 International truckage.
International truckage.
 C. M. R. CMR - commodity waybill for registration of international transportation. Is documents proving the fact of conclusion of the agreement on road transport of goods. The CMR consignment note specifies the sender, the recipient, the place of origin of the goods, place of delivery, weight, description of the route and method of transportation, the cost of delivery. CMR essentially contains all information that a bill of lading, but unlike the latter. CMR is not a commodity and administrative documents.
C. M. R. CMR - commodity waybill for registration of international transportation. Is documents proving the fact of conclusion of the agreement on road transport of goods. The CMR consignment note specifies the sender, the recipient, the place of origin of the goods, place of delivery, weight, description of the route and method of transportation, the cost of delivery. CMR essentially contains all information that a bill of lading, but unlike the latter. CMR is not a commodity and administrative documents.
 Features of CMR convention provides that a contract of carriage of goods by road must be confirmed on the shipping invoice. It shall be issued in triplicate and signed by the consignor and the carrier. The first copy is issued to the sender, the second - is attached to the goods, and the third - retained by the carrier. Invoice on shipping is proof of the contract of carriage, its conditions and the receipt by the carrier of the goods.
Features of CMR convention provides that a contract of carriage of goods by road must be confirmed on the shipping invoice. It shall be issued in triplicate and signed by the consignor and the carrier. The first copy is issued to the sender, the second - is attached to the goods, and the third - retained by the carrier. Invoice on shipping is proof of the contract of carriage, its conditions and the receipt by the carrier of the goods.
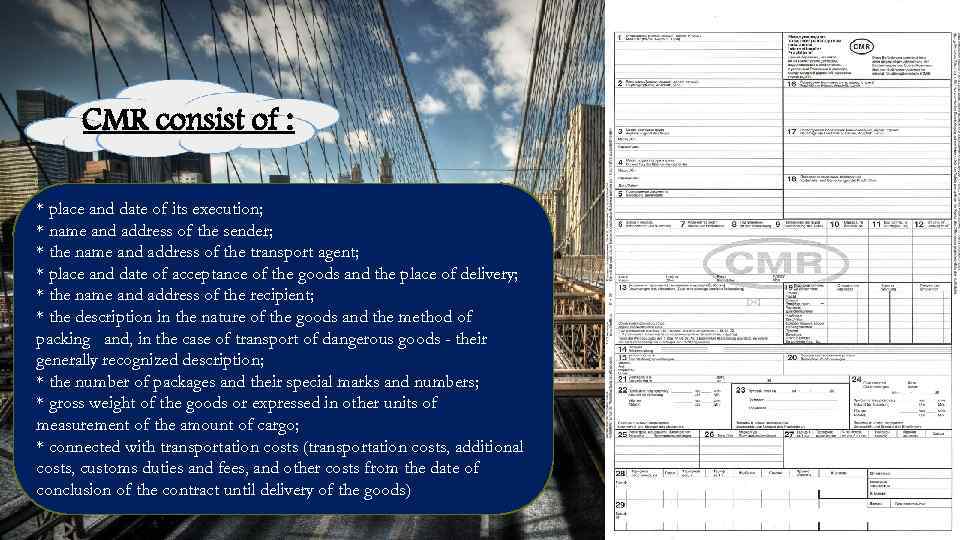 CMR consist of : * place and date of its execution; * name and address of the sender; * the name and address of the transport agent; * place and date of acceptance of the goods and the place of delivery; * the name and address of the recipient; * the description in the nature of the goods and the method of packing and, in the case of transport of dangerous goods - their generally recognized description; * the number of packages and their special marks and numbers; * gross weight of the goods or expressed in other units of measurement of the amount of cargo; * connected with transportation costs (transportation costs, additional costs, customs duties and fees, and other costs from the date of conclusion of the contract until delivery of the goods)
CMR consist of : * place and date of its execution; * name and address of the sender; * the name and address of the transport agent; * place and date of acceptance of the goods and the place of delivery; * the name and address of the recipient; * the description in the nature of the goods and the method of packing and, in the case of transport of dangerous goods - their generally recognized description; * the number of packages and their special marks and numbers; * gross weight of the goods or expressed in other units of measurement of the amount of cargo; * connected with transportation costs (transportation costs, additional costs, customs duties and fees, and other costs from the date of conclusion of the contract until delivery of the goods)
 Access to international transport. The conditions of admission of the carrier to the international road transport are as follows: - availability of licenses for transportation of passengers and goods in accordance with the in the field of licensing; - the presence of vehicles belonging to the right of ownership or on grounds and meet international technical standards; - meet the designated responsible persons with the qualification req the organization of road transport in international traffic; - stable financial position; - required insurance of civil liability of owners of vehicles.
Access to international transport. The conditions of admission of the carrier to the international road transport are as follows: - availability of licenses for transportation of passengers and goods in accordance with the in the field of licensing; - the presence of vehicles belonging to the right of ownership or on grounds and meet international technical standards; - meet the designated responsible persons with the qualification req the organization of road transport in international traffic; - stable financial position; - required insurance of civil liability of owners of vehicles.
 Rights and obligations of the transporter. o ceargf an f c o c ee a t o acccptpnce go a car g ng ipippin sh p i sh r. fe trans cargo
Rights and obligations of the transporter. o ceargf an f c o c ee a t o acccptpnce go a car g ng ipippin sh p i sh r. fe trans cargo
 * the sender has the right to dispose of the goods * if the sender transmits a transporter of dangerous goods, he shall specify the exact nature of the danger represented by these goods * the sender can determine by making an appropriate entry in the consignment note and payment of the prescribed by mutual agreement surcharge to the fare, the amount corresponding to the added value of the goods, on the loss of or damage to goods in case, as well as the undelivered goods in the agreed term. The rights and obligations of the sender.
* the sender has the right to dispose of the goods * if the sender transmits a transporter of dangerous goods, he shall specify the exact nature of the danger represented by these goods * the sender can determine by making an appropriate entry in the consignment note and payment of the prescribed by mutual agreement surcharge to the fare, the amount corresponding to the added value of the goods, on the loss of or damage to goods in case, as well as the undelivered goods in the agreed term. The rights and obligations of the sender.
 Responsibility of carrier 1. The carrier is liable for the total or partial loss of the goods and for damage. 2. The person so entitled may, without requiring the submission of other evidence, take the goods lost if he had not been delivered within thirty days after the deadline or, where such has been established, within sixty days from the date of acceptance of goods by the carrier. 3. If the sender transmits a carrier of dangerous goods, he shall specify the exact nature of the danger, and, if necessary, to specify the necessary precautions to be taken.
Responsibility of carrier 1. The carrier is liable for the total or partial loss of the goods and for damage. 2. The person so entitled may, without requiring the submission of other evidence, take the goods lost if he had not been delivered within thirty days after the deadline or, where such has been established, within sixty days from the date of acceptance of goods by the carrier. 3. If the sender transmits a carrier of dangerous goods, he shall specify the exact nature of the danger, and, if necessary, to specify the necessary precautions to be taken.
 Responsibility of sender The sender must be liable to the carrier for the damage caused to persons, equipment or other goods, as well as for the costs caused by defective packing of the goods, if the external conveyor or known at the time of acceptance of the cargo transporter malfunction was not made reservations concerning it.
Responsibility of sender The sender must be liable to the carrier for the damage caused to persons, equipment or other goods, as well as for the costs caused by defective packing of the goods, if the external conveyor or known at the time of acceptance of the cargo transporter malfunction was not made reservations concerning it.
 Clamsand lawsuits The Convention provides for the Complaint settlement of disputes between the carrier and the recipient of the goods. The claim must be notified to the carrier in the following terms: * at the time of receipt of the goods, in the case of apparent loss or damage; * within 7 working days from the date of delivery, in the case of apparent loss a damage; * within 21 days from the date of delivery of the goods to the recipient, in the case of delay in delivery. * Calculation of these deadlines start from the day following the delivery date or the date of delivery of the goods to the recipient.
Clamsand lawsuits The Convention provides for the Complaint settlement of disputes between the carrier and the recipient of the goods. The claim must be notified to the carrier in the following terms: * at the time of receipt of the goods, in the case of apparent loss or damage; * within 7 working days from the date of delivery, in the case of apparent loss a damage; * within 21 days from the date of delivery of the goods to the recipient, in the case of delay in delivery. * Calculation of these deadlines start from the day following the delivery date or the date of delivery of the goods to the recipient.
 To sum up
To sum up


