14e3e12bc1a58a22fd5d2c1ba897fd62.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 International Organization for Standardization (ISO) • SEVAL 2010 • • Berne 10 September 2010 • Sean Mac Curtain • ISO Head of Conformity Assessment • CASCO Secretary
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) • SEVAL 2010 • • Berne 10 September 2010 • Sean Mac Curtain • ISO Head of Conformity Assessment • CASCO Secretary
 Outline • • • Introduction and megatrends ISO System ISO’s international network Some key principles Types of standards A world in turmoil Emerging areas Topical standards areas Examples of standards in key issues Conformity assessment ISO Award
Outline • • • Introduction and megatrends ISO System ISO’s international network Some key principles Types of standards A world in turmoil Emerging areas Topical standards areas Examples of standards in key issues Conformity assessment ISO Award
 Introduction: - A World in turmoil and new paradigms • Volatile financial markets and economies in recession / fragile recovery? • Aspiration for sustainable development. Inter-related issues of climate change, energy, food and water • UN Millenium Goals and developing countries • Converging technologies • Speed to market and new ways of getting information • World trade and who leads ?
Introduction: - A World in turmoil and new paradigms • Volatile financial markets and economies in recession / fragile recovery? • Aspiration for sustainable development. Inter-related issues of climate change, energy, food and water • UN Millenium Goals and developing countries • Converging technologies • Speed to market and new ways of getting information • World trade and who leads ?
 Who benefits from standards • States and communities – Economic competitivity and access to world markets, regulation, sustainable development, loyal competition, public purchases… • Companies – Technology transfer, market knowledge, good management practices, quality recognition… • Consumers – Products and services comparison, quality improvement, information on performance, security and impact on environment • Researchers – Measurements, risk assessment, dissemination of innovation, not re-inventing the wheel!
Who benefits from standards • States and communities – Economic competitivity and access to world markets, regulation, sustainable development, loyal competition, public purchases… • Companies – Technology transfer, market knowledge, good management practices, quality recognition… • Consumers – Products and services comparison, quality improvement, information on performance, security and impact on environment • Researchers – Measurements, risk assessment, dissemination of innovation, not re-inventing the wheel!
 Standards help business thrive • Impact internal business quality culture and product reliability - give competitive edge • Help business adopt sustainable development practices (e. g. environmental management, social responsibility, life cycle assessment for products, energy efficiency and management, etc. ) • Assists efficient resource allocation (e. g. government procurement, public works, services, etc. ) • Bridge the knowledge gap and enhance innovation
Standards help business thrive • Impact internal business quality culture and product reliability - give competitive edge • Help business adopt sustainable development practices (e. g. environmental management, social responsibility, life cycle assessment for products, energy efficiency and management, etc. ) • Assists efficient resource allocation (e. g. government procurement, public works, services, etc. ) • Bridge the knowledge gap and enhance innovation
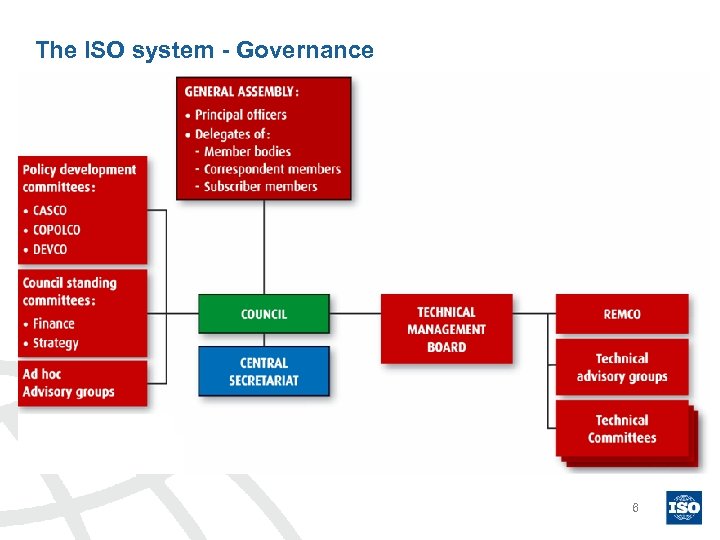 The ISO system - Governance 6
The ISO system - Governance 6
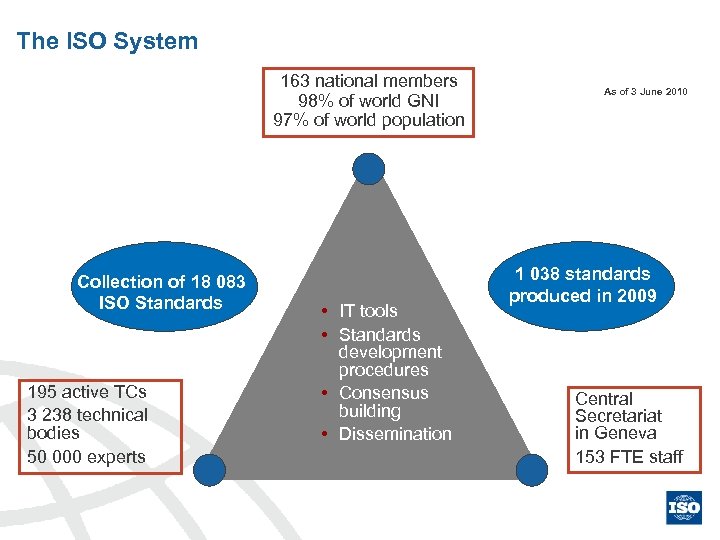 The ISO System 163 national members 98% of world GNI 97% of world population Collection of 18 083 ISO Standards 195 active TCs 3 238 technical bodies 50 000 experts • IT tools • Standards development procedures • Consensus building • Dissemination As of 3 June 2010 1 038 standards produced in 2009 Central Secretariat in Geneva 153 FTE staff
The ISO System 163 national members 98% of world GNI 97% of world population Collection of 18 083 ISO Standards 195 active TCs 3 238 technical bodies 50 000 experts • IT tools • Standards development procedures • Consensus building • Dissemination As of 3 June 2010 1 038 standards produced in 2009 Central Secretariat in Geneva 153 FTE staff
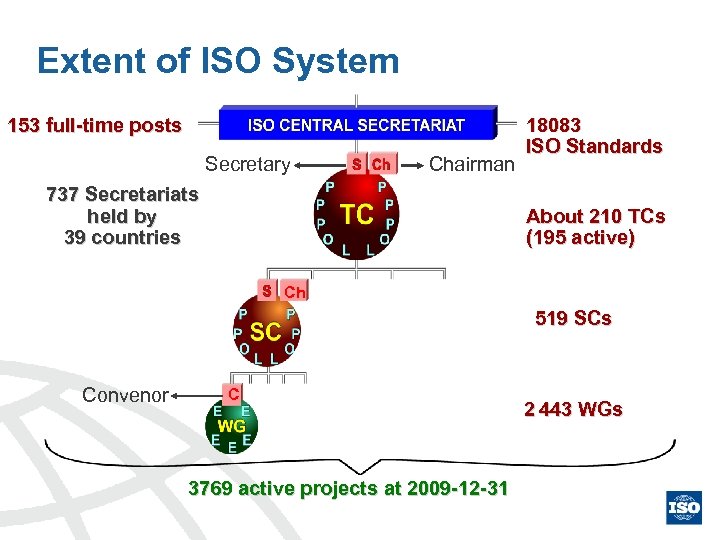 Extent of ISO System 153 full-time posts Secretary Chairman 737 Secretariats held by 39 countries 18083 ISO Standards About 210 TCs (195 active) Ch 519 SCs Convenor C 3769 active projects at 2009 -12 -31 2 443 WGs
Extent of ISO System 153 full-time posts Secretary Chairman 737 Secretariats held by 39 countries 18083 ISO Standards About 210 TCs (195 active) Ch 519 SCs Convenor C 3769 active projects at 2009 -12 -31 2 443 WGs
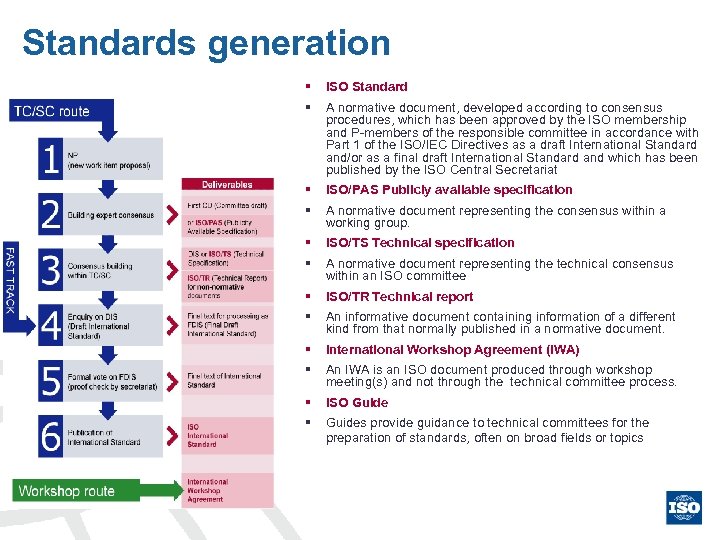 Standards generation § ISO Standard § A normative document, developed according to consensus procedures, which has been approved by the ISO membership and P-members of the responsible committee in accordance with Part 1 of the ISO/IEC Directives as a draft International Standard and/or as a final draft International Standard and which has been published by the ISO Central Secretariat § ISO/PAS Publicly available specification § A normative document representing the consensus within a working group. § ISO/TS Technical specification § A normative document representing the technical consensus within an ISO committee § ISO/TR Technical report § An informative document containing information of a different kind from that normally published in a normative document. § International Workshop Agreement (IWA) § An IWA is an ISO document produced through workshop meeting(s) and not through the technical committee process. § ISO Guide § Guides provide guidance to technical committees for the preparation of standards, often on broad fields or topics
Standards generation § ISO Standard § A normative document, developed according to consensus procedures, which has been approved by the ISO membership and P-members of the responsible committee in accordance with Part 1 of the ISO/IEC Directives as a draft International Standard and/or as a final draft International Standard and which has been published by the ISO Central Secretariat § ISO/PAS Publicly available specification § A normative document representing the consensus within a working group. § ISO/TS Technical specification § A normative document representing the technical consensus within an ISO committee § ISO/TR Technical report § An informative document containing information of a different kind from that normally published in a normative document. § International Workshop Agreement (IWA) § An IWA is an ISO document produced through workshop meeting(s) and not through the technical committee process. § ISO Guide § Guides provide guidance to technical committees for the preparation of standards, often on broad fields or topics
 The World Standards Cooperation (WSC) The leading international standards organizations l Multi-discipline and cross sector l For electrotechnology l For telecommunications Collaborate to meet the challenges of converging 10 technologies
The World Standards Cooperation (WSC) The leading international standards organizations l Multi-discipline and cross sector l For electrotechnology l For telecommunications Collaborate to meet the challenges of converging 10 technologies
 ISO’s international network • WTO : TBT, SPS and GATS (services) agreements • UN and UN agencies: CODEX, ILO, IMO, ITC, UNECE, UNEP, UNGC, UNIDO, WHO, etc • 591 liaisons with international organizations in technical work • Links with six regional bodies (ACCSQ, AIDMO, ARSO, CEN, COPANT, EASC) and PASC • Economic actors: Accreditation: IAF and ILAC, Consumers International, ICC, IFAN, World Economic Forum, etc…
ISO’s international network • WTO : TBT, SPS and GATS (services) agreements • UN and UN agencies: CODEX, ILO, IMO, ITC, UNECE, UNEP, UNGC, UNIDO, WHO, etc • 591 liaisons with international organizations in technical work • Links with six regional bodies (ACCSQ, AIDMO, ARSO, CEN, COPANT, EASC) and PASC • Economic actors: Accreditation: IAF and ILAC, Consumers International, ICC, IFAN, World Economic Forum, etc…
 Formal International Standardization Some key principles • • • Transparency * Openness * Consensus and impartiality * Market relevance and effectiveness * Coherence * Development dimension * Stakeholder engagement Due process National implementation/adoption * explicit principles for the “development of international standards, guides and recommendations with relation to articles 2, 5 and Annex 3 of the WTO/TBT agreement”
Formal International Standardization Some key principles • • • Transparency * Openness * Consensus and impartiality * Market relevance and effectiveness * Coherence * Development dimension * Stakeholder engagement Due process National implementation/adoption * explicit principles for the “development of international standards, guides and recommendations with relation to articles 2, 5 and Annex 3 of the WTO/TBT agreement”
 Different types of ISO International Standards • Terms and definitions • Graphical symbols, pictograms and labeling • Measurement, analysis and test methods • Interoperability requirements • Processing, validation and exchange of data • Performance characteristics for safety, security, health, environmental requirements • Organizational and management practices • Packaging and labeling • Conformity assessment
Different types of ISO International Standards • Terms and definitions • Graphical symbols, pictograms and labeling • Measurement, analysis and test methods • Interoperability requirements • Processing, validation and exchange of data • Performance characteristics for safety, security, health, environmental requirements • Organizational and management practices • Packaging and labeling • Conformity assessment
 Topical standards areas in ISO § Oil and gas § Industrial engineering § Automobile § Ships and marine technology § Food and nutrition § Healthcare § Building and construction § Security § Climate change § Consumer protection and information § Energy efficiency § Services § Water § Social responsibility § Finance § Sustainability § Biotechnology § Quality management § Information technologies § Conformity assessment
Topical standards areas in ISO § Oil and gas § Industrial engineering § Automobile § Ships and marine technology § Food and nutrition § Healthcare § Building and construction § Security § Climate change § Consumer protection and information § Energy efficiency § Services § Water § Social responsibility § Finance § Sustainability § Biotechnology § Quality management § Information technologies § Conformity assessment
 Examples of standardization in key sectors The oil and gas industry § ISO/TC 67 - Materials, equipment and offshore structures for the petroleum, petrochemical and natural gas industries – – 164 IS and 60 in progress – § Products and component specification and interoperability Involvement of and adoption by CEN and American Petroleum Institute ISO/TS 29001: application of ISO 9001 for suppliers of the oil and gas industry
Examples of standardization in key sectors The oil and gas industry § ISO/TC 67 - Materials, equipment and offshore structures for the petroleum, petrochemical and natural gas industries – – 164 IS and 60 in progress – § Products and component specification and interoperability Involvement of and adoption by CEN and American Petroleum Institute ISO/TS 29001: application of ISO 9001 for suppliers of the oil and gas industry
 Examples of standardization in key sectors Automobiles • ISO/TC 22 on motor vehicles – Collaboration with regulators: WP. 29 of UNECE – Testing for safety, noise and environmental impact – Ergonomics and graphical symbols • Quality management: ISO 16949 and the IATF • Road traffic safety management: ISO/TC 241 • Intelligent Transport Systems : ISO/TC 204 • Battery Technology • Natural gas fuelling stations for vehicles: PC 252
Examples of standardization in key sectors Automobiles • ISO/TC 22 on motor vehicles – Collaboration with regulators: WP. 29 of UNECE – Testing for safety, noise and environmental impact – Ergonomics and graphical symbols • Quality management: ISO 16949 and the IATF • Road traffic safety management: ISO/TC 241 • Intelligent Transport Systems : ISO/TC 204 • Battery Technology • Natural gas fuelling stations for vehicles: PC 252
 Example of standardization on key issues Responding to climate change • Environmental management: the ISO 14000 series • ISO 14064/65: Greenhouse gas (GHG) quantification, verification, validation - ‘GHG Protocol’ and ‘Voluntary Carbon Standard’ real-life implementations • Others in ISO 14000 series on environmental management, lifecycle assessment, labelling … • “Carbon Footprint” investigations underway • FAO/WMO with ISO/TC 211 to help track ‘essential climate variables’ • ISO at Bali UNFCCC, at COP 15 in Copenhagen • Expanding cooperation with UNEP
Example of standardization on key issues Responding to climate change • Environmental management: the ISO 14000 series • ISO 14064/65: Greenhouse gas (GHG) quantification, verification, validation - ‘GHG Protocol’ and ‘Voluntary Carbon Standard’ real-life implementations • Others in ISO 14000 series on environmental management, lifecycle assessment, labelling … • “Carbon Footprint” investigations underway • FAO/WMO with ISO/TC 211 to help track ‘essential climate variables’ • ISO at Bali UNFCCC, at COP 15 in Copenhagen • Expanding cooperation with UNEP
 Example of standardization on key issues Energy • Over 20 ISO Technical Committees involved in aspects of energy efficiency and renewables • ISO SAG on Energy efficiency and renewable sources (SAG-E) • Joint ISO/IEC PC on international terminology for energy efficiency and renewable energy sources • Significant progress on energy management systems (ISO 50001, ISO/PC 242) • Industrial energy efficiency (SAG-E recommendation) • Increase of efficiency and emission reduction of road vehicles (ISO/TC 22, partnership with UNECE WP 29 and ITF) • Sustainability in construction and energy efficiency of buildings • New committees on biofuels including sustainability of biofuels • Cooperation with IEA, WEC, ITF and UNIDO Updated Sept. 2009
Example of standardization on key issues Energy • Over 20 ISO Technical Committees involved in aspects of energy efficiency and renewables • ISO SAG on Energy efficiency and renewable sources (SAG-E) • Joint ISO/IEC PC on international terminology for energy efficiency and renewable energy sources • Significant progress on energy management systems (ISO 50001, ISO/PC 242) • Industrial energy efficiency (SAG-E recommendation) • Increase of efficiency and emission reduction of road vehicles (ISO/TC 22, partnership with UNECE WP 29 and ITF) • Sustainability in construction and energy efficiency of buildings • New committees on biofuels including sustainability of biofuels • Cooperation with IEA, WEC, ITF and UNIDO Updated Sept. 2009
 Example of standardization on key issues The water challenge • ISO/TC 30 – important work on “water metering” in closed conduits in close collaboraton with CEN and OIML • ISO/TC 113, Hydrometry: open channels & groundwater: assessment of water resources possible only by its proper measurement • ISO/TC 147, Water quality – 245 published standards: sampling and measurement of physical, (bio-)chemical, (micro-)biological water characteristics • ISO/TC 224, Water treatment and drinking water – quality of services – providing confidence in areas of public/private transition • NWIP on «Treated wastewater reuse implementation» accepted Updated Sept. 2009
Example of standardization on key issues The water challenge • ISO/TC 30 – important work on “water metering” in closed conduits in close collaboraton with CEN and OIML • ISO/TC 113, Hydrometry: open channels & groundwater: assessment of water resources possible only by its proper measurement • ISO/TC 147, Water quality – 245 published standards: sampling and measurement of physical, (bio-)chemical, (micro-)biological water characteristics • ISO/TC 224, Water treatment and drinking water – quality of services – providing confidence in areas of public/private transition • NWIP on «Treated wastewater reuse implementation» accepted Updated Sept. 2009
 Example of standardization on key issues Food, agriculture and nutrition § ISO/TC 34, Food products • • • 756 standards Food safety (ISO 22000 series) Detection of GMOs Food traceability systems Good manufacturing practices Quality management systems for crop production Irradiation of food Microbiological examination methods Many test methods for seeds, fruits and vegetables, cereals, milk, meat and poultry, spices, coffee, tea. . ISO/TC 93 on starch – established test methods ISO/TC 234 on fishery and aquaculture – ensuring sound ‘farmed fish’ production Relations with WHO/FAO (Codex Alimentarius ), OECD, UN-ECE + WTO/SPS + Retailers + Consumers
Example of standardization on key issues Food, agriculture and nutrition § ISO/TC 34, Food products • • • 756 standards Food safety (ISO 22000 series) Detection of GMOs Food traceability systems Good manufacturing practices Quality management systems for crop production Irradiation of food Microbiological examination methods Many test methods for seeds, fruits and vegetables, cereals, milk, meat and poultry, spices, coffee, tea. . ISO/TC 93 on starch – established test methods ISO/TC 234 on fishery and aquaculture – ensuring sound ‘farmed fish’ production Relations with WHO/FAO (Codex Alimentarius ), OECD, UN-ECE + WTO/SPS + Retailers + Consumers
 Example of standardization on key issues Security • Supply chain: ISO 28000 series • Societal security: ISO/TC 223 • Information security: ISO 27000 • Biometrics
Example of standardization on key issues Security • Supply chain: ISO 28000 series • Societal security: ISO/TC 223 • Information security: ISO 27000 • Biometrics
 Example of standardization on key issues Information and Communication • Information security: Technologies the ISO/IEC 27000 series • Quality of IT services: the ISO/IEC 20000 series • Enabling e-business and supporting financial services • IT in buildings: building control systems design
Example of standardization on key issues Information and Communication • Information security: Technologies the ISO/IEC 27000 series • Quality of IT services: the ISO/IEC 20000 series • Enabling e-business and supporting financial services • IT in buildings: building control systems design
 Example of standardization on key issues Health and safety • Standards provides for an invaluable resource supporting public health and safety policies and infrastructures • Safety requirements are addressd by a large variety of products standards • A large number of ISO standards covers the healthcare sector: e. g. : – Clinical evaluation and testing of medical devices – Clinical laboratories – Health informatics and interoperability – Quality management in health services
Example of standardization on key issues Health and safety • Standards provides for an invaluable resource supporting public health and safety policies and infrastructures • Safety requirements are addressd by a large variety of products standards • A large number of ISO standards covers the healthcare sector: e. g. : – Clinical evaluation and testing of medical devices – Clinical laboratories – Health informatics and interoperability – Quality management in health services
 Example of standardization on key sectors Services • Financial services : ISO/TC 68 • Tourism : ISO/TC 228 • Water services : ISO/TC 224 • Education and training : ISO/TC 232 • COPOLCO Guide on services to consumers
Example of standardization on key sectors Services • Financial services : ISO/TC 68 • Tourism : ISO/TC 228 • Water services : ISO/TC 224 • Education and training : ISO/TC 232 • COPOLCO Guide on services to consumers
 Example of standardization on key issues Consumer information and protection • Safety, quality, comparability of consumer products and domestic appliances • Integrity of claims and informative labelling (quality, safety, environment, ethical trade, and others) • COPOLCO as catalyst for new policy and standardization areas: – Social responsibility – Needs of vulnerable populations: elderly, persons with disabilities, children – Product recall – Customer service (codes of conduct, complaints handling, dispute resolution)
Example of standardization on key issues Consumer information and protection • Safety, quality, comparability of consumer products and domestic appliances • Integrity of claims and informative labelling (quality, safety, environment, ethical trade, and others) • COPOLCO as catalyst for new policy and standardization areas: – Social responsibility – Needs of vulnerable populations: elderly, persons with disabilities, children – Product recall – Customer service (codes of conduct, complaints handling, dispute resolution)
 Example of standardization on key issues Quality Management • Over 1 million ISO 9001: 2000 certificates in 179 countries (in 2009) • Sector implementations of ISO 9000: automobile, aeronautics, telecoms, railways, medical devices… • Market surveillance of certification to ISO management system standards
Example of standardization on key issues Quality Management • Over 1 million ISO 9001: 2000 certificates in 179 countries (in 2009) • Sector implementations of ISO 9000: automobile, aeronautics, telecoms, railways, medical devices… • Market surveillance of certification to ISO management system standards
 Conformity assessment • Conformity assessment means checking whether products, services, materials, processes, systems and personnel measure up to the requirements of standards, regulations or other specifications. • Conformity assessment benefits manufacturers, service providers, users, consumers and regulators. It facilitates international trade and supports sustainable development. • ISO and IEC jointly develop International Standards and Guides through the ISO Committee on conformity assessment (CASCO), these documents are referred to as the ‘CASCO toolbox’.
Conformity assessment • Conformity assessment means checking whether products, services, materials, processes, systems and personnel measure up to the requirements of standards, regulations or other specifications. • Conformity assessment benefits manufacturers, service providers, users, consumers and regulators. It facilitates international trade and supports sustainable development. • ISO and IEC jointly develop International Standards and Guides through the ISO Committee on conformity assessment (CASCO), these documents are referred to as the ‘CASCO toolbox’.
 ISO/CASCO: The ISO Committee for Conformity Assessment § § § The CASCO Toolbox consists of 111 ISO members are 27 documents (IS and Guides) represented in CASCO, of which 69 are participating members and covering: 42 observers ‒ Vocabulary, principles and 17 international organizations are liaison members of CASCO: BIPM, CAC, CEOC, EOQ, Eurolab, IAF, IFAN, IFIA, IIOC, ILAC, INLAC, IPC, IQNet, ITU-T, OIML, UNFCCC and UILI common elements of conformity assessment ‒ Code of good practice ‒ Product, system, and persons certification ‒ Testing, calibration, inspection, marks of conformity ‒ Supplier’s declaration of conformity, accreditation, peer assessment, and mutual recognition arrangements
ISO/CASCO: The ISO Committee for Conformity Assessment § § § The CASCO Toolbox consists of 111 ISO members are 27 documents (IS and Guides) represented in CASCO, of which 69 are participating members and covering: 42 observers ‒ Vocabulary, principles and 17 international organizations are liaison members of CASCO: BIPM, CAC, CEOC, EOQ, Eurolab, IAF, IFAN, IFIA, IIOC, ILAC, INLAC, IPC, IQNet, ITU-T, OIML, UNFCCC and UILI common elements of conformity assessment ‒ Code of good practice ‒ Product, system, and persons certification ‒ Testing, calibration, inspection, marks of conformity ‒ Supplier’s declaration of conformity, accreditation, peer assessment, and mutual recognition arrangements
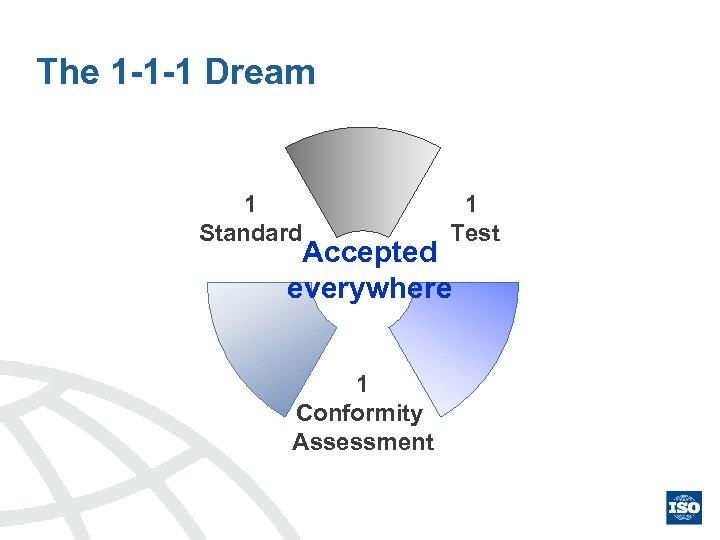 The 1 -1 -1 Dream 1 Test 1 Standard Accepted everywhere 1 Conformity Assessment
The 1 -1 -1 Dream 1 Test 1 Standard Accepted everywhere 1 Conformity Assessment
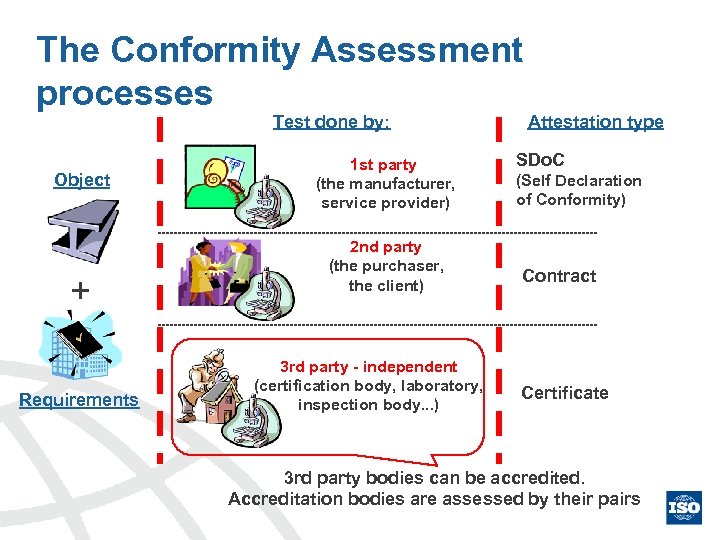 The Conformity Assessment processes Test done by: Object + Requirements 1 st party (the manufacturer, service provider) 2 nd party (the purchaser, the client) 3 rd party - independent (certification body, laboratory, inspection body. . . ) Attestation type SDo. C (Self Declaration of Conformity) Contract Certificate 3 rd party bodies can be accredited. Accreditation bodies are assessed by their pairs
The Conformity Assessment processes Test done by: Object + Requirements 1 st party (the manufacturer, service provider) 2 nd party (the purchaser, the client) 3 rd party - independent (certification body, laboratory, inspection body. . . ) Attestation type SDo. C (Self Declaration of Conformity) Contract Certificate 3 rd party bodies can be accredited. Accreditation bodies are assessed by their pairs
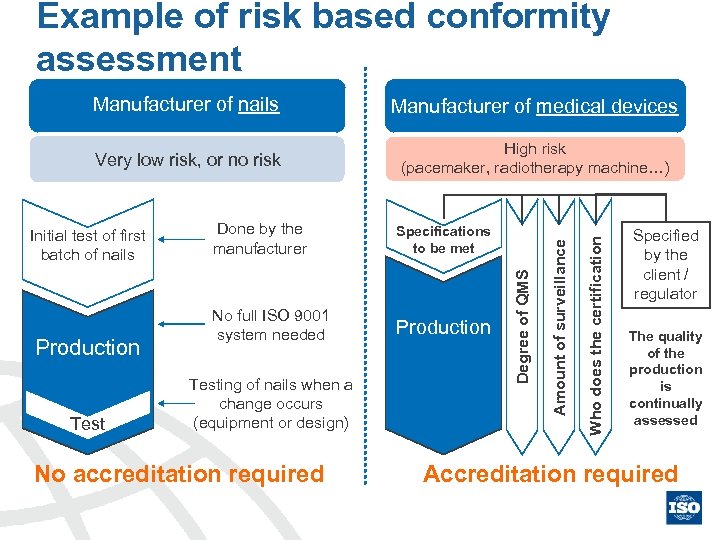 Example of risk based conformity assessment Very low risk, or no risk High risk (pacemaker, radiotherapy machine…) Production Test Done by the manufacturer Specifications to be met No full ISO 9001 system needed Production Testing of nails when a change occurs (equipment or design) No accreditation required Degree of QMS Initial test of first batch of nails Who does the certification Manufacturer of medical devices Amount of surveillance Manufacturer of nails Specified by the client / regulator The quality of the production is continually assessed Accreditation required
Example of risk based conformity assessment Very low risk, or no risk High risk (pacemaker, radiotherapy machine…) Production Test Done by the manufacturer Specifications to be met No full ISO 9001 system needed Production Testing of nails when a change occurs (equipment or design) No accreditation required Degree of QMS Initial test of first batch of nails Who does the certification Manufacturer of medical devices Amount of surveillance Manufacturer of nails Specified by the client / regulator The quality of the production is continually assessed Accreditation required
 Topical issues related to conformity assessment • Product (incl. service and process) certification (ISO/IEC 17065) + fundamentals of product certification (ISO/IEC 17067) • Requirements on inspection bodies (ISO/IEC 17020) • Certification of persons (ISO/IEC 17024) • ISO’s neutrality policy • Qualification of assessors (AB) / auditors specific requirements (CB) • Manual on conformity assessment and market surveillance
Topical issues related to conformity assessment • Product (incl. service and process) certification (ISO/IEC 17065) + fundamentals of product certification (ISO/IEC 17067) • Requirements on inspection bodies (ISO/IEC 17020) • Certification of persons (ISO/IEC 17024) • ISO’s neutrality policy • Qualification of assessors (AB) / auditors specific requirements (CB) • Manual on conformity assessment and market surveillance
 ISO Award on Higher Education in Standardization
ISO Award on Higher Education in Standardization
 THANK YOU ! Sean Mac Curtain maccurtain@iso. org www. iso. org
THANK YOU ! Sean Mac Curtain maccurtain@iso. org www. iso. org


