a53e04af7b78e6d978ad72561cc30955.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 International Financial Reporting Standards 1 IFRS for SMEs IFRS Foundation-World Bank 18– 20 October 2011 Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina Copyright © 2010 IFRS Foundation. All rights reserved.
International Financial Reporting Standards 1 IFRS for SMEs IFRS Foundation-World Bank 18– 20 October 2011 Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina Copyright © 2010 IFRS Foundation. All rights reserved.
 The IFRS for SMEs 2 Topic 2. 1(b) Section 12 Other Financial. Inst. Issues Section 22 Liabilities and Equity Michael Wells © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
The IFRS for SMEs 2 Topic 2. 1(b) Section 12 Other Financial. Inst. Issues Section 22 Liabilities and Equity Michael Wells © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Recognition and measurement 3 • Initial recognition: – When entity becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument • Initial measurement: – At FV (normally the transaction price) – Transaction costs are charged to expense © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Recognition and measurement 3 • Initial recognition: – When entity becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument • Initial measurement: – At FV (normally the transaction price) – Transaction costs are charged to expense © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Recognition and measurement 4 • Subsequent measurement: – At FVTPL except: – Equity instrument that is not publicly traded and cannot get FV reliably, then measure at cost less impairment – Also measure a contract linked to such equity instrument at cost less impairment – If previously at FVTPL, but now a reliable FV measure is no longer available, treat most recent FV measure as ‘cost’ going forward. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Recognition and measurement 4 • Subsequent measurement: – At FVTPL except: – Equity instrument that is not publicly traded and cannot get FV reliably, then measure at cost less impairment – Also measure a contract linked to such equity instrument at cost less impairment – If previously at FVTPL, but now a reliable FV measure is no longer available, treat most recent FV measure as ‘cost’ going forward. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 5 • ‘Hedging’ and ‘hedge accounting’ are two different things • What is hedging? – Managing risks by using one financial instrument (‘hedging instrument’) purposely to offset the variability in FV or cash flows of a recognised asset or liability, firm commitment, or future cash flows (‘hedged item’) © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 5 • ‘Hedging’ and ‘hedge accounting’ are two different things • What is hedging? – Managing risks by using one financial instrument (‘hedging instrument’) purposely to offset the variability in FV or cash flows of a recognised asset or liability, firm commitment, or future cash flows (‘hedged item’) © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 6 • What is hedge accounting? – Matching the change in FV of the hedging instrument and the hedged item in the same income statement – Hedge accounting is only an issue when normal accounting would put the two FV changes in different periods – sometimes referred to as an ‘accounting mismatch’ © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 6 • What is hedge accounting? – Matching the change in FV of the hedging instrument and the hedged item in the same income statement – Hedge accounting is only an issue when normal accounting would put the two FV changes in different periods – sometimes referred to as an ‘accounting mismatch’ © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 7 • The hedger’s accounting dilemma: – I have a risk in an asset or liability measured at amortised cost – Any change in FV or cash flows from that asset or liability is recognised only when realised in cash (asset is sold, liability is settled, cash flows occur) – To hedge, I buy a derivative, which is measured at FVTPL at each reporting date • I need special hedge accounting to fix this ‘mismatch’ © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 7 • The hedger’s accounting dilemma: – I have a risk in an asset or liability measured at amortised cost – Any change in FV or cash flows from that asset or liability is recognised only when realised in cash (asset is sold, liability is settled, cash flows occur) – To hedge, I buy a derivative, which is measured at FVTPL at each reporting date • I need special hedge accounting to fix this ‘mismatch’ © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting • The hedger’s accounting dilemma – an illustration: 8 – Entity has note payable at a fixed rate of interest due in 3 years. Note measured at amortised cost. – Buys swap to convert receive fixed interest to pay variable. Swap is measured at FVTPL. – End of year 1, interest rate declines. Therefore loss on derivative immediately recognised – but an offsetting gain (not yet recognised) because we will be paying the lower variable rate of interest in future. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting • The hedger’s accounting dilemma – an illustration: 8 – Entity has note payable at a fixed rate of interest due in 3 years. Note measured at amortised cost. – Buys swap to convert receive fixed interest to pay variable. Swap is measured at FVTPL. – End of year 1, interest rate declines. Therefore loss on derivative immediately recognised – but an offsetting gain (not yet recognised) because we will be paying the lower variable rate of interest in future. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 9 • Hedge accounting matching the gain (loss) on the derivative with the loss (gain) on the hedged item. • Hedge accounting is optional. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 9 • Hedge accounting matching the gain (loss) on the derivative with the loss (gain) on the hedged item. • Hedge accounting is optional. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 10 • To qualify for hedge accounting: – Designate and document hedging relationship up front – Clearly identify the hedged risk – Hedged risk is listed in ¶ 12. 17 – Hedging instrument is listed in ¶ 12. 18 – Entity expects hedging instrument to be ‘highly effective’ in offsetting the designated hedged risk. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 10 • To qualify for hedge accounting: – Designate and document hedging relationship up front – Clearly identify the hedged risk – Hedged risk is listed in ¶ 12. 17 – Hedging instrument is listed in ¶ 12. 18 – Entity expects hedging instrument to be ‘highly effective’ in offsetting the designated hedged risk. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 11 • Hedged risk must be (12. 17): – Interest rate risk in debt measured at cost – FX or interest rate risk in firm commitment or highly probable forecast transaction – Price risk in a commodity owned or to be acquired in a firm commitment or highly probable forecast transaction – FX risk in a net investment in a foreign operation © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 11 • Hedged risk must be (12. 17): – Interest rate risk in debt measured at cost – FX or interest rate risk in firm commitment or highly probable forecast transaction – Price risk in a commodity owned or to be acquired in a firm commitment or highly probable forecast transaction – FX risk in a net investment in a foreign operation © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 12 • Hedged risk must be (12. 17): – FX risk in debt instrument measured at cost is not in this list. Why? – Under ¶ 30. 10 (FX) the debt is translated at spot rate and FX gain or loss is recognised in profit or loss – Change in FV of the swap (hedging instrument) is also recognised in profit or loss (measured using forward rate) – ‘Natural hedge’ © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 12 • Hedged risk must be (12. 17): – FX risk in debt instrument measured at cost is not in this list. Why? – Under ¶ 30. 10 (FX) the debt is translated at spot rate and FX gain or loss is recognised in profit or loss – Change in FV of the swap (hedging instrument) is also recognised in profit or loss (measured using forward rate) – ‘Natural hedge’ © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 13 • Hedging instrument must be (12. 18): – Interest rate swap, FX forward, commodity forward – Entered into with external party – Notional amount = principal or notional amount of hedged item – Specified maturity not later than maturity or settlement of hedged item – Cannot be prepaid or terminated early © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 13 • Hedging instrument must be (12. 18): – Interest rate swap, FX forward, commodity forward – Entered into with external party – Notional amount = principal or notional amount of hedged item – Specified maturity not later than maturity or settlement of hedged item – Cannot be prepaid or terminated early © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 14 Section 12 – Hedge accounting • Hedge of fixed interest rate risk or commodity price risk of commodity held – Recognise hedging instrument as asset or liability – Change in FV of hedging instrument in P&L – Change in FV of hedged item in P&L and adjustment of carrying amount of hedged item – even though hedged item is otherwise measured at cost This is called Fair Value Hedge in IAS 39. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
14 Section 12 – Hedge accounting • Hedge of fixed interest rate risk or commodity price risk of commodity held – Recognise hedging instrument as asset or liability – Change in FV of hedging instrument in P&L – Change in FV of hedged item in P&L and adjustment of carrying amount of hedged item – even though hedged item is otherwise measured at cost This is called Fair Value Hedge in IAS 39. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 15 • Hedge of fixed interest rate risk or commodity price risk of commodity held (continued) – If hedged risk was fixed interest in debt measured at cost, recognise in P&L the periodic net settlements from the derivative (interest rate swap) in the period in which the net settlements occur. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 15 • Hedge of fixed interest rate risk or commodity price risk of commodity held (continued) – If hedged risk was fixed interest in debt measured at cost, recognise in P&L the periodic net settlements from the derivative (interest rate swap) in the period in which the net settlements occur. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 16 • Example – Assumptions: – Entity borrows 1, 000, 3 years, 5% fixed rate, payable measured at amortised cost – Hedged with a derivative whose value is linked to an interest rate index – End of year 1, market rate = 6%. FV of 1, 000 payable 2 years 6% = 1, 000 x. 889996 = 890, but this 110 ‘gain’ is not recognised – Value of the derivative declines to -112 – Note there is small ineffectiveness = 2 © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 16 • Example – Assumptions: – Entity borrows 1, 000, 3 years, 5% fixed rate, payable measured at amortised cost – Hedged with a derivative whose value is linked to an interest rate index – End of year 1, market rate = 6%. FV of 1, 000 payable 2 years 6% = 1, 000 x. 889996 = 890, but this 110 ‘gain’ is not recognised – Value of the derivative declines to -112 – Note there is small ineffectiveness = 2 © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 17 • Balance sheet at time loan is made: Cash 1, 000 Loan payable 1, 000 • Adjust loan end of year 1 to reflect rate change: Loan payable 110 P&L 2 Derivative (Liability) 112 • Balance sheet end of year 1: Cash 1, 000 Derivative (Liability) 112 Loan payable 890 Equity (2) © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 17 • Balance sheet at time loan is made: Cash 1, 000 Loan payable 1, 000 • Adjust loan end of year 1 to reflect rate change: Loan payable 110 P&L 2 Derivative (Liability) 112 • Balance sheet end of year 1: Cash 1, 000 Derivative (Liability) 112 Loan payable 890 Equity (2) © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 18 • Conceptual question regarding the previous example: – Does the 890 carrying amount of the loan payable at end of year 1 represent the Fair Value of the loan? – Hint: Does the 890 reflect change in credit risk or prepayment risk? – If 890 is not Fair Value, what is it? © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 18 • Conceptual question regarding the previous example: – Does the 890 carrying amount of the loan payable at end of year 1 represent the Fair Value of the loan? – Hint: Does the 890 reflect change in credit risk or prepayment risk? – If 890 is not Fair Value, what is it? © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 19 • Hedge of fixed interest rate risk and commodity price risk (continued) – Discontinue hedge accounting when: – Hedging instrument expires – Hedge no longer meets conditions – Entity revokes designation – Any gain or loss that was included in the carrying amount of the hedged item is amortised to P&L over remaining life of hedged item. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 19 • Hedge of fixed interest rate risk and commodity price risk (continued) – Discontinue hedge accounting when: – Hedging instrument expires – Hedge no longer meets conditions – Entity revokes designation – Any gain or loss that was included in the carrying amount of the hedged item is amortised to P&L over remaining life of hedged item. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 20 • Hedge of variable interest rate risk, FX or commodity price risk of commodity held, highly probable forecast transaction, or net investment in foreign operation – Recognise change in FV of hedging instrument in OCI (assuming it was effective; ineffectiveness reported in P&L) – 'Recycle' amount recognised in OCI when hedged item hits P&L or hedging relationship ends. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 20 • Hedge of variable interest rate risk, FX or commodity price risk of commodity held, highly probable forecast transaction, or net investment in foreign operation – Recognise change in FV of hedging instrument in OCI (assuming it was effective; ineffectiveness reported in P&L) – 'Recycle' amount recognised in OCI when hedged item hits P&L or hedging relationship ends. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 21 Section 12 – Hedge accounting • Hedge of variable interest rate risk, FX or commodity price risk of commodity held, highly probable forecast transaction, or net investment in foreign operation (continued) – If hedged risk was variable interest in debt measured at cost, recognise in P&L the periodic net settlements from the interest rate swap in the period in which the net settlements occur. This is called Cash Flow Hedge in IAS 39. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
21 Section 12 – Hedge accounting • Hedge of variable interest rate risk, FX or commodity price risk of commodity held, highly probable forecast transaction, or net investment in foreign operation (continued) – If hedged risk was variable interest in debt measured at cost, recognise in P&L the periodic net settlements from the interest rate swap in the period in which the net settlements occur. This is called Cash Flow Hedge in IAS 39. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 22 • Example – Assumptions: – Entity sells goods for 1, 000 floating rate 3 year note receivable – Interest rate risk managed with a derivative (interest rate swap) – End of year 1 interest rates increase – PV of cumulative cash flows increase by 100 – But FV of swap decreases by 105 – Note: Some hedge ineffectiveness © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 22 • Example – Assumptions: – Entity sells goods for 1, 000 floating rate 3 year note receivable – Interest rate risk managed with a derivative (interest rate swap) – End of year 1 interest rates increase – PV of cumulative cash flows increase by 100 – But FV of swap decreases by 105 – Note: Some hedge ineffectiveness © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 23 • Opening balance sheet: Receivable Equity 1, 000 • Ineffective portion of hedge: P&L* 5* OCI (Equity) 100 Derivative (Liability) 105 *Ineffective portion of hedge example continued next slide. . . © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 23 • Opening balance sheet: Receivable Equity 1, 000 • Ineffective portion of hedge: P&L* 5* OCI (Equity) 100 Derivative (Liability) 105 *Ineffective portion of hedge example continued next slide. . . © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 24 • Closing balance sheet: Receivable 1, 000 Equity (OCI)* 100* Derivative (Liability) 105 Equity 995 *Effective portion of the hedge (loss on derivative), which will be amortised to P&L as the higher floating rate interest payments are earned and recognised in P&L in years 2 & 3 © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 24 • Closing balance sheet: Receivable 1, 000 Equity (OCI)* 100* Derivative (Liability) 105 Equity 995 *Effective portion of the hedge (loss on derivative), which will be amortised to P&L as the higher floating rate interest payments are earned and recognised in P&L in years 2 & 3 © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 25 • Hedge of variable interest rate risk etc. . . – Discontinue hedge accounting when: – Hedging instrument expires – Hedge no longer meets conditions – Forecast transaction no longer probable – Entity revokes designation – Any prior gain or loss on forecast transaction that was recognised in OCI is recycled to P&L © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 25 • Hedge of variable interest rate risk etc. . . – Discontinue hedge accounting when: – Hedging instrument expires – Hedge no longer meets conditions – Forecast transaction no longer probable – Entity revokes designation – Any prior gain or loss on forecast transaction that was recognised in OCI is recycled to P&L © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 12 – Hedge accounting 26 • Disclosures relating to hedge accounting – For each type of hedge: Description of hedge (risk, hedged item, instrument) – Special disclosures for hedge of fixed interest rate risk and commodity price risk of commodity held – Special disclosures for hedge of variable interest rate risk, FX or commodity price risk of commodity held, highly probable forecast transaction, or net investment in foreign operation © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 12 – Hedge accounting 26 • Disclosures relating to hedge accounting – For each type of hedge: Description of hedge (risk, hedged item, instrument) – Special disclosures for hedge of fixed interest rate risk and commodity price risk of commodity held – Special disclosures for hedge of variable interest rate risk, FX or commodity price risk of commodity held, highly probable forecast transaction, or net investment in foreign operation © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 27 • Scope of Section 22 – Principles for classifying an instrument as debt or equity – Original issuance of shares and other equity instruments – Sale of options, rights, warrants – Bonus issues and share splits – Issuance of convertible debt continues. . . © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 27 • Scope of Section 22 – Principles for classifying an instrument as debt or equity – Original issuance of shares and other equity instruments – Sale of options, rights, warrants – Bonus issues and share splits – Issuance of convertible debt continues. . . © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 28 • Scope of Section 22, continued – Treasury shares – Distributions to owners – Non-controlling interest and transactions in shares of a consolidated subsidiary © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 28 • Scope of Section 22, continued – Treasury shares – Distributions to owners – Non-controlling interest and transactions in shares of a consolidated subsidiary © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 29 • Principles for classifying an instrument as debt or equity – Equity = residual interest in assets minus liabilities – Liability is a present obligation (entity does not have a right to avoid paying cash) © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 29 • Principles for classifying an instrument as debt or equity – Equity = residual interest in assets minus liabilities – Liability is a present obligation (entity does not have a right to avoid paying cash) © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 30 • The following are equity: – Puttable instrument that entitles holder to pro rata share of net assets on liquidation – Instrument that is automatically redeemed if an uncertain future event occurs or death or retirement of holder – Subordinated instrument payable only on liquidation © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 30 • The following are equity: – Puttable instrument that entitles holder to pro rata share of net assets on liquidation – Instrument that is automatically redeemed if an uncertain future event occurs or death or retirement of holder – Subordinated instrument payable only on liquidation © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 31 • The following are liabilities: – Instrument is payable on liquidation, but the amount is subject to a maximum ceiling – Entity is obliged to make payments before liquidation – such as mandatory dividend – Mandatorily redeemable preference shares © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 31 • The following are liabilities: – Instrument is payable on liquidation, but the amount is subject to a maximum ceiling – Entity is obliged to make payments before liquidation – such as mandatory dividend – Mandatorily redeemable preference shares © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 32 • Members’ shares in a cooperative are equity only if: – Coop has unconditional right to refuse redemption of members’ shares, or – Redemption is unconditionally prohibited by law or entity’s charter • Otherwise – liability © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 32 • Members’ shares in a cooperative are equity only if: – Coop has unconditional right to refuse redemption of members’ shares, or – Redemption is unconditionally prohibited by law or entity’s charter • Otherwise – liability © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 33 • Original issuance of shares and other equity instruments – Recognise when equity is issued and subscriber is obligated to invest – If equity is issued before the entity gets cash, the receivable is an offset to equity (not an asset) – If entity gets (nonrefundable) cash before equity is issued, equity is increased – No increase in equity is recognised for subscribed shares that have not been issued and entity has not received cash © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 33 • Original issuance of shares and other equity instruments – Recognise when equity is issued and subscriber is obligated to invest – If equity is issued before the entity gets cash, the receivable is an offset to equity (not an asset) – If entity gets (nonrefundable) cash before equity is issued, equity is increased – No increase in equity is recognised for subscribed shares that have not been issued and entity has not received cash © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 34 • Sale of options, rights, warrants – Same principles as for original issuance of shares (previous slide) • Transaction costs in issuing equity instruments – Accounted for as a reduction of equity (not an expense) © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 34 • Sale of options, rights, warrants – Same principles as for original issuance of shares (previous slide) • Transaction costs in issuing equity instruments – Accounted for as a reduction of equity (not an expense) © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 35 • Bonus issues (stock dividends) and share splits – These do not change equity – Accounted for as reclassification of amounts within equity (out of retained earnings and into permanent capital) – Amounts reclassified should be based on local laws © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 35 • Bonus issues (stock dividends) and share splits – These do not change equity – Accounted for as reclassification of amounts within equity (out of retained earnings and into permanent capital) – Amounts reclassified should be based on local laws © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 36 • Issuance of convertible debt – Must account separately for debt component and equity component (conversion right) – Debt proceeds = FV of similar risk debt without conversion feature (PV calculation) – Equity proceeds are the residual – Recorded at issuance; not subsequently revised – Subsequently, debt discount = additional interest expense (effective interest method) © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 36 • Issuance of convertible debt – Must account separately for debt component and equity component (conversion right) – Debt proceeds = FV of similar risk debt without conversion feature (PV calculation) – Equity proceeds are the residual – Recorded at issuance; not subsequently revised – Subsequently, debt discount = additional interest expense (effective interest method) © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 37 • Issuance of convertible debt - Example – 1/1/X 1 issue at par a 4% convertible bond, par and maturity amount = 50, 000, maturity in 5 years – If no conversion feature, would have paid 6% – Calculate present value of cash flows at 6%: – PV 50, 000 due in 5 years @ 6% = 37, 363 – PV annuity 2, 000/year 5 years @ 6% = 8, 425 – Total PV = 45, 788 Debit cash 50, 000 Credit financial liability 45, 788 Credit equity (conversion right) 4, 212 © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 37 • Issuance of convertible debt - Example – 1/1/X 1 issue at par a 4% convertible bond, par and maturity amount = 50, 000, maturity in 5 years – If no conversion feature, would have paid 6% – Calculate present value of cash flows at 6%: – PV 50, 000 due in 5 years @ 6% = 37, 363 – PV annuity 2, 000/year 5 years @ 6% = 8, 425 – Total PV = 45, 788 Debit cash 50, 000 Credit financial liability 45, 788 Credit equity (conversion right) 4, 212 © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
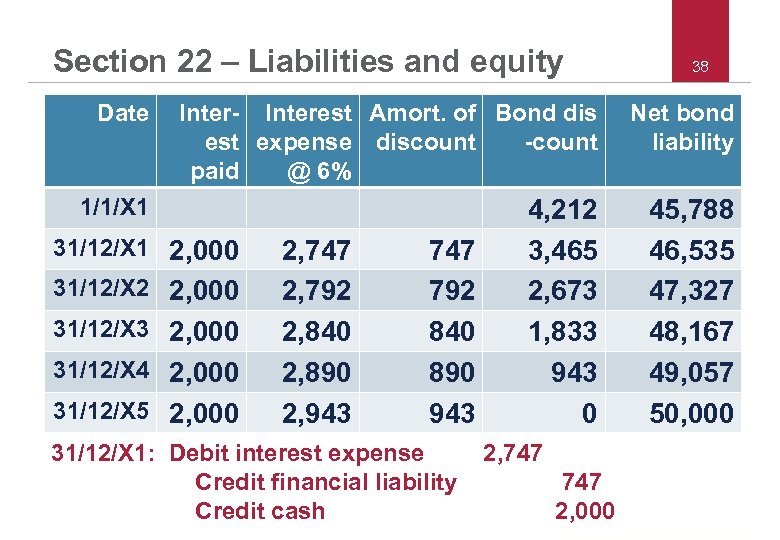 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 38 Date Inter- Interest Amort. of Bond dis est expense discount -count paid @ 6% Net bond liability 1/1/X 1 4, 212 3, 465 2, 673 1, 833 943 0 45, 788 46, 535 47, 327 48, 167 49, 057 50, 000 31/12/X 1 2, 000 31/12/X 2 2, 000 31/12/X 3 2, 000 31/12/X 4 2, 000 31/12/X 5 2, 000 2, 747 2, 792 2, 840 2, 890 2, 943 747 792 840 890 943 31/12/X 1: Debit interest expense Credit financial liability Credit cash © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org 2, 747 2, 000
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 38 Date Inter- Interest Amort. of Bond dis est expense discount -count paid @ 6% Net bond liability 1/1/X 1 4, 212 3, 465 2, 673 1, 833 943 0 45, 788 46, 535 47, 327 48, 167 49, 057 50, 000 31/12/X 1 2, 000 31/12/X 2 2, 000 31/12/X 3 2, 000 31/12/X 4 2, 000 31/12/X 5 2, 000 2, 747 2, 792 2, 840 2, 890 2, 943 747 792 840 890 943 31/12/X 1: Debit interest expense Credit financial liability Credit cash © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org 2, 747 2, 000
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 39 • Treasury shares – Equity instruments entity has issued and later reacquired – Measure at cash paid or FV of other consideration given to acquire – Present as deduction from equity (not asset) – No gain or loss recognised on purchase, sale, or cancellation © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 39 • Treasury shares – Equity instruments entity has issued and later reacquired – Measure at cash paid or FV of other consideration given to acquire – Present as deduction from equity (not asset) – No gain or loss recognised on purchase, sale, or cancellation © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 40 • Distributions to owners – If cash – measurement = cash paid – If non-cash – measurement = FV of assets distributed – Amount reduces equity – If entity gets tax deduction for dividend, tax benefit is adjustment of equity – Not reduction of income tax expense – If entity pays withholding tax on dividends paid, tax reduces equity as part of dividend © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 40 • Distributions to owners – If cash – measurement = cash paid – If non-cash – measurement = FV of assets distributed – Amount reduces equity – If entity gets tax deduction for dividend, tax benefit is adjustment of equity – Not reduction of income tax expense – If entity pays withholding tax on dividends paid, tax reduces equity as part of dividend © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 41 • Non-controlling interest (NCI) and transactions in shares of a consolidated subsidiary – In consolidated balance sheet NCI is part of equity (not liability or ‘in between’) – Change in parent’s controlling interest that does not result in loss of control is a transaction with owners – Equity adjustment, not through P&L – No adjustment of carrying amounts of assets or goodwill © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
Section 22 – Liabilities and equity 41 • Non-controlling interest (NCI) and transactions in shares of a consolidated subsidiary – In consolidated balance sheet NCI is part of equity (not liability or ‘in between’) – Change in parent’s controlling interest that does not result in loss of control is a transaction with owners – Equity adjustment, not through P&L – No adjustment of carrying amounts of assets or goodwill © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
 Questions or comments? Expressions of individual views by members of the IASB and its staff are encouraged. The views expressed in this presentation are those of the presenter. Official positions of the IASB on accounting matters are determined only after extensive due process and deliberation. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org 42
Questions or comments? Expressions of individual views by members of the IASB and its staff are encouraged. The views expressed in this presentation are those of the presenter. Official positions of the IASB on accounting matters are determined only after extensive due process and deliberation. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org 42
 43 This presentation may be modified from time to time. The latest version may be downloaded from: http: //www. ifrs. org/IFRS+for+SMEs/SME+Workshops. htm The accounting requirements applicable to small and medium‑sized entities (SMEs) are set out in the International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS) for SMEs, which was issued by the IASB in July 2009. The IFRS Foundation, the authors, the presenters and the publishers do not accept responsibility for loss caused to any person who acts or refrains from acting in reliance on the material in this Power. Point presentation, whether such loss is caused by negligence or otherwise. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org
43 This presentation may be modified from time to time. The latest version may be downloaded from: http: //www. ifrs. org/IFRS+for+SMEs/SME+Workshops. htm The accounting requirements applicable to small and medium‑sized entities (SMEs) are set out in the International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS) for SMEs, which was issued by the IASB in July 2009. The IFRS Foundation, the authors, the presenters and the publishers do not accept responsibility for loss caused to any person who acts or refrains from acting in reliance on the material in this Power. Point presentation, whether such loss is caused by negligence or otherwise. © 2011 IFRS Foundation | 30 Cannon Street | London EC 4 M 6 XH | UK | www. ifrs. org


