8c29d55e0f522015cd91f02cff3ea8bf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 International Cooperation • • Anarchy – No central authority outside of states to require or enforce cooperation Cooperation can be military, economic, other National interests: Some common interests, some interests may be in competition or conflict Cooperation requires – – Positive sum mentality (vs zero-sum) Potential for greater rewards/gains if cooperate Communication mechanism Not TOO many countervaling interests
International Cooperation • • Anarchy – No central authority outside of states to require or enforce cooperation Cooperation can be military, economic, other National interests: Some common interests, some interests may be in competition or conflict Cooperation requires – – Positive sum mentality (vs zero-sum) Potential for greater rewards/gains if cooperate Communication mechanism Not TOO many countervaling interests
 Stag Hunt: What’s the Rational Choice • Cooperate with other cavemen & hunt the stag? – If all cooperate, all get lots of meat – If even one defects to go after a rabbit on his own, the rest get nothing (stag gets away) • Defect and go for the rabbit? – Definite source of a little meat • What will the other hunters do? Can you trust them and will they trust you? What is the risk? • Pursue immediate short-term self interest or is there a basis for long-term common interest?
Stag Hunt: What’s the Rational Choice • Cooperate with other cavemen & hunt the stag? – If all cooperate, all get lots of meat – If even one defects to go after a rabbit on his own, the rest get nothing (stag gets away) • Defect and go for the rabbit? – Definite source of a little meat • What will the other hunters do? Can you trust them and will they trust you? What is the risk? • Pursue immediate short-term self interest or is there a basis for long-term common interest?
 Consider the Caveman’s Options • In addition to food, needs security against bears • Similar benefits and risks as with Stag Hunt • Cooperate with other cavemen & fight bear? – If all cooperate (a few guard, all rally to fight bear): • All are generally safer, can sleep better • But each risk death in fighting bear – If even one guard defects to go sleep or hide, the rest may get eaten • Or do you defect and go hide or sleep? – Definite short term safety (assuming bear goes into someone else’s cave)
Consider the Caveman’s Options • In addition to food, needs security against bears • Similar benefits and risks as with Stag Hunt • Cooperate with other cavemen & fight bear? – If all cooperate (a few guard, all rally to fight bear): • All are generally safer, can sleep better • But each risk death in fighting bear – If even one guard defects to go sleep or hide, the rest may get eaten • Or do you defect and go hide or sleep? – Definite short term safety (assuming bear goes into someone else’s cave)
 Consider the Caveman’s Options II • What will the other cavemen do? Can you trust them and will they trust you? What is the risk? • Pursue immediate short-term self interest or is there a basis for long-term common interest? • Options: – Wait until bear shows up, then try to rally (Coalition) – Agree ahead of time that if bear appears, all will rally to fight it (Collective Security) – Subset of cavemen form a tribe (maybe on basis of who feels most threatened), organize a guard, practice to fight bear (Alliance or Collective Defense)
Consider the Caveman’s Options II • What will the other cavemen do? Can you trust them and will they trust you? What is the risk? • Pursue immediate short-term self interest or is there a basis for long-term common interest? • Options: – Wait until bear shows up, then try to rally (Coalition) – Agree ahead of time that if bear appears, all will rally to fight it (Collective Security) – Subset of cavemen form a tribe (maybe on basis of who feels most threatened), organize a guard, practice to fight bear (Alliance or Collective Defense)
 Security Cooperation: Coalitions • Ad Hoc group formed to cooperate in fighting a specific conflict • Both 1991 and 2003 Persian Gulf wars against Iraq were fought by coalitions, formed just for those conflicts • Everything may have to be done on the fly, procedures and agreements made up as the operation progresses – Minimal chance for partners to practice together – Language, equipment and cultural differences may be a problem
Security Cooperation: Coalitions • Ad Hoc group formed to cooperate in fighting a specific conflict • Both 1991 and 2003 Persian Gulf wars against Iraq were fought by coalitions, formed just for those conflicts • Everything may have to be done on the fly, procedures and agreements made up as the operation progresses – Minimal chance for partners to practice together – Language, equipment and cultural differences may be a problem
 Cooperation: Collective Security • Any aggression must be met by all as a matter of law enforcement • League of Nations, United Nations (somewhat) • Limitations: – Requires some agreement on what to do – Enforces status quo rather than address injustice – Members may promise action but not deliver – Takes time to put together operation for each event – Not as flexible or fast as a unilateral response – Small conflict can escalate as more join operation • Free Rider problem
Cooperation: Collective Security • Any aggression must be met by all as a matter of law enforcement • League of Nations, United Nations (somewhat) • Limitations: – Requires some agreement on what to do – Enforces status quo rather than address injustice – Members may promise action but not deliver – Takes time to put together operation for each event – Not as flexible or fast as a unilateral response – Small conflict can escalate as more join operation • Free Rider problem
 Cooperation: Collective Defense • Formal Alliances for long term threat • Attack against one by outsider is attack against all – All may have to agree on HOW to respond • NATO, World War I alliances • Big investment – Develop combined procedures, communications, weapons standards – Practice together – Requires sizable military expenditures • May have free rider problem • If threat changes, alliance may falter
Cooperation: Collective Defense • Formal Alliances for long term threat • Attack against one by outsider is attack against all – All may have to agree on HOW to respond • NATO, World War I alliances • Big investment – Develop combined procedures, communications, weapons standards – Practice together – Requires sizable military expenditures • May have free rider problem • If threat changes, alliance may falter
 Economic Cooperation • Trade agreements such as NAFTA or WTO • Producer Cartels such as OPEC • Financial institutions such as – World Bank – International Monetary Fund • Health: WHO • Communications: How to divide the electronic spectrum
Economic Cooperation • Trade agreements such as NAFTA or WTO • Producer Cartels such as OPEC • Financial institutions such as – World Bank – International Monetary Fund • Health: WHO • Communications: How to divide the electronic spectrum
 World Government? • Discussed many times • Has some benefits • Seems unlikely that world actors such as states would all give up their sovereignty to such a body – Cultures differ: Democracy vs Authoritarianism – Significant trust needed. High stakes stag hunt? • United Nations? • A federation?
World Government? • Discussed many times • Has some benefits • Seems unlikely that world actors such as states would all give up their sovereignty to such a body – Cultures differ: Democracy vs Authoritarianism – Significant trust needed. High stakes stag hunt? • United Nations? • A federation?
 UN Charter and Legal Use of Force • Charter authorizes force under three conditions: – Unilaterally in self-defense: US Afghanistan in 2001 – Multilaterally if authorized by UN Security Council “to maintain or restore international peace & security” – Multilaterally by regional collective defense action to aid alliance member in self-defense: NATO & Afghanistan • Preserves each state’s sovereignty • Does not legalize intervention in civil wars or humanitarian/human rights problems unless – State authorizes OR – UN Security Council feels conflict will spread
UN Charter and Legal Use of Force • Charter authorizes force under three conditions: – Unilaterally in self-defense: US Afghanistan in 2001 – Multilaterally if authorized by UN Security Council “to maintain or restore international peace & security” – Multilaterally by regional collective defense action to aid alliance member in self-defense: NATO & Afghanistan • Preserves each state’s sovereignty • Does not legalize intervention in civil wars or humanitarian/human rights problems unless – State authorizes OR – UN Security Council feels conflict will spread
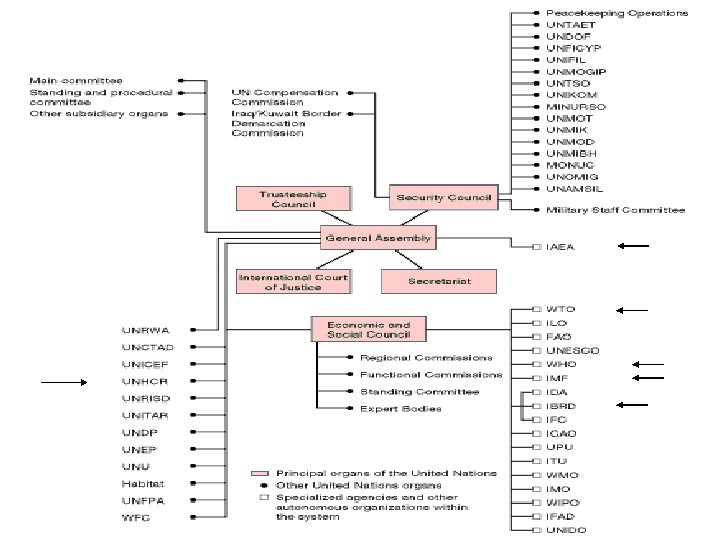
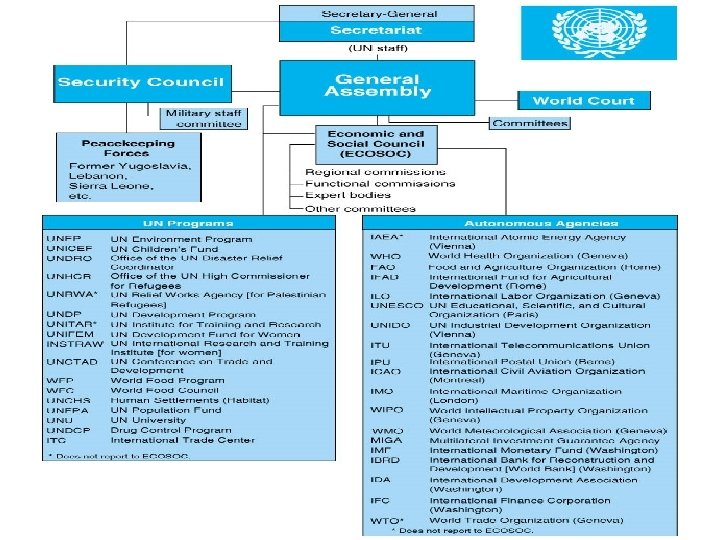
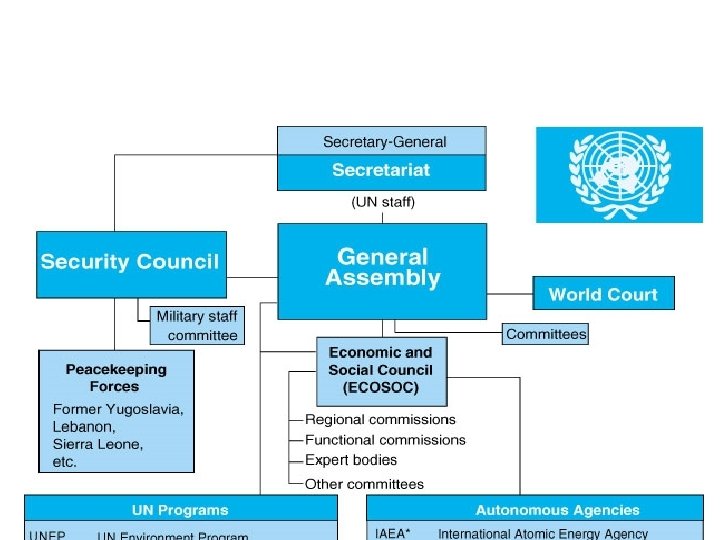
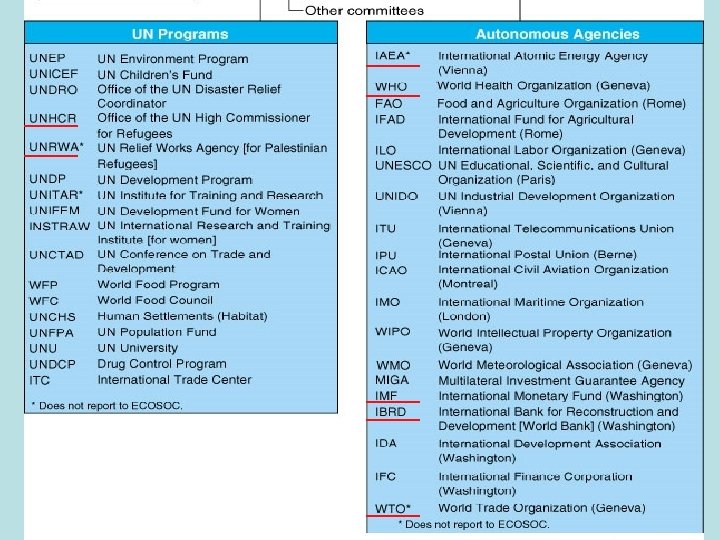
 United Nations • General Assembly: All members have a vote – 2/3 majority for budget, big issues – Elects members to bodies and commissions • Security Council (15 members) – Maintain international peace & security – Permanent Members (5) can veto resolutions, need 9 – Military activity rare • • No military of its own; Requires member contributions Korea was UN action: UNCMAC still there today 1991 Gulf War was UN authorized, but not UN action Frequently paralyzed during Cold War or over Israel – Peacekeeping
United Nations • General Assembly: All members have a vote – 2/3 majority for budget, big issues – Elects members to bodies and commissions • Security Council (15 members) – Maintain international peace & security – Permanent Members (5) can veto resolutions, need 9 – Military activity rare • • No military of its own; Requires member contributions Korea was UN action: UNCMAC still there today 1991 Gulf War was UN authorized, but not UN action Frequently paralyzed during Cold War or over Israel – Peacekeeping
 Peacekeeping – A Misnomer? • Consensual between warring parties with a truce • Not to take sides. Provides “honest broker” to: – Lessen surprise, slow an attack – Act as tripwire for other nations’ involvement • Defends self only – Does not impose or enforce peace • Examples – Egypt & Israel 1956 -1967, 1975 to today – US in Lebanon 1983 – Somalia 1993 – Bosnia 1990 s
Peacekeeping – A Misnomer? • Consensual between warring parties with a truce • Not to take sides. Provides “honest broker” to: – Lessen surprise, slow an attack – Act as tripwire for other nations’ involvement • Defends self only – Does not impose or enforce peace • Examples – Egypt & Israel 1956 -1967, 1975 to today – US in Lebanon 1983 – Somalia 1993 – Bosnia 1990 s



