63c919ee9261b1e7d4226736fec772f2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 74
 INTERNATIONAL TRADE PRACTICE
INTERNATIONAL TRADE PRACTICE
 Chapter Four • Export Price • 出口价格
Chapter Four • Export Price • 出口价格
 A:key terms build-up 2. contingency 3. resource intensive 4. allocation cost 5. fixed cost 6. overhead 7. insurance premium 8. tariff 9. Tedious 10. outlet 11. Factory price 1. 建立、累计 2. 、偶然事件、意外事故 3. 资源密集 4. 分摊成本 5. 固定成本 6. 管理经费 7. 保险费 8、关税 9:hard, boring 10 甩卖, 厂清仓 11、出厂价
A:key terms build-up 2. contingency 3. resource intensive 4. allocation cost 5. fixed cost 6. overhead 7. insurance premium 8. tariff 9. Tedious 10. outlet 11. Factory price 1. 建立、累计 2. 、偶然事件、意外事故 3. 资源密集 4. 分摊成本 5. 固定成本 6. 管理经费 7. 保险费 8、关税 9:hard, boring 10 甩卖, 厂清仓 11、出厂价
 B:key terms 11. Surplus production 12. Consumption power 13. Per capita income 14. segment 15. Feasible 16. dynamics 17. Marketing strategy 11. 生产过剩 12. 消费能力 13. 个人平均收入 14. 市场细分 15. 可行的 16. 动态 17、营销策略
B:key terms 11. Surplus production 12. Consumption power 13. Per capita income 14. segment 15. Feasible 16. dynamics 17. Marketing strategy 11. 生产过剩 12. 消费能力 13. 个人平均收入 14. 市场细分 15. 可行的 16. 动态 17、营销策略
 C:key terms 18. Production cost 19. Sales cost 20 Delivery cost 21. Financing cost 22. anticipated profit 23、terms of payment 24、cost-plus pricing 25、marginal cost pricing 26、buyer based pricing 27、competition based pricing 18. 生产成本 19. 销售成本 20. 运送成本 21、融资成本 22、预期利润 23、支付条件、付款条件 24、成本加成定价法 25、边际成本定价法 26、买方价值定价法 27 竞争定价法
C:key terms 18. Production cost 19. Sales cost 20 Delivery cost 21. Financing cost 22. anticipated profit 23、terms of payment 24、cost-plus pricing 25、marginal cost pricing 26、buyer based pricing 27、competition based pricing 18. 生产成本 19. 销售成本 20. 运送成本 21、融资成本 22、预期利润 23、支付条件、付款条件 24、成本加成定价法 25、边际成本定价法 26、买方价值定价法 27 竞争定价法
 C:key terms 28. Middleperson 29. broker 30. Benchmark of comparison 31. Referencing index 32. Export profit margin 33、 export cost foreign exchange 34、 firm offers 35、 offeror 36、 offeree 37、 terminate 28. 中间人,经纪人 29. 中间人,经纪人 30. 比较基准 31、 参照系数 32、 出口盈亏率 33、 出口换汇成本 34、实盘 35、发盘方(人) 36、受盘方(人) 37、终止
C:key terms 28. Middleperson 29. broker 30. Benchmark of comparison 31. Referencing index 32. Export profit margin 33、 export cost foreign exchange 34、 firm offers 35、 offeror 36、 offeree 37、 terminate 28. 中间人,经纪人 29. 中间人,经纪人 30. 比较基准 31、 参照系数 32、 出口盈亏率 33、 出口换汇成本 34、实盘 35、发盘方(人) 36、受盘方(人) 37、终止
 C:key terms 38. contingency 39. break-even point 40. Local currency 41. markup 42. Face value 43、 replacement 44、 premium rate 45、 net price 46、 commission 47、 discount 38. 意外事件 39. 盈亏平衡点 40. 本币 41、 加价,上浮 42、 票面值,表面价值 43、 替换 44、 保险率 45、 净价 46、 佣金 47 折扣
C:key terms 38. contingency 39. break-even point 40. Local currency 41. markup 42. Face value 43、 replacement 44、 premium rate 45、 net price 46、 commission 47、 discount 38. 意外事件 39. 盈亏平衡点 40. 本币 41、 加价,上浮 42、 票面值,表面价值 43、 替换 44、 保险率 45、 净价 46、 佣金 47 折扣
 C:key terms 48. acceptance 49. Counter-offer 50. enquiry 51. exchange 52. Final price 53、 total price 54、 unfixed price 55、 money of account 56、 initial price 57、 irrevocable offer 38. 接受 39. 还盘 40. 询价 41、 交换、交流 42、 最终价格 43、 总价 44、 非固定价 45、 计价货币 46、最初价格 47 不可撤销发盘
C:key terms 48. acceptance 49. Counter-offer 50. enquiry 51. exchange 52. Final price 53、 total price 54、 unfixed price 55、 money of account 56、 initial price 57、 irrevocable offer 38. 接受 39. 还盘 40. 询价 41、 交换、交流 42、 最终价格 43、 总价 44、 非固定价 45、 计价货币 46、最初价格 47 不可撤销发盘
 C:key terms 58. Money of payment 59. Unit price 60. Validity period 61. Price adjustment clause 62. Price including commission 63、 quotation 64、 rebate 65、 revocation of an offer 66、 wage index 67、 withdraw of an offer 58. 支付货币 59. 单价 60. 有效期 61、 价格调整条款 62、 含佣价 63、 报盘 64、 减免、退款 65、 撤销发盘 66、 资指数 67、 撤回发盘
C:key terms 58. Money of payment 59. Unit price 60. Validity period 61. Price adjustment clause 62. Price including commission 63、 quotation 64、 rebate 65、 revocation of an offer 66、 wage index 67、 withdraw of an offer 58. 支付货币 59. 单价 60. 有效期 61、 价格调整条款 62、 含佣价 63、 报盘 64、 减免、退款 65、 撤销发盘 66、 资指数 67、 撤回发盘
 D: Abbreviations 1: ECFFE 2: FCL 3: LCL 1. 出口换汇成本 2. (集装箱)整柜 3. (集装箱)散装
D: Abbreviations 1: ECFFE 2: FCL 3: LCL 1. 出口换汇成本 2. (集装箱)整柜 3. (集装箱)散装
 4. 1 Expression of export price 4. 2 Pricing considerations 4. 3 Calculation of price 4. 4 Understanding the price 4. 5 Exercises
4. 1 Expression of export price 4. 2 Pricing considerations 4. 3 Calculation of price 4. 4 Understanding the price 4. 5 Exercises
 4. 1 Expression of export price • Four components in a standard format of a price: – A code of currency: USD, CAD, CNY, EUR, GBP(货币代 码) – A number indicating the price unit – A unit for measuring quantity: kg, gr, m/t, yd, set – A certain trade term: FOB, CFR, CIF • Examples: – USD 225. 30/piece CIF New York – FOB Guangzhou EUR 12. 80/set
4. 1 Expression of export price • Four components in a standard format of a price: – A code of currency: USD, CAD, CNY, EUR, GBP(货币代 码) – A number indicating the price unit – A unit for measuring quantity: kg, gr, m/t, yd, set – A certain trade term: FOB, CFR, CIF • Examples: – USD 225. 30/piece CIF New York – FOB Guangzhou EUR 12. 80/set
 4. 2 Pricing considerations • Cost of production(生产成本) – Direct cost(直接成本): material costs, labour costs, allocation of fixed costs, packing costs, etc. – Administrative costs: overhead – Cost of sales • Marketing costs: advertising, sales trip expenses, commissions ,intermediary services – Cost of delivery • Warehousing and transporting charge, insurance premium, taxes and tariffs, customs duties (进口税) • •
4. 2 Pricing considerations • Cost of production(生产成本) – Direct cost(直接成本): material costs, labour costs, allocation of fixed costs, packing costs, etc. – Administrative costs: overhead – Cost of sales • Marketing costs: advertising, sales trip expenses, commissions ,intermediary services – Cost of delivery • Warehousing and transporting charge, insurance premium, taxes and tariffs, customs duties (进口税) • •
 4. 2 Pricing considerations Anticipated profit margin(预期利润率) – in an absolute number – in a percentage → profit margin • Capability of target market(目标市场潜力) – Referring to the consumption power(消费能力), income level, supply and demand relationship – The higher the capital income of the target market, the higher the price • Payment terms(付款条件) – The lower the financing charges, the higher the risk of payment • Other factors to be considered – foreign exchange rates – international market price for similar products – policies and regulations in a particular market area •
4. 2 Pricing considerations Anticipated profit margin(预期利润率) – in an absolute number – in a percentage → profit margin • Capability of target market(目标市场潜力) – Referring to the consumption power(消费能力), income level, supply and demand relationship – The higher the capital income of the target market, the higher the price • Payment terms(付款条件) – The lower the financing charges, the higher the risk of payment • Other factors to be considered – foreign exchange rates – international market price for similar products – policies and regulations in a particular market area •
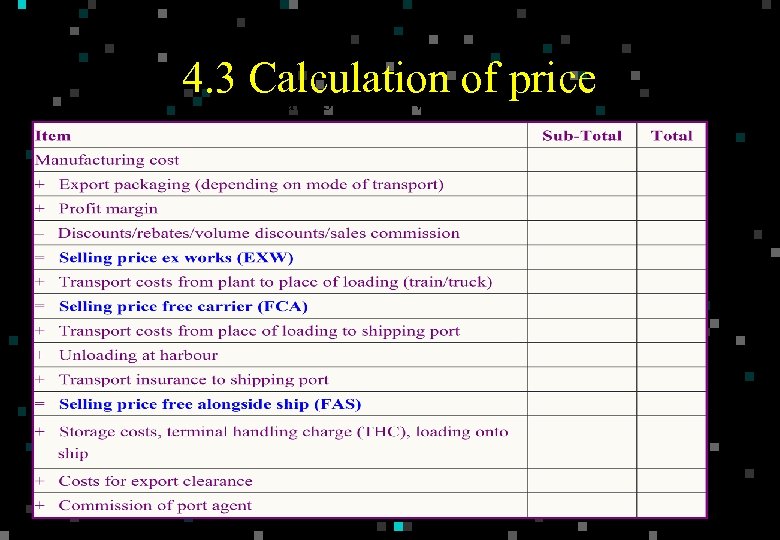 4. 3 Calculation of price Table 3. 1 Costing Worksheet
4. 3 Calculation of price Table 3. 1 Costing Worksheet
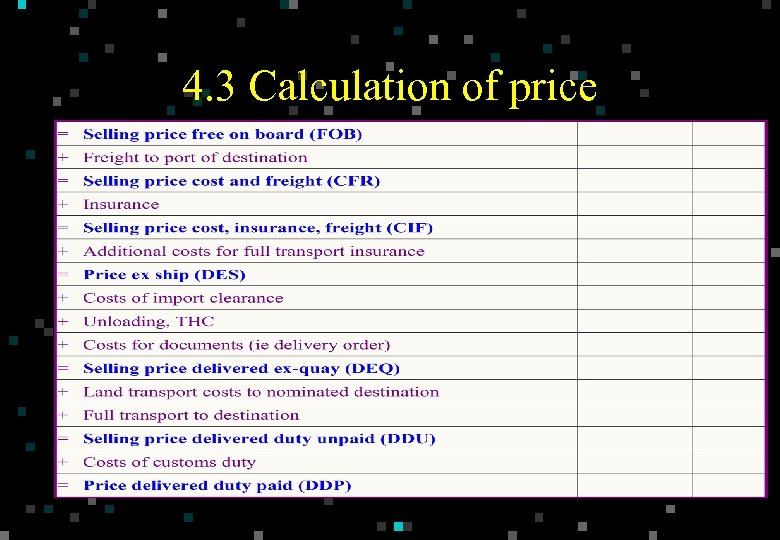 4. 3 Calculation of price
4. 3 Calculation of price
 4. 3. 1 FOB Price • FOB in local currency (当地货币) Table 3. 2 FOB Costing Worksheet • FOB in freight currency – FOB in freight currency = (Total Cost + Profit)/Exchange Rate
4. 3. 1 FOB Price • FOB in local currency (当地货币) Table 3. 2 FOB Costing Worksheet • FOB in freight currency – FOB in freight currency = (Total Cost + Profit)/Exchange Rate
 4. 3. 2 CFR Price • If FOB price is available – CFR = FOB + Ocean Freight • Ocean freight(海洋运费) – Provided by shipping lines(航运公司) – Quoted as packaged price(组合价格) – Others like “additionals” and “surcharges”(附加费)
4. 3. 2 CFR Price • If FOB price is available – CFR = FOB + Ocean Freight • Ocean freight(海洋运费) – Provided by shipping lines(航运公司) – Quoted as packaged price(组合价格) – Others like “additionals” and “surcharges”(附加费)
 4. 3. 3 CIF Price • If FOB price is available – CIF = FOB + Ocean Freight + Insurance Premium • If CFR price is available – CIF = CFR + Insurance Premium • Calculation of Insurance Premium (I) – Based on contract value/invoice value + – A markup(上浮,涨价幅度) (normally 10%) to cover incidental costs(杂费) – Formula: I = CIF x (1+10%) x Premium Rate (R)(保险费率) • Therefore – CIF = CFR + CIF x (1+10%) x Premium Rate (R) or – CIF = CFR / (1 – 110% x R)
4. 3. 3 CIF Price • If FOB price is available – CIF = FOB + Ocean Freight + Insurance Premium • If CFR price is available – CIF = CFR + Insurance Premium • Calculation of Insurance Premium (I) – Based on contract value/invoice value + – A markup(上浮,涨价幅度) (normally 10%) to cover incidental costs(杂费) – Formula: I = CIF x (1+10%) x Premium Rate (R)(保险费率) • Therefore – CIF = CFR + CIF x (1+10%) x Premium Rate (R) or – CIF = CFR / (1 – 110% x R)
 Conversion of FOB, CFR & CIF Prices • Conversion of FOB to other prices • CFR = FOB + F – CIF = (FOB + F) / [1 – (1+markup) x R] • Conversion of CFR to other prices – FOB = CFR – F – CIF = CFR / [1 – (1+markup) x R] • Conversion of CIF to other prices – FOB = CIF x [1 – (1+markup) x R] – F – CFR = CIF x [1 – (1+markup) x R]
Conversion of FOB, CFR & CIF Prices • Conversion of FOB to other prices • CFR = FOB + F – CIF = (FOB + F) / [1 – (1+markup) x R] • Conversion of CFR to other prices – FOB = CFR – F – CIF = CFR / [1 – (1+markup) x R] • Conversion of CIF to other prices – FOB = CIF x [1 – (1+markup) x R] – F – CFR = CIF x [1 – (1+markup) x R]
 4. 3. 4 Price including commission • Net price(净价,实价) = basic costs + profit • Commission – An incentive payment made to the middlepersons for their intermediary services – Expressed in a fixed figure or in a percentage – Examples • • CFR London GBP 100 per doz, including 2% commission USD 200 per M/T CIFC 2% London CIFC 3 Hamburg USD 100/set CAD 150 per M/T FOB Toronto, including CAD 8 per M/T commission
4. 3. 4 Price including commission • Net price(净价,实价) = basic costs + profit • Commission – An incentive payment made to the middlepersons for their intermediary services – Expressed in a fixed figure or in a percentage – Examples • • CFR London GBP 100 per doz, including 2% commission USD 200 per M/T CIFC 2% London CIFC 3 Hamburg USD 100/set CAD 150 per M/T FOB Toronto, including CAD 8 per M/T commission
 4. 3. 4 Price including commission • Two ways of calculating commission – based on invoice/contract value • C = contract value x C rate – based on FOB or FCA: • Under such terms as CFR, CIF, C is calculated before F( freight) and I( insurance) are deducted • Formula: – C = price including C (FOB/FCA) x C rate – Net price = price including C (FOB/FCA) – C = price including C x (1 C rate) – Price including C (FOB/FCA) = net price / (1 C rate)
4. 3. 4 Price including commission • Two ways of calculating commission – based on invoice/contract value • C = contract value x C rate – based on FOB or FCA: • Under such terms as CFR, CIF, C is calculated before F( freight) and I( insurance) are deducted • Formula: – C = price including C (FOB/FCA) x C rate – Net price = price including C (FOB/FCA) – C = price including C x (1 C rate) – Price including C (FOB/FCA) = net price / (1 C rate)
 Illustration 1 • USD 100 per m/t CFRC 5%, C? – C = 100 x 5% = USD 5 • USD 100 per m/t CFRC 5%, CFR net? – CFR net price = 100 5 = USD 95 • USD 100 per m/t Net CFR, CFRC 5%? – CFRC 5% = 100/(1 5%) = USD 105. 26
Illustration 1 • USD 100 per m/t CFRC 5%, C? – C = 100 x 5% = USD 5 • USD 100 per m/t CFRC 5%, CFR net? – CFR net price = 100 5 = USD 95 • USD 100 per m/t Net CFR, CFRC 5%? – CFRC 5% = 100/(1 5%) = USD 105. 26
 • USD 200 per case FOB Xiamen, freight USD 22 per case, CFRC 5? • CFRC 5 = (200+22)/(1 5%) = USD 233. 68 • USD 50 per m/t CIF Washington, I rate 1. 05%, markup 10%, CFRC 5? • CFRC 5 = (50 50 x 110%x 1. 05%) / (1 5%) = USD 52. 02
• USD 200 per case FOB Xiamen, freight USD 22 per case, CFRC 5? • CFRC 5 = (200+22)/(1 5%) = USD 233. 68 • USD 50 per m/t CIF Washington, I rate 1. 05%, markup 10%, CFRC 5? • CFRC 5 = (50 50 x 110%x 1. 05%) / (1 5%) = USD 52. 02
 • Illustration markup 10%, freight 15, 1 USD 150 per barrel FOB Xiamen, I rate 1%, CIFC 3? – Solution 1 – CIF = (FOB + F)/(1 U x R) = (150 + 15)/(1 110%x 1%) = USD 166. 835 • CIFC 3 = CIF / (1 C%) = 166. 835 / (1 3%) = USD 171. 99 – Solutions 2 • I = CIF x U x R = (FOB + F + I) x (1+markup)x R I = (FOB + F ) x 110%x R 1–Ux. R = (150 + 15) x 110% x 1% = USD 1. 835 1 110% x 1% • CIFC 3 = CIF / (1 C%) = (FOB + F + I) / (1 C%) = (150 + 15 + 1. 835) / ( 1 3%) = USD 171. 99
• Illustration markup 10%, freight 15, 1 USD 150 per barrel FOB Xiamen, I rate 1%, CIFC 3? – Solution 1 – CIF = (FOB + F)/(1 U x R) = (150 + 15)/(1 110%x 1%) = USD 166. 835 • CIFC 3 = CIF / (1 C%) = 166. 835 / (1 3%) = USD 171. 99 – Solutions 2 • I = CIF x U x R = (FOB + F + I) x (1+markup)x R I = (FOB + F ) x 110%x R 1–Ux. R = (150 + 15) x 110% x 1% = USD 1. 835 1 110% x 1% • CIFC 3 = CIF / (1 C%) = (FOB + F + I) / (1 C%) = (150 + 15 + 1. 835) / ( 1 3%) = USD 171. 99
 Illustration 2 • Suppose your company made an offer at USD 1200 per metric ton FOB Xiamen. Your customer counter offered and asked you to offer CIF Melbourne price. Suppose freight per metric ton is USD 130, markup 10% and insurance rate 1%, what would CIF Melbourne be? – CIF – =(FOB + F) / (1 U x R) = (1200+130) / (1 110%x 1 %) = USD 1344. 80
Illustration 2 • Suppose your company made an offer at USD 1200 per metric ton FOB Xiamen. Your customer counter offered and asked you to offer CIF Melbourne price. Suppose freight per metric ton is USD 130, markup 10% and insurance rate 1%, what would CIF Melbourne be? – CIF – =(FOB + F) / (1 U x R) = (1200+130) / (1 110%x 1 %) = USD 1344. 80
 • Supposing… – – Illustration 3 Your offer: USD 3000 per metric ton CIF Singapore Counter offer: USD 2880 per metric ton FOB China port Freight from China port to Singapore: USD 89 Insurance premium rate: 0. 95%, markup: 10% • Question: will you accept the counter offer? • Solution – Convert CIF to FOB • FOB = CIF – I = 3000 – 89 – 3000 x 110%x 0. 95% = USD 2879. 65 • FOB = CIF x (1 – Ux. R) –F = 3000 x (1– 110%x 0. 95%) – 89 = USD 2879. 65 – Convert FOB to CIF • CIF = (FOB + F) / (1 – U x R) = (2880 + 89) / (1 – 0. 95%x 110%) = USD 3000. 35 – YES
• Supposing… – – Illustration 3 Your offer: USD 3000 per metric ton CIF Singapore Counter offer: USD 2880 per metric ton FOB China port Freight from China port to Singapore: USD 89 Insurance premium rate: 0. 95%, markup: 10% • Question: will you accept the counter offer? • Solution – Convert CIF to FOB • FOB = CIF – I = 3000 – 89 – 3000 x 110%x 0. 95% = USD 2879. 65 • FOB = CIF x (1 – Ux. R) –F = 3000 x (1– 110%x 0. 95%) – 89 = USD 2879. 65 – Convert FOB to CIF • CIF = (FOB + F) / (1 – U x R) = (2880 + 89) / (1 – 0. 95%x 110%) = USD 3000. 35 – YES
 计算 1 • 1 、 我国某出口商品报价为: USD 300 Per Set CFR C 3 % NEWYORK 。试计算 CFR 净 价和佣金各为多少?如对方要求将佣金增加 到 5 %, 我方同意,但出口净收入不变。试 问 CFRC 5 %应如何报价?
计算 1 • 1 、 我国某出口商品报价为: USD 300 Per Set CFR C 3 % NEWYORK 。试计算 CFR 净 价和佣金各为多少?如对方要求将佣金增加 到 5 %, 我方同意,但出口净收入不变。试 问 CFRC 5 %应如何报价?
 计算 1 • • 佣金 = 含佣价 X 佣金率 =300 X 3%=USD. 9 净价 =含佣价 佣金=300 9=291 含佣价 =净价/(1 5%)=306. 32
计算 1 • • 佣金 = 含佣价 X 佣金率 =300 X 3%=USD. 9 净价 =含佣价 佣金=300 9=291 含佣价 =净价/(1 5%)=306. 32
 计算 2 • 2 、 某商品每公吨 CIF 热那亚£ 500, 设运费 每公吨£ 45, 投保加一成 , 保险费率为 8 ‰ , 求 FOB 价 • FOB • = CIF x [1 – (1+markup) x R] – F • =500*(1 110%*0. 8%) 45=495. 6 45=450. 6 •
计算 2 • 2 、 某商品每公吨 CIF 热那亚£ 500, 设运费 每公吨£ 45, 投保加一成 , 保险费率为 8 ‰ , 求 FOB 价 • FOB • = CIF x [1 – (1+markup) x R] – F • =500*(1 110%*0. 8%) 45=495. 6 45=450. 6 •
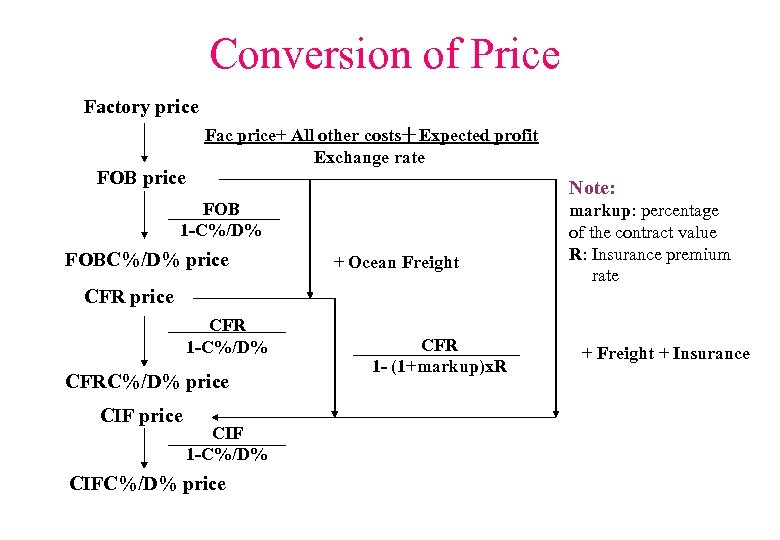 Conversion of Price Factory price FOB price Fac price+ All other costs+Expected profit Exchange rate Note: FOB 1 -C%/D% FOBC%/D% price + Ocean Freight CFR price CFR 1 -C%/D% CFRC%/D% price CIF 1 -C%/D% CIFC%/D% price CFR 1 - (1+markup)x. R markup: percentage of the contract value R: Insurance premium rate + Freight + Insurance
Conversion of Price Factory price FOB price Fac price+ All other costs+Expected profit Exchange rate Note: FOB 1 -C%/D% FOBC%/D% price + Ocean Freight CFR price CFR 1 -C%/D% CFRC%/D% price CIF 1 -C%/D% CIFC%/D% price CFR 1 - (1+markup)x. R markup: percentage of the contract value R: Insurance premium rate + Freight + Insurance
 4. 3. 5 Price with discount • Discount – a certain percent of price reduction, a special favor given by the exporter to the importer • Reasons for discounting: – – To increase market competitiveness To get rid of stocked goods As a motivator for B to introduce goods into new markets As a compensation for settling disputes or previous orders
4. 3. 5 Price with discount • Discount – a certain percent of price reduction, a special favor given by the exporter to the importer • Reasons for discounting: – – To increase market competitiveness To get rid of stocked goods As a motivator for B to introduce goods into new markets As a compensation for settling disputes or previous orders
 4. 3. 5 Price with discount • Discount expressed in % or fixed number – USD 200 per M/T CIF New York less 3% discount – CIFD 3 New York GBP 200 per M/T – EUR 200 per unit CIF London including 1% discount • Calculation – Based on the contract value – Discount = contract price x discount rate – Actual price = contract price – discount = contract price x ( 1 discount rate )
4. 3. 5 Price with discount • Discount expressed in % or fixed number – USD 200 per M/T CIF New York less 3% discount – CIFD 3 New York GBP 200 per M/T – EUR 200 per unit CIF London including 1% discount • Calculation – Based on the contract value – Discount = contract price x discount rate – Actual price = contract price – discount = contract price x ( 1 discount rate )
 增值税和退税 • VAT : value added tax, 商品进入流通环节所 发生的增值额为课税对象的一种流转税。 • Tax rebate 国家鼓励出口,为了提高本国商 品竞争力,对出口商品采取按增值税款或按 一定比例退还的做法。
增值税和退税 • VAT : value added tax, 商品进入流通环节所 发生的增值额为课税对象的一种流转税。 • Tax rebate 国家鼓励出口,为了提高本国商 品竞争力,对出口商品采取按增值税款或按 一定比例退还的做法。
 成本 • • • 购货成本=货价o+增值税 =货价+货价*增值税率 =货价(1+增值税率) 货价=购货成本/(1+增值税率) 实际成本=购货成本 出口退税额 =货价*(1+增值税率) 货价*出口退税率 =货价*(1+增值税率 出口退税率) =[购货成本/(1+增值税率)]* (1+增值税率 出口退税率) 购货成本=【实际成本*(1+增值税率)】/(1+增值税率 出口退税 率)
成本 • • • 购货成本=货价o+增值税 =货价+货价*增值税率 =货价(1+增值税率) 货价=购货成本/(1+增值税率) 实际成本=购货成本 出口退税额 =货价*(1+增值税率) 货价*出口退税率 =货价*(1+增值税率 出口退税率) =[购货成本/(1+增值税率)]* (1+增值税率 出口退税率) 购货成本=【实际成本*(1+增值税率)】/(1+增值税率 出口退税 率)
![Case • 购货成本CNY 200, including 17% VAT, rebate rate 9%, Actual cost? • =[购货成本/(1+增值税率)] Case • 购货成本CNY 200, including 17% VAT, rebate rate 9%, Actual cost? • =[购货成本/(1+增值税率)]](https://present5.com/presentation/63c919ee9261b1e7d4226736fec772f2/image-36.jpg) Case • 购货成本CNY 200, including 17% VAT, rebate rate 9%, Actual cost? • =[购货成本/(1+增值税率)] *(1+增值税率 出口退税率) • = =CNY 184. 6
Case • 购货成本CNY 200, including 17% VAT, rebate rate 9%, Actual cost? • =[购货成本/(1+增值税率)] *(1+增值税率 出口退税率) • = =CNY 184. 6
 4. 4 Understanding the price • Export profit margin – a ratio for measuring profitability of an export transaction – Standing for how much profit can be generated for every unit of currency in cost – Formula as follows: Export revenue (FOB) – Export cost (FOB) Export Profit Margin = X 100% Export Cost (FOB) Note: • • • Figures calculated in exporter’s local currency Export revenue and cost excluding overseas transport charges and insurance cost export revenue > export cost, profitable; export revenue
4. 4 Understanding the price • Export profit margin – a ratio for measuring profitability of an export transaction – Standing for how much profit can be generated for every unit of currency in cost – Formula as follows: Export revenue (FOB) – Export cost (FOB) Export Profit Margin = X 100% Export Cost (FOB) Note: • • • Figures calculated in exporter’s local currency Export revenue and cost excluding overseas transport charges and insurance cost export revenue > export cost, profitable; export revenue
 Chinese Equivalent • 出口商品 盈亏率 = 出口销售人民币净收入 - 出口总成本 • 出口总成本 X 100%
Chinese Equivalent • 出口商品 盈亏率 = 出口销售人民币净收入 - 出口总成本 • 出口总成本 X 100%
 Case • 上海新诚外贸公司 出口 美国 • USD 280. 00 per dozen CIF NEW YORK • 300 dozens • Freight USD 10 per dozen , insurance USD 1. 0 per dozen • raw material purchasing CNY 300, 000. 00 含 17%的增值税 • 生产加 费CNY 200, 000, 加 损耗费 2%, 管理费用 10%, 仓 储费用 6%, 退税率12%,USD 1=CNY 8. 2 • 计算出口盈亏率.
Case • 上海新诚外贸公司 出口 美国 • USD 280. 00 per dozen CIF NEW YORK • 300 dozens • Freight USD 10 per dozen , insurance USD 1. 0 per dozen • raw material purchasing CNY 300, 000. 00 含 17%的增值税 • 生产加 费CNY 200, 000, 加 损耗费 2%, 管理费用 10%, 仓 储费用 6%, 退税率12%,USD 1=CNY 8. 2 • 计算出口盈亏率.
 Process • • • 1、export revenue = 280*300*8. 2=CNY 688, 800 2、export cost =300, 000+200, 000+300, 000*(2%+10%+^%) 300, 000/(1+17%) *12% =CNY 523, 231 3、 Export revenue F R –Export cost = 688, 800 (3000+300)* 8. 2 523, 231 =CNY 138,509 4、EPM 138,509/523,231 =26%
Process • • • 1、export revenue = 280*300*8. 2=CNY 688, 800 2、export cost =300, 000+200, 000+300, 000*(2%+10%+^%) 300, 000/(1+17%) *12% =CNY 523, 231 3、 Export revenue F R –Export cost = 688, 800 (3000+300)* 8. 2 523, 231 =CNY 138,509 4、EPM 138,509/523,231 =26%
 4. 4 Understanding the price • Export cost foreign exchange (ECFFE) – Interpreting profitability with currency factor – Sanding for how many units of local currency the exporter should pay to make one unit of foreign currency – Formula as follows: Export cost in Local Currency ECFFE = Export Revenue in Foreign Currency (FOB) Note: • • The less the ECFFE is, the more profit the exporter can make See Example on Page 65
4. 4 Understanding the price • Export cost foreign exchange (ECFFE) – Interpreting profitability with currency factor – Sanding for how many units of local currency the exporter should pay to make one unit of foreign currency – Formula as follows: Export cost in Local Currency ECFFE = Export Revenue in Foreign Currency (FOB) Note: • • The less the ECFFE is, the more profit the exporter can make See Example on Page 65
 Chinese Equivalent • • 出口商品换汇成本 = • 出口总成本(人民币) / 出口销售外汇净收入(美 元) •
Chinese Equivalent • • 出口商品换汇成本 = • 出口总成本(人民币) / 出口销售外汇净收入(美 元) •
 Case • 上海新诚外贸公司 出口 美国 • USD 280. 00 per dozen CIF NEW YORK • 300 dozens • Freight USD 10 per dozen , insurance USD 1. 0 per dozen • raw material purchasing CNY 300, 000. 00 含 17%的增值税 • 生产加 费CNY 200, 000, 加 损耗费 2%, 管理费用 10%, 仓 储费用 6%, 退税率12%,USD 1=CNY 8. 2 • 计算出口换汇成本
Case • 上海新诚外贸公司 出口 美国 • USD 280. 00 per dozen CIF NEW YORK • 300 dozens • Freight USD 10 per dozen , insurance USD 1. 0 per dozen • raw material purchasing CNY 300, 000. 00 含 17%的增值税 • 生产加 费CNY 200, 000, 加 损耗费 2%, 管理费用 10%, 仓 储费用 6%, 退税率12%,USD 1=CNY 8. 2 • 计算出口换汇成本
 Process • • • 1、export revenue = 280*300*8. 2=CNY 688, 800 2、export cost =300, 000+200, 000+300, 000*(2%+10%+^%) 300, 000/(1+17%) *12% =CNY 523, 231 3、 Export revenue F R –Export cost = 688, 800 (3000+300)* 8. 2 523, 231 =CNY 138,509 4、 138,509/523,231 =26%
Process • • • 1、export revenue = 280*300*8. 2=CNY 688, 800 2、export cost =300, 000+200, 000+300, 000*(2%+10%+^%) 300, 000/(1+17%) *12% =CNY 523, 231 3、 Export revenue F R –Export cost = 688, 800 (3000+300)* 8. 2 523, 231 =CNY 138,509 4、 138,509/523,231 =26%
 • 1、Revenue= • USD 84000 USD 3000 –USD 300 • =USD 80, 700 • COST= • CNY 523, 231 • 6. 5 CNY/USD
• 1、Revenue= • USD 84000 USD 3000 –USD 300 • =USD 80, 700 • COST= • CNY 523, 231 • 6. 5 CNY/USD
 Illustration 4 • X company signed a contract to export 1000 of USD 20 per unit CIF New York. The total amount is USD 20000, including freight USD 3000 and Premium USD 200. The total purchase price is CNY 100000, cost before export is 10% of the purchase price. The present foreign exchange rate of USD against CNY is 7. • Q: What is the export profit margin and export cost foreign exchange? • Solution: – – – Export revenue in USD = USD(20000 3000 120) = USD 16800 Export revenue in CNY = 16800 x 7 = CNY 117600 Export cost in CNY = 100000 + 100000 x 10% = CNY 110000 Export profit margin = [(117600 110000)/117600] x 100% = 6. 46% ECFFE = CNY 110000 / USD 16800= 6. 548
Illustration 4 • X company signed a contract to export 1000 of USD 20 per unit CIF New York. The total amount is USD 20000, including freight USD 3000 and Premium USD 200. The total purchase price is CNY 100000, cost before export is 10% of the purchase price. The present foreign exchange rate of USD against CNY is 7. • Q: What is the export profit margin and export cost foreign exchange? • Solution: – – – Export revenue in USD = USD(20000 3000 120) = USD 16800 Export revenue in CNY = 16800 x 7 = CNY 117600 Export cost in CNY = 100000 + 100000 x 10% = CNY 110000 Export profit margin = [(117600 110000)/117600] x 100% = 6. 46% ECFFE = CNY 110000 / USD 16800= 6. 548
 Wording of Prices in Contract • • • HKD 100 per doz EXW GUANGZHOU (5 Beijing Road) CAD 200 per gr FCA Toronto (Airport) EUR 150 per pr FOB Shanghai JPY 600 per lb FAS Tokyo AUD 120 per pc CFR Sydney CHF 300 per set Carriage Paid To 5 Maple Rd. Geneva (sea/air shipment: from Guangzhou to Dubai by sea, then by air to Geneva) • USD 250 per set Delivered at Sino Mongolian Frontier (Erlian) • EUR 350 per M/T DES Guangzhou • GBP 500 per unit DEQ London
Wording of Prices in Contract • • • HKD 100 per doz EXW GUANGZHOU (5 Beijing Road) CAD 200 per gr FCA Toronto (Airport) EUR 150 per pr FOB Shanghai JPY 600 per lb FAS Tokyo AUD 120 per pc CFR Sydney CHF 300 per set Carriage Paid To 5 Maple Rd. Geneva (sea/air shipment: from Guangzhou to Dubai by sea, then by air to Geneva) • USD 250 per set Delivered at Sino Mongolian Frontier (Erlian) • EUR 350 per M/T DES Guangzhou • GBP 500 per unit DEQ London
 4. 6 Exercises I: multiple choices 1. A message bearing the content as “…have the intention to purchase 1000 gross ‘Black Girl’ toothpaste, please quote us the best price and the earliest shipment time” is called _ B. • A. an offer B. an inquiry • C. a counteroffer D. an acceptance 2. If the CIF price of a product is USD 100/set, freight charge USD 10/set , insurance premium USD 10/set , commission rate 2%, the commission payment based on CIF price should be _ D. B. USD 1. 63/Set • A. USD 1. 6/set • C. USD 2. 00/set D. USD 2. 04/set 返回
4. 6 Exercises I: multiple choices 1. A message bearing the content as “…have the intention to purchase 1000 gross ‘Black Girl’ toothpaste, please quote us the best price and the earliest shipment time” is called _ B. • A. an offer B. an inquiry • C. a counteroffer D. an acceptance 2. If the CIF price of a product is USD 100/set, freight charge USD 10/set , insurance premium USD 10/set , commission rate 2%, the commission payment based on CIF price should be _ D. B. USD 1. 63/Set • A. USD 1. 6/set • C. USD 2. 00/set D. USD 2. 04/set 返回
 4. 6 Exercises I: multiple choices • 3. which one of the following prices is correctly expressed? _. D. • A. CNY 3. 50 per piece CIF Hong Kong B. USD 3. 50 per piece CIF • C. RMB 3. 50 per piece CIFC London D. USD 3. 50 per piece CIFC 2 London • 4. According to CISG, a contract can be established when _. • A. an acceptance becomes effective • B. the seller and buyer sign on a written contract A • C. the contract is approved by authorities • D. an offer reaches the offeree 返回
4. 6 Exercises I: multiple choices • 3. which one of the following prices is correctly expressed? _. D. • A. CNY 3. 50 per piece CIF Hong Kong B. USD 3. 50 per piece CIF • C. RMB 3. 50 per piece CIFC London D. USD 3. 50 per piece CIFC 2 London • 4. According to CISG, a contract can be established when _. • A. an acceptance becomes effective • B. the seller and buyer sign on a written contract A • C. the contract is approved by authorities • D. an offer reaches the offeree 返回
 4. 6 Exercises I: multiple choices • 5. When the offeree makes modification to _, his reply cannot be seen as a counteroffer. C. • • • A. the price B. the payment term C. the packing D. the quality and above 6. An offer will be terminated when _. D. A. it is rejected B. it is ounteroffered C. it is legally D. all of the above
4. 6 Exercises I: multiple choices • 5. When the offeree makes modification to _, his reply cannot be seen as a counteroffer. C. • • • A. the price B. the payment term C. the packing D. the quality and above 6. An offer will be terminated when _. D. A. it is rejected B. it is ounteroffered C. it is legally D. all of the above
 4. 6 Exercises I: multiple choices • 7. A cabled offer buyer the offeree on 12/03. However one day before the offeror had informed the offeree by fax that the offer had been invalid. This act can be considered as _. A • A. a withdrawal of an offer B. an amendment of an offer • C. a new offer D. a revocation of an offer • 8. A foreign buyer cabled that “offer dated 10 Aug. accepted. if 5% commission included”. This is _. B • A. an acceptance B. a counteroffer • C. an inquiry D. an offer 返回
4. 6 Exercises I: multiple choices • 7. A cabled offer buyer the offeree on 12/03. However one day before the offeror had informed the offeree by fax that the offer had been invalid. This act can be considered as _. A • A. a withdrawal of an offer B. an amendment of an offer • C. a new offer D. a revocation of an offer • 8. A foreign buyer cabled that “offer dated 10 Aug. accepted. if 5% commission included”. This is _. B • A. an acceptance B. a counteroffer • C. an inquiry D. an offer 返回
 4. 6 Exercises I: multiple choices • • • 9. ABC made an offer to XYZ. Under which condition can the two parties establish adeal? _. A. EFG which is recognized by XYZ accepted the offer within validity period. D B. Based on previous experience, XYZ indicated acceptance without receiving the offer C. XYZ accepted the offer within validity period, but suggested earlier shipment A D. Within the validity period, XYZ accepted the offer completely. • 10. The standard form of a price consists of the following items EXCEPT _. • A. currency B. port or place of destination C. unit D. number 9 返回
4. 6 Exercises I: multiple choices • • • 9. ABC made an offer to XYZ. Under which condition can the two parties establish adeal? _. A. EFG which is recognized by XYZ accepted the offer within validity period. D B. Based on previous experience, XYZ indicated acceptance without receiving the offer C. XYZ accepted the offer within validity period, but suggested earlier shipment A D. Within the validity period, XYZ accepted the offer completely. • 10. The standard form of a price consists of the following items EXCEPT _. • A. currency B. port or place of destination C. unit D. number 9 返回
 4. 6 Exercises II: True or False • • • 1_F Offer and a counteroffer are the two essential stages in the communication of price 2_ Discount is a deduction on the original price. T given to the buyer as incentive. 3_ Export profit margin directly reflects the F local currency cost of each unit of foreign currency. 返回
4. 6 Exercises II: True or False • • • 1_F Offer and a counteroffer are the two essential stages in the communication of price 2_ Discount is a deduction on the original price. T given to the buyer as incentive. 3_ Export profit margin directly reflects the F local currency cost of each unit of foreign currency. 返回
 4. 6 Exercises II: True or False • • 4 _In a price communication, it is always the F buyer who makes an inquiry and the seller makes an offer. F 5_A buyer cabled an acceptance to an offer, but requiring to change payment from D/P at sight to D/A. The seller kept silence. A contract could be established at this moment. 返回
4. 6 Exercises II: True or False • • 4 _In a price communication, it is always the F buyer who makes an inquiry and the seller makes an offer. F 5_A buyer cabled an acceptance to an offer, but requiring to change payment from D/P at sight to D/A. The seller kept silence. A contract could be established at this moment. 返回
 4. 6 Exercises II: True or False 6 _ T If an effective offer is accepted unconditionally, a contract can be achieved. 7_ T CISG stipulates that an offer will be effective when it reaches the offeree. 8_ FThe nature of relationship between the seller and buyer is irrelevant to the pricing decision in international trade. 返回
4. 6 Exercises II: True or False 6 _ T If an effective offer is accepted unconditionally, a contract can be achieved. 7_ T CISG stipulates that an offer will be effective when it reaches the offeree. 8_ FThe nature of relationship between the seller and buyer is irrelevant to the pricing decision in international trade. 返回
 4. 6 Exercises II: True or False 9 _ F The commission payment of an FOB price should be calculated based on the FOB net price. 10_F There is a rule of thumb(经验法则, 粗 略计算) in international trade stating that any transaction having a profit margin over 10% is a good deal. 返回
4. 6 Exercises II: True or False 9 _ F The commission payment of an FOB price should be calculated based on the FOB net price. 10_F There is a rule of thumb(经验法则, 粗 略计算) in international trade stating that any transaction having a profit margin over 10% is a good deal. 返回
 4. 6 Exercises IV • • 1、What are the four components of the standard form of a price? A code of currency, a number, a unit and a trade term 2、 While making pricing decision, what major factors should de considered? cost, anticipated profit, capacity of target market, terms of payment, competition and relationship between the exporter and the importer. • 返回
4. 6 Exercises IV • • 1、What are the four components of the standard form of a price? A code of currency, a number, a unit and a trade term 2、 While making pricing decision, what major factors should de considered? cost, anticipated profit, capacity of target market, terms of payment, competition and relationship between the exporter and the importer. • 返回
 4. 6 Exercises • 3、What are the differences and similarities between commission and discount? Similarities: both are used as incentive to promote transactions. Differences: Commission payment is an add up on top of the original price, while discount a reduction, ; Commission mainly applies to transactions which involves middleperson or agent. Discount can be used without particular pre • • 返回
4. 6 Exercises • 3、What are the differences and similarities between commission and discount? Similarities: both are used as incentive to promote transactions. Differences: Commission payment is an add up on top of the original price, while discount a reduction, ; Commission mainly applies to transactions which involves middleperson or agent. Discount can be used without particular pre • • 返回
 4. 6 Exercises V case study • 1 、BB Company signed a contract to export clothing. Its export costs totaled RMB 800, 000, and export revenue totaled USD 100, 000. If the exchange rate was USD 1=RMB 8. 2, Calculate: – Its export cost foreign exchange; – Its export profit/boss rate. 返回
4. 6 Exercises V case study • 1 、BB Company signed a contract to export clothing. Its export costs totaled RMB 800, 000, and export revenue totaled USD 100, 000. If the exchange rate was USD 1=RMB 8. 2, Calculate: – Its export cost foreign exchange; – Its export profit/boss rate. 返回
 • (a)=2. 5% Export revenue (FOB) – Export cost (FOB) Export Profit Margin = X 100% Export Cost (FOB)
• (a)=2. 5% Export revenue (FOB) – Export cost (FOB) Export Profit Margin = X 100% Export Cost (FOB)
 4. 6 Exercises V • (b) • =800, 000/100, 000 • =8 返回
4. 6 Exercises V • (b) • =800, 000/100, 000 • =8 返回
 4. 6 Exercises V • • • 2、The price quoted by a Shanghai exporter was “USD 1200 per M/T CFR Liverpool”. The freight for Shanghai Liverpool was USD 200 per M/T. To keep the export revenue constant, what would FOBC 2% price be ? = FOBC 2=FOB/(1 commisiion) =FOB Shanghai USD 1020. 41 /M/T 返回
4. 6 Exercises V • • • 2、The price quoted by a Shanghai exporter was “USD 1200 per M/T CFR Liverpool”. The freight for Shanghai Liverpool was USD 200 per M/T. To keep the export revenue constant, what would FOBC 2% price be ? = FOBC 2=FOB/(1 commisiion) =FOB Shanghai USD 1020. 41 /M/T 返回
 4. 6 Exercises V • • • 3、AC Company offered to sell goods at “USD 100 per case CIF New York”. The importer requested a revised quote for CFRC 5%. The premium rate for insurance was 1. 05% and mark up for insurance was 10%. To get same export revenue , what would AC’s new offer be ? CFRC 5= CFR/(1 commision rate) CFR=CIF –I I=CIF*(1+Markup)*R =CFRC 5% New York USD 104. 5%/case 返回
4. 6 Exercises V • • • 3、AC Company offered to sell goods at “USD 100 per case CIF New York”. The importer requested a revised quote for CFRC 5%. The premium rate for insurance was 1. 05% and mark up for insurance was 10%. To get same export revenue , what would AC’s new offer be ? CFRC 5= CFR/(1 commision rate) CFR=CIF –I I=CIF*(1+Markup)*R =CFRC 5% New York USD 104. 5%/case 返回
 4. 6 Exercises V 4、DD Company offered to sell goods at”USD 2000 per M/T CIF Toronto with ‘all risks’ and ‘war risk’ for 110% of the value”. The importer requested a revised quote for FOB Guangzhou. The freight for Guangzhou Toronto was USD 50 per M/T, and the premium rates for “all risks” and “war risks” were 1% and 0. 2% respectively. To get the same export revenue, what FOB price should the exporter offer? 返回
4. 6 Exercises V 4、DD Company offered to sell goods at”USD 2000 per M/T CIF Toronto with ‘all risks’ and ‘war risk’ for 110% of the value”. The importer requested a revised quote for FOB Guangzhou. The freight for Guangzhou Toronto was USD 50 per M/T, and the premium rates for “all risks” and “war risks” were 1% and 0. 2% respectively. To get the same export revenue, what FOB price should the exporter offer? 返回
 4. 6 Exercises V • • FOB= =CIF F –I I=CIF *110%* R FOB Guangzhou USD 1923. 6/M/T 返回
4. 6 Exercises V • • FOB= =CIF F –I I=CIF *110%* R FOB Guangzhou USD 1923. 6/M/T 返回
 4. 6 Exercises V • 5、 The price quoted by an exporter was “USD 450 per case FOB Shanghai”. The importer requested a revised quote for CIF Auckland. If the freight was USD 50 per case, 110% of the value was to be insured, and the premium rate for insurance was 0. 8%, what would the new price be ? 返回
4. 6 Exercises V • 5、 The price quoted by an exporter was “USD 450 per case FOB Shanghai”. The importer requested a revised quote for CIF Auckland. If the freight was USD 50 per case, 110% of the value was to be insured, and the premium rate for insurance was 0. 8%, what would the new price be ? 返回
 4. 6 Exercises V • • CIF= =CFR/(1 110%*r) =FOB + F =CIF Auckland USD 504. 44/case 返回
4. 6 Exercises V • • CIF= =CFR/(1 110%*r) =FOB + F =CIF Auckland USD 504. 44/case 返回
 4. 6 Exercises V • • • 6、X Company signed a contract to export two machines at an initial price (PO) of USD 5 million each. At the time of setting PO, the material price index (MO) was 110, the wage index (MO) was 120. The contract contained a price revision clause that allowed the final price to be set on delivery. At the time of delivery, the material price index (M) become 125. If the following ratios remained constant: A (the management fee and profit as a percentage of the price ) =15% B (the material cost as a percentage of the price) =30% C(the wage cost as a percentage of the price )=55% What is the final price (P) ? 返回
4. 6 Exercises V • • • 6、X Company signed a contract to export two machines at an initial price (PO) of USD 5 million each. At the time of setting PO, the material price index (MO) was 110, the wage index (MO) was 120. The contract contained a price revision clause that allowed the final price to be set on delivery. At the time of delivery, the material price index (M) become 125. If the following ratios remained constant: A (the management fee and profit as a percentage of the price ) =15% B (the material cost as a percentage of the price) =30% C(the wage cost as a percentage of the price )=55% What is the final price (P) ? 返回
 4. 6 Exercises V 7、On Nov. 20 th , Lee Co. offered to sell goods to Dee Inc. at USD 500 per case CIF London , ”Offer valid if reply here 11/27. ”On Nov. 22 nd Dee cabled back , “Offer accepted if USD 480 per case. ” As Lee was considering the bid, the market price went over Could Lee reject Dee’s acceptance ? Yes: what is counter offer when offer ineffective 返回
4. 6 Exercises V 7、On Nov. 20 th , Lee Co. offered to sell goods to Dee Inc. at USD 500 per case CIF London , ”Offer valid if reply here 11/27. ”On Nov. 22 nd Dee cabled back , “Offer accepted if USD 480 per case. ” As Lee was considering the bid, the market price went over Could Lee reject Dee’s acceptance ? Yes: what is counter offer when offer ineffective 返回
 边际成本 • 杭州开往南京的长途车即将出发。无论哪个公司的 车,票价均为 50元。一个匆匆赶来的乘客见一家国 营公司的车上尚有空位,要求以 30元上车,被拒绝 了。他又找到一家也有空位的私人公司的车,售票 员二话没说,收了30元允许他上车了。哪家公司的 行为更理性呢?乍一看,私人公司允许这名乘客用 30元享受 50元的运输服务,当然亏了。但如果用边 际分析法分析,私人公司的确比国营公司精明。
边际成本 • 杭州开往南京的长途车即将出发。无论哪个公司的 车,票价均为 50元。一个匆匆赶来的乘客见一家国 营公司的车上尚有空位,要求以 30元上车,被拒绝 了。他又找到一家也有空位的私人公司的车,售票 员二话没说,收了30元允许他上车了。哪家公司的 行为更理性呢?乍一看,私人公司允许这名乘客用 30元享受 50元的运输服务,当然亏了。但如果用边 际分析法分析,私人公司的确比国营公司精明。
 • 我们可以用最后一名乘客的票价这个例子来 说明边际分析法的用处。当我们考虑是否让 这名乘客以 30元的票价上车时,实际上我们 应该考虑的是边际成本和边际收益这两个概 念。边际成本是增加一名乘客(自变量)所增 加的收入(因变量)。
• 我们可以用最后一名乘客的票价这个例子来 说明边际分析法的用处。当我们考虑是否让 这名乘客以 30元的票价上车时,实际上我们 应该考虑的是边际成本和边际收益这两个概 念。边际成本是增加一名乘客(自变量)所增 加的收入(因变量)。
 案例 • 在我们这个例子中,增加这一名乘客,所需磨损的 汽车、汽油费、 作人员 资和过路费等都无需增 加,对汽车来说多拉一个人少拉一个人都一样,所 增加的成本仅仅是发给这个乘客的食物和饮料,假 设这些东西值 10元,边际成本也就是 10元。边际收 益是增加一名乘客(自变量)所增加的收入(因变量)。 在这个例子中,增加这一名乘客增加收入 30元,边 际收益就是 30元。
案例 • 在我们这个例子中,增加这一名乘客,所需磨损的 汽车、汽油费、 作人员 资和过路费等都无需增 加,对汽车来说多拉一个人少拉一个人都一样,所 增加的成本仅仅是发给这个乘客的食物和饮料,假 设这些东西值 10元,边际成本也就是 10元。边际收 益是增加一名乘客(自变量)所增加的收入(因变量)。 在这个例子中,增加这一名乘客增加收入 30元,边 际收益就是 30元。
 案例 • 某企业生产一种零部件产品,其生产性 费用为:直接材料 10元/件,直接人 5元/件, 变动制造费用(能源)7元/件,固定制造费 (折旧)4000元。其非生产性费用为:管理 费用(保险)400元,销售费用:其中变动 费用 3元/件(买一送一),固定费用(广告 费)600元。期初库存为 0,本月生产 1000件, 销售 600件,售价 40元/件。
案例 • 某企业生产一种零部件产品,其生产性 费用为:直接材料 10元/件,直接人 5元/件, 变动制造费用(能源)7元/件,固定制造费 (折旧)4000元。其非生产性费用为:管理 费用(保险)400元,销售费用:其中变动 费用 3元/件(买一送一),固定费用(广告 费)600元。期初库存为 0,本月生产 1000件, 销售 600件,售价 40元/件。
 案例 • • 2、用边际成本法计算的利润如下: 单位生产成本: 10 + 5 + 7 = 22元 销售收入: 600 件 × 40 = 24000元 减:销售成本(全部变动): 600件× (22 + 3) = 15000元 • 贡献毛益: 9000元 • 减:全部固定: 4000 + 400 + 600 = 5000元 • 净利: 4000元 返回
案例 • • 2、用边际成本法计算的利润如下: 单位生产成本: 10 + 5 + 7 = 22元 销售收入: 600 件 × 40 = 24000元 减:销售成本(全部变动): 600件× (22 + 3) = 15000元 • 贡献毛益: 9000元 • 减:全部固定: 4000 + 400 + 600 = 5000元 • 净利: 4000元 返回


