f7865abd4dfe6724633c4c2130e115eb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 International Laser Ranging Service GGOS Meeting GFZ Potsdam Germany March 1 and 2, 2005 March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 1
International Laser Ranging Service GGOS Meeting GFZ Potsdam Germany March 1 and 2, 2005 March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 1
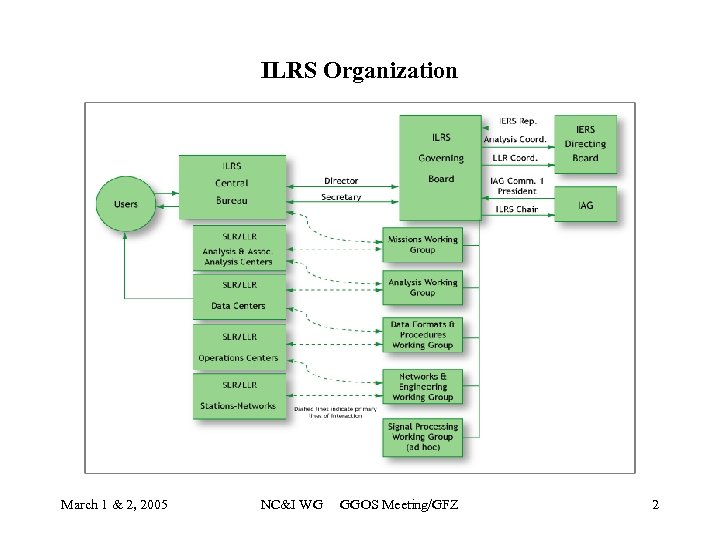 ILRS Organization March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 2
ILRS Organization March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 2
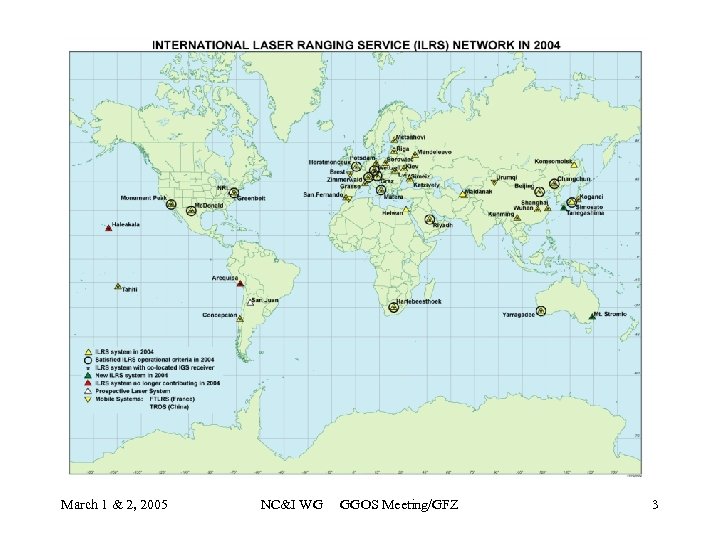 March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 3
March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 3
 Data Applications • Earth orientation parameters (polar motion and LOD) • 3 -D coordinates and velocities of the ILRS tracking stations • Time-varying geocenter coordinates • Static and time-varying coefficients of the Earth's gravity field • Precision Orbit Determination • Fundamental physical constants • Lunar ephemerides and librations • Lunar orientation parameters March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 4
Data Applications • Earth orientation parameters (polar motion and LOD) • 3 -D coordinates and velocities of the ILRS tracking stations • Time-varying geocenter coordinates • Static and time-varying coefficients of the Earth's gravity field • Precision Orbit Determination • Fundamental physical constants • Lunar ephemerides and librations • Lunar orientation parameters March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 4
 ILRS Analysis and Associate Analysis Centers • ILRS SLR Official Combination Centers – Prime: ASI/CGS, Italian Space Agency/Space Geodesy Center, Italy – Alternate: DGFI, Deutsches Geodaetisches Forschungs. Institut, Germany • Active Contributors to the SLR Combination Products – ASI/CGS, Italian Space Agency/Space Geodesy Center "G. Colombo", Italy – DGFI, Deutsches Geodaetisches Forschungs. Institut, Germany – BKG, Bundesamt fuer Kartographi und Geodaesie, Germany – GFZ, Geo. Forschungs. Zentrum, Germany – JCET, Joint Center for Earth Systems Technology, USA – NSGF, NERC Space Geodesy Facility, UK • Lunar Analysis Centers – FFI, Forsvarets Forsknings. Institut, Norway – JPL, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, USA (SLR and Lunar) – OCA, Observatoire de la Cote d'Azure, France (Lunar) – POLAC, Paris Observatory Lunar Analysis Center, France (Lunar) – University of Texas, Lunar Analysis Center (Lunar) March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 5
ILRS Analysis and Associate Analysis Centers • ILRS SLR Official Combination Centers – Prime: ASI/CGS, Italian Space Agency/Space Geodesy Center, Italy – Alternate: DGFI, Deutsches Geodaetisches Forschungs. Institut, Germany • Active Contributors to the SLR Combination Products – ASI/CGS, Italian Space Agency/Space Geodesy Center "G. Colombo", Italy – DGFI, Deutsches Geodaetisches Forschungs. Institut, Germany – BKG, Bundesamt fuer Kartographi und Geodaesie, Germany – GFZ, Geo. Forschungs. Zentrum, Germany – JCET, Joint Center for Earth Systems Technology, USA – NSGF, NERC Space Geodesy Facility, UK • Lunar Analysis Centers – FFI, Forsvarets Forsknings. Institut, Norway – JPL, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, USA (SLR and Lunar) – OCA, Observatoire de la Cote d'Azure, France (Lunar) – POLAC, Paris Observatory Lunar Analysis Center, France (Lunar) – University of Texas, Lunar Analysis Center (Lunar) March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 5
 Other SLR Analysis and Associate Analysis Centers – AIUB, Astronomical Institute of Berne, Switzerland – CSR, Center for Space Research, U. of Texas – DUT, Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands – ESA/ESOC, European Space Agency/ESA Space Operations Center, Germany – GAOUA, Main Astronomical Obser. , National Academy of Sciences, Ukraine – Geoscience Australia – IAA, Institute of Applied Astronomy, Russia – JAXA, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency – JPL, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, USA – MCC, Mission Control Center, Russia – Newcastle University, UK – NICT, National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, Japan March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 6
Other SLR Analysis and Associate Analysis Centers – AIUB, Astronomical Institute of Berne, Switzerland – CSR, Center for Space Research, U. of Texas – DUT, Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands – ESA/ESOC, European Space Agency/ESA Space Operations Center, Germany – GAOUA, Main Astronomical Obser. , National Academy of Sciences, Ukraine – Geoscience Australia – IAA, Institute of Applied Astronomy, Russia – JAXA, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency – JPL, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, USA – MCC, Mission Control Center, Russia – Newcastle University, UK – NICT, National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, Japan March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 6
 ILRS Customers • • Supported Missions (POD) • ILRS Analysis Centers • Academic Research Centers • National Agencies and Laboratories • March 1 & 2, 2005 IERS Commercial Organizations NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 7
ILRS Customers • • Supported Missions (POD) • ILRS Analysis Centers • Academic Research Centers • National Agencies and Laboratories • March 1 & 2, 2005 IERS Commercial Organizations NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 7
 Current ILRS Missions Support Gravity Probe-B ICESat GRACE-A/B CHAMP GFO-1 ** Envisat ERS-2 ** Jason TOPEX/Poseidon ** Larets * Starlette, Stella * Meteor-3 M ** Ajisai * LAGEOS- 1, 2 * Beacon-C * Etalon-1, 2 * GLONASS-84, 87, 89 GPS-35, 36 Relativity Global Topography (Ice, Oceans, and Land) Static and Time Varying Gravity Field Gravity and Magnetic Field Ocean Topography, Atmosphere Ocean Topography Technology, Gravity Field Static and Time Varying Gravity Field, Tides Technology, SAGE Gravity Field Ref. Frame, Positioning, Static and T/V Gravity Static and Time Varying Gravity Field Positioning, EOP Orbit calibration and validation Lunar Reflectors: Apollo 15, Apollo 11, Apollo 14, Luna 21, Luna 17 Key: * Passive Satellites March 1 & 2, 2005 ** Active satellites with SLR tracking only NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 8
Current ILRS Missions Support Gravity Probe-B ICESat GRACE-A/B CHAMP GFO-1 ** Envisat ERS-2 ** Jason TOPEX/Poseidon ** Larets * Starlette, Stella * Meteor-3 M ** Ajisai * LAGEOS- 1, 2 * Beacon-C * Etalon-1, 2 * GLONASS-84, 87, 89 GPS-35, 36 Relativity Global Topography (Ice, Oceans, and Land) Static and Time Varying Gravity Field Gravity and Magnetic Field Ocean Topography, Atmosphere Ocean Topography Technology, Gravity Field Static and Time Varying Gravity Field, Tides Technology, SAGE Gravity Field Ref. Frame, Positioning, Static and T/V Gravity Static and Time Varying Gravity Field Positioning, EOP Orbit calibration and validation Lunar Reflectors: Apollo 15, Apollo 11, Apollo 14, Luna 21, Luna 17 Key: * Passive Satellites March 1 & 2, 2005 ** Active satellites with SLR tracking only NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 8
 Upcoming Missions Mission Application Launch CRYOSat Ice budget July 2005 Galileo (2) Orbit calibration and validation October 2005 ALOS Environmental remote sensing Late 2005 GOCE Gravity Field, Geoid, Ocean Surface 2006 March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 9
Upcoming Missions Mission Application Launch CRYOSat Ice budget July 2005 Galileo (2) Orbit calibration and validation October 2005 ALOS Environmental remote sensing Late 2005 GOCE Gravity Field, Geoid, Ocean Surface 2006 March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 9
 ILRS Station Operations • • • Location of Stations • Most stations are located close to participating agencies • Some are located to enhance global distribution (South Africa, Tahiti, Arequipa) • Voids in global distribution Satellite Priorities • Priorities decrease with increasing orbital altitude and then increasing orbital inclination • Priorities may be increased to intensify support for active missions (such as altimetry), special campaigns, and post-launch intensive tracking • Priorities are reviewed and approved by the Governing Board • See http: //ilrs. gsfc. nasa. gov/satellite_missions/priorities/index. html Scheduling, Coordination and Delivery of Observations • Stations tracking schedules range from 1 to 4 shifts per week • Stations track according to priorities, predictions and their local capabilities • The Governing Board approves special campaigns • Special procedures (e. g. for vulnerable satellites) are approved by the Governing Board and managed by the Central Bureau • Data is delivered in 1 -2 hours from acquisition March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 10
ILRS Station Operations • • • Location of Stations • Most stations are located close to participating agencies • Some are located to enhance global distribution (South Africa, Tahiti, Arequipa) • Voids in global distribution Satellite Priorities • Priorities decrease with increasing orbital altitude and then increasing orbital inclination • Priorities may be increased to intensify support for active missions (such as altimetry), special campaigns, and post-launch intensive tracking • Priorities are reviewed and approved by the Governing Board • See http: //ilrs. gsfc. nasa. gov/satellite_missions/priorities/index. html Scheduling, Coordination and Delivery of Observations • Stations tracking schedules range from 1 to 4 shifts per week • Stations track according to priorities, predictions and their local capabilities • The Governing Board approves special campaigns • Special procedures (e. g. for vulnerable satellites) are approved by the Governing Board and managed by the Central Bureau • Data is delivered in 1 -2 hours from acquisition March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 10
 Laser Ranging Data and Data Products • Satellite Laser Ranging • Data series spanning 3 decades at ftp: //cddis. gsfc. nasa. gov/pub/slr/data) • Operational Satellite Ephemerides/predictions at ftp: //cddis. gsfc. nasa. gov/pub/slr/predicts) • ILRS Station and EOP Combination Product (SINEX format) – Station Coordinates: 3 mm; 2 mm/year – EOP: 0. 2 milliarcsec: LOD 60 microsec. • Analysis Center contributions – Station Coordinates – Earth Origin – Temporal and static gravity field (long wavelength) – LAGEOS Orbits (10 mm/weekly) • • Position and EOP contributions available at ftp: //cddis. gsfc. nasa. gov/pub/slr/products Lunar Laser Ranging • • Lunar Libration: . 01 arcsec. • • Lunar Ephemerides: 5 - 10 cm Products available at http: //ssd. jpl. nasa. gov/horizons. html Measurement and product standards? • Station Qualification Criteria ( data quantity, data quality, operational compliance) • See http: //ilrs. gsfc. nasa. gov/stations/site_info/global_report_cards/ • Analyses follows IERS conventions March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 11
Laser Ranging Data and Data Products • Satellite Laser Ranging • Data series spanning 3 decades at ftp: //cddis. gsfc. nasa. gov/pub/slr/data) • Operational Satellite Ephemerides/predictions at ftp: //cddis. gsfc. nasa. gov/pub/slr/predicts) • ILRS Station and EOP Combination Product (SINEX format) – Station Coordinates: 3 mm; 2 mm/year – EOP: 0. 2 milliarcsec: LOD 60 microsec. • Analysis Center contributions – Station Coordinates – Earth Origin – Temporal and static gravity field (long wavelength) – LAGEOS Orbits (10 mm/weekly) • • Position and EOP contributions available at ftp: //cddis. gsfc. nasa. gov/pub/slr/products Lunar Laser Ranging • • Lunar Libration: . 01 arcsec. • • Lunar Ephemerides: 5 - 10 cm Products available at http: //ssd. jpl. nasa. gov/horizons. html Measurement and product standards? • Station Qualification Criteria ( data quantity, data quality, operational compliance) • See http: //ilrs. gsfc. nasa. gov/stations/site_info/global_report_cards/ • Analyses follows IERS conventions March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 11
 ILRS Future Activities • Upgrades for improved performance (short term, long term) • kilohertz ranging • autonomous operation (24/7) • improved event timers • two-color ranging (refraction) • better control systems for more efficient satellite pass interleaving • more compact retroreflector arrays • continuous data flow • transponder operations (LLR and planetary ranging) • broader applications (communications) • Improved modeling (S/C center of mass, propagation, etc. ) • New Missions that will improve measurement quality • Additional passive, high mass density satellites in new orbits • Key Issues • Deterioration of the network • Non-performing stations • Global distribution March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 12
ILRS Future Activities • Upgrades for improved performance (short term, long term) • kilohertz ranging • autonomous operation (24/7) • improved event timers • two-color ranging (refraction) • better control systems for more efficient satellite pass interleaving • more compact retroreflector arrays • continuous data flow • transponder operations (LLR and planetary ranging) • broader applications (communications) • Improved modeling (S/C center of mass, propagation, etc. ) • New Missions that will improve measurement quality • Additional passive, high mass density satellites in new orbits • Key Issues • Deterioration of the network • Non-performing stations • Global distribution March 1 & 2, 2005 NC&I WG GGOS Meeting/GFZ 12


