3ee09c964fa1f1c561fad629d7d88641.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 International Transportation
International Transportation
 NAFTA • North American Free Trade Agreement • Ratified by Congress in 1994 • Trade agreement between Mexico, Canada, & the United States • Purposes – Unimpeded flow of goods – Most-favored-nation (MNF) status – Enhancement of cross-border movement of goods & services
NAFTA • North American Free Trade Agreement • Ratified by Congress in 1994 • Trade agreement between Mexico, Canada, & the United States • Purposes – Unimpeded flow of goods – Most-favored-nation (MNF) status – Enhancement of cross-border movement of goods & services
 Issues with Mexico • Original agreement allowed U. S. or Mexican based carriers to either pick or deliver (but not both) in each country’s border states with their own equipment & personnel • Mexican regulations still do not allow US-owned trailers to operate more than 12. 5 from the border without a specially-issued permit – US firm must post a bond for each trailer & bond fees are not refundable – Permit is good for only 30 days – Only good for one entrance & one exit for that trailer during life of permit
Issues with Mexico • Original agreement allowed U. S. or Mexican based carriers to either pick or deliver (but not both) in each country’s border states with their own equipment & personnel • Mexican regulations still do not allow US-owned trailers to operate more than 12. 5 from the border without a specially-issued permit – US firm must post a bond for each trailer & bond fees are not refundable – Permit is good for only 30 days – Only good for one entrance & one exit for that trailer during life of permit
 Issues with Mexico • Most US carriers employ a standard 53 ft. trailer • Although Mexican regulations allow 53 ft. trailers, overall combination tractor & trailer length is limited to 68 ft. • This only allows the use of 15 ft. tractors
Issues with Mexico • Most US carriers employ a standard 53 ft. trailer • Although Mexican regulations allow 53 ft. trailers, overall combination tractor & trailer length is limited to 68 ft. • This only allows the use of 15 ft. tractors
 INCOTERMS • International terms of sale • Developed by the International Chamber of Commerce • Define responsibilities of buyer & seller in any international contract of sale • 13 different INCOTERMS
INCOTERMS • International terms of sale • Developed by the International Chamber of Commerce • Define responsibilities of buyer & seller in any international contract of sale • 13 different INCOTERMS
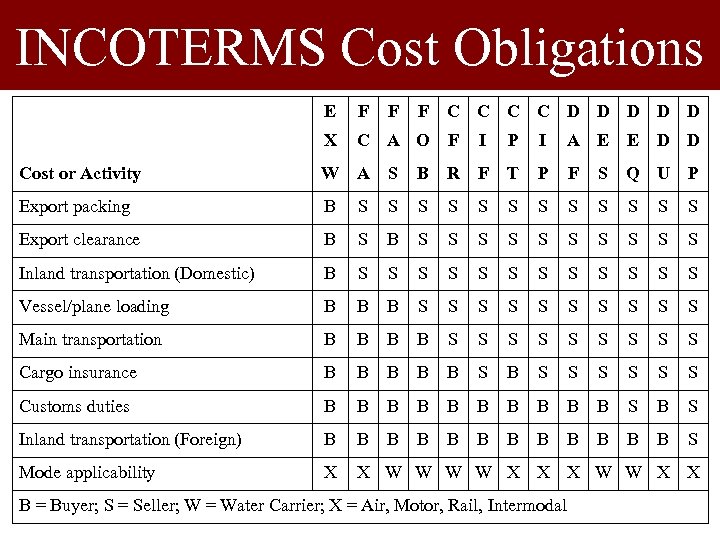 INCOTERMS Cost Obligations E F F F C C D D D X C A O F I P I A E E D D Cost or Activity W A S B R F T P F S Q U P Export packing B S S S Export clearance B S S S Inland transportation (Domestic) B S S S Vessel/plane loading B B B S S S S S Main transportation B B S S S S S Cargo insurance B B B S S S S Customs duties B B B B B S B S Inland transportation (Foreign) B B B S Mode applicability X X W W X X B = Buyer; S = Seller; W = Water Carrier; X = Air, Motor, Rail, Intermodal
INCOTERMS Cost Obligations E F F F C C D D D X C A O F I P I A E E D D Cost or Activity W A S B R F T P F S Q U P Export packing B S S S Export clearance B S S S Inland transportation (Domestic) B S S S Vessel/plane loading B B B S S S S S Main transportation B B S S S S S Cargo insurance B B B S S S S Customs duties B B B B B S B S Inland transportation (Foreign) B B B S Mode applicability X X W W X X B = Buyer; S = Seller; W = Water Carrier; X = Air, Motor, Rail, Intermodal
 E Terms • Only E Term is Ex Works – Departure contract that gives buyer total responsibility for the shipment – Seller only has to make shipment available at its facility – Buyer agrees to take possession at the point of origin – Buyer bears all the costs & risks of transporting the goods to their destination
E Terms • Only E Term is Ex Works – Departure contract that gives buyer total responsibility for the shipment – Seller only has to make shipment available at its facility – Buyer agrees to take possession at the point of origin – Buyer bears all the costs & risks of transporting the goods to their destination
 F Terms • 3 F INCOTERMS • Obligate seller to incur cost of delivering shipment cleared for export to carrier designated by buyer • Buyer selects & incurs cost of main transportation, insurance, & customs clearance
F Terms • 3 F INCOTERMS • Obligate seller to incur cost of delivering shipment cleared for export to carrier designated by buyer • Buyer selects & incurs cost of main transportation, insurance, & customs clearance
 F Terms • Free Carrier (FCA) – Used with any transportation mode – Buyer assumes risk of damage once seller delivers goods to carrier designated by the buyer • Free Alongside Ship (FAS) – Only used in water transportation – Damage risk transfers when goods delivered on the dock – Buyer pays lifting (loading) costs • Free On Board (FOB) – Only used in water transportation – Damage risk transfers when goods cross the ship’s rail – Seller pays lifting costs
F Terms • Free Carrier (FCA) – Used with any transportation mode – Buyer assumes risk of damage once seller delivers goods to carrier designated by the buyer • Free Alongside Ship (FAS) – Only used in water transportation – Damage risk transfers when goods delivered on the dock – Buyer pays lifting (loading) costs • Free On Board (FOB) – Only used in water transportation – Damage risk transfers when goods cross the ship’s rail – Seller pays lifting costs
 C Terms • 4 C INCOTERMS • Obligate seller to obtain and pay for the main carriage and/or cargo insurance • Cost and Freight (CFR) – – Seller selects and pays for main carriage Seller incurs all costs to port of destination Buyer assumes damage risk once goods pass the ship’s rail Only used for water shipments • Carriage Paid To (CPT) – – Seller selects and pays for main carriage Seller incurs all costs to port of destination Buyer assumes damage risk once goods delivered to main carrier Only for any transportation mode
C Terms • 4 C INCOTERMS • Obligate seller to obtain and pay for the main carriage and/or cargo insurance • Cost and Freight (CFR) – – Seller selects and pays for main carriage Seller incurs all costs to port of destination Buyer assumes damage risk once goods pass the ship’s rail Only used for water shipments • Carriage Paid To (CPT) – – Seller selects and pays for main carriage Seller incurs all costs to port of destination Buyer assumes damage risk once goods delivered to main carrier Only for any transportation mode
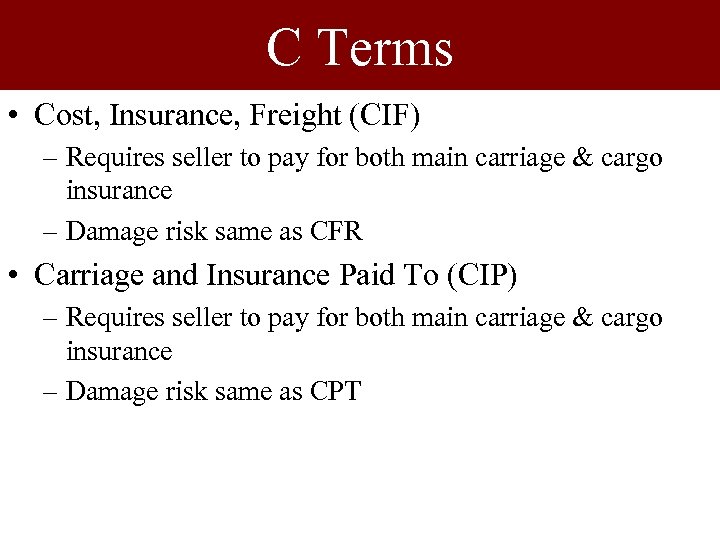 C Terms • Cost, Insurance, Freight (CIF) – Requires seller to pay for both main carriage & cargo insurance – Damage risk same as CFR • Carriage and Insurance Paid To (CIP) – Requires seller to pay for both main carriage & cargo insurance – Damage risk same as CPT
C Terms • Cost, Insurance, Freight (CIF) – Requires seller to pay for both main carriage & cargo insurance – Damage risk same as CFR • Carriage and Insurance Paid To (CIP) – Requires seller to pay for both main carriage & cargo insurance – Damage risk same as CPT
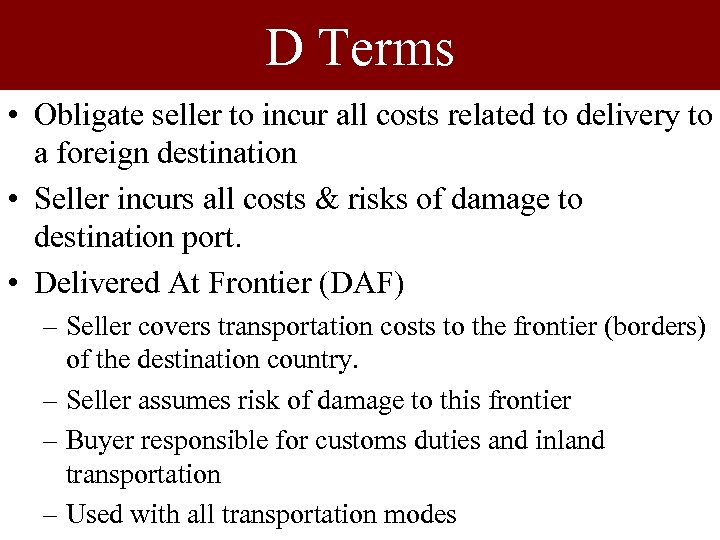 D Terms • Obligate seller to incur all costs related to delivery to a foreign destination • Seller incurs all costs & risks of damage to destination port. • Delivered At Frontier (DAF) – Seller covers transportation costs to the frontier (borders) of the destination country. – Seller assumes risk of damage to this frontier – Buyer responsible for customs duties and inland transportation – Used with all transportation modes
D Terms • Obligate seller to incur all costs related to delivery to a foreign destination • Seller incurs all costs & risks of damage to destination port. • Delivered At Frontier (DAF) – Seller covers transportation costs to the frontier (borders) of the destination country. – Seller assumes risk of damage to this frontier – Buyer responsible for customs duties and inland transportation – Used with all transportation modes
 D Terms • Delivered Ex Ship (DES) – Seller pays for main carriage – Risk of damage transferred on board ship just prior to import clearance – Buyer responsible for customs clearance & inland transportation – Only used in water transportation
D Terms • Delivered Ex Ship (DES) – Seller pays for main carriage – Risk of damage transferred on board ship just prior to import clearance – Buyer responsible for customs clearance & inland transportation – Only used in water transportation
 D Terms • Delivered Ex Quay (or wharf) (DEQ) – Seller pays for main carriage – Risk of damage transferred on quay once goods have cleared customs – Buyer responsible for inland transportation – Only used in water transportation
D Terms • Delivered Ex Quay (or wharf) (DEQ) – Seller pays for main carriage – Risk of damage transferred on quay once goods have cleared customs – Buyer responsible for inland transportation – Only used in water transportation
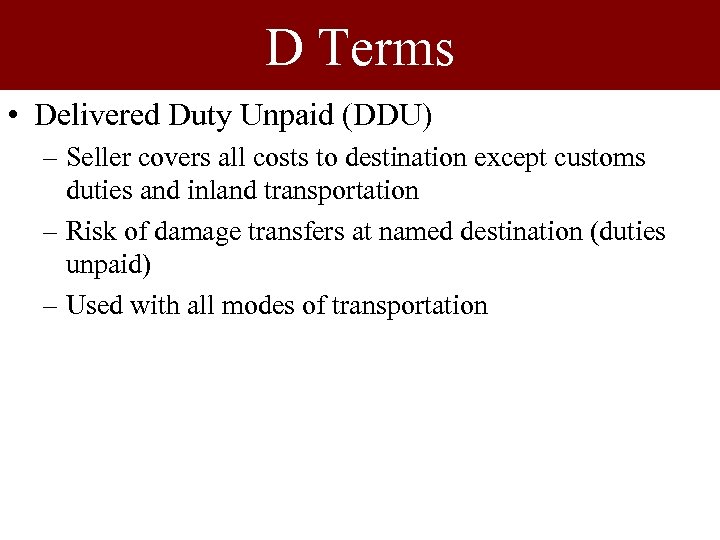 D Terms • Delivered Duty Unpaid (DDU) – Seller covers all costs to destination except customs duties and inland transportation – Risk of damage transfers at named destination (duties unpaid) – Used with all modes of transportation
D Terms • Delivered Duty Unpaid (DDU) – Seller covers all costs to destination except customs duties and inland transportation – Risk of damage transfers at named destination (duties unpaid) – Used with all modes of transportation
 D Terms • Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) – Seller covers all costs to destination except inland transportation – Risk of damage transfers at named destination (duties paid) – Used with all modes of transportation
D Terms • Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) – Seller covers all costs to destination except inland transportation – Risk of damage transfers at named destination (duties paid) – Used with all modes of transportation
 Documentation • Export License – No special authority necessary to export • President can control exports for national security, foreign policy, or for items in short supply • Federal agency may require export license for commodities over which it may have jurisdiction – Types of Licenses • Issued by Department of Commerce • Validated Export License – Required for commodities and/or destinations deemed important to national security, foreign policy, or for items in short supply • General Export License – Used in all instances when validated license not required – No actual license is issued
Documentation • Export License – No special authority necessary to export • President can control exports for national security, foreign policy, or for items in short supply • Federal agency may require export license for commodities over which it may have jurisdiction – Types of Licenses • Issued by Department of Commerce • Validated Export License – Required for commodities and/or destinations deemed important to national security, foreign policy, or for items in short supply • General Export License – Used in all instances when validated license not required – No actual license is issued
 Documentation • Sales Documents – Pro-forma invoice • Issued by seller • Provides shipment details to importer & import government authorities – Commercial invoice • • Issued by seller Serves as bill of sale Serves as basis for determining shipment value & import duties Required for customs clearance – Consular invoice • Same as commercial except prescribed by importing country and must be in language of the importing country
Documentation • Sales Documents – Pro-forma invoice • Issued by seller • Provides shipment details to importer & import government authorities – Commercial invoice • • Issued by seller Serves as bill of sale Serves as basis for determining shipment value & import duties Required for customs clearance – Consular invoice • Same as commercial except prescribed by importing country and must be in language of the importing country
 Documentation • Financial Documents – Letter of Credit • Issued by buyer’s bank • Guarantee by the bank to seller that payment will be made if certain terms & conditions are met – Documentation provided, shipment dates, time limits, etc. – Draft • Credit extended by seller, not the buyer’s bank • Written order for money to be paid by buyer on certain date • Draft is presented to buyer’s bank, bank collects money from buyer, bank releases documentation necessary for buyer to receive shipment, payment is remitted to seller
Documentation • Financial Documents – Letter of Credit • Issued by buyer’s bank • Guarantee by the bank to seller that payment will be made if certain terms & conditions are met – Documentation provided, shipment dates, time limits, etc. – Draft • Credit extended by seller, not the buyer’s bank • Written order for money to be paid by buyer on certain date • Draft is presented to buyer’s bank, bank collects money from buyer, bank releases documentation necessary for buyer to receive shipment, payment is remitted to seller
 Documentation • Customs Documents – Export Declaration • Issued by seller • Controls export of restricted goods • Used to provide statistics regarding export activity – Certificate of Origin • Issued by buyer • Certifies the country in which the commodities were produced • Necessary when countries have special import duty treaties
Documentation • Customs Documents – Export Declaration • Issued by seller • Controls export of restricted goods • Used to provide statistics regarding export activity – Certificate of Origin • Issued by buyer • Certifies the country in which the commodities were produced • Necessary when countries have special import duty treaties
 Documentation • Transportation Documents – Bill of Lading • • • Contract for carriage Receipt for goods Provides delivery instructions to carrier Water: ocean bill of lading Air: airway bill – Packing lists • Detailed information about package contents, dimensions, and weight – Dock receipt • Used by water carriers • Transfers accountability from domestic carrier to international carrier prior to loading on the ship (I. e. , while goods are still on the quay).
Documentation • Transportation Documents – Bill of Lading • • • Contract for carriage Receipt for goods Provides delivery instructions to carrier Water: ocean bill of lading Air: airway bill – Packing lists • Detailed information about package contents, dimensions, and weight – Dock receipt • Used by water carriers • Transfers accountability from domestic carrier to international carrier prior to loading on the ship (I. e. , while goods are still on the quay).
 International Transportation Providers: Ocean Transportation • Liners – Ply fixed routes on published schedules – Charge according to published tariffs – Goods moved to liner’s terminal – Types of Liner Services • Break-bulk services – Freight is not containerized and must be loaded by machine – May take days to load & unload the vessel • Container services – Freight packed in standard containers & is loaded by crane – Typically takes less than 12 hours for container vessel to enter port, unload, and clear the port – Typical container ship can carry about 1000 containers – Must be support by 1500 to 2500 containers
International Transportation Providers: Ocean Transportation • Liners – Ply fixed routes on published schedules – Charge according to published tariffs – Goods moved to liner’s terminal – Types of Liner Services • Break-bulk services – Freight is not containerized and must be loaded by machine – May take days to load & unload the vessel • Container services – Freight packed in standard containers & is loaded by crane – Typically takes less than 12 hours for container vessel to enter port, unload, and clear the port – Typical container ship can carry about 1000 containers – Must be support by 1500 to 2500 containers
 International Transportation Providers: Ocean Transportation • Liners – Types of Liners • Container Vessels • Lighter-Aboard Ship (LASH) – Liner carries barges that were loaded at inland river port and moved to ocean port via water tow. – LASH carries the barges with their loads intact to destination port • Roll-on/Roll-off Ship (RORO) – Transport trucks, trailers, & construction equipment – In essence, the freight is rolled-on & -off the vessel, rather than lifted over the vessel’s rail
International Transportation Providers: Ocean Transportation • Liners – Types of Liners • Container Vessels • Lighter-Aboard Ship (LASH) – Liner carries barges that were loaded at inland river port and moved to ocean port via water tow. – LASH carries the barges with their loads intact to destination port • Roll-on/Roll-off Ship (RORO) – Transport trucks, trailers, & construction equipment – In essence, the freight is rolled-on & -off the vessel, rather than lifted over the vessel’s rail
 International Transportation Providers: Ocean Transportation • Tramp Ships – Hired like a taxi or leased auto – Hired on a voyage or time basis – Tramps do not run regular routes on published schedules like liners • Private Vessels – Ships owned/leased on long-term basis by firm moving the goods – Enjoy much the same economies as private motor carriers
International Transportation Providers: Ocean Transportation • Tramp Ships – Hired like a taxi or leased auto – Hired on a voyage or time basis – Tramps do not run regular routes on published schedules like liners • Private Vessels – Ships owned/leased on long-term basis by firm moving the goods – Enjoy much the same economies as private motor carriers
 International Transportation Providers: Ocean Transportation • Ship Registry – Vessels may be “flagged” or registered in the ship owner’s domestic nation, or in another nation – Vessel is taxed, manned, and operated under the rules & regulations of the nation under which it is flagged – Flags of Convenience • Nations that “flag” foreign-owned vessels • Most common are Liberia and Panama
International Transportation Providers: Ocean Transportation • Ship Registry – Vessels may be “flagged” or registered in the ship owner’s domestic nation, or in another nation – Vessel is taxed, manned, and operated under the rules & regulations of the nation under which it is flagged – Flags of Convenience • Nations that “flag” foreign-owned vessels • Most common are Liberia and Panama
 International Transportation Providers: Air Transportation • Air Parcel Post – Provided by the postal service of a country – Designed to handle small packages – Air carrier hired to pick up and deliver parcel items from one country to another – Each nation sets its own limits on size & weight • US restrictions are 108 inches in length & girth; no more than 70 lbs of weight
International Transportation Providers: Air Transportation • Air Parcel Post – Provided by the postal service of a country – Designed to handle small packages – Air carrier hired to pick up and deliver parcel items from one country to another – Each nation sets its own limits on size & weight • US restrictions are 108 inches in length & girth; no more than 70 lbs of weight
 International Transportation Providers: Ancillary Services • Air Freight Forwarders – Book space on air carrier’s plan – Solicits freight from shippers to fill booked space • International Freight Forwarders – Arrange movements for shippers – Represent shipper in arranging various activities • Inland transportation, packaging, documentation, booking, legal fees – Do not serve as freight consolidators
International Transportation Providers: Ancillary Services • Air Freight Forwarders – Book space on air carrier’s plan – Solicits freight from shippers to fill booked space • International Freight Forwarders – Arrange movements for shippers – Represent shipper in arranging various activities • Inland transportation, packaging, documentation, booking, legal fees – Do not serve as freight consolidators
 International Transportation Providers: Ancillary Services • Nonvessel Operating Common Carriers (NVOCC) – Assemble/disperse less-than-container shipments – Move them as full-container shipments • Ship Brokers – Acts as intermediaries between tramp ship owners and chartering shippers or receivers • Ship Agents – Represent liner or tramps in facilitating ship arrival, clearance, un/loading, fee payment at specific ports – Used when not economical to maintain permanent agent in particular ports
International Transportation Providers: Ancillary Services • Nonvessel Operating Common Carriers (NVOCC) – Assemble/disperse less-than-container shipments – Move them as full-container shipments • Ship Brokers – Acts as intermediaries between tramp ship owners and chartering shippers or receivers • Ship Agents – Represent liner or tramps in facilitating ship arrival, clearance, un/loading, fee payment at specific ports – Used when not economical to maintain permanent agent in particular ports
 International Transportation Providers: Ancillary Services • Land Bridges – System of containers moving between Japan and Europe by rail and ship • Mini-Bridges – System of containers moving on specified route between US port locations (I. e. , Seattle to New York) • Micro-Bridges – Essentially the same as mini-bridges, but routes are between port and non-port cities (I. e. , New Orleans to Kansas City)
International Transportation Providers: Ancillary Services • Land Bridges – System of containers moving between Japan and Europe by rail and ship • Mini-Bridges – System of containers moving on specified route between US port locations (I. e. , Seattle to New York) • Micro-Bridges – Essentially the same as mini-bridges, but routes are between port and non-port cities (I. e. , New Orleans to Kansas City)


