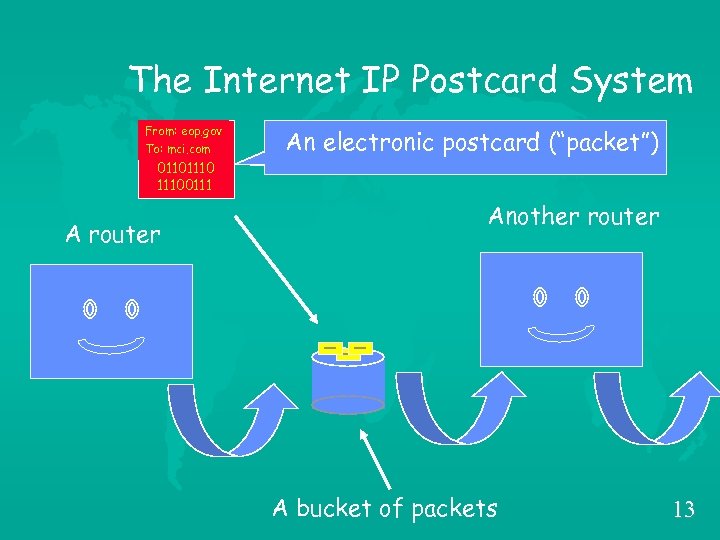 The Internet IP Postcard System From: eop. gov To: mci. com An electronic postcard (“packet”) 011011100111 A router Another router A bucket of packets 13
The Internet IP Postcard System From: eop. gov To: mci. com An electronic postcard (“packet”) 011011100111 A router Another router A bucket of packets 13
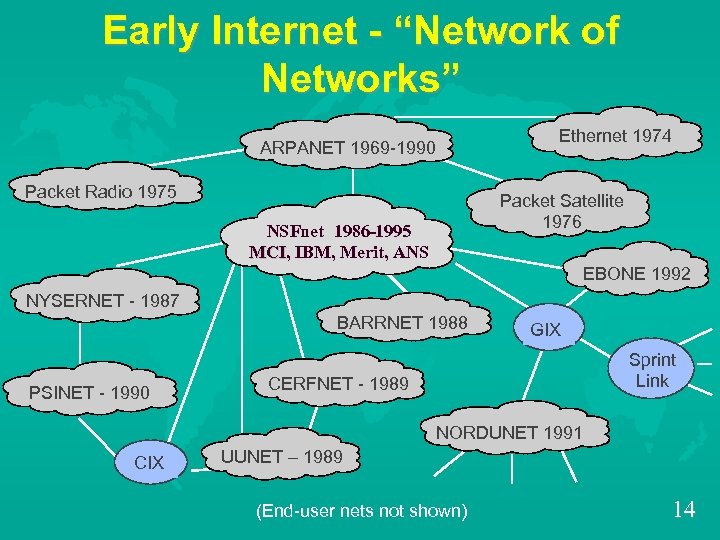 Early Internet - “Network of Networks” Ethernet 1974 ARPANET 1969 -1990 Packet Radio 1975 Packet Satellite 1976 NSFnet 1986 -1995 MCI, IBM, Merit, ANS MCI EBONE 1992 NYSERNET - 1987 BARRNET 1988 PSINET - 1990 GIX Sprint Link CERFNET - 1989 NORDUNET 1991 CIX UUNET – 1989 (End-user nets not shown) 14
Early Internet - “Network of Networks” Ethernet 1974 ARPANET 1969 -1990 Packet Radio 1975 Packet Satellite 1976 NSFnet 1986 -1995 MCI, IBM, Merit, ANS MCI EBONE 1992 NYSERNET - 1987 BARRNET 1988 PSINET - 1990 GIX Sprint Link CERFNET - 1989 NORDUNET 1991 CIX UUNET – 1989 (End-user nets not shown) 14
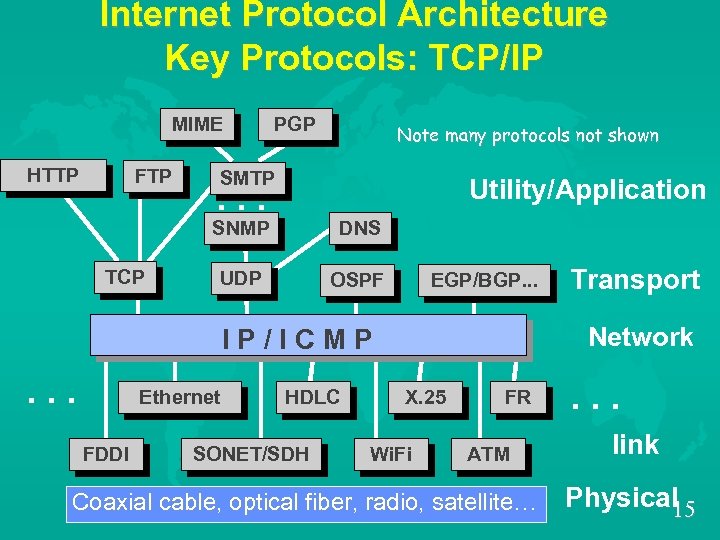 Internet Protocol Architecture Key Protocols: TCP/IP MIME HTTP FTP PGP Note many protocols not shown SMTP Utility/Application . . . SNMP TCP DNS UDP OSPF EGP/BGP. . . Network IP/ICMP . . . Ethernet FDDI HDLC SONET/SDH Transport X. 25 Wi. Fi FR ATM Coaxial cable, optical fiber, radio, satellite… . . . link Physical 15
Internet Protocol Architecture Key Protocols: TCP/IP MIME HTTP FTP PGP Note many protocols not shown SMTP Utility/Application . . . SNMP TCP DNS UDP OSPF EGP/BGP. . . Network IP/ICMP . . . Ethernet FDDI HDLC SONET/SDH Transport X. 25 Wi. Fi FR ATM Coaxial cable, optical fiber, radio, satellite… . . . link Physical 15
 How Does TCP Work? u. Like Sending a Novel on Postcards – Page numbering (ordering, duplicate detection) – Positive Acknowledgement – Retransmission on Timeout – Finite Mailbox 16
How Does TCP Work? u. Like Sending a Novel on Postcards – Page numbering (ordering, duplicate detection) – Positive Acknowledgement – Retransmission on Timeout – Finite Mailbox 16
 Protocol Layering u Key concept – like floors of a building: lower floors support upper ones u Layers form a kind of stair case – users have access to each layer (floor, step) u To understand the Internet, you must look at it from the side to see the layers – looking down from the top conflates all functions into one solid mass. 17
Protocol Layering u Key concept – like floors of a building: lower floors support upper ones u Layers form a kind of stair case – users have access to each layer (floor, step) u To understand the Internet, you must look at it from the side to see the layers – looking down from the top conflates all functions into one solid mass. 17
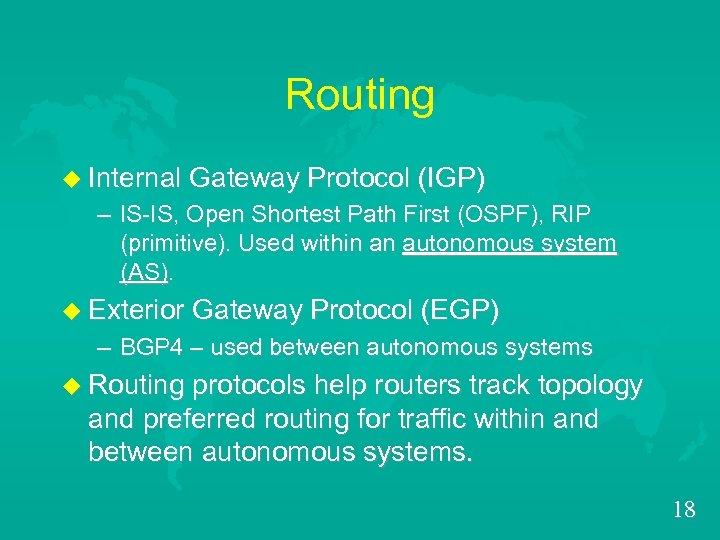 Routing u Internal Gateway Protocol (IGP) – IS-IS, Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), RIP (primitive). Used within an autonomous system (AS) u Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) – BGP 4 – used between autonomous systems u Routing protocols help routers track topology and preferred routing for traffic within and between autonomous systems. 18
Routing u Internal Gateway Protocol (IGP) – IS-IS, Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), RIP (primitive). Used within an autonomous system (AS) u Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) – BGP 4 – used between autonomous systems u Routing protocols help routers track topology and preferred routing for traffic within and between autonomous systems. 18
 Interconnecting Internet Service Providers (ISPs) u Peering and Transit – Peers exchange routing information directly or through Internet Exchanges; and exchange traffic only between their customers (not their peers) – Transit: one net purchases full Internet connectivity from another u Internet Exchanges – London Internet e. Xchange (LINX) – MAE-EAST, MAE-WEST, … – Multiple nets peer at the exchanges 19
Interconnecting Internet Service Providers (ISPs) u Peering and Transit – Peers exchange routing information directly or through Internet Exchanges; and exchange traffic only between their customers (not their peers) – Transit: one net purchases full Internet connectivity from another u Internet Exchanges – London Internet e. Xchange (LINX) – MAE-EAST, MAE-WEST, … – Multiple nets peer at the exchanges 19
 Firewalls u Introduced between edge networks (e. g. corporate nets, home networks) and public Internet u Filter traffic (in either direction) to control access to edge network resources u Vary in complexity and layers of protocol examined for access control. Some observe set-up and tear-down of TCP connections for example. 20
Firewalls u Introduced between edge networks (e. g. corporate nets, home networks) and public Internet u Filter traffic (in either direction) to control access to edge network resources u Vary in complexity and layers of protocol examined for access control. Some observe set-up and tear-down of TCP connections for example. 20
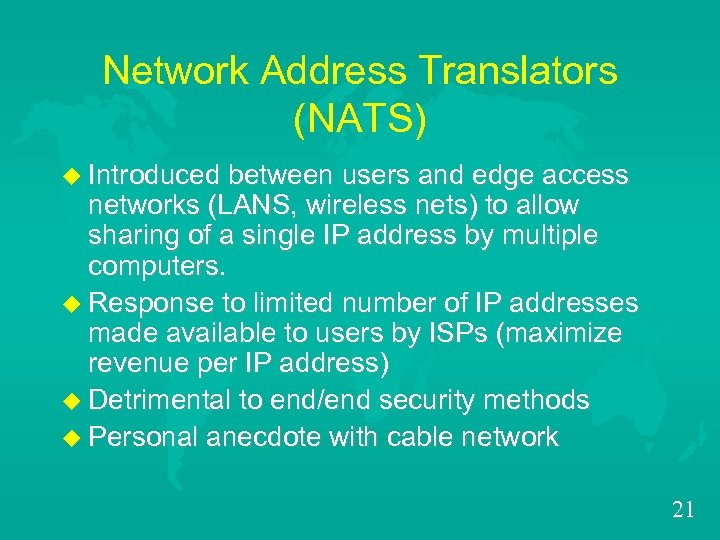 Network Address Translators (NATS) u Introduced between users and edge access networks (LANS, wireless nets) to allow sharing of a single IP address by multiple computers. u Response to limited number of IP addresses made available to users by ISPs (maximize revenue per IP address) u Detrimental to end/end security methods u Personal anecdote with cable network 21
Network Address Translators (NATS) u Introduced between users and edge access networks (LANS, wireless nets) to allow sharing of a single IP address by multiple computers. u Response to limited number of IP addresses made available to users by ISPs (maximize revenue per IP address) u Detrimental to end/end security methods u Personal anecdote with cable network 21
 Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) via IPSEC tunnels u Packets from private (edge) network are encapsulated in IP packets flowing through the public Internet. The payload of each packet is encrypted to protect it while in transit (this creates the “tunnel”) u The edge networks may use private IP addresses rather than public IP addresses without penalty. 22
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) via IPSEC tunnels u Packets from private (edge) network are encapsulated in IP packets flowing through the public Internet. The payload of each packet is encrypted to protect it while in transit (this creates the “tunnel”) u The edge networks may use private IP addresses rather than public IP addresses without penalty. 22
 Domain Names and Addresses u www. isoc. org is a “domain name” – “org” is the “non-commercial top level domain” u 208. 234. 102. 119 is an Internet address – this is really just a way to represent a 32 bit number which how Internet Protocol version 4 represents locations in the Internet, like telephone numbers in the telephone network 23
Domain Names and Addresses u www. isoc. org is a “domain name” – “org” is the “non-commercial top level domain” u 208. 234. 102. 119 is an Internet address – this is really just a way to represent a 32 bit number which how Internet Protocol version 4 represents locations in the Internet, like telephone numbers in the telephone network 23
 Domain Names u Latin characters “A”-”Z”, numbers “ 0”” 9” and “-” (encoded in US ASCII) u They appear in embedded constructs such as email: vcerf@mci. net u In Uniform Resource Locators: – http: //www. mci. com/cerfsup u And in other protocol constructs 24
Domain Names u Latin characters “A”-”Z”, numbers “ 0”” 9” and “-” (encoded in US ASCII) u They appear in embedded constructs such as email: vcerf@mci. net u In Uniform Resource Locators: – http: //www. mci. com/cerfsup u And in other protocol constructs 24
 Top Level Domain Names (TLDs) u u u Generic TLDs: . edu, . com, . org, . net, . mil, . gov, . int, . biz, . aero, . coop, . museum, . name, . pro, . info and country code TLDs: . US, . UK, . FR, . DE, . JP, . ZA, . AU, … But note: . tv, . md, . to, . cc… are operated like generics Infrastructure TLD: . arpa (inverse IP address lookup and also e 164 telephone number entries) The system is hierarchical and each name is unique: www. cnri. reston. va. us The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) delegates responsibility for each TLD to an appropriate entity. 25
Top Level Domain Names (TLDs) u u u Generic TLDs: . edu, . com, . org, . net, . mil, . gov, . int, . biz, . aero, . coop, . museum, . name, . pro, . info and country code TLDs: . US, . UK, . FR, . DE, . JP, . ZA, . AU, … But note: . tv, . md, . to, . cc… are operated like generics Infrastructure TLD: . arpa (inverse IP address lookup and also e 164 telephone number entries) The system is hierarchical and each name is unique: www. cnri. reston. va. us The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) delegates responsibility for each TLD to an appropriate entity. 25
 DNS Components and Mechanics u Domain Name Servers – Associate domain names with IP addresses (among other things) or point to lower level servers with more information – “Root” = “. ” – TLD =. biz (for instance) – Second Level Domain = alpha. biz (e. g. ) – Third Level Domain = www. alpha. biz (e. g. ) 26
DNS Components and Mechanics u Domain Name Servers – Associate domain names with IP addresses (among other things) or point to lower level servers with more information – “Root” = “. ” – TLD =. biz (for instance) – Second Level Domain = alpha. biz (e. g. ) – Third Level Domain = www. alpha. biz (e. g. ) 26
 DNS Components and Mechanics (cont. ) u Domain Name Resolvers – Queries (a sequence of) Domain Name Servers to find the IP address of a given domain name. – If not known by the Resolver already, Resolver may query a Root Server to find a TLD DNS server which will point to a server for second level names, etc. – Resolver returns the results to the party originally asking “what is the address of this domain name? ” – The answer may be: “there is no such domain name in the DNS system”. 27
DNS Components and Mechanics (cont. ) u Domain Name Resolvers – Queries (a sequence of) Domain Name Servers to find the IP address of a given domain name. – If not known by the Resolver already, Resolver may query a Root Server to find a TLD DNS server which will point to a server for second level names, etc. – Resolver returns the results to the party originally asking “what is the address of this domain name? ” – The answer may be: “there is no such domain name in the DNS system”. 27
 Root Servers in the DNS u u u There are 13 Root Servers in the DNS Each of them has a complete table of the addresses of all TLD servers. This table is sometimes called the “Root Zone File. ” There can be many copies of each Root Server (using the “anycast” feature of the Internet routing system) and these copies can be anywhere in the Internet. Each root server system is operated on a volunteer basis by an independent entity. Changes to the Root Zone File must be approved by the US Department of Commerce (National Telecommunications and Information Agency) after approval by IANA. 28
Root Servers in the DNS u u u There are 13 Root Servers in the DNS Each of them has a complete table of the addresses of all TLD servers. This table is sometimes called the “Root Zone File. ” There can be many copies of each Root Server (using the “anycast” feature of the Internet routing system) and these copies can be anywhere in the Internet. Each root server system is operated on a volunteer basis by an independent entity. Changes to the Root Zone File must be approved by the US Department of Commerce (National Telecommunications and Information Agency) after approval by IANA. 28
 Internationalized Domain Names u u u IETF has developed standards for incorporating UNICODE strings into domain names. They are mapped into ASCII code strings of the form “xn-
Internationalized Domain Names u u u IETF has developed standards for incorporating UNICODE strings into domain names. They are mapped into ASCII code strings of the form “xn-
 Domain Name Registration u u u Registry: entity that maintains a database of second level domain name registrations and associated servers Registrar: entity that accepts registrations from users on behalf of registries. Registrars forward relevant information to Registries using standard protocols Some TLD operators perform registrar and registry functions (e. g. many cc. TLD operators) Life of a Domain Name (unregistered, registry hold, in redemption/grace period, expired…) 30
Domain Name Registration u u u Registry: entity that maintains a database of second level domain name registrations and associated servers Registrar: entity that accepts registrations from users on behalf of registries. Registrars forward relevant information to Registries using standard protocols Some TLD operators perform registrar and registry functions (e. g. many cc. TLD operators) Life of a Domain Name (unregistered, registry hold, in redemption/grace period, expired…) 30
 WHOIS u Information about registrants (owner, administrative and technical contact) is kept in the WHOIS database along with many other kinds of information. u There is much controversy over how much of this information should be publicly accessible and what should be protected (there are privacy, law enforcement and intellectual property protection issues involved. ) 31
WHOIS u Information about registrants (owner, administrative and technical contact) is kept in the WHOIS database along with many other kinds of information. u There is much controversy over how much of this information should be publicly accessible and what should be protected (there are privacy, law enforcement and intellectual property protection issues involved. ) 31
 EMAIL u One of the oldest Internet applications u
EMAIL u One of the oldest Internet applications u
 EMAIL u EMAIL is sent from the email client to an email relay using the Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMTP). u A feature of DNS allows one relay to server as a proxy for another through a DNS “MX” entry: u XYZ. COM MX ABC. COM means ABC. COM serves as proxy for XYZ. COM 33
EMAIL u EMAIL is sent from the email client to an email relay using the Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMTP). u A feature of DNS allows one relay to server as a proxy for another through a DNS “MX” entry: u XYZ. COM MX ABC. COM means ABC. COM serves as proxy for XYZ. COM 33
 SPAM u SPAM is unsolicited commercial email and is sometimes consider the scourge of the Internet. u Many efforts are underway to limit the influx of spam, including legislation, technical measures to resist mail relay “hijacking” but the spammers find many ways to circumvent them. 34
SPAM u SPAM is unsolicited commercial email and is sometimes consider the scourge of the Internet. u Many efforts are underway to limit the influx of spam, including legislation, technical measures to resist mail relay “hijacking” but the spammers find many ways to circumvent them. 34
 World Wide Web u Layered atop TCP/IP, WWW uses hypertext transport protocol (http) to carry objects encoded in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) or Extensible Markup Language (XML) between browsers (clients) and servers. u Web Proxies can be configured to intervene between clients and servers acting as filters or as aggregators of web traffic, caching web pages for efficiency. 35
World Wide Web u Layered atop TCP/IP, WWW uses hypertext transport protocol (http) to carry objects encoded in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) or Extensible Markup Language (XML) between browsers (clients) and servers. u Web Proxies can be configured to intervene between clients and servers acting as filters or as aggregators of web traffic, caching web pages for efficiency. 35
 WWW (cont. ) u The WWW system uses hyperlinks that are embedded in HTML or XML pages to allow users to “point and click” to move to new places in the web. u Embedded hyperlinks are expressed as Universal Resource Names, Identifiers or Locators: http: //www. isoc. org/internet/history/doc. html 36
WWW (cont. ) u The WWW system uses hyperlinks that are embedded in HTML or XML pages to allow users to “point and click” to move to new places in the web. u Embedded hyperlinks are expressed as Universal Resource Names, Identifiers or Locators: http: //www. isoc. org/internet/history/doc. html 36
 WWW (cont. ) u Secure Socket Layer (SSL) – This allows client/server communication to be encrypted for privacy using Public Key Cryptography infrastructure (PKI) to transport symmetric cryptographic keys between the parties. – This is an important enabler of ecommerce 37
WWW (cont. ) u Secure Socket Layer (SSL) – This allows client/server communication to be encrypted for privacy using Public Key Cryptography infrastructure (PKI) to transport symmetric cryptographic keys between the parties. – This is an important enabler of ecommerce 37
 Streaming Audio/Video u Usually uses UDP streams (ie. Not guaranteed to be delivered or in order) u Some use Real Time Protocol (RTP) u Some use multicasting capability of the router systems u Some use special distribution services such as those of Akamai and Real Networks. u Quality of Service issues sometimes arise with respect to ISP service level agreements. 38
Streaming Audio/Video u Usually uses UDP streams (ie. Not guaranteed to be delivered or in order) u Some use Real Time Protocol (RTP) u Some use multicasting capability of the router systems u Some use special distribution services such as those of Akamai and Real Networks. u Quality of Service issues sometimes arise with respect to ISP service level agreements. 38
 Voice over Internet (or IP) u Sometime use private IP networks u Sound is encoded, compressed, packetized and sent u Bandwidth requirements may be reduced (no packets when no one is speaking) u Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) a key element in call processing 39
Voice over Internet (or IP) u Sometime use private IP networks u Sound is encoded, compressed, packetized and sent u Bandwidth requirements may be reduced (no packets when no one is speaking) u Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) a key element in call processing 39
 VOIP u u u SIP Proxies can locate Internet VOIP terminations and route traffic to them. SIP destination identifiers may look like email addresses: SIP: vinton. g. cerf@sip. mci. com Media gateways convert to/from packet mode and serial digitized voice in the public switched telephone network. They also convert SIP signaling into conventional SS#7 for example. Free Internet “telephony” from SKYPE, Free World Dialup, or reduced price services including access to PSTN from Vonage, among a number of others. 40
VOIP u u u SIP Proxies can locate Internet VOIP terminations and route traffic to them. SIP destination identifiers may look like email addresses: SIP: vinton. g. cerf@sip. mci. com Media gateways convert to/from packet mode and serial digitized voice in the public switched telephone network. They also convert SIP signaling into conventional SS#7 for example. Free Internet “telephony” from SKYPE, Free World Dialup, or reduced price services including access to PSTN from Vonage, among a number of others. 40
 ENUM u ENUM: maps e 164 international telephone numbers into DNS: u +1 703 886 1690 becomes u 0. 9. 6. 1. 6. 8. 8. 3. 0. 7. 1. e 164. arpa u And the lookup produces a SIP address or other Internet destination (web page, email address) or fax or telephone number, etc. 41
ENUM u ENUM: maps e 164 international telephone numbers into DNS: u +1 703 886 1690 becomes u 0. 9. 6. 1. 6. 8. 8. 3. 0. 7. 1. e 164. arpa u And the lookup produces a SIP address or other Internet destination (web page, email address) or fax or telephone number, etc. 41
 Search Engines u Google, YAHOO!, Alta-Vista, etc. u Systems scan billions of web pages, index them according to text content, rank order them (e. g. by number of hyperlinks pointing to the page) and respond to search queries. u Enormous experimentation with advertising mechanisms – Google instant auctions, etc. 42
Search Engines u Google, YAHOO!, Alta-Vista, etc. u Systems scan billions of web pages, index them according to text content, rank order them (e. g. by number of hyperlinks pointing to the page) and respond to search queries. u Enormous experimentation with advertising mechanisms – Google instant auctions, etc. 42
 Portals u AOL, YAHOO!, MSN, Corporate ebusiness portals, directory services u These are web sites intended to guide users to resources, to perform services for them. u FEDEX, UPS, DHL package tracking systems; Airline flight status information u Travel and shopping services u Business to Business and Business to Consumer services 43
Portals u AOL, YAHOO!, MSN, Corporate ebusiness portals, directory services u These are web sites intended to guide users to resources, to perform services for them. u FEDEX, UPS, DHL package tracking systems; Airline flight status information u Travel and shopping services u Business to Business and Business to Consumer services 43
 GRID Computing u Open Grid Standard Architecture (OGSA) u Virtualize computing, networking and storage resources; allow computer services to register and be “discovered” in directories. u Potential to create network-based supercomputing capability at low cost 44
GRID Computing u Open Grid Standard Architecture (OGSA) u Virtualize computing, networking and storage resources; allow computer services to register and be “discovered” in directories. u Potential to create network-based supercomputing capability at low cost 44
 Security u Many layers of vulnerability and security responses u Denial of Service Attacks (DOS) – Direct attack against routers, DNS servers, hosts – Many avenues: IP, TCP, HTTP, operating system holes…) – Ordinary overload sometimes not distinguishable from DOS attack 45
Security u Many layers of vulnerability and security responses u Denial of Service Attacks (DOS) – Direct attack against routers, DNS servers, hosts – Many avenues: IP, TCP, HTTP, operating system holes…) – Ordinary overload sometimes not distinguishable from DOS attack 45
 Security (cont. ) u Distributed – – – Denial of Service (DDOS) Compromise of many hosts Remote control to launch attacks Always-on DSL and Cable Modem services expose user computers to co-opting u Worms – self propagating software u Viruses – piggy back on email, eg. u Trojan Horses – code embedded into operating system or application software 46
Security (cont. ) u Distributed – – – Denial of Service (DDOS) Compromise of many hosts Remote control to launch attacks Always-on DSL and Cable Modem services expose user computers to co-opting u Worms – self propagating software u Viruses – piggy back on email, eg. u Trojan Horses – code embedded into operating system or application software 46
 Security (cont. ) u Mitigation – Firewalls including personal firewalls (but not sufficient) – ISP DOS detection and mitigation – Virus filters in email relays – “BOT” detectors (system scanning software) – Cyber-hygiene (periodically) 47
Security (cont. ) u Mitigation – Firewalls including personal firewalls (but not sufficient) – ISP DOS detection and mitigation – Virus filters in email relays – “BOT” detectors (system scanning software) – Cyber-hygiene (periodically) 47
 Wireless Access u Wi. Fi (IEEE 802. 11 a, b, g, i, etc. ) u Wi. Max (IEEE 802. 16) u 3 G (mobiles) u GPRS (mobiles) u VSATS (satellite) u Hotspots, SIP/Wi. Fi telephones 48
Wireless Access u Wi. Fi (IEEE 802. 11 a, b, g, i, etc. ) u Wi. Max (IEEE 802. 16) u 3 G (mobiles) u GPRS (mobiles) u VSATS (satellite) u Hotspots, SIP/Wi. Fi telephones 48
 Evolution of Low Level Services u Quality of Service (QOS) u IPv 6 u Domain Name System Security (DNSSEC) – many technical questions u Secure Routing (SBGP) – many technical questions u Intrusion Detection and Mitigation Services 49
Evolution of Low Level Services u Quality of Service (QOS) u IPv 6 u Domain Name System Security (DNSSEC) – many technical questions u Secure Routing (SBGP) – many technical questions u Intrusion Detection and Mitigation Services 49
 GRAND Collaboration u Hardware and software makers u Internet Service Providers, Corporate and institutional Internets u Broadband Wireless Access Providers (mobiles, hotspots, …) u Domain Name Registries, Registrars, Resellers 50
GRAND Collaboration u Hardware and software makers u Internet Service Providers, Corporate and institutional Internets u Broadband Wireless Access Providers (mobiles, hotspots, …) u Domain Name Registries, Registrars, Resellers 50
 Grand Collaboration u Root Server Operators u Regional Internet Registries (ARIN, LACNIC, RIPE-NCC, APNIC, [AFRINIC]) and the Number Resources Organization (NRO) u Web Application Service providers u Hosting service centers 51
Grand Collaboration u Root Server Operators u Regional Internet Registries (ARIN, LACNIC, RIPE-NCC, APNIC, [AFRINIC]) and the Number Resources Organization (NRO) u Web Application Service providers u Hosting service centers 51
 Grand Collaboration u ICANN – Generic Domain Name Support Org (GNSO) – Country Code Domain Name SO (cc. NSO) – Address Support Organization (ASO/NRO) – Gov’t Advisory Committee (GAC) – Security+Stability Advisory Comm (SSAC) – Root Server System Advisory Comm (RSSAC) – At Large Advisory Comm (ALAC) + Regional At Large Organizations (RALO) – Standing Committees (audit, finance, governance, nominations…) 52
Grand Collaboration u ICANN – Generic Domain Name Support Org (GNSO) – Country Code Domain Name SO (cc. NSO) – Address Support Organization (ASO/NRO) – Gov’t Advisory Committee (GAC) – Security+Stability Advisory Comm (SSAC) – Root Server System Advisory Comm (RSSAC) – At Large Advisory Comm (ALAC) + Regional At Large Organizations (RALO) – Standing Committees (audit, finance, governance, nominations…) 52
 Grand Collaboration u Internet Society (ISOC) u Internet Architecture Board (IAB) u Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) u Internet Engineering Steering Group (IESG) u Internet Research Task Force (IRTF) 53
Grand Collaboration u Internet Society (ISOC) u Internet Architecture Board (IAB) u Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) u Internet Engineering Steering Group (IESG) u Internet Research Task Force (IRTF) 53
 Grand Collaboration u International Telecommunications Union – ITU-T, ITU-D u United Nations – UN Development Program, Food and Agriculture Organization (!), UN Information and Communications Technology Task Force, UNESCO, ECOSOC, … 54
Grand Collaboration u International Telecommunications Union – ITU-T, ITU-D u United Nations – UN Development Program, Food and Agriculture Organization (!), UN Information and Communications Technology Task Force, UNESCO, ECOSOC, … 54
 Grand Collaboration u Professional Societies – IEEE, ACM, IEE, … u International Chamber of Commerce u World Intellectual Property Organization u And many more! 55
Grand Collaboration u Professional Societies – IEEE, ACM, IEE, … u International Chamber of Commerce u World Intellectual Property Organization u And many more! 55
 Internet Policy u u Many layers – see papers by Lawrence Solum, Larry Lessig and Richard Whitt Extremely Broad – – – – – Technical Policy (address alloc, DNS integrity, …) Intellectual property protection Consumer protection (fraud, libel…) Abuse (child pornography, drugs…) Dispute Resolution (business, consumer…) Privacy Censorship Freedom of speech … 56
Internet Policy u u Many layers – see papers by Lawrence Solum, Larry Lessig and Richard Whitt Extremely Broad – – – – – Technical Policy (address alloc, DNS integrity, …) Intellectual property protection Consumer protection (fraud, libel…) Abuse (child pornography, drugs…) Dispute Resolution (business, consumer…) Privacy Censorship Freedom of speech … 56
 Recommendation u Identify Issues and concerns FIRST u Develop a Taxonomy of issues u THEN consider venues in which issues and policy concerns can be address u Humbly but strongly urge that the policy issues be viewed IN LAYERED form to understand constituent responsibilities 57
Recommendation u Identify Issues and concerns FIRST u Develop a Taxonomy of issues u THEN consider venues in which issues and policy concerns can be address u Humbly but strongly urge that the policy issues be viewed IN LAYERED form to understand constituent responsibilities 57
 Last Note u Governance does not mean government u It INCLUDES government where this is appropriate but it is a distributed, multilayer responsibility involving private, public sectors and civil society in a wide variety of ways. 58
Last Note u Governance does not mean government u It INCLUDES government where this is appropriate but it is a distributed, multilayer responsibility involving private, public sectors and civil society in a wide variety of ways. 58


