01a0489778812d9871cd7b74ff49190e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

International perspective on BIM Building Information Modeling. Experiences Internationally and in Norway Svein Willy Danielsen, SINTEF Byggforsk, Norway Launching the Icelandic Construction Technology Platform at Grand Hotel Reykjavik 17 th August 2007 SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 1
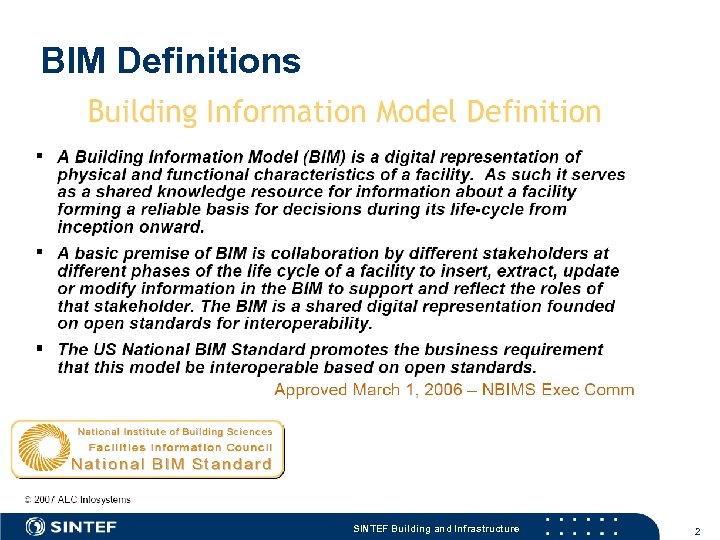
BIM Definitions SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 2

National Institute of BUILDING SCIENCE takes the responsibility (Feb. 2006) SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 3

SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 4

SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 5
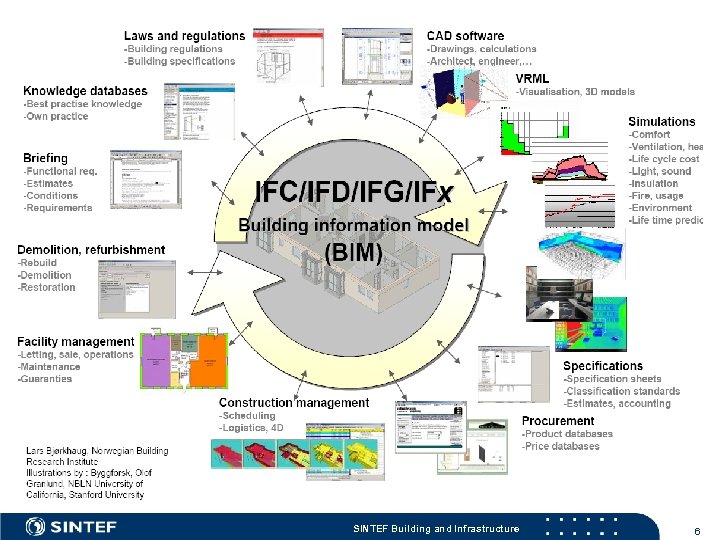
SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 6
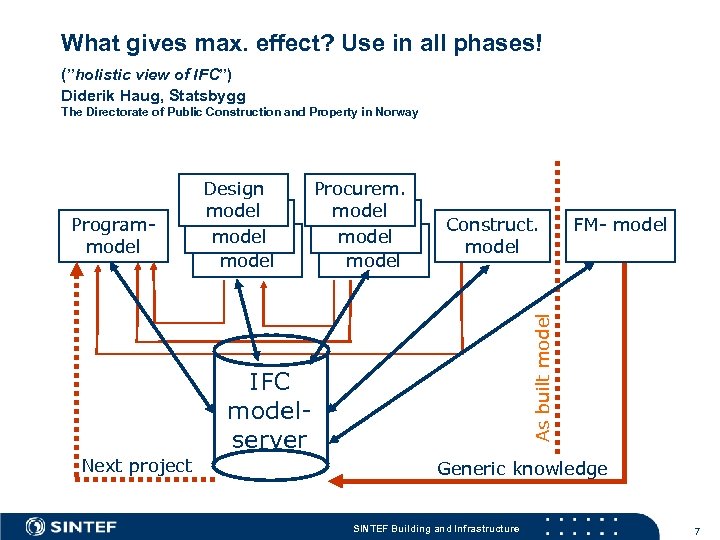
What gives max. effect? Use in all phases! (”holistic view of IFC”) Diderik Haug, Statsbygg The Directorate of Public Construction and Property in Norway Procurem. model Design model Construct. model IFC modelserver Next project FM- model As built model Programmodel Design model Generic knowledge SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 7
SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 8
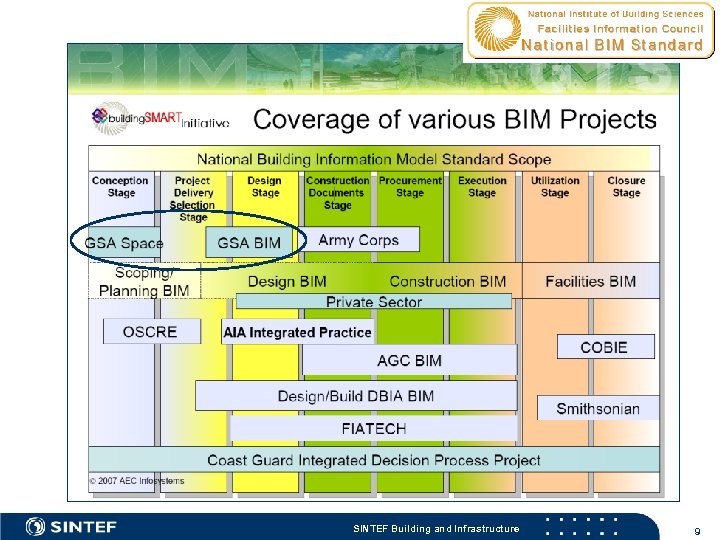
SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 9
SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 10
3 D-4 D Building Information Modeling (1) The following are highlights of the GSA National 3 D-4 D-BIM Program: n Establish policy to phase in 3 D, 4 D, and BIM adoption for all major projects n Lead 3 D-4 D-BIM pilot application on current capital projects n Provide expert support and assessment for ongoing capital projects to incorporate 3 D, 4 D, and BIM technologies n Assess industry readiness and technology maturity n Create GSA-specific incentives for 3 D-4 D-BIM n Develop solicitation and contractual language for 3 D-4 D-BIM services SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 11
3 D-4 D Building Information Modeling (2) n Develop solicitation and contractual language for 3 D-4 D-BIM services n Partner with BIM vendors, professional associations, open standard organizations, and academic/research institutions n Construct GSA BIM Toolkit n Publish BIM Guide Series n Series 01 – 3 D-4 D-BIM Overview n Series 02 – Spatial Program Validation n Formulate additional BIM Guide Series: n n Series 03 - 3 D Laser Scanning Series 04 - 4 D Phasing Series 05 - Energy Performance and Operations Series 06 - Circulation and Security Validation n Establish knowledge portal community n Foster community of GSA BIM Champions n Form Community of GSA BIM Champions SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 12
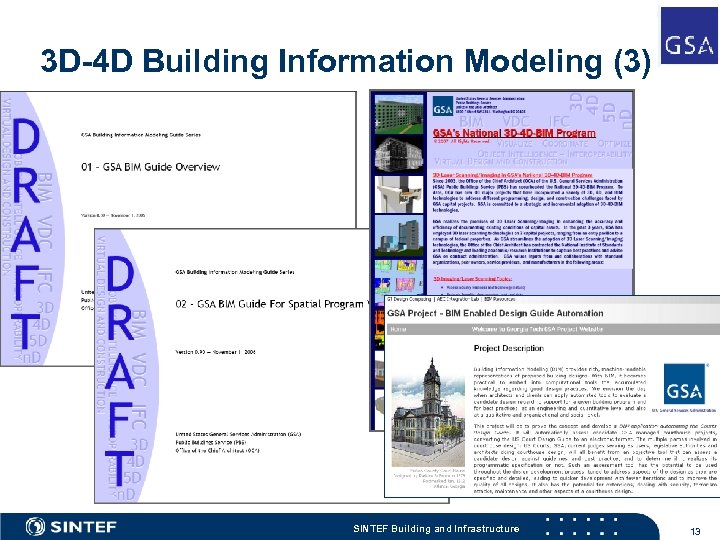
3 D-4 D Building Information Modeling (3) SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 13
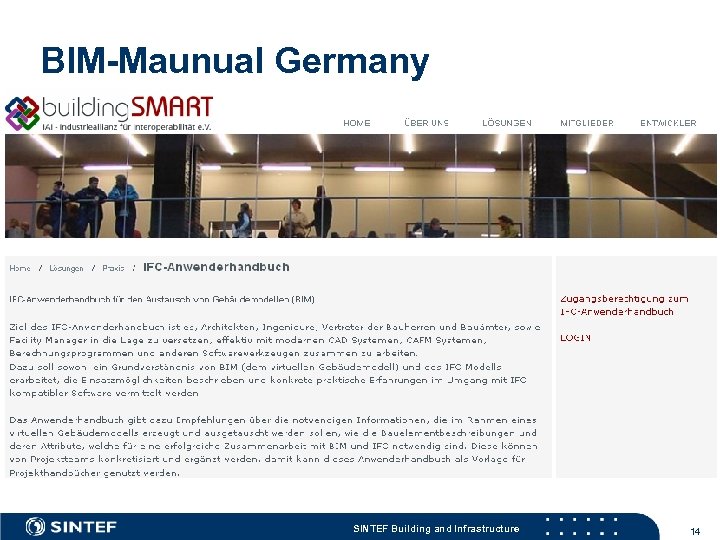
BIM-Maunual Germany SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 14
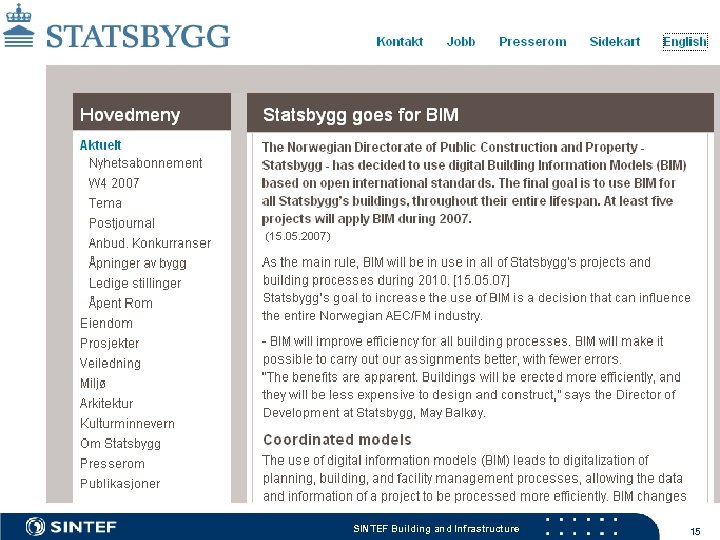
SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 15

Statsbygg’s BIM-manual SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 16
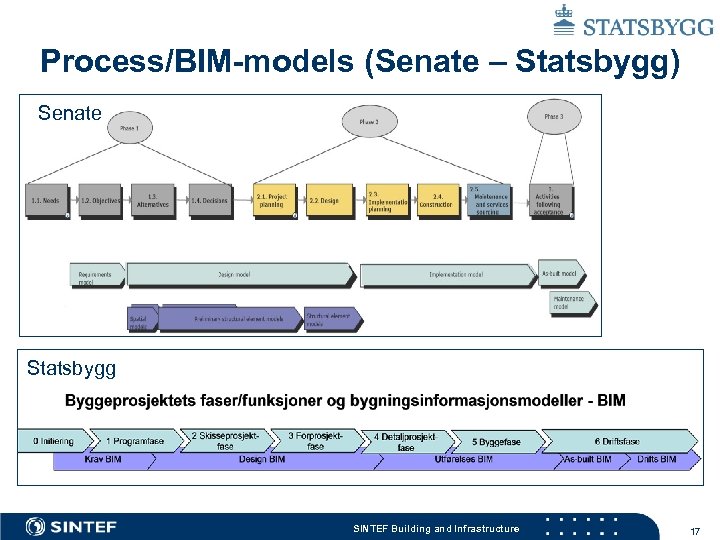
Process/BIM-models (Senate – Statsbygg) Senate Statsbygg SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 17
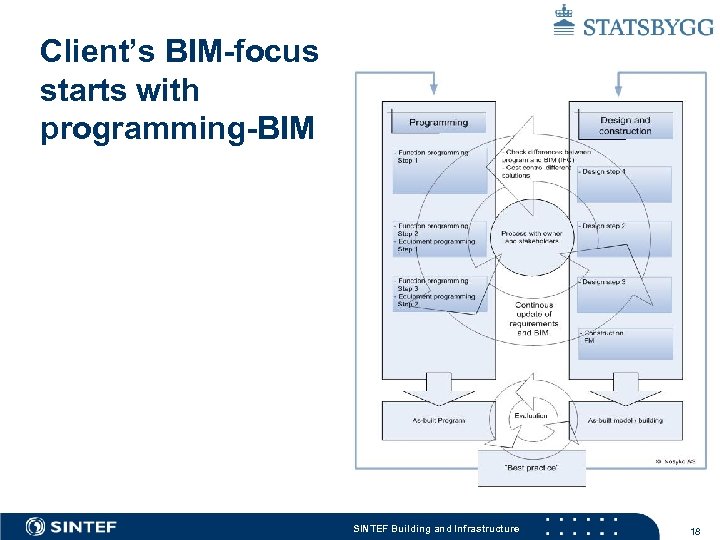
Client’s BIM-focus starts with programming-BIM SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 18
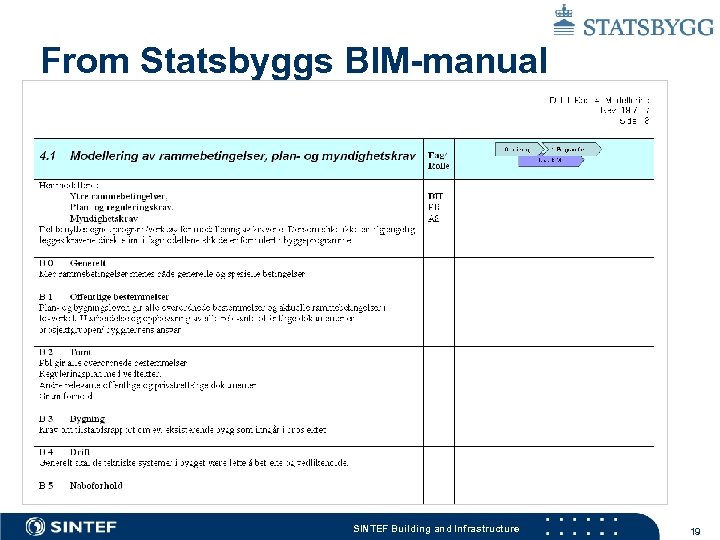
From Statsbyggs BIM-manual SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 19

STREP Proposal 2007. 05. 08 (1) SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 20
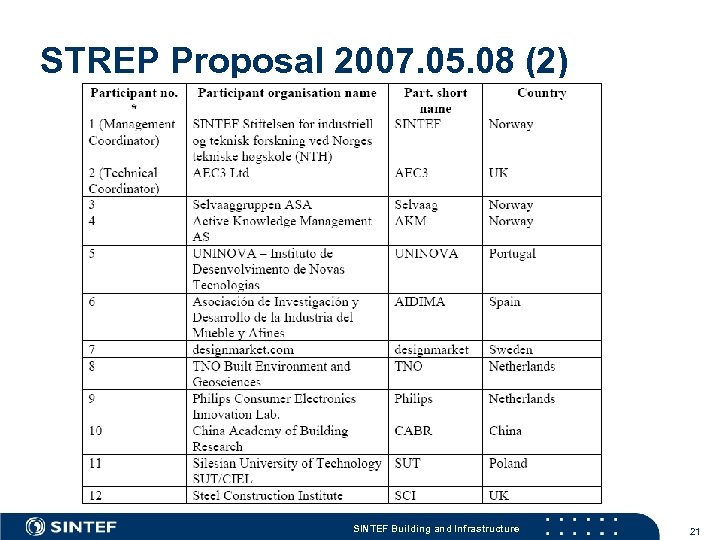
STREP Proposal 2007. 05. 08 (2) SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 21

Erabuild – BIM Barometer 2007 (1) n State of the art regarding development, implementation and deployment of BIM and IFC n Lessons learned in the process of development and implementation of BIM and IFC n Necessary future steps to move towards the use of integrated BIM processes n Total price, Euro 75. 000 SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 22
Erabuild – BIM Barometer 2007 (2) "Review of the Development and Implementation of IFC compatible BIM“ n Questionnaire: The use of Building Information Models (BIM) and Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) in building construction sector. n The questionnaire includes 10 questions related to the use of BIM and IFC in the building construction sector. The questionnaire is a part of ERAbuild program's study n Funded by Danish Authority for Enterprise and construction (Denmark), Formas (Sweden), Forskningsrådet (Norway), PSIBouw (Netherlands) and Tekes (Finland). n The study is performed by SINTEF (Norway), VTT (Finland), Eurostep (Sweden) and Ramboll (Denmark). SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 23

STAND-INN project IFC based open standards & sustainability standards for sustainable construction Role of government in standards and innovation Mr Svein E. Haagenrud, SINTEF, Norway Europe INNOVA Workshop Standards and Innovation, Madeira, 29 March 2007 SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 24

STAND-INN Vision/mission n Vision: n Sustainable Value creation for customers over the life-cycle of buildings using information models. n Mission: n To provide guidance on how standardisation supports innovation and ”Building Smart”. n To disseminate information about sustainability - and IFC/BIM standards. SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 25

STAND-INN The Consortium n 2 partners from China and 1 from Australia and with n 5 European (World) wide networks providers n IAI (13 chapters), CIB, ECCREDI, ENBRI, CEN) entailing major stakeholders from n Industry including SMEs, users, R&D and national Standardisation organisations n 30 members from 11 European countries n Norway, Finland, France, UK, Sweden, Italy, Lithuenia, Spain, Portugal, Germany, Belgium SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 26

STAND-INN Construction industry is: n -the 40% industry (environmental) n 40% of all emissions n 40% of material & energy consumption n Needs to become ”sustainable” n -the 30/30 Industry n 30% of any Country’s GDP is “construction” related (26 million jobs in EU) n 30% is waste (non-value transactions) n Lack of Communication (interoperability) is a key problem n US Report, 2004: Inadequate Interoperability in the U. S Capital Facilitates Industry costs Approximately $15. 8 billion annually , representing 2% of industry revenue. n Needs to ”change-transform”. SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 27
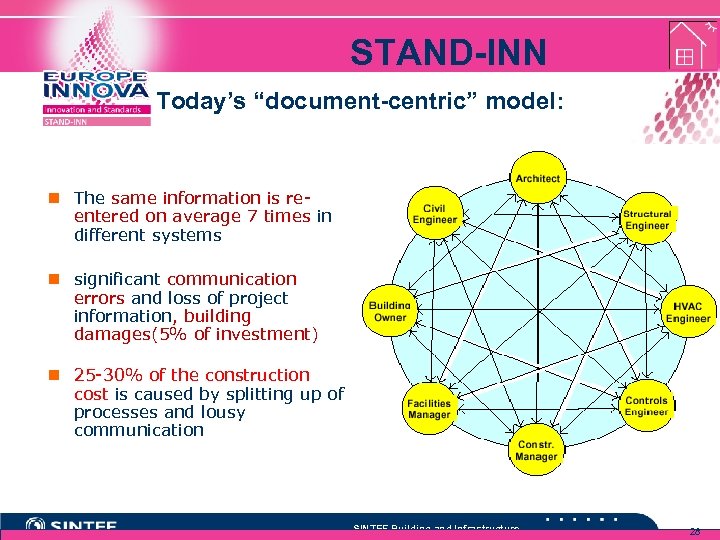
STAND-INN Today’s “document-centric” model: n The same information is reentered on average 7 times in different systems n significant communication errors and loss of project information, building damages(5% of investment) n 25 -30% of the construction cost is caused by splitting up of processes and lousy communication SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 28
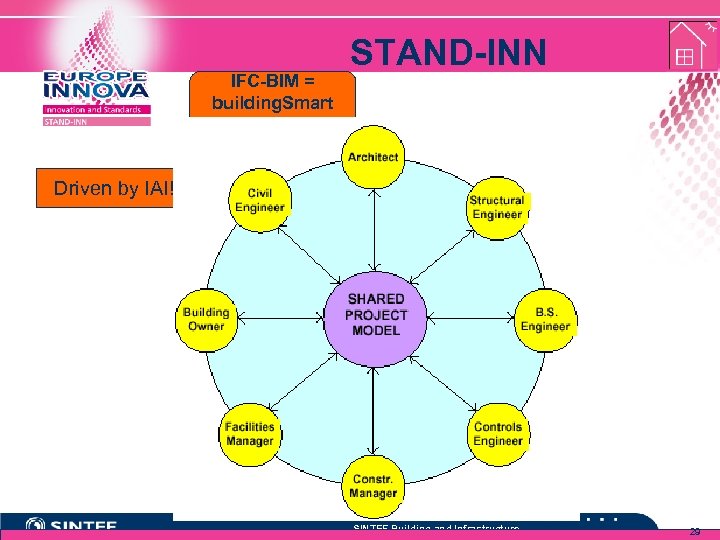
STAND-INN Tomorrows “information centric” IFC-BIM = model building. Smart concept Driven by IAI! SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 29
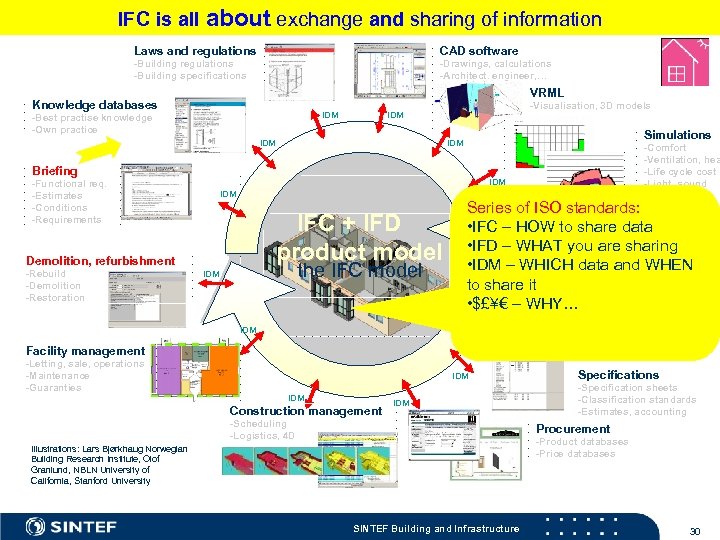
IFC is all about exchange and sharing of information Laws and regulations CAD software -Building regulations -Building specifications -Drawings, calculations -Architect, engineer, … VRML Knowledge databases IDM -Best practise knowledge -Own practice -Visualisation, 3 D models IDM Simulations IDM Briefing IDM -Functional req. -Estimates -Conditions -Requirements IDM IFC + IFD product model Demolition, refurbishment -Rebuild -Demolition -Restoration -Comfort -Ventilation, hea -Life cycle cost -Light, sound -Insulation -Fire, usage -Environment -Life time predic the IFC model IDM Series of ISO standards: • IFC – HOW to share data IDM • IFD – WHAT you are sharing • IDM – WHICH data and WHEN to share it • $£¥€ – WHY… IDM Facility management -Letting, sale, operations -Maintenance -Guaranties IDM Construction management IDM -Scheduling -Logistics, 4 D Specifications -Specification sheets -Classification standards -Estimates, accounting Procurement -Product databases -Price databases Illustrations: Lars Bjørkhaug Norwegian Building Research Institute, Olof Granlund, NBLN University of California, Stanford University SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 30
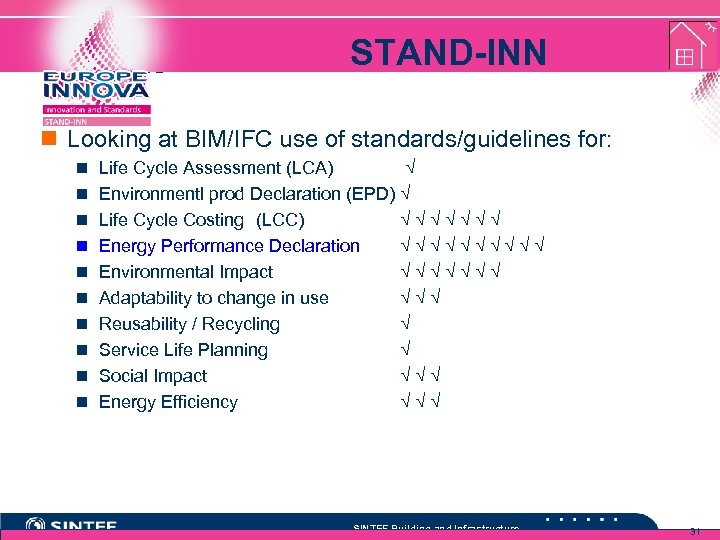
Results STAND-INN n Looking at BIM/IFC use of standards/guidelines for: n Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) √ n Environmentl prod Declaration (EPD) √ n Life Cycle Costing (LCC) √ √ √ √ n Energy Performance Declaration √ √ √ √ √ n Environmental Impact √ √ √ √ n Adaptability to change in use √ √ √ n Reusability / Recycling √ n Service Life Planning √ n Social Impact √ √ √ n Energy Efficiency √ √ √ SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 31
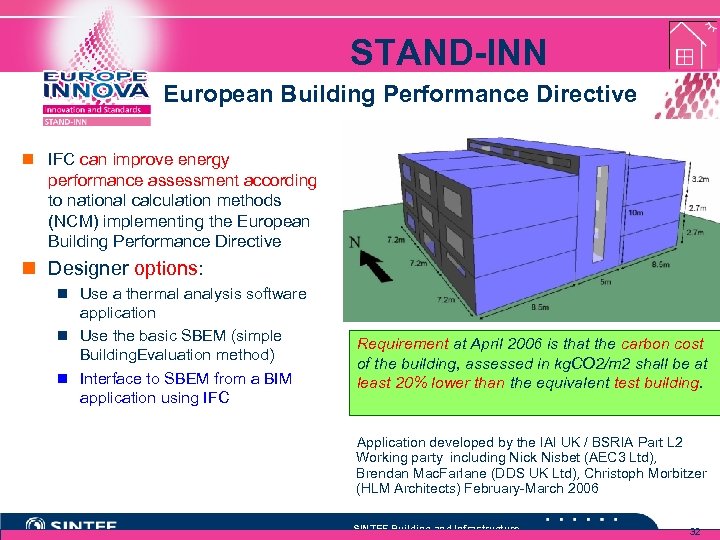
STAND-INN European Building Performance Directive n IFC can improve energy performance assessment according to national calculation methods (NCM) implementing the European Building Performance Directive n Designer options: n Use a thermal analysis software application n Use the basic SBEM (simple Building. Evaluation method) n Interface to SBEM from a BIM application using IFC Requirement at April 2006 is that the carbon cost of the building, assessed in kg. CO 2/m 2 shall be at least 20% lower than the equivalent test building. Application developed by the IAI UK / BSRIA Part L 2 Working party including Nick Nisbet (AEC 3 Ltd), Brendan Mac. Farlane (DDS UK Ltd), Christoph Morbitzer (HLM Architects) February-March 2006 SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 32
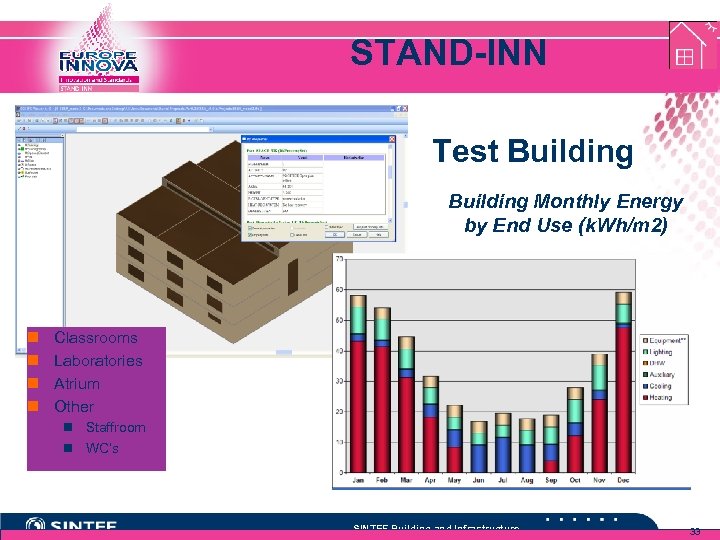
STAND-INN Test Building Monthly Energy by End Use (k. Wh/m 2) n n Classrooms Laboratories Atrium Other n Staffroom n WC’s SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 33
STAND-INN Conclusion on Role of Government n Key drivers for change/innovation n As ”adopters” n As ”influencers” n As ”implemetenrs” n Governments mandate IFC/BIM n Norwegian Government (Bygningsteknisk Etat and Statsbygg) mandated IFC in 2005. n Singapore Government deployed CORENET e-Plan Check System in 2005. n US: Public Building Services' requires GSA to use IFC by 2006 n New York City will run a Singapore e-Plan. Check Prototype n Shanghai plan for a “Singapore Prototype” in 2007 n Denmark and Finland from 1. 09. 2007 n Etc n When will we see EU requiring IFC/BIM &sustainability standards in building projects? SINTEF Building and Infrastructure 34
01a0489778812d9871cd7b74ff49190e.ppt