ae729bc4a0178ef89628798eeb4e9a9e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis IIASA Multi-pollutant / multi-effects: Cost-effectiveness Analysis for the 2 nd NOx Protocol
International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis IIASA Multi-pollutant / multi-effects: Cost-effectiveness Analysis for the 2 nd NOx Protocol
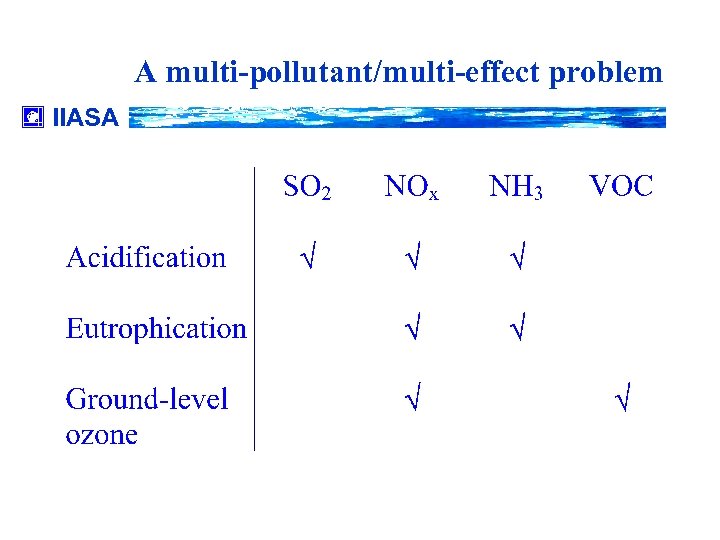 A multi-pollutant/multi-effect problem IIASA
A multi-pollutant/multi-effect problem IIASA
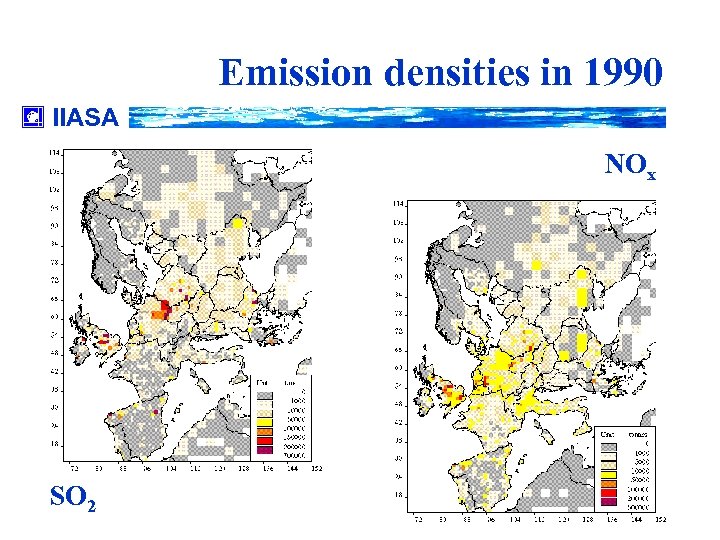 Emission densities in 1990 IIASA NOx SO 2
Emission densities in 1990 IIASA NOx SO 2
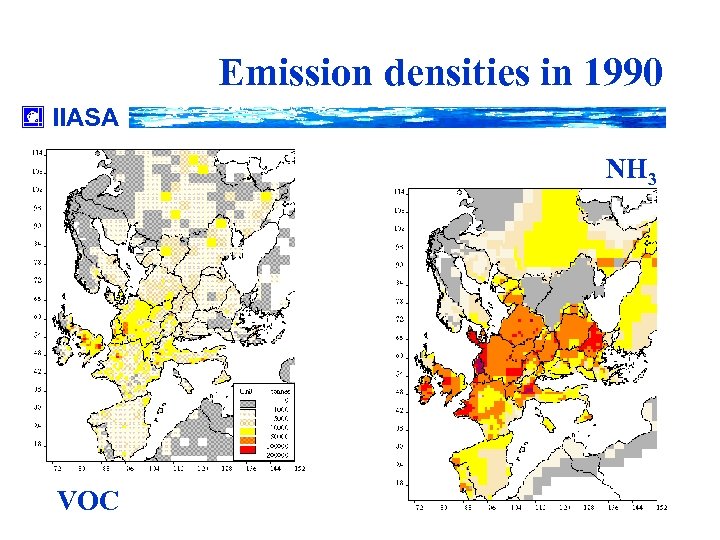 Emission densities in 1990 IIASA NH 3 VOC
Emission densities in 1990 IIASA NH 3 VOC
 Environmental targets IIASA In the year 2010, reduce • health-relevant excess ozone exposure by 2/3, • the area of ecosystems not protected against acidification by 1/2, • vegetation-relevant excess ozone exposure by 1/3, • excess nitrogen deposition (eutrophication) by 60%. Additional targets for ‘hot-spots’
Environmental targets IIASA In the year 2010, reduce • health-relevant excess ozone exposure by 2/3, • the area of ecosystems not protected against acidification by 1/2, • vegetation-relevant excess ozone exposure by 1/3, • excess nitrogen deposition (eutrophication) by 60%. Additional targets for ‘hot-spots’
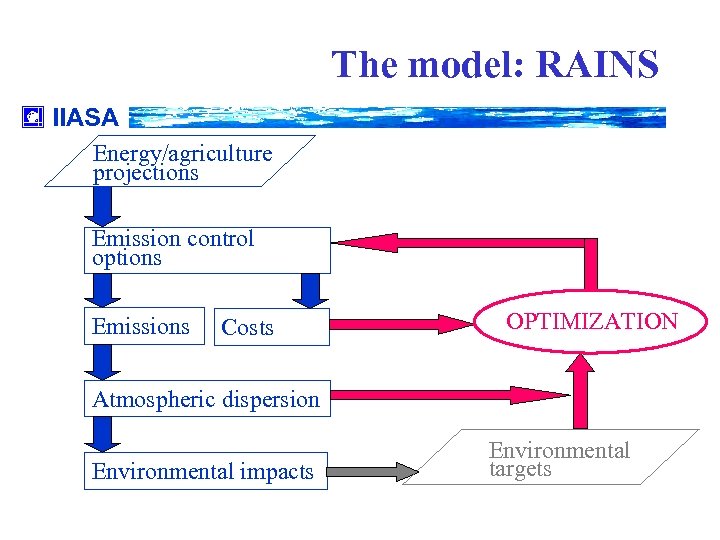 The model: RAINS IIASA Energy/agriculture projections Emission control options Emissions Costs OPTIMIZATION Atmospheric dispersion Environmental impacts Environmental targets
The model: RAINS IIASA Energy/agriculture projections Emission control options Emissions Costs OPTIMIZATION Atmospheric dispersion Environmental impacts Environmental targets
 Input assumptions IIASA Energy projections: ‘Pre-Kyoto’, – EU: 10 national, 5 DG-XVII ‘Business as usual’, consistent with EU NEC scenarios – Non-EU: National projections via UN reporting Agricultural projections: – Reviewed by Member States
Input assumptions IIASA Energy projections: ‘Pre-Kyoto’, – EU: 10 national, 5 DG-XVII ‘Business as usual’, consistent with EU NEC scenarios – Non-EU: National projections via UN reporting Agricultural projections: – Reviewed by Member States
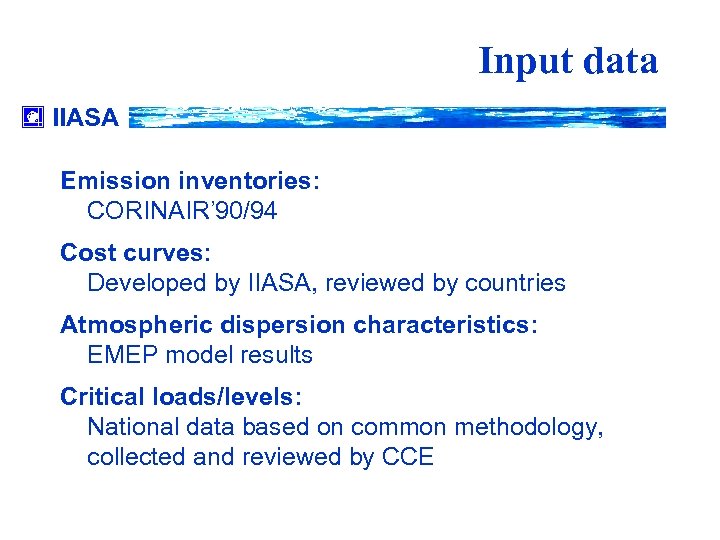 Input data IIASA Emission inventories: CORINAIR’ 90/94 Cost curves: Developed by IIASA, reviewed by countries Atmospheric dispersion characteristics: EMEP model results Critical loads/levels: National data based on common methodology, collected and reviewed by CCE
Input data IIASA Emission inventories: CORINAIR’ 90/94 Cost curves: Developed by IIASA, reviewed by countries Atmospheric dispersion characteristics: EMEP model results Critical loads/levels: National data based on common methodology, collected and reviewed by CCE
 Emission control options SO 2 IIASA Low sulfur coal, coke Low sulfur heavy fuel oil Low sulfur gas oil Limestone injection/Fluidized bed combustion Flue gas desulfurization (FGD) Advanced flue gas desulfurization
Emission control options SO 2 IIASA Low sulfur coal, coke Low sulfur heavy fuel oil Low sulfur gas oil Limestone injection/Fluidized bed combustion Flue gas desulfurization (FGD) Advanced flue gas desulfurization
 Emission control options IIASA NOx - Stationary sources Combustion modifications - Low NOx burners, exhaust gas re-circulation, staged combustion, etc. Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) for large boilers Non-selective catalytic reduction (SNCR) for medium and large boilers Control of industrial process emissions
Emission control options IIASA NOx - Stationary sources Combustion modifications - Low NOx burners, exhaust gas re-circulation, staged combustion, etc. Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) for large boilers Non-selective catalytic reduction (SNCR) for medium and large boilers Control of industrial process emissions
 Emission control options Transport sector IIASA Gasoline cars Euro-III, Euro-IV (post 2005 standards), small carbon canisters Diesel cars Euro-III, Euro-IV (post 2005 standards) Diesel heavy duty vehicles Euro-III, Euro-IV (post 2005 standards) Two-stroke engines Oxidation catalysts Off-road machinery Standards equivalent to Euro-III, Euro-IV
Emission control options Transport sector IIASA Gasoline cars Euro-III, Euro-IV (post 2005 standards), small carbon canisters Diesel cars Euro-III, Euro-IV (post 2005 standards) Diesel heavy duty vehicles Euro-III, Euro-IV (post 2005 standards) Two-stroke engines Oxidation catalysts Off-road machinery Standards equivalent to Euro-III, Euro-IV
 Emission control options VOC Stationary sources (1) IIASA Dry cleaning: Good housekeeping and adsorption, closed circuit machines Degreasing: Primary measures, carbon adsorption, conveyored degreaser with integrated adsorption, water based systems, low temperature plasma Domestic solvents: Reformulation Non-industrial paint use: Low solvent paints Industrial paint use: Water based-, high solid-, powderpaints, application modifications, adsorption, incineration
Emission control options VOC Stationary sources (1) IIASA Dry cleaning: Good housekeeping and adsorption, closed circuit machines Degreasing: Primary measures, carbon adsorption, conveyored degreaser with integrated adsorption, water based systems, low temperature plasma Domestic solvents: Reformulation Non-industrial paint use: Low solvent paints Industrial paint use: Water based-, high solid-, powderpaints, application modifications, adsorption, incineration
 Emission control options VOC Stationary sources (2) IIASA Production of rubber, paint, ink, etc. : Substitution, solvent plans , ‘end-of-pipe’ Application of glues, adhesives (in industry): Housekeeping, substitution, incineration Printing: Housekeeping, water-based ink, ‘end-of-pipe’ Wood preservation: Double vacuum impregnation, dryer enclosure, ‘end-of-pipe’ Refineries, chemical industry: Regular inspection & maintenance, internal floating covers, vapor recovery Fuel storage and distribution: Internal floating covers, Stage II
Emission control options VOC Stationary sources (2) IIASA Production of rubber, paint, ink, etc. : Substitution, solvent plans , ‘end-of-pipe’ Application of glues, adhesives (in industry): Housekeeping, substitution, incineration Printing: Housekeeping, water-based ink, ‘end-of-pipe’ Wood preservation: Double vacuum impregnation, dryer enclosure, ‘end-of-pipe’ Refineries, chemical industry: Regular inspection & maintenance, internal floating covers, vapor recovery Fuel storage and distribution: Internal floating covers, Stage II
 Emission control options NH 3 IIASA Low nitrogen feed - multi-phase, synthetic amino acids Bio-filtration - bio scrubbers Animal house adaptation - improved design, floor modifications, low NH 3 poultry housing, etc. Covered outdoor storage of manure - rigid lids, floating covers Low ammonia application techniques - immediate incorporation, deep and shallow injection, etc. Fertilizers - urea substitution
Emission control options NH 3 IIASA Low nitrogen feed - multi-phase, synthetic amino acids Bio-filtration - bio scrubbers Animal house adaptation - improved design, floor modifications, low NH 3 poultry housing, etc. Covered outdoor storage of manure - rigid lids, floating covers Low ammonia application techniques - immediate incorporation, deep and shallow injection, etc. Fertilizers - urea substitution
 The starting point (REF) IIASA National legislation of countries + for EU Member States: present EU legislation and recent Commission proposals/Council agreements – – – – Auto-Oil 1 Solvents Directive Sulfur in liquid fuels Directive Off-road machinery Directive IPPC Heavy duty vehicles post-2005 standards LCP-II, etc.
The starting point (REF) IIASA National legislation of countries + for EU Member States: present EU legislation and recent Commission proposals/Council agreements – – – – Auto-Oil 1 Solvents Directive Sulfur in liquid fuels Directive Off-road machinery Directive IPPC Heavy duty vehicles post-2005 standards LCP-II, etc.
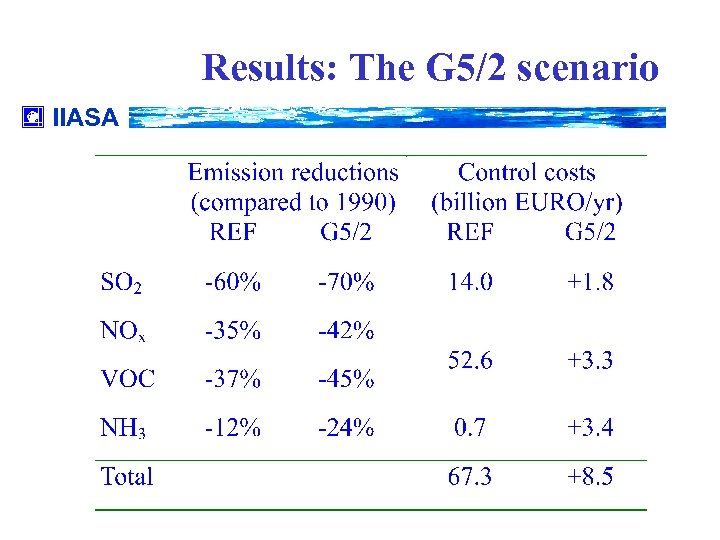 Results: The G 5/2 scenario IIASA
Results: The G 5/2 scenario IIASA
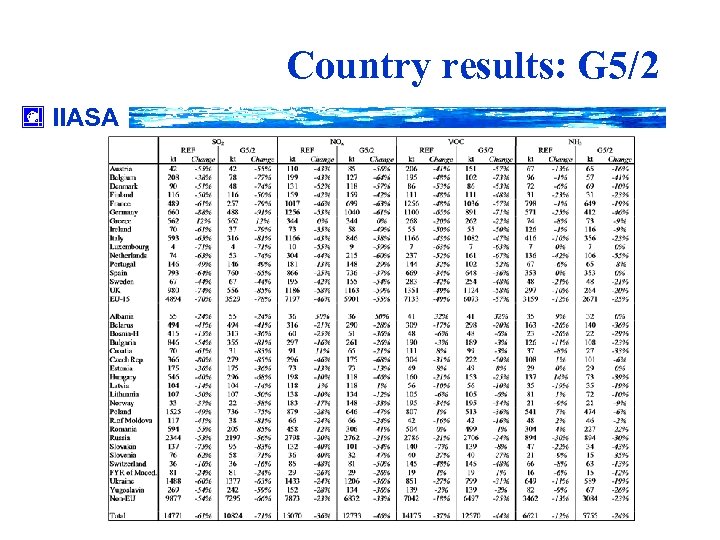 Country results: G 5/2 IIASA
Country results: G 5/2 IIASA
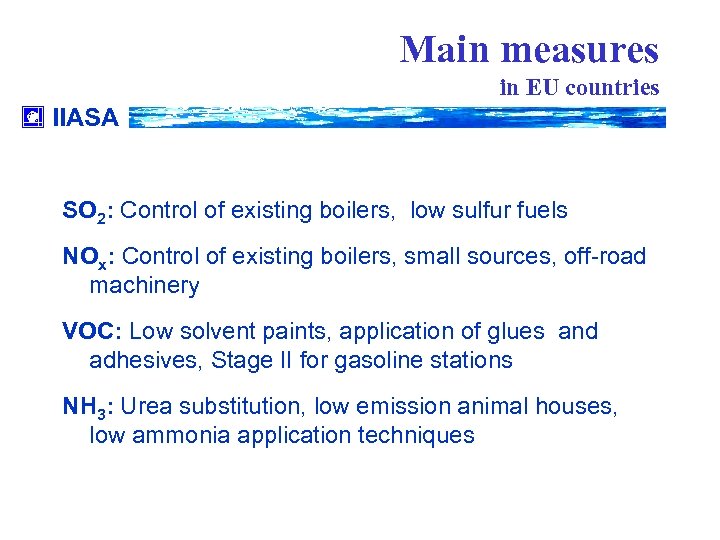 Main measures in EU countries IIASA SO 2: Control of existing boilers, low sulfur fuels NOx: Control of existing boilers, small sources, off-road machinery VOC: Low solvent paints, application of glues and adhesives, Stage II for gasoline stations NH 3: Urea substitution, low emission animal houses, low ammonia application techniques
Main measures in EU countries IIASA SO 2: Control of existing boilers, low sulfur fuels NOx: Control of existing boilers, small sources, off-road machinery VOC: Low solvent paints, application of glues and adhesives, Stage II for gasoline stations NH 3: Urea substitution, low emission animal houses, low ammonia application techniques
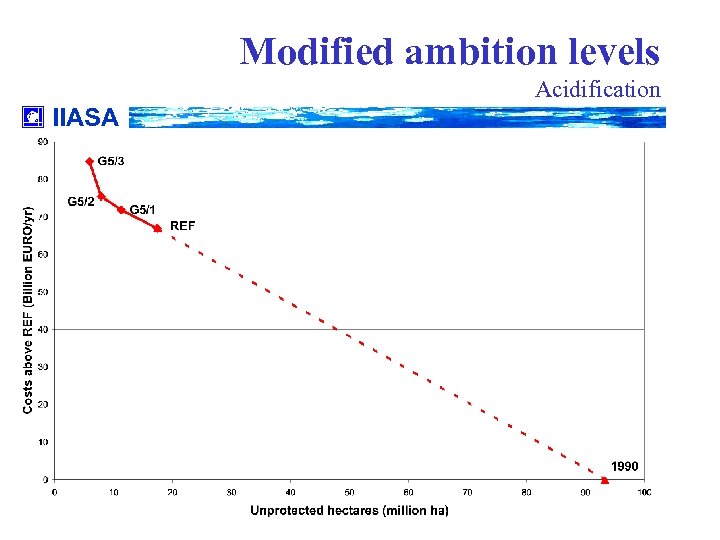 Modified ambition levels Acidification IIASA
Modified ambition levels Acidification IIASA
 Modified ambition levels Population exposure index IIASA
Modified ambition levels Population exposure index IIASA
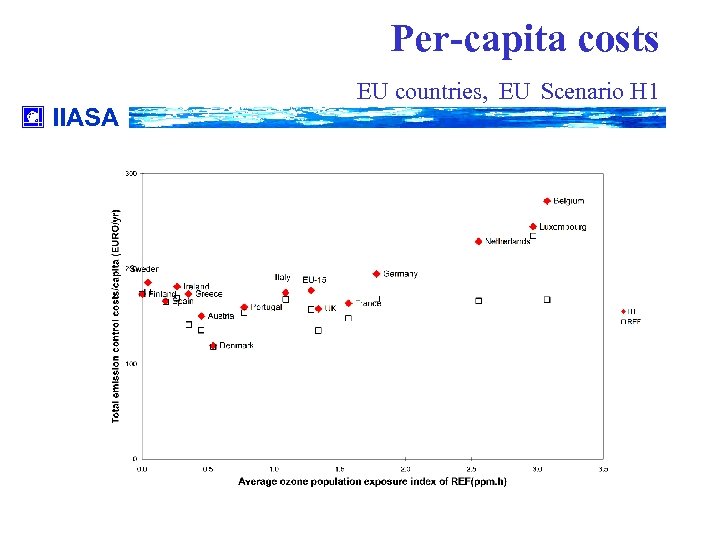 Per-capita costs IIASA EU countries, EU Scenario H 1
Per-capita costs IIASA EU countries, EU Scenario H 1
 Uncertainty treatment IIASA • Standard uncertainty analysis is time consuming • Potential influence of uncertainties minimized by – Explicit model confidence intervals – Integral functions for environmental exposure – Compensation mechanism for targets – Excluding extreme situations – Use of ‘gap closure’ targets (relative improvements) • Identification of potential biases
Uncertainty treatment IIASA • Standard uncertainty analysis is time consuming • Potential influence of uncertainties minimized by – Explicit model confidence intervals – Integral functions for environmental exposure – Compensation mechanism for targets – Excluding extreme situations – Use of ‘gap closure’ targets (relative improvements) • Identification of potential biases
 Potential biases (1) IIASA • Critical loads could be stricter. . . – Dynamic effects ignored – Limited spatial resolution • Critical levels for vegetation (ozone) could be too strict. . . – Level 2 approach • Population exposure (ozone) … – overestimated in city centers – underestimated in suburbs
Potential biases (1) IIASA • Critical loads could be stricter. . . – Dynamic effects ignored – Limited spatial resolution • Critical levels for vegetation (ozone) could be too strict. . . – Level 2 approach • Population exposure (ozone) … – overestimated in city centers – underestimated in suburbs
 Potential biases (2) IIASA • Constant background ozone …. – ignores decreasing emissions in Europe and N. America – ignores increasing emissions in Asia • Emission control costs too high … – ‘Pre-Kyoto’ energy projections – Add-on technologies only • Emission control potential too small … – Technological progress ignored – No structural changes considered
Potential biases (2) IIASA • Constant background ozone …. – ignores decreasing emissions in Europe and N. America – ignores increasing emissions in Asia • Emission control costs too high … – ‘Pre-Kyoto’ energy projections – Add-on technologies only • Emission control potential too small … – Technological progress ignored – No structural changes considered
 Sensitivity analyses IIASA ‘Post-Kyoto’ energy projections ‘Low NH 3’ agriculture ‘High SO 2’ energy scenario ‘High NH 3’ agriculture
Sensitivity analyses IIASA ‘Post-Kyoto’ energy projections ‘Low NH 3’ agriculture ‘High SO 2’ energy scenario ‘High NH 3’ agriculture
 Sensitivity analysis - results IIASA Variations in SO 2 reductions
Sensitivity analysis - results IIASA Variations in SO 2 reductions
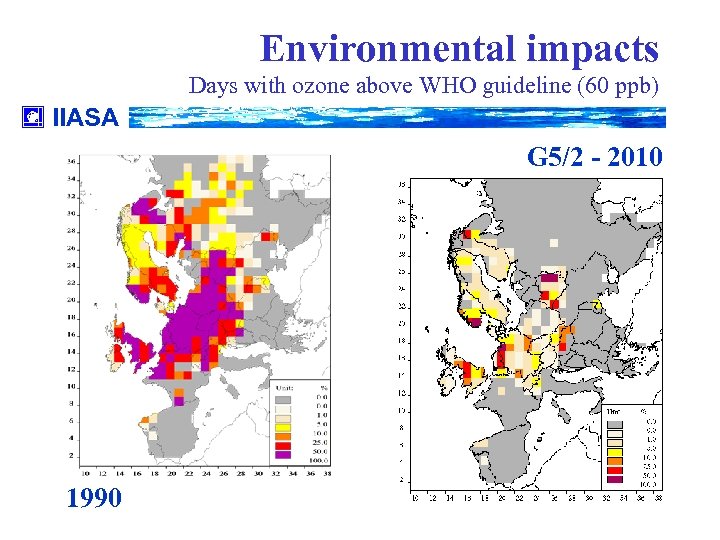 Environmental impacts Days with ozone above WHO guideline (60 ppb) IIASA G 5/2 - 2010 1990
Environmental impacts Days with ozone above WHO guideline (60 ppb) IIASA G 5/2 - 2010 1990
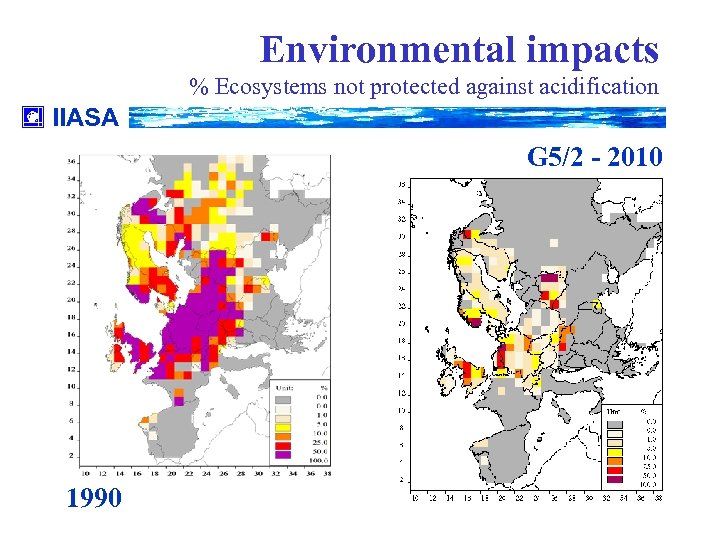 Environmental impacts % Ecosystems not protected against acidification IIASA G 5/2 - 2010 1990
Environmental impacts % Ecosystems not protected against acidification IIASA G 5/2 - 2010 1990
 Environmental impacts % Ecosystems not protected against eutrophication IIASA G 5/2 - 2010 1990
Environmental impacts % Ecosystems not protected against eutrophication IIASA G 5/2 - 2010 1990
 Uniform or effect-based scenarios? IIASA
Uniform or effect-based scenarios? IIASA
 Documentation IIASA • Methodology papers • Latest databases • All scenario analyses, interim reports to ECE and EU • On-line model (web version) available at http: //www. iiasa. ac. at/~rains
Documentation IIASA • Methodology papers • Latest databases • All scenario analyses, interim reports to ECE and EU • On-line model (web version) available at http: //www. iiasa. ac. at/~rains


