115ad5a198af9c4507c21af2455cafcb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

International Workshop on the Evaluation of Publicly Funded Research Quantitative Models for Guiding Complex S&T Investment Strategies Robert E. Roberts Pamela Ebert Flattau Bhavya Lal 26 September 2005 Berlin S T P I

Complex S&T Investments Strategies S T P I • The US government routinely engages in the assessment of its S&T programs as part of the federal budget process • However, recent emphasis on inter-agency research “priority areas” has revealed shortcomings in federal assessment practices • These shortcomings are chiefly related to current data collection practices. • Improvements in data collection strategies are needed even as appropriate methods are being developed to guide complex S&T investment decisions 2

Presentation Overview S T P I • “Relevance, Quality and Performance” • “Hot Topics” and the S&T Investment Process • Emerging Directions – Harmonization of administrative recordkeeping – Monitoring changes in the S&T infrastructure – Assessing Federal S&T investments on innovation and economic development 3

Complex S&T Investments Strategies S T P I “Relevance, Quality and Performance” 4

The US Federal S&T Budget S T P I “The budget system of the United States Government (USG) provides the means for the President and Congress to decide how much money to spend, what to spend it on, and how to raise the money they have decided to spend. ” “Analytic Perspectives, Budget of the US Government FY 2006” www. omb. gov The USG budget process has 3 key stages: 1. Formulation of the President’s proposed budget, 2. Congressional action on the budget, and 3. Budget implementation by the agencies 5
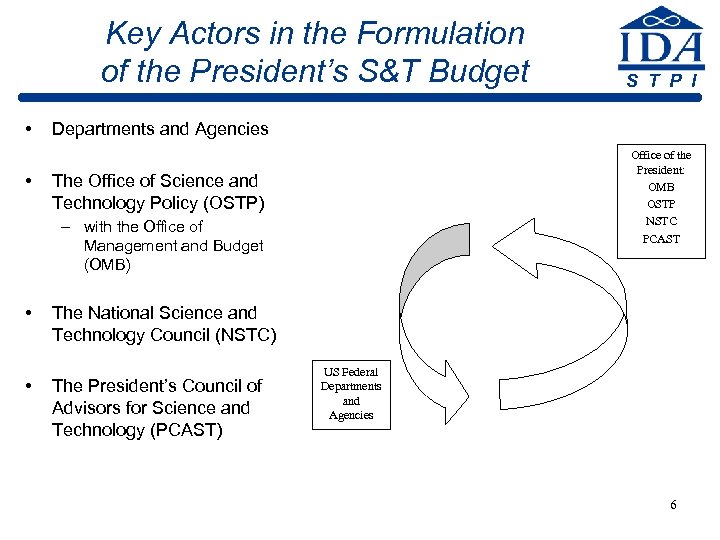
Key Actors in the Formulation of the President’s S&T Budget • • Departments and Agencies Office of the President: OMB OSTP NSTC PCAST The Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) – with the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) • • S T P I The National Science and Technology Council (NSTC) The President’s Council of Advisors for Science and Technology (PCAST) US Federal Departments and Agencies 6

The White House Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) • • Congress established OSTP in 1976 with a broad mandate to advise the President and others within the Executive Office of the President on the effects of science and technology on domestic and international affairs The 1976 Act also authorizes OSTP to lead an interagency effort: • • S T P I Dr. John H. Marburger, Director, confirmed in October 2001, serves as Science Advisor to President Bush. Dr. Marburger also co-chairs the President’s Committee of Advisors on Science and Technology (PCAST) and supports the President’s National Science and Technology Council (NSTC) – to develop and to implement sound science and technology policies and budgets, and – to work with the private sector, state and local governments, the science and higher education communities, and other nations toward this end 7
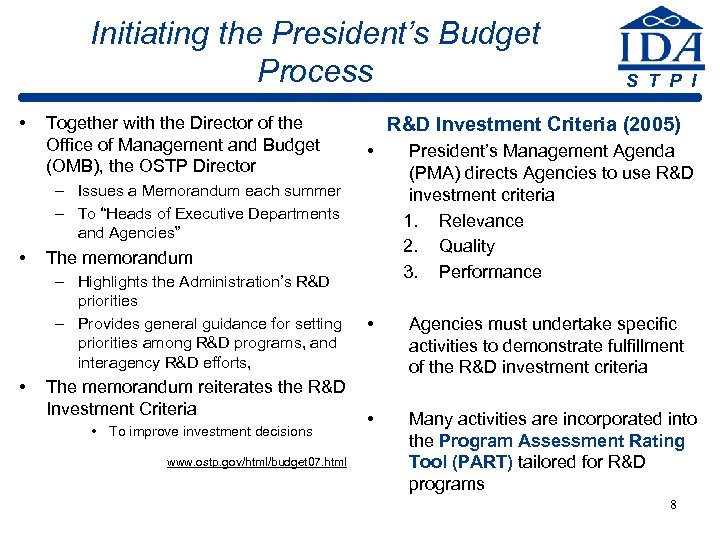
Initiating the President’s Budget Process • Together with the Director of the Office of Management and Budget (OMB), the OSTP Director R&D Investment Criteria (2005) • President’s Management Agenda (PMA) directs Agencies to use R&D investment criteria 1. Relevance 2. Quality 3. Performance • Agencies must undertake specific activities to demonstrate fulfillment of the R&D investment criteria • Many activities are incorporated into the Program Assessment Rating Tool (PART) tailored for R&D programs – Issues a Memorandum each summer – To “Heads of Executive Departments and Agencies” • The memorandum – Highlights the Administration’s R&D priorities – Provides general guidance for setting priorities among R&D programs, and interagency R&D efforts, • The memorandum reiterates the R&D Investment Criteria • To improve investment decisions www. ostp. gov/html/budget 07. html S T P I 8

The Program Assessment Rating Tool (PART) S T P I “The Program Assessment Rating Tool (PART) is a systematic method of assessing the performance of program activities across the Federal government. The PART is a diagnostic tool; the main objective of the PART review is to improve program performance. The PART assessments help link performance to budget decisions and provide a basis for making recommendations to improve results. ” 9 http: //www. whitehouse. gov/omb/part/fy 2006/2006_guidance. pdf
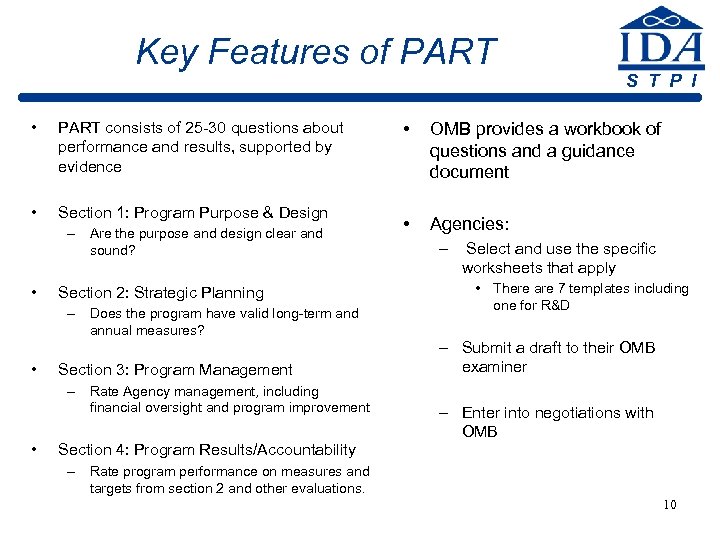
Key Features of PART • PART consists of 25 -30 questions about performance and results, supported by evidence • Section 1: Program Purpose & Design – Are the purpose and design clear and sound? • Section 2: Strategic Planning – Does the program have valid long-term and annual measures? • Section 3: Program Management – Rate Agency management, including financial oversight and program improvement • Section 4: Program Results/Accountability S T P I • OMB provides a workbook of questions and a guidance document • Agencies: – Select and use the specific worksheets that apply • There are 7 templates including one for R&D – Submit a draft to their OMB examiner – Enter into negotiations with OMB – Rate program performance on measures and targets from section 2 and other evaluations. 10
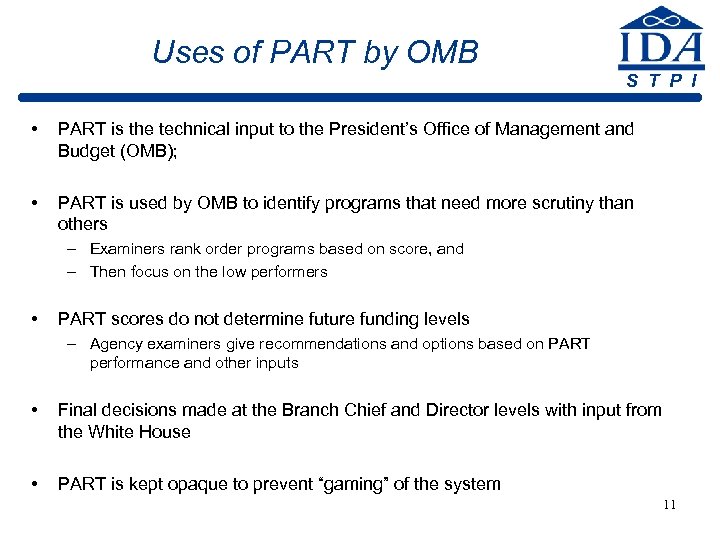
Uses of PART by OMB S T P I • PART is the technical input to the President’s Office of Management and Budget (OMB); • PART is used by OMB to identify programs that need more scrutiny than others – Examiners rank order programs based on score, and – Then focus on the low performers • PART scores do not determine future funding levels – Agency examiners give recommendations and options based on PART performance and other inputs • Final decisions made at the Branch Chief and Director levels with input from the White House • PART is kept opaque to prevent “gaming” of the system 11
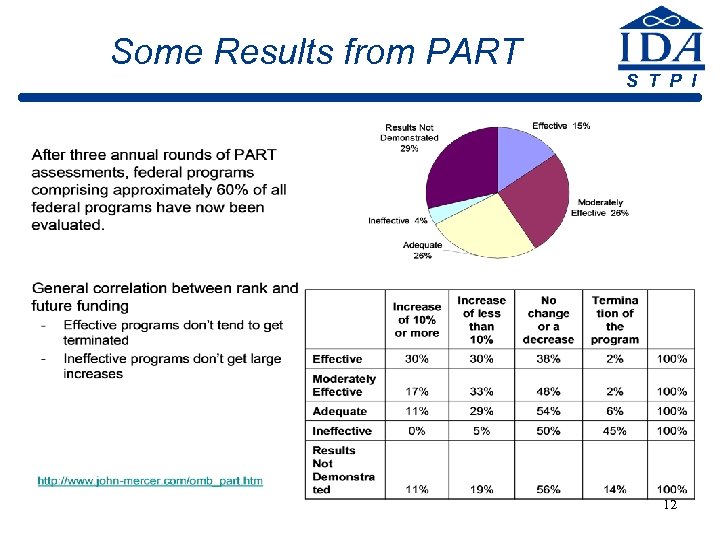
Some Results from PART S T P I 12
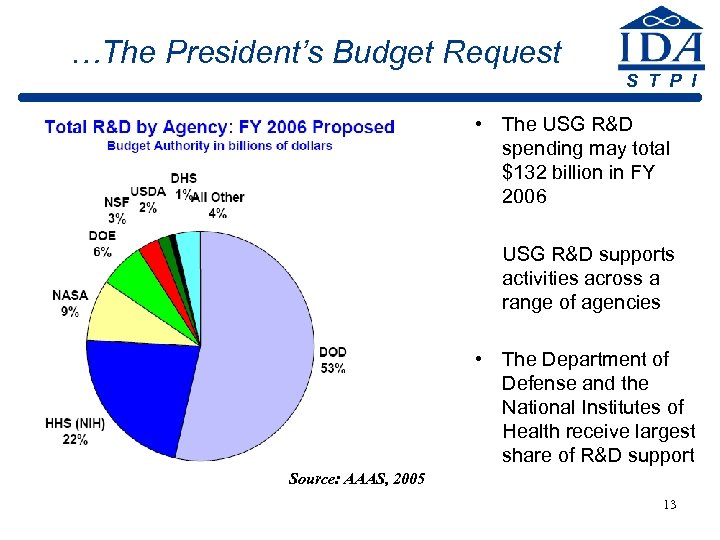
…The President’s Budget Request S T P I • The USG R&D spending may total $132 billion in FY 2006 • USG R&D supports activities across a range of agencies • The Department of Defense and the National Institutes of Health receive largest share of R&D support Source: AAAS, 2005 13

The US Congress S T P I After the President’s S&T Budget has been submitted to the US Congress – Congress engages in careful analysis of the proposed package of S&T funding on an agency-by-agency basis – There is extensive use of expert testimony during the course of Congressional deliberations • To further guide their deliberations, Congress passed the Government Performance and Results Act (GPRA) – Although in reality there is limited use of GPRA when it comes to Congressional S&T budgeting 14

Government Performance and Results Act (GPRA) S T P I • The Government Performance and Results Act (GPRA) – Instructs agencies to prepare strategic plans, performance plans, and performance reports that set goals and report on achieving them • GPRA differs from PART – PART is a tool of the Executive Branch of government; GPRA results in a series of reports to Congress – PART is a method for assessing program performance and how the program achieves goals; GPRA results in an Agency-based goal-setting procedure 15
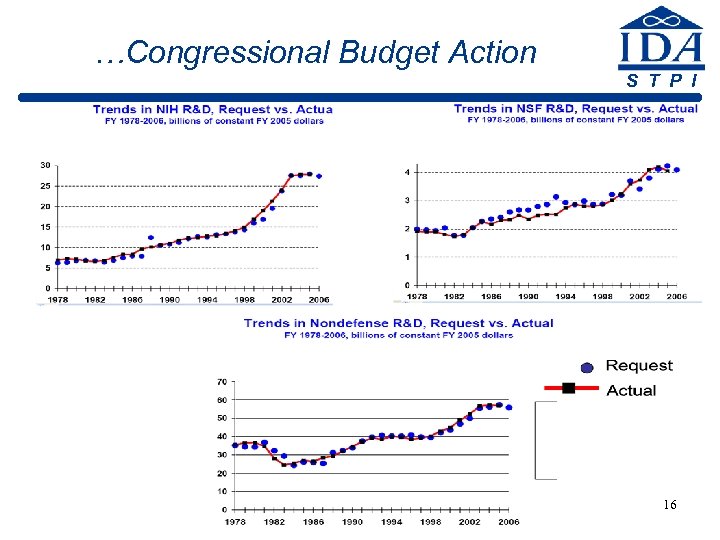
…Congressional Budget Action S T P I 16

Budgeting within US Federal Agencies… S T P I • DOE – Decision-making driven by large “field reviews” and expert panels – Expert recommendations turned into budget priorities • NASA – Decentralized – though changing especially since the new administrator came onboard – Decision-making has a strong quantitative flavor • Sometimes decisions driven by historical and political factors • Optimization and sensitivity studies form the basis of recommendations • NSF – Bottom-up – Driven by program managers and division directors working in consultation with the Agency director 17

“Relevance, Quality, and Performance”– In Summary S T P I • The US government uses a combination of qualitative and quantitative information at various stages of developing its S&T investment strategies • There is greater evidence for the use of formal tools like PART in decisionmaking at the program level when formulating the President’s budget proposal to the US Congress • GPRA represents an important step by the US Congress to require more formal performance reporting at the Agency-level – But chiefly depends on expert testimony for making S&T investment decisions at all levels 18

Complex S&T Investments Strategies S T P I “Hot Topics” and The S&T Investment Process 19

Complex S&T Investments Strategies S T P I • The US Administration often identifies S&T “priority areas” apart from those announced by individual agencies • These priorities typically represent “hot topics” in science and technology – In the national interest – In which the Federal government may initiate funding • Often with the expectation that private sector funding will follow • Agencies may align their S&T activities in support of these announced “priority areas” • The National Nanotechnology Initiative represents a recent example of a priority area 20
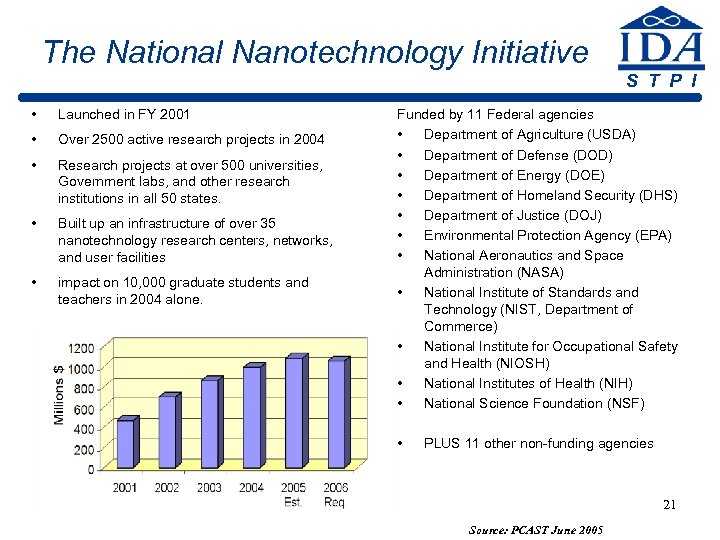
The National Nanotechnology Initiative S T P I • Launched in FY 2001 • Over 2500 active research projects in 2004 • Research projects at over 500 universities, Government labs, and other research institutions in all 50 states. • Built up an infrastructure of over 35 nanotechnology research centers, networks, and user facilities • impact on 10, 000 graduate students and teachers in 2004 alone. Funded by 11 Federal agencies • Department of Agriculture (USDA) • Department of Defense (DOD) • Department of Energy (DOE) • Department of Homeland Security (DHS) • Department of Justice (DOJ) • Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) • National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) • National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST, Department of Commerce) • National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) • National Institutes of Health (NIH) • National Science Foundation (NSF) • PLUS 11 other non-funding agencies 21 Source: PCAST June 2005

This Example Alone Demonstrates the Need for… S T P I • Comparable administrative record-keeping across agencies • Information to understand the role of Federal S&T investments in developing the S&T infrastructure in “priority areas” • The development of realistic models to estimate and monitor the outcomes and impacts of public and private S&T investments in the economy 22

National Science and Technology Council (NSTC) S T P I NSTC plays a critical role in the resolution of many of these measurement challenges • The National Science and Technology Council (NSTC) was established by an Executive Order of the President of the United States on November 23, 1993. • This Cabinet-level Council is the principal means for the President to coordinate the diverse parts of the Federal research and development enterprise • The President chairs the NSTC • Membership consists of: – the Vice President of the United States, – Assistant to the President for Science and Technology (OSTP) • The President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology (PCAST) – Cabinet Secretaries – And Agency Heads with significant science and technology responsibilities, – As well as other White House officials 23
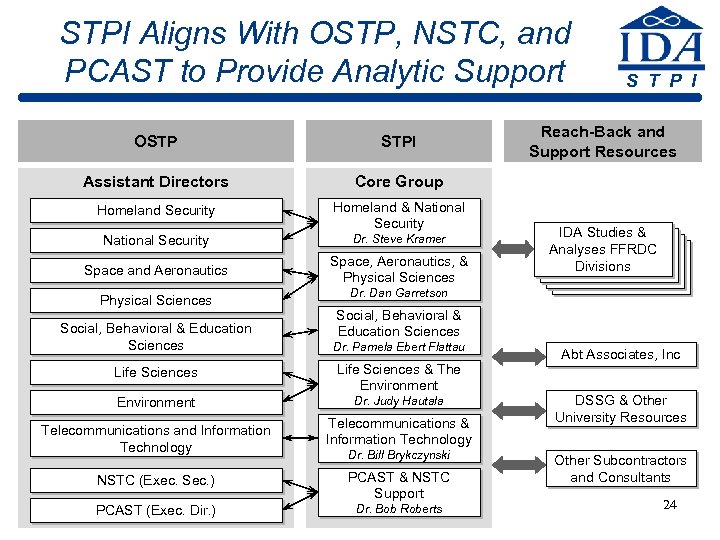
STPI Aligns With OSTP, NSTC, and PCAST to Provide Analytic Support OSTP STPI Assistant Directors Homeland & National Security Dr. Steve Kramer Space and Aeronautics Space, Aeronautics, & Physical Sciences Reach-Back and Support Resources Core Group Homeland Security S T P I Physical Sciences Social, Behavioral & Education Sciences Dr. Dan Garretson Division Directors Social, Behavioral & Education Sciences Dr. Pamela Ebert Flattau Life Sciences & The Environment Dr. Judy Hautala Telecommunications and Information Technology IDA Studies & Analyses FFRDC Studies & Analyses FFRDC Divisions FFRDC Division Directors Telecommunications & Information Technology Dr. Bill Brykczynski NSTC (Exec. Sec. ) PCAST & NSTC Support PCAST (Exec. Dir. ) Dr. Bob Roberts Abt Associates, Inc DSSG & Other University Resources Other Subcontractors and Consultants 24

Complex S&T Investments Strategies S T P I Emerging Directions 25

Harmonization of Administrative Practices S T P I • Many areas of research today • The “E-Government Act of require multi -institutional, 2002” promotes integrated sectoral, and -disciplinary teams reporting across agencies • To facilitate team research, OSTP • The harmonization of issued a a memorandum to all administrative practices can be Federal research agencies in expected to lead to the January 2005 harmonization of administrative recordkeeping – Requiring them to allow formally more than one principal • In 2004, NSTC explored the investigator (PI) on individual utility of administrative records research awards analysis using text-mining and – Implementation planning data visualization techniques to launched formally in July 2005 understand inter-agency and multidisciplinary S&T funding Source: Federal Register July 18 2005 patterns 26
Text-Mining and Data Visualization S T P I Text mining tools coupled with data visualization techniques can facilitate interagency and multidisciplinary S&T planning and evaluation 27

Data Visualization as an Evaluation Tool S T P I • Federal agencies have already begun to examine the role of text-mining and data visualization in understanding large and complex S&T investments – The US Department of Energy analyses of patterns of publications and patenting in Nanotechnology demonstrates the utility of such techniques 28
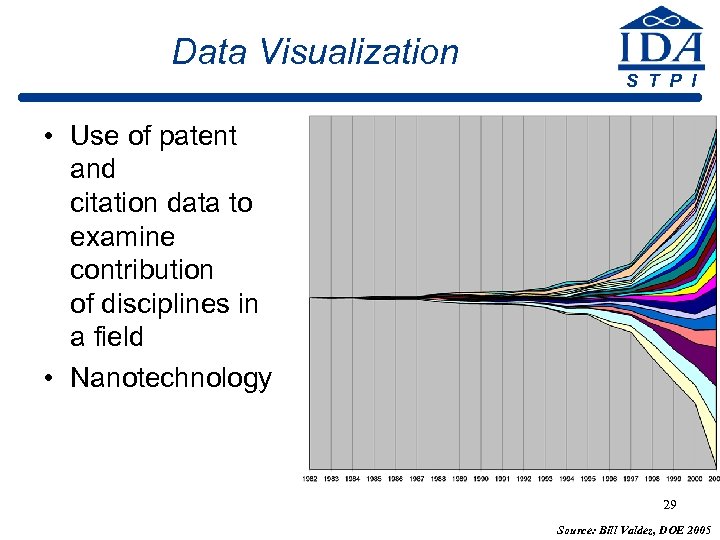
Data Visualization S T P I • Use of patent and citation data to examine contribution of disciplines in a field • Nanotechnology 29 Source: Bill Valdez, DOE 2005
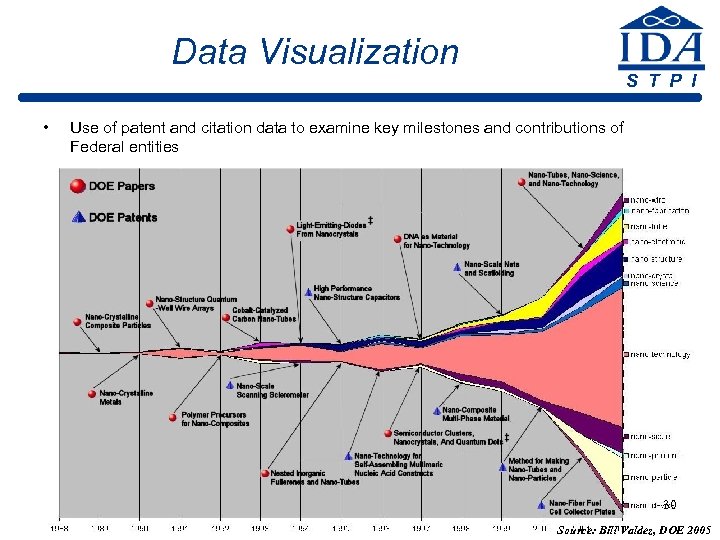
Data Visualization • S T P I Use of patent and citation data to examine key milestones and contributions of Federal entities 30 Source: Bill Valdez, DOE 2005
Monitoring Changes in the S&T Infrastructure • Federal statistical budget ranges from • – High of $629 million (Census Bureau) – Low of $32 million for NSF Science Resources Statistics Division (FY 2004) • S T P I A recent study by the US National Research Council outlined important changes that will make the Federal survey system more responsive to changes in the S&T infrastructure, including: – Taxonomy (i. e. , field definitions) – Emerging definitions of the complex innovation system Complex array of surveys and analyses – S&T workers • Degree production • Employment patterns – S&T investments • Federal • Industrial • Other – S&T performers • In 2004, PCAST convened a workshop on the Federal-State S&T innovation infrastructure – Pointing to further framework development and data collection issues at the Federal-regional interface 31
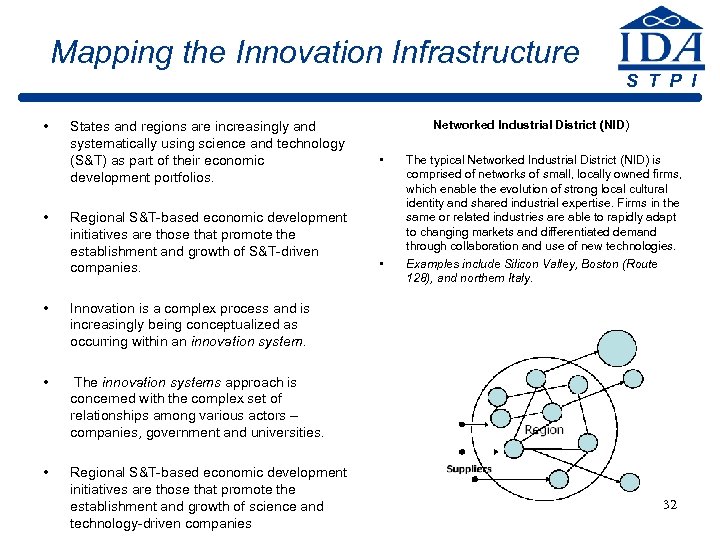
Mapping the Innovation Infrastructure S T P I • • States and regions are increasingly and systematically using science and technology (S&T) as part of their economic development portfolios. Regional S&T-based economic development initiatives are those that promote the establishment and growth of S&T-driven companies. • Regional S&T-based economic development initiatives are those that promote the establishment and growth of science and technology-driven companies • The typical Networked Industrial District (NID) is comprised of networks of small, locally owned firms, which enable the evolution of strong local cultural identity and shared industrial expertise. Firms in the same or related industries are able to rapidly adapt to changing markets and differentiated demand through collaboration and use of new technologies. Examples include Silicon Valley, Boston (Route 128), and northern Italy. The innovation systems approach is concerned with the complex set of relationships among various actors – companies, government and universities. • • Innovation is a complex process and is increasingly being conceptualized as occurring within an innovation system. • Networked Industrial District (NID) 32
There is a Need for Large-Scale Models… • “The combination of finite resources and a multitude of new research opportunities requires careful attention to funding priorities and wise choices by agency managers. . . Agencies must vigorously evaluate existing programs and, wherever possible, consider them for modification, redirection, reduction, or termination in keeping with national needs and priorities…” • S T P I “… We need econometric models…” in sufficient detail to guide complex decision-making Jack Marburger, May 20 Editorial Science magazine • In July 2005, STPI convened a panel of experts to respond to this challenge. July 8 2005 “Memorandum for the Heads of Executive Departments and Agencies” 33

How Case Studies Could Advance Modeling S T P I • Studies of private-sector R&D show that: – The financial returns can be significant; probably as high or higher than other investments; – Social returns may exceed the direct financial returns to investors by a factor of about 2 to 1. • Studies of Federal R&D – Range from large-scale agency-wide analyses to project-level costbenefit studies – Show small to medium financial returns to research, though may be subject to selection biases, and – Use disparate methods that make it difficult to aggregate across studies • A systematic program of case studies of Federal R&D programs, decisions and practices could provide – Better understanding of needed R&D data (metrics, relationships) – Important lessons for decision-making – Improved measures of the social returns to federal R&D 34

Implications for Evaluation Strategies S T P I • Evaluation is becoming increasingly forward-looking and adapting to the new “innovation ecosystem” – Emerging frameworks • Portfolio/system-level assessments – Advanced bibliometrics, paper-patent analysis • Increasingly moving beyond citation analysis to understand linkages between basic research and innovation (paper-patent analysis) • Increasingly looking internationally (triadic patents) – Social network methods • Assess collaboration, multi-disciplinarity by understanding who works with whom and how – Most useful when assessing initiatives where collaborations, interdisciplinarity are critical to achieving outcomes • Often use bibliometric data as input, but can use any data source (administrative records, surveys) • Incorporate visualization and quantitative tools 35
Final Thoughts • • Improvements in data collection strategies are needed even as appropriate methods are being developed to guide complex S&T investment decisions Activities already underway today : – Important changes in Federal administrative practices and recordkeeping – Use of text-mining and data visualization tools can lead to a better understanding of Federal patterns of support of multidisciplinary, interagency funding – Evaluators have already demonstrated the use of data visualization to document complex patterns of S&T investment over time • S T P I Furthermore, numerous sources have described what changes are needed in Federal statistical surveys to reflect the emergence of multidisciplinary, interagency investments in science and technology – One remaining challenge occurs at the Federal-regional interface • • Case studies of the relationship between Federal investment in innovative S&T also has the potential for refining large-scale econometric models to meet the needs of planners and policymakers …so clearly laid out by the President’s Science Advisor. 36
115ad5a198af9c4507c21af2455cafcb.ppt