dff0138d867cffd8f2e7f3101ee09090.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

International Dissemination of Evidence Based Practice Fernando Salazar, Ph. D. Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia San Francisco 30 May, 2013

• What is happening and what is needed to support the development of effective practice in South/Central America and for it to become and agendas item for policy makers and practitioners

Focus attention on the need: • Better understanding of wide range of determinants of the use and abuse of drugs including biological factors and environmental, as well as social and behavioral determinants on health and well-being; • Promoting research about social and physical environments, in all the social gradient, with emphasis on underserved and vulnerable communities; • Focus on research strategies that can better serve to reduce existing inequalities of access to prevention and treatment of the use and abuse of drugs, including inequalities within and between the countries; Based on: IADR Global Health Inequalities Research Agenda (IADR-GOHIRA®): A Call to Action. J Dent Res 92(3): 209 -211, 2013

Some research challenges as: • Gaps in knowledge of prevention and treatment of the use and abuse of drugs and, in particular, the insufficient focus on social policy. • The separation of drug use and abuse from general health; and • Inadequate evidence-based data (including research-driven programs, capacity-building strategies, standardized systems for measuring and monitoring, etc. ).

To address these challenges: • • Identify critical gaps in knowledge about the use and abuse of drugs. Develop and implement, in partnership with peer evidence-based organizations, a knowledge base that uses a standard set of reporting criteria and includes a registry of implementation trials. Give emphasis to the importance of social and psychological determinants of the use and abuse of drugs, behavior related to their use, abuse and search for services, in the general population and at-risk and vulnerable populations. Emphasis on the importance of the integrating research on inequities in the prevention and attention of the use and abuse of drugs. Approach should be broad to impact in reduction of health inequalities as a whole.

To address these challenges: • Emphasize the importance of multi-disciplinary and translational research, seeking input from a range of social scientists and health professionals. • Develop strategies prevention of the use and abuse of drugs based on their social determinants and environmental, as well as combining population wide strategies (upstream) with strategies at local level and individual (downstream). • Advocate for the inclusion of policies of prevention and treatment of the use and abuse of drugs in policies of elsewhere, in line with the Adelaide Declaration on health in all policies (WHO, 2010).

A PRACTICAL APPROACH

The CICAD model: • Use of quality standards as guidance for prevention programs. • Competence based certification of practitioners. • Prevention programs accreditation. Based on: Salazar F, Luna M. Minimum quality standards for drug abuse prevention programs. OEA/CICAD, Washington DC, 2012

A quality prevention program: • Core principles: ethics and scientific approach. • A general process: continuous quality improvement (CQI). • Sequential steps: needs and resources assessment, strategic planning and delivery, process and outcome evaluation and dissemination.
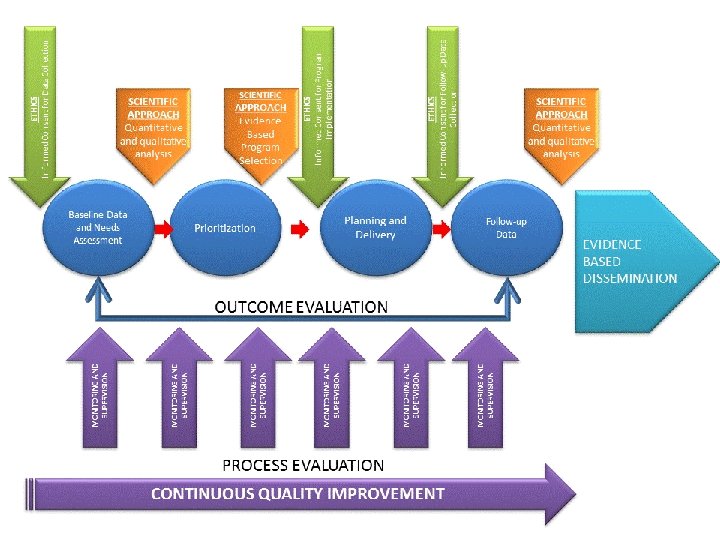

The quality indicators: • • Informed consent. Proof of efficacy. PDCA plan. Baseline information and explicit prioritization of problems susceptible of prevention. • Intervention strategic plan. • Outcome evaluation and dissemination plan.

Competence based certification: • Development of a curriculum based training program to strengthen and certify the needed prevention competences of the field workers.


Prevention programs accreditation. • Fulfillment of the MQS • Certification of prevention programs staff.


Thanks
dff0138d867cffd8f2e7f3101ee09090.ppt