afbb93bdd5a7d999bd0ce637428d7cd1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

International Environment – Trade, Globalization 11 th of December

Globalization • • • Marketing products and services around the world Increasing world merchandise trade Big Emerging Markets (BEMs) Disposable income level International wants and desires

Why global marketing is imperative • • • Saturation of domestic markets Emerging markets Global competition Need for global cooperation Internet revolution – The Internet adds a new dimension to global marketing – E-commerce retailers gain substantial savings by selling online

The production possibilities frontier • Australia can produce either 100 Agricultural products or 50 electronic products • Malaysia can produce either 40 agricultural products or 50 electronic products.

World Output • The need to specialize! • When countries specialize world output increases.

Comparative advantage. • The ability of a country to price a good at a lower opportunity cost than another country. Absolute advantage. • The ability of a country to produce a good using a fewer resources than another country.

Another Comparative vs Absolute Advantage Example • Assume that both France and Italy have enough resources to produce either wine or cheese, but not both. • France can produce 20 units of wine or 10 units of cheese. – The opportunity cost of each unit of wine, therefore, is 10 / 20, or 0. 5 units of cheese. – The opportunity cost of each unit of cheese is 20 / 10, or 2 units of wine. • Italy is able to produce 30 units of wine or 22 units of cheese. – Italy has an absolute advantage for the production of both wine and cheese

Free trade vs Fair Trade • Free Trade – The flow of good and services between countries without restrictions. • Fair Trade – a county should only reduce its barriers to entry if the other country does not have some sort of “unfair competitive” advantage. And also provided that the other country also reduces its trade barriers. • Type of protections – Embargo – Tariff – Quota

Common arguments for protection • The infant industry argument – New domestic industries need protection because it is not yet ready to compete. • National Security argument. – A nation should not be dependent on other countries for defense. • Employment argument. – Job increases in protected industries. • Cheap foreign labor argument. – Other countries have cheaper labour, it is difficult to compete.

Free Trade Agreements • • ASEAN – Association of South Eastern Asian Nations EEC – European Economic Community NAFTA – North American Free Trade Agreement. APEC – Asian Pacific Economic Cooperation.

Advantages of Free Trade Agreements 1. Increased economic growth. The U. S. Trade Representative Office estimates that NAFTA increased U. S. economic growth by 0. 5% a year. 2. More dynamic business climate. Often, businesses were protected before the agreement. As a result, these local industries risked becoming stagnant and non-competitive on the global market. With the protection removed, they have the motivation to become a true global competitor. 3. Lower government spending. Many governments subsidize Source: https: //www. thebalance. com/free-trade-agreement-pros-and-cons-3305845 local industry segments. When these are removed after the trade

Disadvantages of Free Trade Agreements 1. Increased jobs outsourcing. 2. Theft of intellectual property. Many developing countries don't have the same protection for patents, inventions, and new processes as the United States and the laws they do have aren't always strictly enforced 3. Crowd out domestic industries. Many Source: https: //www. thebalance. com/free-trade-agreement-pros-and-cons-3305845

Supply and Demand foreign exchange. • When the SL Rupee is low or depreciates. – Sri-Lankan goods and services will cost foreign consumers less. – Foreigners will buy more SL products. – For Sri-Lankans foreign products become more expensive. • When the SL rupee is high or appreciates. – SL goods will cost foreign consumers more. – Foreigners will buy less SL products – Sri-Lankans will buy more foreign products.

4 shifts in supply and demand of a currency. • • Taste and Preference. Relative Incomes Relative Price levels Relative Real Interest Rates • Depreciation – A fall in the price of one currency relative to another • Appreciate – A rise in the price of one currency relative to

Brexit • UK’s exit of the European Union is known as Brexit. • 52% of England voted to leave • UK will invoke article 50 in March 2017 which would mean that in 2 years (2019) they would leave. • So why is this important?
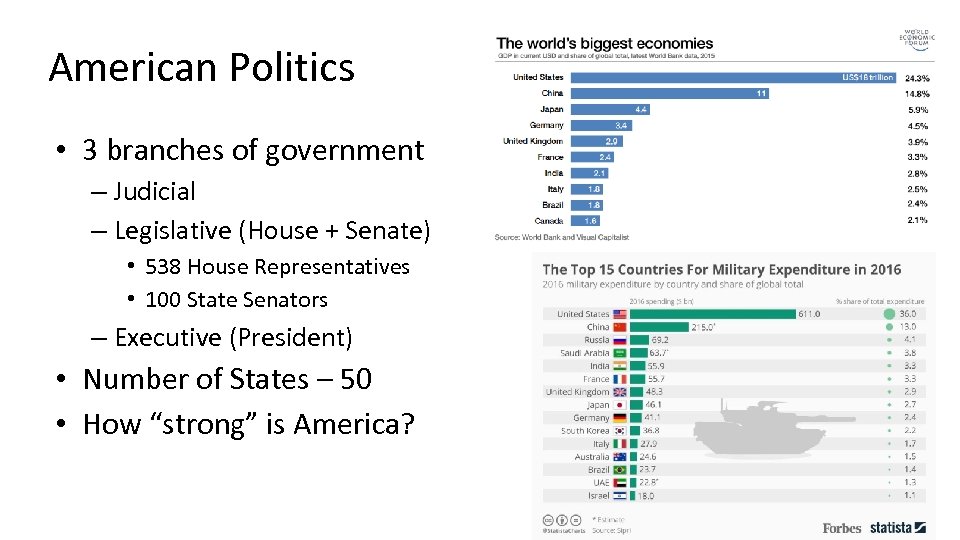
American Politics • 3 branches of government – Judicial – Legislative (House + Senate) • 538 House Representatives • 100 State Senators – Executive (President) • Number of States – 50 • How “strong” is America?
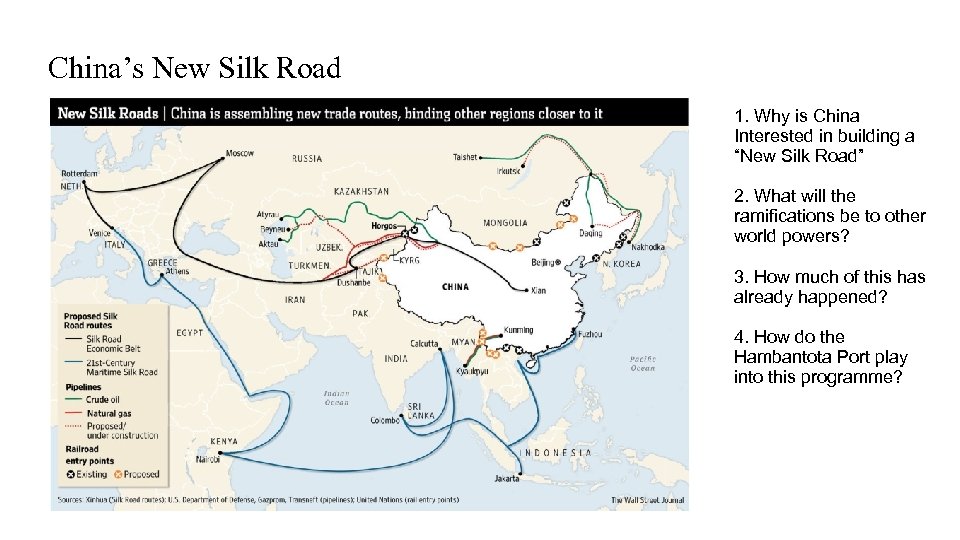
China’s New Silk Road 1. Why is China Interested in building a “New Silk Road” 2. What will the ramifications be to other world powers? 3. How much of this has already happened? 4. How do the Hambantota Port play into this programme?
afbb93bdd5a7d999bd0ce637428d7cd1.ppt