20b4e7832fde9617baea7a3ae8945166.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

 International Trade Voluntary Trade Creates Wealth
International Trade Voluntary Trade Creates Wealth
 Reasons for International Trade n Possession of special resources – Raw materials, skilled labor, geography n Economic advantages – Comparative & Absolute Advantage n Politics – Trade organizations, agreements – OPEC, NAFTA
Reasons for International Trade n Possession of special resources – Raw materials, skilled labor, geography n Economic advantages – Comparative & Absolute Advantage n Politics – Trade organizations, agreements – OPEC, NAFTA
 Possession of special resources n Unique Climate or Terrain – Hawaii – pineapple, Wisconsin - cheese n Valuable Raw Materials – Middle East – Oil, South Africa - Diamonds n Skilled Labor Force – U. S. – Engineers, India – Software writers n Capital Resources – Developed Countries, Tools - inventions n Favorable Geographic Location – Resources, Harbors, Transportation
Possession of special resources n Unique Climate or Terrain – Hawaii – pineapple, Wisconsin - cheese n Valuable Raw Materials – Middle East – Oil, South Africa - Diamonds n Skilled Labor Force – U. S. – Engineers, India – Software writers n Capital Resources – Developed Countries, Tools - inventions n Favorable Geographic Location – Resources, Harbors, Transportation
 International Trade Economic Advantages Comparative Advantage Do what you are best at. Absolute Advantage When best at compared to others. ideas of David Ricardo
International Trade Economic Advantages Comparative Advantage Do what you are best at. Absolute Advantage When best at compared to others. ideas of David Ricardo
 Hatfields vs Mc. Coys Should they Trade? n Hatfields Corn 8 hours Cloth 10 hours n Mc. Coys Corn 15 hours Cloth 12 hours Who has an absolute advantage in CORN production? Who has an absolute advantage in CLOTH production? Who has a comparative advantage in CORN production? Who has a comparative advantage in CLOTH production? If the Hatfields and Mc. Coys specialize & trade will they both gain?
Hatfields vs Mc. Coys Should they Trade? n Hatfields Corn 8 hours Cloth 10 hours n Mc. Coys Corn 15 hours Cloth 12 hours Who has an absolute advantage in CORN production? Who has an absolute advantage in CLOTH production? Who has a comparative advantage in CORN production? Who has a comparative advantage in CLOTH production? If the Hatfields and Mc. Coys specialize & trade will they both gain?
 Trade n Specialization raises standard of living n Specialization makes us interdependent
Trade n Specialization raises standard of living n Specialization makes us interdependent
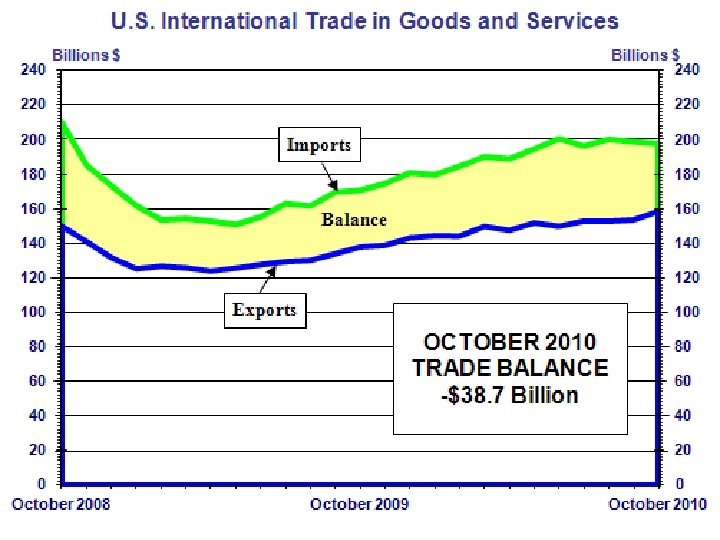
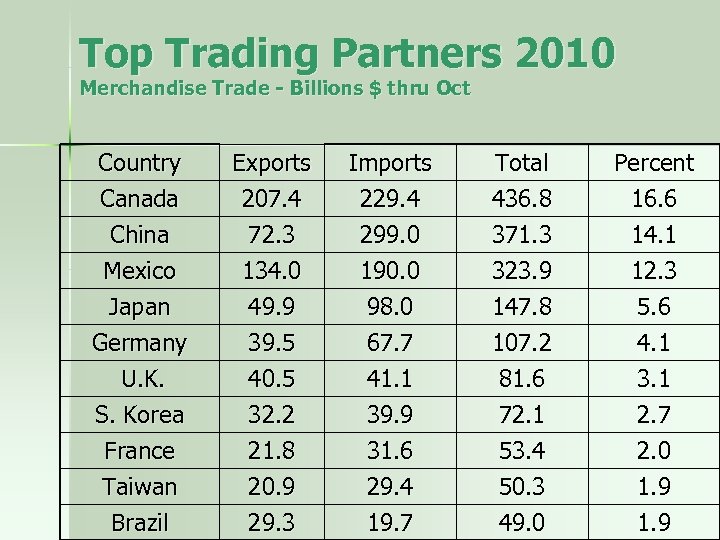 Top Trading Partners 2010 Merchandise Trade - Billions $ thru Oct Country Canada China Mexico Exports 207. 4 72. 3 134. 0 Imports 229. 4 299. 0 190. 0 Total 436. 8 371. 3 323. 9 Percent 16. 6 14. 1 12. 3 Japan Germany U. K. S. Korea France Taiwan 49. 9 39. 5 40. 5 32. 2 21. 8 20. 9 98. 0 67. 7 41. 1 39. 9 31. 6 29. 4 147. 8 107. 2 81. 6 72. 1 53. 4 50. 3 5. 6 4. 1 3. 1 2. 7 2. 0 1. 9 Brazil 29. 3 19. 7 49. 0 1. 9
Top Trading Partners 2010 Merchandise Trade - Billions $ thru Oct Country Canada China Mexico Exports 207. 4 72. 3 134. 0 Imports 229. 4 299. 0 190. 0 Total 436. 8 371. 3 323. 9 Percent 16. 6 14. 1 12. 3 Japan Germany U. K. S. Korea France Taiwan 49. 9 39. 5 40. 5 32. 2 21. 8 20. 9 98. 0 67. 7 41. 1 39. 9 31. 6 29. 4 147. 8 107. 2 81. 6 72. 1 53. 4 50. 3 5. 6 4. 1 3. 1 2. 7 2. 0 1. 9 Brazil 29. 3 19. 7 49. 0 1. 9
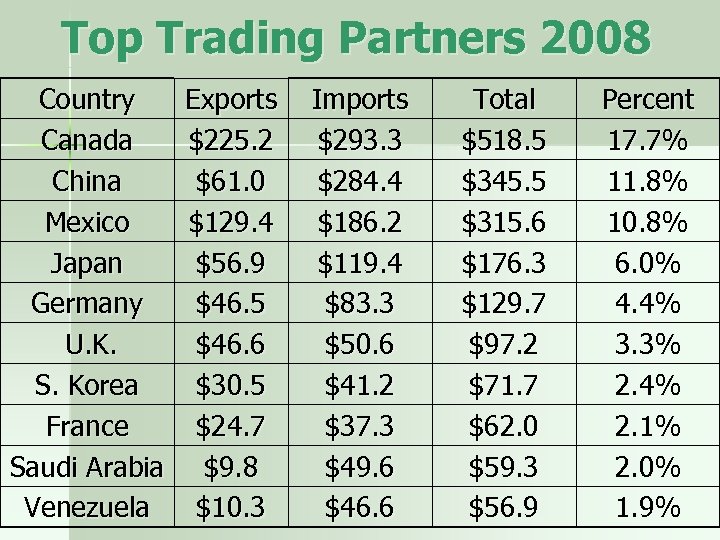 Top Trading Partners 2008 Country Canada China Mexico Japan Germany U. K. S. Korea France Saudi Arabia Venezuela Exports $225. 2 $61. 0 $129. 4 $56. 9 $46. 5 $46. 6 $30. 5 $24. 7 $9. 8 $10. 3 Imports $293. 3 $284. 4 $186. 2 $119. 4 $83. 3 $50. 6 $41. 2 $37. 3 $49. 6 $46. 6 Total $518. 5 $345. 5 $315. 6 $176. 3 $129. 7 $97. 2 $71. 7 $62. 0 $59. 3 $56. 9 Percent 17. 7% 11. 8% 10. 8% 6. 0% 4. 4% 3. 3% 2. 4% 2. 1% 2. 0% 1. 9%
Top Trading Partners 2008 Country Canada China Mexico Japan Germany U. K. S. Korea France Saudi Arabia Venezuela Exports $225. 2 $61. 0 $129. 4 $56. 9 $46. 5 $46. 6 $30. 5 $24. 7 $9. 8 $10. 3 Imports $293. 3 $284. 4 $186. 2 $119. 4 $83. 3 $50. 6 $41. 2 $37. 3 $49. 6 $46. 6 Total $518. 5 $345. 5 $315. 6 $176. 3 $129. 7 $97. 2 $71. 7 $62. 0 $59. 3 $56. 9 Percent 17. 7% 11. 8% 10. 8% 6. 0% 4. 4% 3. 3% 2. 4% 2. 1% 2. 0% 1. 9%
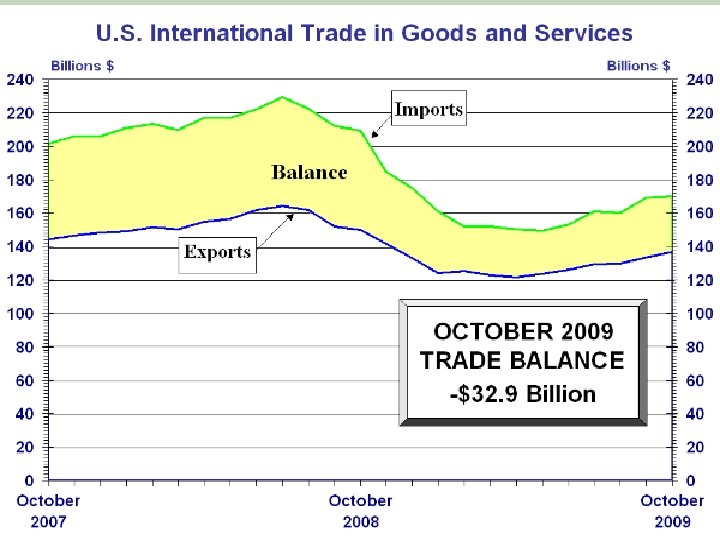
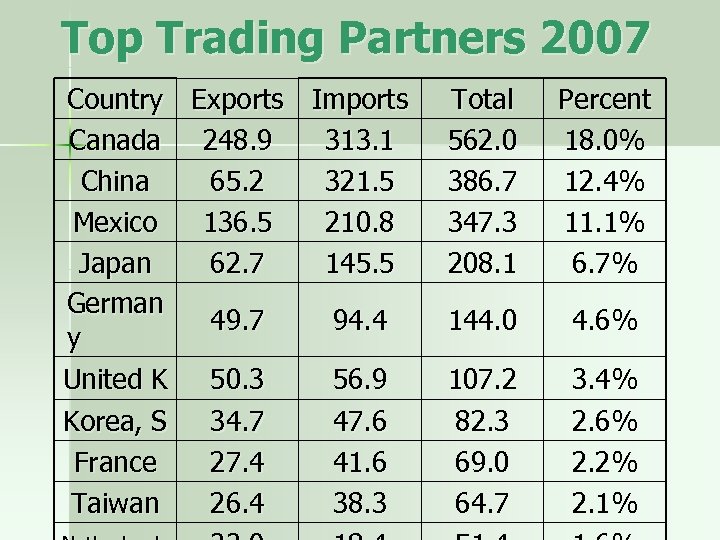 Top Trading Partners 2007 Country Exports Imports Canada 248. 9 313. 1 China 65. 2 321. 5 Mexico 136. 5 210. 8 Japan 62. 7 145. 5 German 49. 7 94. 4 y United K 50. 3 56. 9 Korea, S 34. 7 47. 6 France 27. 4 41. 6 Taiwan 26. 4 38. 3 Total 562. 0 386. 7 347. 3 208. 1 Percent 18. 0% 12. 4% 11. 1% 6. 7% 144. 0 4. 6% 107. 2 82. 3 69. 0 64. 7 3. 4% 2. 6% 2. 2% 2. 1%
Top Trading Partners 2007 Country Exports Imports Canada 248. 9 313. 1 China 65. 2 321. 5 Mexico 136. 5 210. 8 Japan 62. 7 145. 5 German 49. 7 94. 4 y United K 50. 3 56. 9 Korea, S 34. 7 47. 6 France 27. 4 41. 6 Taiwan 26. 4 38. 3 Total 562. 0 386. 7 347. 3 208. 1 Percent 18. 0% 12. 4% 11. 1% 6. 7% 144. 0 4. 6% 107. 2 82. 3 69. 0 64. 7 3. 4% 2. 6% 2. 2% 2. 1%
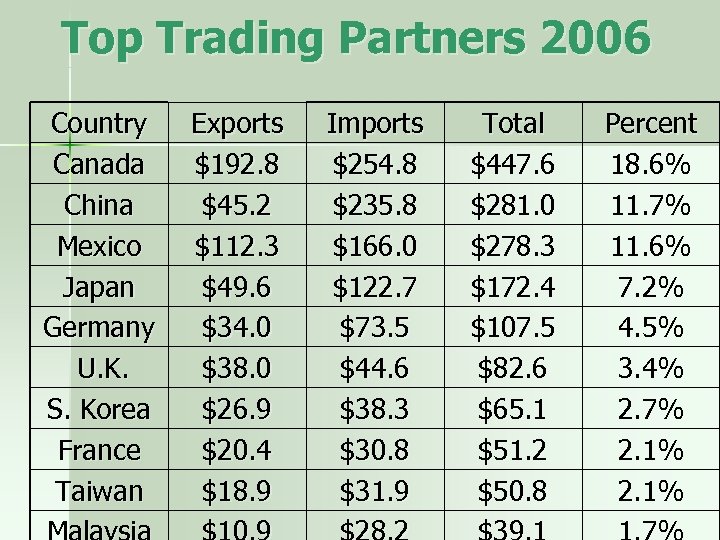 Top Trading Partners 2006 Country Canada China Mexico Japan Germany U. K. S. Korea France Taiwan Exports $192. 8 $45. 2 $112. 3 $49. 6 $34. 0 $38. 0 $26. 9 $20. 4 $18. 9 Imports $254. 8 $235. 8 $166. 0 $122. 7 $73. 5 $44. 6 $38. 3 $30. 8 $31. 9 Total $447. 6 $281. 0 $278. 3 $172. 4 $107. 5 $82. 6 $65. 1 $51. 2 $50. 8 Percent 18. 6% 11. 7% 11. 6% 7. 2% 4. 5% 3. 4% 2. 7% 2. 1%
Top Trading Partners 2006 Country Canada China Mexico Japan Germany U. K. S. Korea France Taiwan Exports $192. 8 $45. 2 $112. 3 $49. 6 $34. 0 $38. 0 $26. 9 $20. 4 $18. 9 Imports $254. 8 $235. 8 $166. 0 $122. 7 $73. 5 $44. 6 $38. 3 $30. 8 $31. 9 Total $447. 6 $281. 0 $278. 3 $172. 4 $107. 5 $82. 6 $65. 1 $51. 2 $50. 8 Percent 18. 6% 11. 7% 11. 6% 7. 2% 4. 5% 3. 4% 2. 7% 2. 1%
 International Trade Politics and Mechanics
International Trade Politics and Mechanics
 Protectionism n The viewpoint that trade with a foreign country will do harm to the national economy. n Must “protect” country from foreign competition. n Difficult to apply standards of one country to another.
Protectionism n The viewpoint that trade with a foreign country will do harm to the national economy. n Must “protect” country from foreign competition. n Difficult to apply standards of one country to another.
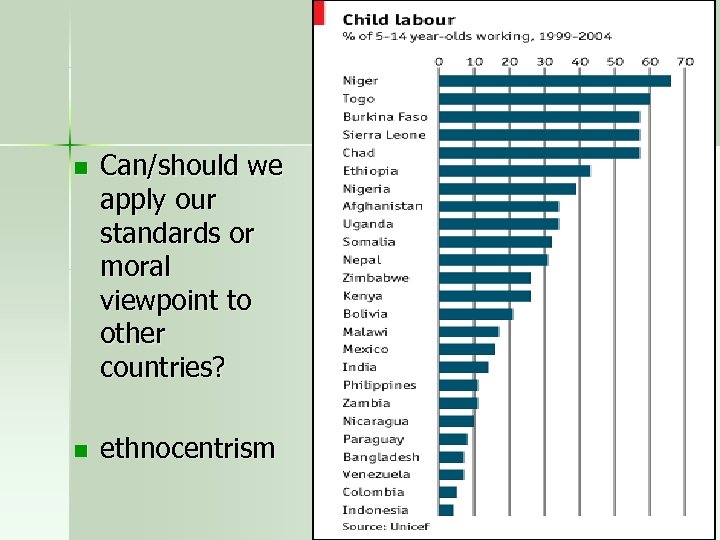 n Can/should we apply our standards or moral viewpoint to other countries? n ethnocentrism
n Can/should we apply our standards or moral viewpoint to other countries? n ethnocentrism
 Protectionism Arguments n National Security – Self-sufficient in military & defense goods n Agricultural Self-sufficiency – Nation should feed itself n Employment Protection – Prevent job loss to imports
Protectionism Arguments n National Security – Self-sufficient in military & defense goods n Agricultural Self-sufficiency – Nation should feed itself n Employment Protection – Prevent job loss to imports
 Protectionism Arguments n Infant / Emerging Industry – New industries need help until they become efficient n Wage Protection – Competition from “cheap foreign labor” n Diversified Economy – Don’t want to be dependent on single product
Protectionism Arguments n Infant / Emerging Industry – New industries need help until they become efficient n Wage Protection – Competition from “cheap foreign labor” n Diversified Economy – Don’t want to be dependent on single product
 Trade Barriers n n Used to “protect” domestic economy imposition of some sort of cost on trade that raises the price of the traded products When two or more nations repeatedly use trade barriers against each other a trade war results. Economists generally agree that trade barriers are detrimental and decrease overall economic efficiency
Trade Barriers n n Used to “protect” domestic economy imposition of some sort of cost on trade that raises the price of the traded products When two or more nations repeatedly use trade barriers against each other a trade war results. Economists generally agree that trade barriers are detrimental and decrease overall economic efficiency
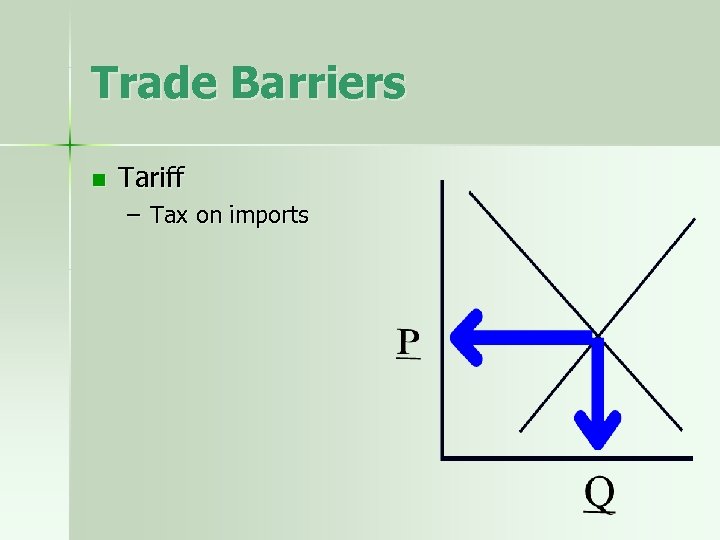 Trade Barriers n Tariff – Tax on imports
Trade Barriers n Tariff – Tax on imports
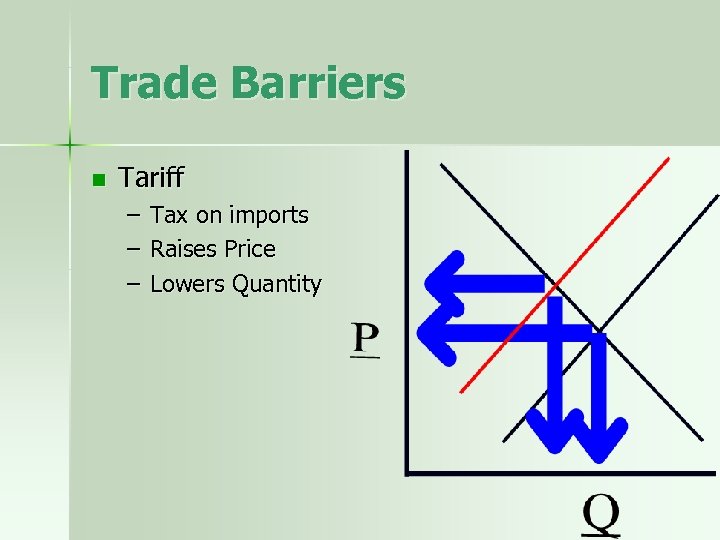 Trade Barriers n Tariff – – – Tax on imports Raises Price Lowers Quantity
Trade Barriers n Tariff – – – Tax on imports Raises Price Lowers Quantity
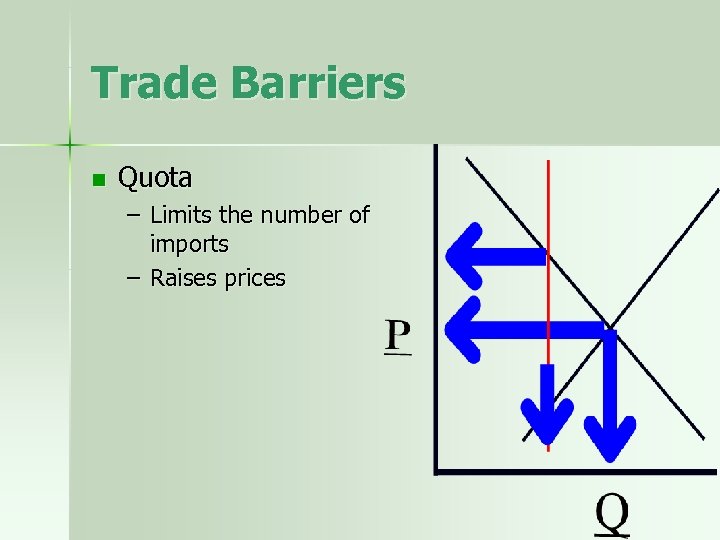 Trade Barriers n Quota – Limits the number of imports – Raises prices
Trade Barriers n Quota – Limits the number of imports – Raises prices
 Trade Barriers n Embargo – No trade at all – Specific country n Cuba, North Korea – Specific products - imports/exports n Military Goods –Arms – ITAR - International Traffic in Arms Regulations (UN) n Endangered Species n Drugs, narcotics n Technology
Trade Barriers n Embargo – No trade at all – Specific country n Cuba, North Korea – Specific products - imports/exports n Military Goods –Arms – ITAR - International Traffic in Arms Regulations (UN) n Endangered Species n Drugs, narcotics n Technology
 Current US Trade Embargoes n n n Cuba Iran North Korea Sudan Syria Burma/Myanmar Belarus Zimbabwe Ivory Coast Congo State Dept list
Current US Trade Embargoes n n n Cuba Iran North Korea Sudan Syria Burma/Myanmar Belarus Zimbabwe Ivory Coast Congo State Dept list
 Trade Barriers n Product standards – Quality control on imports – Customs and cultural mores n Electric power system n Driving on right side of road
Trade Barriers n Product standards – Quality control on imports – Customs and cultural mores n Electric power system n Driving on right side of road
 Trade Barriers n Subsidy – Aid to domestic producers – Lowers cost to consumer – Preserves jobs
Trade Barriers n Subsidy – Aid to domestic producers – Lowers cost to consumer – Preserves jobs
 Most Favored Nation Normal Trade Relations 1998 – Gives country the lowest trade barriers. – Reciprocal or bilateral agreement – WTO members – Exceptions are made – Political tool
Most Favored Nation Normal Trade Relations 1998 – Gives country the lowest trade barriers. – Reciprocal or bilateral agreement – WTO members – Exceptions are made – Political tool
 Trade Organizations n World Trade Organization (WTO) – International governing body – main treaty n Regional Organizations – NAFTA, European Union – World regions n Product Organizations – OPEC, Coffee Exporters
Trade Organizations n World Trade Organization (WTO) – International governing body – main treaty n Regional Organizations – NAFTA, European Union – World regions n Product Organizations – OPEC, Coffee Exporters
 Current US Free Trade Agreements n n n n NAFTA – Canada & Mexico Australia Bahrain Chile Costa Rica Dominican Republic El Salvador Guatemala Honduras Israel Jordan Morocco Nicaragua Singapore n Pending – – – Peru Columbia Oman Panama South Korea – Need Congressional Approval
Current US Free Trade Agreements n n n n NAFTA – Canada & Mexico Australia Bahrain Chile Costa Rica Dominican Republic El Salvador Guatemala Honduras Israel Jordan Morocco Nicaragua Singapore n Pending – – – Peru Columbia Oman Panama South Korea – Need Congressional Approval

 Foreign Exchange rate – How much of one currency another buys n One dollar = 2 Euros – Units of Measure n One Mile = 1760 yards = 5280 feet
Foreign Exchange rate – How much of one currency another buys n One dollar = 2 Euros – Units of Measure n One Mile = 1760 yards = 5280 feet
 Foreign Exchange n Fixed Exchange Rates – Bretton Woods – Gold Standard – Pegged or Tied Exchange Rates n Floating Exchange Rates – Supply & Demand in World Market – Stronger – can buy more units of currency – Weaker – can buy less units of currency – Change in relative position not good/bad
Foreign Exchange n Fixed Exchange Rates – Bretton Woods – Gold Standard – Pegged or Tied Exchange Rates n Floating Exchange Rates – Supply & Demand in World Market – Stronger – can buy more units of currency – Weaker – can buy less units of currency – Change in relative position not good/bad

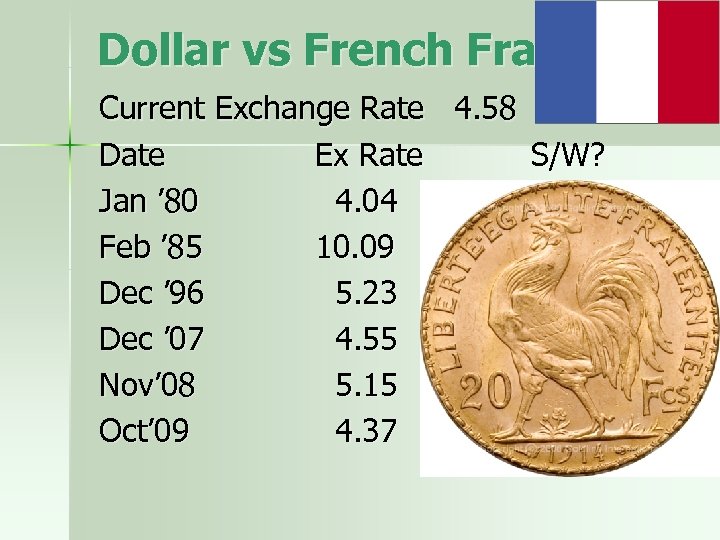 Dollar vs French Franc Current Exchange Rate 4. 58 Date Ex Rate S/W? Stronger Jan ’ 80 4. 04 Weaker Feb ’ 85 10. 09 Weaker Dec ’ 96 5. 23 Stronger Dec ’ 07 4. 55 Weaker Nov’ 08 5. 15 Stronger Oct’ 09 4. 37
Dollar vs French Franc Current Exchange Rate 4. 58 Date Ex Rate S/W? Stronger Jan ’ 80 4. 04 Weaker Feb ’ 85 10. 09 Weaker Dec ’ 96 5. 23 Stronger Dec ’ 07 4. 55 Weaker Nov’ 08 5. 15 Stronger Oct’ 09 4. 37
 Dollar vs British Pound Current Exchange Rate. 6219 1 British Pound Equals $1. 61 Date Ex Rate Stronger Jan ’ 80. 441 Weaker Feb ’ 85. 915 Stronger Dec ’ 96. 601 Stronger Dec ’ 07. 495 Weaker Nov’ 08. 665 Stronger Oct ’ 09. 603
Dollar vs British Pound Current Exchange Rate. 6219 1 British Pound Equals $1. 61 Date Ex Rate Stronger Jan ’ 80. 441 Weaker Feb ’ 85. 915 Stronger Dec ’ 96. 601 Stronger Dec ’ 07. 495 Weaker Nov’ 08. 665 Stronger Oct ’ 09. 603
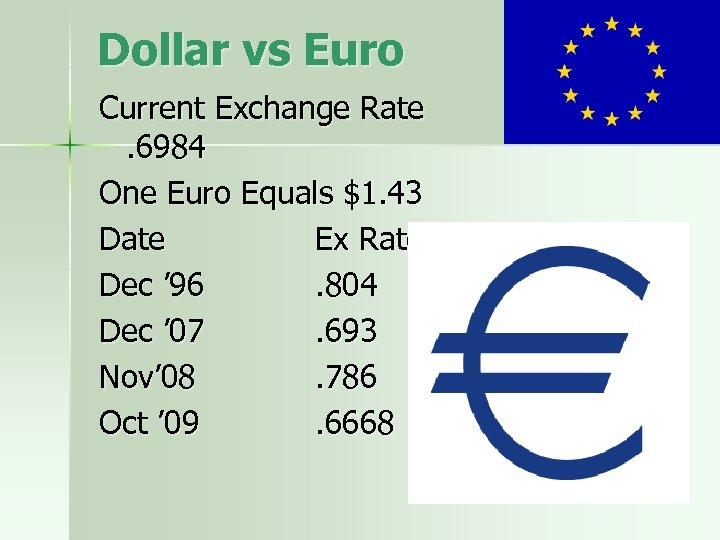 Dollar vs Euro Current Exchange Rate. 6984 One Euro Equals $1. 43 Date Ex Rate Dec ’ 96. 804 Dec ’ 07. 693 Nov’ 08. 786 Oct ’ 09. 6668 Weaker Stronger
Dollar vs Euro Current Exchange Rate. 6984 One Euro Equals $1. 43 Date Ex Rate Dec ’ 96. 804 Dec ’ 07. 693 Nov’ 08. 786 Oct ’ 09. 6668 Weaker Stronger
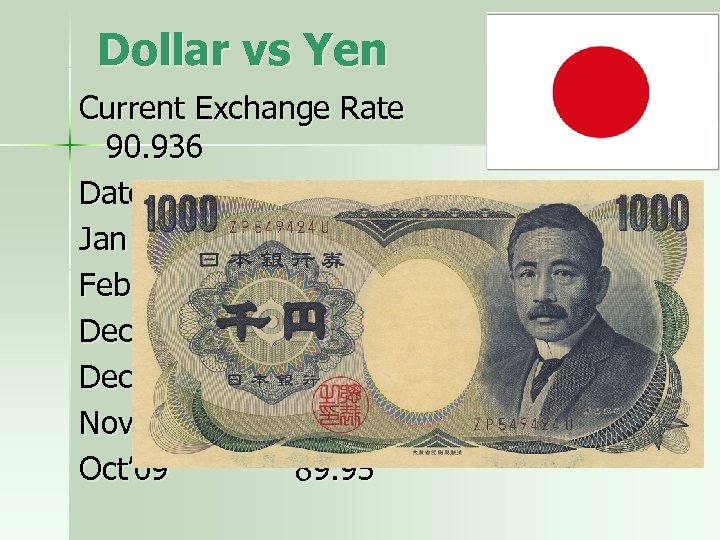 Dollar vs Yen Current Exchange Rate 90. 936 Date Ex Rate Jan ’ 80 237. 88 Feb ’ 85 260. 48 Dec ’ 96 113. 91 Dec ’ 07 113. 36 Nov’ 08 97. 07 Oct’ 09 89. 95 Weaker Weaker Stronger
Dollar vs Yen Current Exchange Rate 90. 936 Date Ex Rate Jan ’ 80 237. 88 Feb ’ 85 260. 48 Dec ’ 96 113. 91 Dec ’ 07 113. 36 Nov’ 08 97. 07 Oct’ 09 89. 95 Weaker Weaker Stronger
 Dollar vs Mexican Peso Current Exchange Rate 12. 82 Date Ex Rate Jan ’ 80 22. 84 Feb ’ 85 236. 05 Mexico devalues it’s currency Dec ’ 96 7. 85 Dec ’ 07 10. 82 Nov ’ 08 13. 84 Stronger Weaker
Dollar vs Mexican Peso Current Exchange Rate 12. 82 Date Ex Rate Jan ’ 80 22. 84 Feb ’ 85 236. 05 Mexico devalues it’s currency Dec ’ 96 7. 85 Dec ’ 07 10. 82 Nov ’ 08 13. 84 Stronger Weaker
 Dollar vs Canadian Dollar Current Exchange Rate $1. 06 Date Ex Rate Jan ’ 80 1. 16 Feb ’ 85 1. 35 Dec ’ 96 1. 36 Dec ’ 07 1. 02 Nov’ 08 1. 22 Oct ‘ 09 1. 04 Weaker Stronger
Dollar vs Canadian Dollar Current Exchange Rate $1. 06 Date Ex Rate Jan ’ 80 1. 16 Feb ’ 85 1. 35 Dec ’ 96 1. 36 Dec ’ 07 1. 02 Nov’ 08 1. 22 Oct ‘ 09 1. 04 Weaker Stronger
 Benefit from Strong or Weak $ ? FARMERS U. S. TOURISTS abroad CLOTHES BUYERS CAR BUYERS AUTOWORKERS ENTERTAINERS JOB SEEKERS WEAK STRONG WEAK DEPENDS
Benefit from Strong or Weak $ ? FARMERS U. S. TOURISTS abroad CLOTHES BUYERS CAR BUYERS AUTOWORKERS ENTERTAINERS JOB SEEKERS WEAK STRONG WEAK DEPENDS



