2010 - IMM IV.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 23
 International Market Segmentation & Targeting Chapter IV
International Market Segmentation & Targeting Chapter IV
 International Market Segmentation Reactive Approach -- Generally, a firm starts international operation by responding to unsolicited enquiries from countries abroad. It is called Reactive Approach. Systematic Approach -- But regular international operations are initiated after going through secondary and primary information about markets. It is called Systematic Approach. 2 -- The process of identifying and dividing customers around the world into distinct subsets that respond to specific marketing strategies in specific manner or have similar need pattern is called International Market Segmentation. Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
International Market Segmentation Reactive Approach -- Generally, a firm starts international operation by responding to unsolicited enquiries from countries abroad. It is called Reactive Approach. Systematic Approach -- But regular international operations are initiated after going through secondary and primary information about markets. It is called Systematic Approach. 2 -- The process of identifying and dividing customers around the world into distinct subsets that respond to specific marketing strategies in specific manner or have similar need pattern is called International Market Segmentation. Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
 -- International or Global Market Segmentation may be defined as the process of identifying specific country groups of customers and potential customers with homogeneous attributes who exhibit similar buying behavior. Bases of International or Global Market Segmentation -- The process of dividing the world into distinct subsets for segmentation may be carried out based on various factors like : 1. Geographic Segmentation When markets are specified notionally as geographic subsets, it is called ‘Geographic Segmentation’ like North America, Eastern Europe , South East Asia etc. 3 2. Demographic segmentation In this, international markets are segmented on the basis of Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018 age, gender, family size, education levels etc.
-- International or Global Market Segmentation may be defined as the process of identifying specific country groups of customers and potential customers with homogeneous attributes who exhibit similar buying behavior. Bases of International or Global Market Segmentation -- The process of dividing the world into distinct subsets for segmentation may be carried out based on various factors like : 1. Geographic Segmentation When markets are specified notionally as geographic subsets, it is called ‘Geographic Segmentation’ like North America, Eastern Europe , South East Asia etc. 3 2. Demographic segmentation In this, international markets are segmented on the basis of Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018 age, gender, family size, education levels etc.
 3. Income based Segmentation -- Countries are segmented by World Bank based on their percapita national incomes (GNI) as under * Low income nations with GNI $ 735 and less p. a. ; e. g. Bangladesh, Pakistan, Kenya, Nigeria etc. * Lower Middle income nations with GNI between $736 to 2935 p. a. ; e. g. India, Egypt, Indonesia, China etc. * Upper Middle income nations with GNI $2936 to 9075 p. a. ; e. g. Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Saudi-Arabia, South Africa etc. * High income nations with GNI $ 9076 p. a. and above e. g. U. S. , Canada, Germany, France, Hong Kong, U. K. etc. 4 4. Psychographic Segmentation Dividing customers and nations based on their lifestyle, personality or value systems are called ‘Psychographic Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly segmentation’. 2/12/2018
3. Income based Segmentation -- Countries are segmented by World Bank based on their percapita national incomes (GNI) as under * Low income nations with GNI $ 735 and less p. a. ; e. g. Bangladesh, Pakistan, Kenya, Nigeria etc. * Lower Middle income nations with GNI between $736 to 2935 p. a. ; e. g. India, Egypt, Indonesia, China etc. * Upper Middle income nations with GNI $2936 to 9075 p. a. ; e. g. Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Saudi-Arabia, South Africa etc. * High income nations with GNI $ 9076 p. a. and above e. g. U. S. , Canada, Germany, France, Hong Kong, U. K. etc. 4 4. Psychographic Segmentation Dividing customers and nations based on their lifestyle, personality or value systems are called ‘Psychographic Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly segmentation’. 2/12/2018
 5. Core -value based Segmentation Attitude and behaviour of customers is greatly influenced by belief system i. e. core-values. People in these segments differ in terms of activities, product preference, their use, media habits etc. accordingly those are segmented. 6. International Marketing Opportunity based Segmentation The state of demand may vary significantly between nations, segmentation may be done accordingly, * Existing Markets - Where marketing opportunities can be measured through consumption and import trends are existing markets; these markets are highly competitive. * Latent Markets -- These countries possess potential customers but no market exists as there are no present suppliers. These are easy to enter markets. 5 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
5. Core -value based Segmentation Attitude and behaviour of customers is greatly influenced by belief system i. e. core-values. People in these segments differ in terms of activities, product preference, their use, media habits etc. accordingly those are segmented. 6. International Marketing Opportunity based Segmentation The state of demand may vary significantly between nations, segmentation may be done accordingly, * Existing Markets - Where marketing opportunities can be measured through consumption and import trends are existing markets; these markets are highly competitive. * Latent Markets -- These countries possess potential customers but no market exists as there are no present suppliers. These are easy to enter markets. 5 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
 * Incipient Markets -- There may be no demand at present in these cluster of nations but have potential for innovated products. Companies may successfully introduce innovated products like computers, internet etc. But are not suitable for me-too products. 7. Segmentation by Economic Development Walt Rostow showed for first time how world markets can be segmented based upon nations’ ‘stages of economic development’. He showed each economic development stage can be measured in terms of cost of labour, technical capability of consumers, scale of operations, interest rates and level of product sophistication. Accordingly, nations are segmented as stages as under: Stage 1 : Traditional Society Stage 2 : Transition to Take-off 6 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
* Incipient Markets -- There may be no demand at present in these cluster of nations but have potential for innovated products. Companies may successfully introduce innovated products like computers, internet etc. But are not suitable for me-too products. 7. Segmentation by Economic Development Walt Rostow showed for first time how world markets can be segmented based upon nations’ ‘stages of economic development’. He showed each economic development stage can be measured in terms of cost of labour, technical capability of consumers, scale of operations, interest rates and level of product sophistication. Accordingly, nations are segmented as stages as under: Stage 1 : Traditional Society Stage 2 : Transition to Take-off 6 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
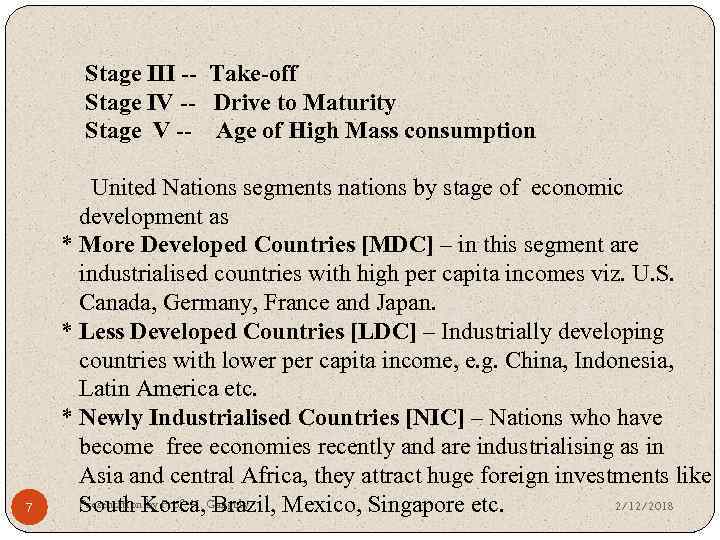 Stage III -- Take-off Stage IV -- Drive to Maturity Stage V -- Age of High Mass consumption 7 United Nations segments nations by stage of economic development as * More Developed Countries [MDC] – in this segment are industrialised countries with high per capita incomes viz. U. S. Canada, Germany, France and Japan. * Less Developed Countries [LDC] – Industrially developing countries with lower per capita income, e. g. China, Indonesia, Latin America etc. * Newly Industrialised Countries [NIC] – Nations who have become free economies recently and are industrialising as in Asia and central Africa, they attract huge foreign investments like Presentation. Korea, Ganguly 2/12/2018 South by Prof. H. Brazil, Mexico, Singapore etc.
Stage III -- Take-off Stage IV -- Drive to Maturity Stage V -- Age of High Mass consumption 7 United Nations segments nations by stage of economic development as * More Developed Countries [MDC] – in this segment are industrialised countries with high per capita incomes viz. U. S. Canada, Germany, France and Japan. * Less Developed Countries [LDC] – Industrially developing countries with lower per capita income, e. g. China, Indonesia, Latin America etc. * Newly Industrialised Countries [NIC] – Nations who have become free economies recently and are industrialising as in Asia and central Africa, they attract huge foreign investments like Presentation. Korea, Ganguly 2/12/2018 South by Prof. H. Brazil, Mexico, Singapore etc.
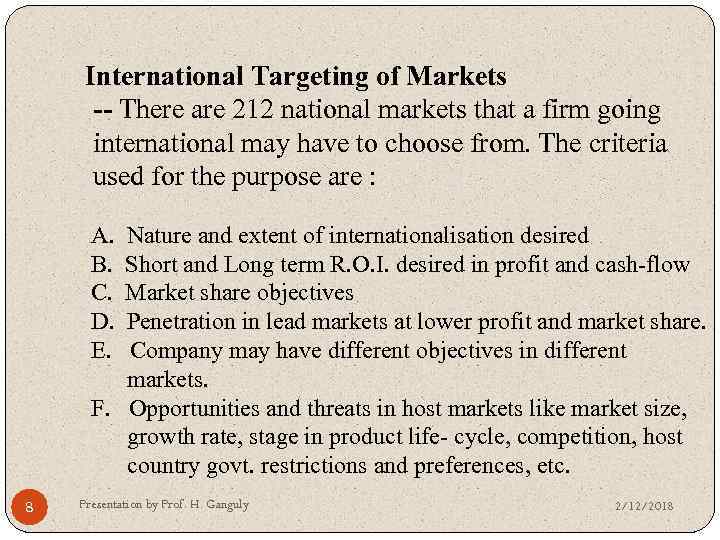 International Targeting of Markets -- There are 212 national markets that a firm going international may have to choose from. The criteria used for the purpose are : A. B. C. D. E. Nature and extent of internationalisation desired Short and Long term R. O. I. desired in profit and cash-flow Market share objectives Penetration in lead markets at lower profit and market share. Company may have different objectives in different markets. F. Opportunities and threats in host markets like market size, growth rate, stage in product life- cycle, competition, host country govt. restrictions and preferences, etc. 8 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
International Targeting of Markets -- There are 212 national markets that a firm going international may have to choose from. The criteria used for the purpose are : A. B. C. D. E. Nature and extent of internationalisation desired Short and Long term R. O. I. desired in profit and cash-flow Market share objectives Penetration in lead markets at lower profit and market share. Company may have different objectives in different markets. F. Opportunities and threats in host markets like market size, growth rate, stage in product life- cycle, competition, host country govt. restrictions and preferences, etc. 8 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
 International Marketing Strategy differs from domestic marketing strategy principally in following directions : 1. Environments of host and home nations. 2. Nature and structure of Organisation. 3. Mode of controlling multicountry operations. Based on above, Marketing Plan of each target market is developed along following lines before comparision -- Situation analysis -- Objectives -- Strategy -- Mode of Entry & -- Budget. 9 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
International Marketing Strategy differs from domestic marketing strategy principally in following directions : 1. Environments of host and home nations. 2. Nature and structure of Organisation. 3. Mode of controlling multicountry operations. Based on above, Marketing Plan of each target market is developed along following lines before comparision -- Situation analysis -- Objectives -- Strategy -- Mode of Entry & -- Budget. 9 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
 World Markets -- Efficiency of marketing strategy depend upon characteristics of market segments. -- Accordingly, cluster of markets around the world are segregated. -- As economic and other parameters of national market changes, their demand pattern, existence of intermediaries and other parameters changes. -- A brief cross-section of prominent world market segments are appended. 10 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
World Markets -- Efficiency of marketing strategy depend upon characteristics of market segments. -- Accordingly, cluster of markets around the world are segregated. -- As economic and other parameters of national market changes, their demand pattern, existence of intermediaries and other parameters changes. -- A brief cross-section of prominent world market segments are appended. 10 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
 1. Less Developed Countries (LDCs) i) Economic Dualism – In less developed nations, exists traditional and also modern sectors of business and industries with lower per capita income e. g. in West African nations, Pakistan, etc. ii) Culturally larger chunk of population in LDCs subscribe to traditional demands. They may have to be educated initially for stepping up of demands e. g. through ‘Rural Marketing’ or e-choupals’ and switching over to high-tech products and services like computers, internet etc. 11 iii)These nations mostly try to encourage development of domestic industries, protect local industries through tariff and non-tariff barriers. They generally suffer from paucity Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly of foreign exchange that impedes their imports. 2/12/2018
1. Less Developed Countries (LDCs) i) Economic Dualism – In less developed nations, exists traditional and also modern sectors of business and industries with lower per capita income e. g. in West African nations, Pakistan, etc. ii) Culturally larger chunk of population in LDCs subscribe to traditional demands. They may have to be educated initially for stepping up of demands e. g. through ‘Rural Marketing’ or e-choupals’ and switching over to high-tech products and services like computers, internet etc. 11 iii)These nations mostly try to encourage development of domestic industries, protect local industries through tariff and non-tariff barriers. They generally suffer from paucity Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly of foreign exchange that impedes their imports. 2/12/2018
 2. Developing Countries and Emerging Nations i) There are 130 or so developing and newly industrialised nations in world, 75% of world population live in these nations. Out of it 50% of world population and GDP comes from Big Emerging Markets (BEMs), other features being * The BEMs have undertaken significant economic reform in recent past, so their rate of growth of economy is high. * These are generally large nations with sizeable population having large sized markets with wide range of products and services. ii) Major BEM nations are China, India, South Korea in Asia; Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Mexico and Venezuela in Latin America; Poland Turkey in Europe and South Africa. 12 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
2. Developing Countries and Emerging Nations i) There are 130 or so developing and newly industrialised nations in world, 75% of world population live in these nations. Out of it 50% of world population and GDP comes from Big Emerging Markets (BEMs), other features being * The BEMs have undertaken significant economic reform in recent past, so their rate of growth of economy is high. * These are generally large nations with sizeable population having large sized markets with wide range of products and services. ii) Major BEM nations are China, India, South Korea in Asia; Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Mexico and Venezuela in Latin America; Poland Turkey in Europe and South Africa. 12 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
 iii) BEM markets import substantial quantity of capital goods to develop their infrastructure and manufacturing industries. These nations are creating economic wealth and employment fast. It is leading to growth in consumption of newer goods and services. iv) IT, environment, transportation, energy production and transmission, healthcare and financial services are growing very fast. v) US, European nations , Japan and NICs are in severe competition to fill demand of these nations vi) Generally it is observed that BEM nations exert significant political influence in their neighbourhood. 13 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
iii) BEM markets import substantial quantity of capital goods to develop their infrastructure and manufacturing industries. These nations are creating economic wealth and employment fast. It is leading to growth in consumption of newer goods and services. iv) IT, environment, transportation, energy production and transmission, healthcare and financial services are growing very fast. v) US, European nations , Japan and NICs are in severe competition to fill demand of these nations vi) Generally it is observed that BEM nations exert significant political influence in their neighbourhood. 13 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
 3. South American Nations i) Military dictatorship in most of these nations have now been replaced by democratically elected Governments. Under earlier regime, state ownership was considered to be ideal engine for economic growth. ii) Now these nations have initiated liberalisation and privatisation of state owned enterprises. iii) Domestic and foreign investors have started investing heavily in banks, airlines, manufacturing units etc. 14 iv) The three BEM nations viz. Argentina, Brazil and Mexico were affected adversely by South East Asian economic crisis and financial crisis of Russia. Foreign investments started moving out of country. As a result Brazil had to devalue its currency. Argentina’s economic growth slowed down due to fall in exports. Mexico also had to devalue Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018 currency
3. South American Nations i) Military dictatorship in most of these nations have now been replaced by democratically elected Governments. Under earlier regime, state ownership was considered to be ideal engine for economic growth. ii) Now these nations have initiated liberalisation and privatisation of state owned enterprises. iii) Domestic and foreign investors have started investing heavily in banks, airlines, manufacturing units etc. 14 iv) The three BEM nations viz. Argentina, Brazil and Mexico were affected adversely by South East Asian economic crisis and financial crisis of Russia. Foreign investments started moving out of country. As a result Brazil had to devalue its currency. Argentina’s economic growth slowed down due to fall in exports. Mexico also had to devalue Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018 currency
 4. East European Markets -- It mainly comprises of erstwhile socialist nations viz. Poland, , Czech Republic, Hungary, Romania etc. , economic development of these nations are at different levels. -- Czech Republic introduced reform process immediately after parting from communists have grown faster compared Hungary , Poland , Romania etc. -- The political and economic condition of Croatia, Slovenia, Macedonia are poor. UN peacekeeping forces are managing those at present. -- Fifteen east European nations joined European Union in 2006. Their economy is in the process of growth. 15 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
4. East European Markets -- It mainly comprises of erstwhile socialist nations viz. Poland, , Czech Republic, Hungary, Romania etc. , economic development of these nations are at different levels. -- Czech Republic introduced reform process immediately after parting from communists have grown faster compared Hungary , Poland , Romania etc. -- The political and economic condition of Croatia, Slovenia, Macedonia are poor. UN peacekeeping forces are managing those at present. -- Fifteen east European nations joined European Union in 2006. Their economy is in the process of growth. 15 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
 5. Selected Asian Nations -- Since 1970 s, economic growth of nations of Asia is substantial. These nations are showing promise to carry forward the phenomenal growth in future too. -- Growth rate is particularly high in Asia Pacific Rim countries viz. Japan, China, South Korea, India, Taiwan, Indonesia, Hong Kong * China : -- China’s dual economic system of socialism along with key tenets of capitalism is producing remarkable economic boom leading to 10% p. a. and more rate of annual GNP growth since 1970. At this rate, it is projected that China shall overtake GNP of US by 2015. 16 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
5. Selected Asian Nations -- Since 1970 s, economic growth of nations of Asia is substantial. These nations are showing promise to carry forward the phenomenal growth in future too. -- Growth rate is particularly high in Asia Pacific Rim countries viz. Japan, China, South Korea, India, Taiwan, Indonesia, Hong Kong * China : -- China’s dual economic system of socialism along with key tenets of capitalism is producing remarkable economic boom leading to 10% p. a. and more rate of annual GNP growth since 1970. At this rate, it is projected that China shall overtake GNP of US by 2015. 16 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
 -- China is deregulating business and industries along with privatising oversized , inefficient State Owned Enterprises (SOE). It is helping in attracting billions of foreign investments. -- Recently, China has increased wage rates in industry, trade and commerce substantially. -- China has become member of World Trade Organisation (WTO) in 2004. -- In 2000, U. S. has granted Permanent Normal Trade Relations (PNTR). -- Both of these are conducive of making China an efficient market player. 17 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
-- China is deregulating business and industries along with privatising oversized , inefficient State Owned Enterprises (SOE). It is helping in attracting billions of foreign investments. -- Recently, China has increased wage rates in industry, trade and commerce substantially. -- China has become member of World Trade Organisation (WTO) in 2004. -- In 2000, U. S. has granted Permanent Normal Trade Relations (PNTR). -- Both of these are conducive of making China an efficient market player. 17 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
 -- From viewpoint of size, diversity and political organisation, China may be thought to be a group of six regions instead of a single market. -- Each region has its own growth strategy, own link with other regions and links to rest of world. -- China has separate Investment and Taxation pattern which is co-ordinated at the top by Central Govt. at Beijing. -- China is continually reinventing itself, in 2002, Chinese Communist Party’s National Congress allowed admission of private entrepreneurs into Communist party. That was how Chinese people got entry into party instead of the membership being restricted to workers and peasants. 18 -- The grey areas that China need to improve upon are its treatment of ‘Human Rights’, reform of legal system and Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018 rampant corruption in different strata of society.
-- From viewpoint of size, diversity and political organisation, China may be thought to be a group of six regions instead of a single market. -- Each region has its own growth strategy, own link with other regions and links to rest of world. -- China has separate Investment and Taxation pattern which is co-ordinated at the top by Central Govt. at Beijing. -- China is continually reinventing itself, in 2002, Chinese Communist Party’s National Congress allowed admission of private entrepreneurs into Communist party. That was how Chinese people got entry into party instead of the membership being restricted to workers and peasants. 18 -- The grey areas that China need to improve upon are its treatment of ‘Human Rights’, reform of legal system and Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018 rampant corruption in different strata of society.
 * Hong Kong -- In 1997, Hong Kong island was returned by British to “People’s Republic of China” as a Special Administrative Region (SAR). -- Now, Hong Kong is being governed by One Country , Two Systems Agreements assuring autonomy in social, economic systems, lifestyle and rights and freedom for at least 50 years. -- Hong Kong market is continued to be operated by freemarket economy, entrepreneurial drive, absence of trade barriers, well-established rule of law, low rate of taxes, complete freedom of capital movement. -- No wonder, Hong Kong is the largest investor in mainland China’s industries and businesses. 19 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
* Hong Kong -- In 1997, Hong Kong island was returned by British to “People’s Republic of China” as a Special Administrative Region (SAR). -- Now, Hong Kong is being governed by One Country , Two Systems Agreements assuring autonomy in social, economic systems, lifestyle and rights and freedom for at least 50 years. -- Hong Kong market is continued to be operated by freemarket economy, entrepreneurial drive, absence of trade barriers, well-established rule of law, low rate of taxes, complete freedom of capital movement. -- No wonder, Hong Kong is the largest investor in mainland China’s industries and businesses. 19 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
 * Taiwan -- Taiwan is a small island geographically separated from mainland China but is a part of political and economic China. -- Taiwan was a member of WTO from before, 1 n 2004 China also became WTO member. -- 12% of all goods exported from China are manufactured at Taiwan. -- Mainland China is the largest market for Hi-Tech products 20 of Taiwan. * Vietnam -- Economy of Vietnam was shattered by 20 years of socialism and war. Vietnam’s population is only 70 million, level of literacy is high. Govt. is trying to achieve economic growth by Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018 opening the economy.
* Taiwan -- Taiwan is a small island geographically separated from mainland China but is a part of political and economic China. -- Taiwan was a member of WTO from before, 1 n 2004 China also became WTO member. -- 12% of all goods exported from China are manufactured at Taiwan. -- Mainland China is the largest market for Hi-Tech products 20 of Taiwan. * Vietnam -- Economy of Vietnam was shattered by 20 years of socialism and war. Vietnam’s population is only 70 million, level of literacy is high. Govt. is trying to achieve economic growth by Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018 opening the economy.
 -- Vietnam require to build its manufacturing industries and infra-structure. -- Most of the capital and technology is provided by Taiwan, Hong Kong and South Korea. -- U. S. investors are also entering into Vietnam market. * South Korea -- South Korea has achieved substantial economic growth driven by exports. -- In 1980 s South Korea started industrialisation by starting to assemble for U. S. and Japanese MNCs. -- Now they are major global players in petrochemicals, electronics, steel and heavy machineries. Hyundai, Posco, Kia, Samsung, Lucky-Goldstar etc. are some of its popular global brands. 21 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
-- Vietnam require to build its manufacturing industries and infra-structure. -- Most of the capital and technology is provided by Taiwan, Hong Kong and South Korea. -- U. S. investors are also entering into Vietnam market. * South Korea -- South Korea has achieved substantial economic growth driven by exports. -- In 1980 s South Korea started industrialisation by starting to assemble for U. S. and Japanese MNCs. -- Now they are major global players in petrochemicals, electronics, steel and heavy machineries. Hyundai, Posco, Kia, Samsung, Lucky-Goldstar etc. are some of its popular global brands. 21 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
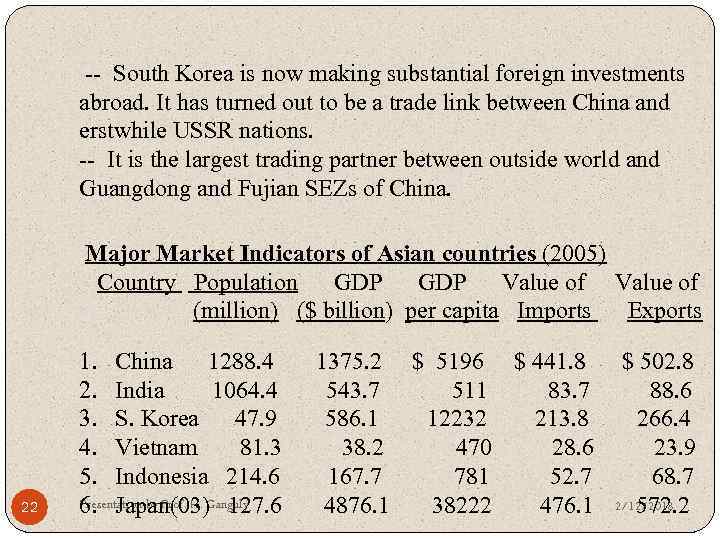 -- South Korea is now making substantial foreign investments abroad. It has turned out to be a trade link between China and erstwhile USSR nations. -- It is the largest trading partner between outside world and Guangdong and Fujian SEZs of China. Major Market Indicators of Asian countries (2005) Country Population GDP Value of (million) ($ billion) per capita Imports Exports 22 1. China 1288. 4 2. India 1064. 4 3. S. Korea 47. 9 4. Vietnam 81. 3 5. Indonesia 214. 6 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 6. Japan(03) 127. 6 1375. 2 $ 5196 $ 441. 8 543. 7 511 83. 7 586. 1 12232 213. 8 38. 2 470 28. 6 167. 7 781 52. 7 4876. 1 38222 476. 1 $ 502. 8 88. 6 266. 4 23. 9 68. 7 2/12/2018 572. 2
-- South Korea is now making substantial foreign investments abroad. It has turned out to be a trade link between China and erstwhile USSR nations. -- It is the largest trading partner between outside world and Guangdong and Fujian SEZs of China. Major Market Indicators of Asian countries (2005) Country Population GDP Value of (million) ($ billion) per capita Imports Exports 22 1. China 1288. 4 2. India 1064. 4 3. S. Korea 47. 9 4. Vietnam 81. 3 5. Indonesia 214. 6 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 6. Japan(03) 127. 6 1375. 2 $ 5196 $ 441. 8 543. 7 511 83. 7 586. 1 12232 213. 8 38. 2 470 28. 6 167. 7 781 52. 7 4876. 1 38222 476. 1 $ 502. 8 88. 6 266. 4 23. 9 68. 7 2/12/2018 572. 2
 6. South Africa -- Because of ‘apartheid’ policy, South Africa was boycotted economically during 1970 s & 80 s. -- But now it has developed its industries and infrastructures to become major commercial base for rest of Africa. The Govt. has deregulated and privatised its economy to make the country investment and consumer friendly. -- The GDP of South Africa is US $ 138. 7 bill. , total population being 45. 8 million, per capita GDP IS US$3026. -- Value of goods and services imported annually is US $ 37. 6 billion, against that exports are US $ 37. 4 billion. -- South Africa has low savings’ rate with large unskilled labour having low productivity. -----23 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018
6. South Africa -- Because of ‘apartheid’ policy, South Africa was boycotted economically during 1970 s & 80 s. -- But now it has developed its industries and infrastructures to become major commercial base for rest of Africa. The Govt. has deregulated and privatised its economy to make the country investment and consumer friendly. -- The GDP of South Africa is US $ 138. 7 bill. , total population being 45. 8 million, per capita GDP IS US$3026. -- Value of goods and services imported annually is US $ 37. 6 billion, against that exports are US $ 37. 4 billion. -- South Africa has low savings’ rate with large unskilled labour having low productivity. -----23 Presentation by Prof. H. Ganguly 2/12/2018


