1e44b0fef04d784878f5be1bd2044a3b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 108
 International Conflicts of the Cold War
International Conflicts of the Cold War
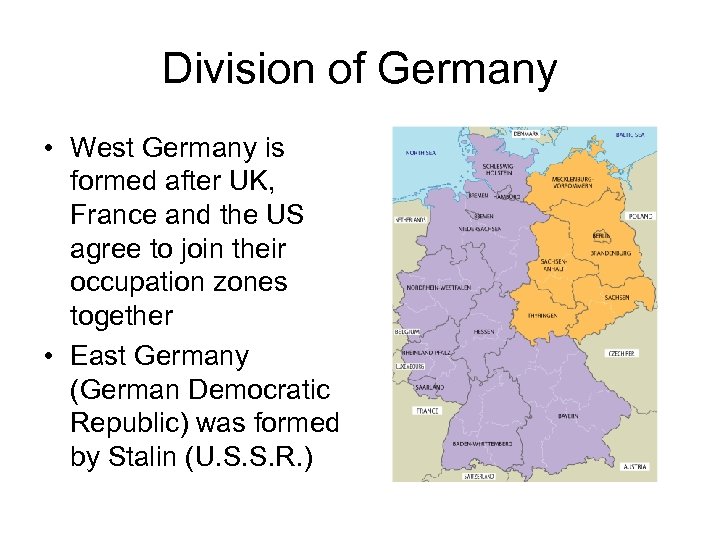 Division of Germany • West Germany is formed after UK, France and the US agree to join their occupation zones together • East Germany (German Democratic Republic) was formed by Stalin (U. S. S. R. )
Division of Germany • West Germany is formed after UK, France and the US agree to join their occupation zones together • East Germany (German Democratic Republic) was formed by Stalin (U. S. S. R. )
 Blockade of Berlin
Blockade of Berlin
 Blockade of Berlin • Western powers introduce a new currency into W. Germany. Soviets refused to accept it in Berlin • Soviets blockaded the corridors, so no supplies could get into W. Berlin • Allies countered with a massive airlift that supplied Berlin for 18 months • Results: • Two separate gov’ts for Berlin • western Allies created NATO
Blockade of Berlin • Western powers introduce a new currency into W. Germany. Soviets refused to accept it in Berlin • Soviets blockaded the corridors, so no supplies could get into W. Berlin • Allies countered with a massive airlift that supplied Berlin for 18 months • Results: • Two separate gov’ts for Berlin • western Allies created NATO
 Berlin Wall, 1961
Berlin Wall, 1961
 Berlin Wall, 1961
Berlin Wall, 1961
 Berlin Wall, 1961 • this barrier was built by the Soviets, intended to stop the massive migration of East Berliners to the West (for jobs, defections, etc)
Berlin Wall, 1961 • this barrier was built by the Soviets, intended to stop the massive migration of East Berliners to the West (for jobs, defections, etc)
 “Checkpoint Charlie”
“Checkpoint Charlie”
 East border guard Conrad Schumann defects to the west
East border guard Conrad Schumann defects to the west
 Berlin Wall, 1989
Berlin Wall, 1989
 Berlin Wall, 1989
Berlin Wall, 1989
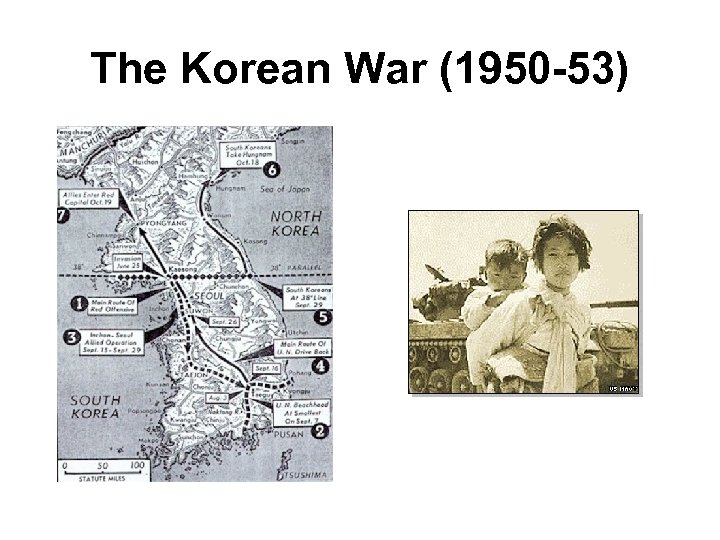 The Korean War (1950 -53)
The Korean War (1950 -53)
 The Korean War (1950 -53) • Korea was divided after Japan’s defeat in WWII Kim II-Sung leader in the North • North became communist • South became democratic • In 1950, the North invaded the South Syngman Rhee leader in South
The Korean War (1950 -53) • Korea was divided after Japan’s defeat in WWII Kim II-Sung leader in the North • North became communist • South became democratic • In 1950, the North invaded the South Syngman Rhee leader in South
 The Korean War (1950 -53) • The UN sent in a force of troops representing 32 countries, including Canada • Over 26 500 Canadians served, 1 000 wounded and 400 were killed • armistice was signed in 1953
The Korean War (1950 -53) • The UN sent in a force of troops representing 32 countries, including Canada • Over 26 500 Canadians served, 1 000 wounded and 400 were killed • armistice was signed in 1953
 The Korean War (1950 -53) What it meant for Canada: • Loss of troops • Showed our support of the UN and our willingness to fight to support those goals
The Korean War (1950 -53) What it meant for Canada: • Loss of troops • Showed our support of the UN and our willingness to fight to support those goals
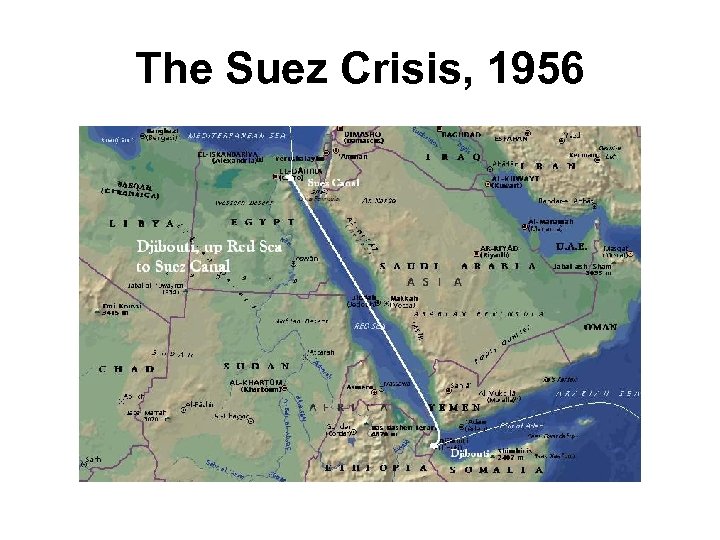 The Suez Crisis, 1956
The Suez Crisis, 1956
 The Suez Crisis, 1956 • Egyptian president Gamel Abdel Nasser seized this trade route from Britain and France • Israel saw this as a direct threat from Egypt • Britain and France joined with Israel to attack Egypt • Soviet Union sided with Nasser of Egypt
The Suez Crisis, 1956 • Egyptian president Gamel Abdel Nasser seized this trade route from Britain and France • Israel saw this as a direct threat from Egypt • Britain and France joined with Israel to attack Egypt • Soviet Union sided with Nasser of Egypt
 The Suez Crisis, 1956 What it meant for Canada: • Canada’s Minister of External Affairs, Lester B. Pearson, went to the UN and suggested the creation of an emergency peacekeeping body • The United Nations Emergency Force went to the Suez to keep the combatants apart while a settlement to the crisis was worked out
The Suez Crisis, 1956 What it meant for Canada: • Canada’s Minister of External Affairs, Lester B. Pearson, went to the UN and suggested the creation of an emergency peacekeeping body • The United Nations Emergency Force went to the Suez to keep the combatants apart while a settlement to the crisis was worked out
 The Suez Crisis, 1956 • Pearson won a Nobel Peace Prize for his efforts in 1957
The Suez Crisis, 1956 • Pearson won a Nobel Peace Prize for his efforts in 1957
 Bomarc Missile Crisis and the AVRO Arrow, 1957
Bomarc Missile Crisis and the AVRO Arrow, 1957
 Bomarc vs AVRO • Canada signs NORAD Treaty with the USA – sets up 3 lines of radar defense in our north • DEW Line, Mid-Canada Line, Pinetree Line • Diefenbaker scraps the AVRO Arrow project in favour of a line of surface to air guided missiles • When Canadians found out the Bomarcs were to be armed with nuclear weapons, protests rose, and the missiles weren’t delivered.
Bomarc vs AVRO • Canada signs NORAD Treaty with the USA – sets up 3 lines of radar defense in our north • DEW Line, Mid-Canada Line, Pinetree Line • Diefenbaker scraps the AVRO Arrow project in favour of a line of surface to air guided missiles • When Canadians found out the Bomarcs were to be armed with nuclear weapons, protests rose, and the missiles weren’t delivered.
 Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962
Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962
 Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962 • The American “Bay of Pigs” invasion fails, Castro of Cuba turns to Khrushchev of the USSR for protection • US spotted Soviet missiles in Cuba • US set up a naval blockade around Cuba, • Soviets continued on their path • The world seemed sure this would lead to nuclear war
Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962 • The American “Bay of Pigs” invasion fails, Castro of Cuba turns to Khrushchev of the USSR for protection • US spotted Soviet missiles in Cuba • US set up a naval blockade around Cuba, • Soviets continued on their path • The world seemed sure this would lead to nuclear war
 Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962 • Khrushchev agrees to dismantle missile bases in exchange for a US promise not to invade Cuba
Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962 • Khrushchev agrees to dismantle missile bases in exchange for a US promise not to invade Cuba
 Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962 • What it meant for Canada: • US expected Canada to support its stance against USSR and Cuba • PM Diefenbaker did not agree to USA’s request of nuclear missiles on our soil • Dief would lose the next election – PM Pearson brought the nuclear warheads into Canada
Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962 • What it meant for Canada: • US expected Canada to support its stance against USSR and Cuba • PM Diefenbaker did not agree to USA’s request of nuclear missiles on our soil • Dief would lose the next election – PM Pearson brought the nuclear warheads into Canada
 Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962 • John F. Kennedy was assassinated in 1963
Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962 • John F. Kennedy was assassinated in 1963
 The Vietnam War, 1965 -1975 • The country was divided between Communist North and the anti-communist South North Vietnam Ho Chi Minh South Vietnam Ngo Dinh Diem
The Vietnam War, 1965 -1975 • The country was divided between Communist North and the anti-communist South North Vietnam Ho Chi Minh South Vietnam Ngo Dinh Diem
 The Vietnam War, 1954 -1975 • The US supported the South, USSR supported the North • President Johnson used the Gulf of Tonkin incident as reason to send 500 000 troops into Vietnam
The Vietnam War, 1954 -1975 • The US supported the South, USSR supported the North • President Johnson used the Gulf of Tonkin incident as reason to send 500 000 troops into Vietnam
 The Vietnam War, 1954 -1975 • This was the first televised war, and protest in America grew as they witnessed the atrocities in Vietnam
The Vietnam War, 1954 -1975 • This was the first televised war, and protest in America grew as they witnessed the atrocities in Vietnam
 ANTI-WAR MOVEMENT… MAKE LOVE, NOT WAR!
ANTI-WAR MOVEMENT… MAKE LOVE, NOT WAR!
 Sit-ins, marches, rallies! @*!#^$
Sit-ins, marches, rallies! @*!#^$
 Kent State Shooting, 1970
Kent State Shooting, 1970
 DOWN WITH THE “ESTABLISHMENT”!
DOWN WITH THE “ESTABLISHMENT”!
 Teen culture didn’t trust anyone over the age of 30
Teen culture didn’t trust anyone over the age of 30
 Hippies and counter-culture
Hippies and counter-culture
 THE SEXUAL REVOLUTION!
THE SEXUAL REVOLUTION!
 “The Pill” is introduced in 1960
“The Pill” is introduced in 1960
 homosexuality is legalized in England (1967)
homosexuality is legalized in England (1967)
 WOMEN’S RIGHTS!
WOMEN’S RIGHTS!
 demand for equal pay
demand for equal pay
 Gloria Steinem
Gloria Steinem
 CIVIL RIGHTS
CIVIL RIGHTS

 Started as a non-violent movement with leaders like Martin Luther King, Jr.
Started as a non-violent movement with leaders like Martin Luther King, Jr.

 And led by more radical leaders like Malcolm X
And led by more radical leaders like Malcolm X
 It evolved into the “Black Power” movement with radical groups like the “Black Panthers”
It evolved into the “Black Power” movement with radical groups like the “Black Panthers”
 ENVIRONMENTAL PROTEST
ENVIRONMENTAL PROTEST
 “Silent Spring”
“Silent Spring”
 There was a growing awareness of environmental pollution…
There was a growing awareness of environmental pollution…
 And the use of pesticides in agriculture
And the use of pesticides in agriculture
 MUSIC OF PROTEST!
MUSIC OF PROTEST!
 The Beatles
The Beatles
 The Rolling Stones
The Rolling Stones
 Jefferson Airplane
Jefferson Airplane
 Jimi Hendrix Experience
Jimi Hendrix Experience
 The Doors
The Doors
 Bob Dylan
Bob Dylan

 The Vietnam War, 1965 -1975
The Vietnam War, 1965 -1975
 The Vietnam War, 1954 -1975 • Nixon as President, promised to remove troops out of Vietnam • The US completely withdrew by 1975 • Vietnam was taken over by the communists of the North
The Vietnam War, 1954 -1975 • Nixon as President, promised to remove troops out of Vietnam • The US completely withdrew by 1975 • Vietnam was taken over by the communists of the North
 What it meant for Canada: • Some Americans did anything they could to avoid the “draft”… so they fled to Canada. (“Draft Dodgers”) • Many refugees fled Vietnam and arrived as immigrants to Canada • Some Canadians profited from sales of goods for the war
What it meant for Canada: • Some Americans did anything they could to avoid the “draft”… so they fled to Canada. (“Draft Dodgers”) • Many refugees fled Vietnam and arrived as immigrants to Canada • Some Canadians profited from sales of goods for the war
 The Persian Gulf War 1990 -1991 Saddam Hussein
The Persian Gulf War 1990 -1991 Saddam Hussein
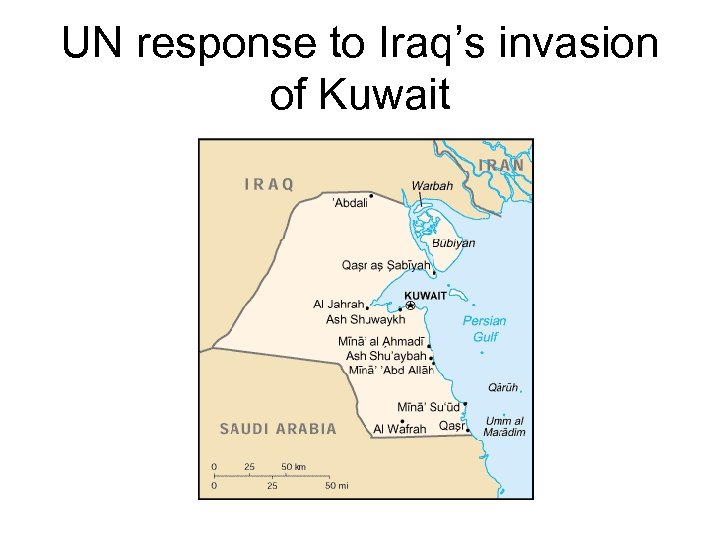 UN response to Iraq’s invasion of Kuwait
UN response to Iraq’s invasion of Kuwait
 UN Operation “Desert Storm”
UN Operation “Desert Storm”
 “Smart” weapons Patriot SCUD
“Smart” weapons Patriot SCUD
 Tomahawk Missiles
Tomahawk Missiles
 Scorched Earth
Scorched Earth
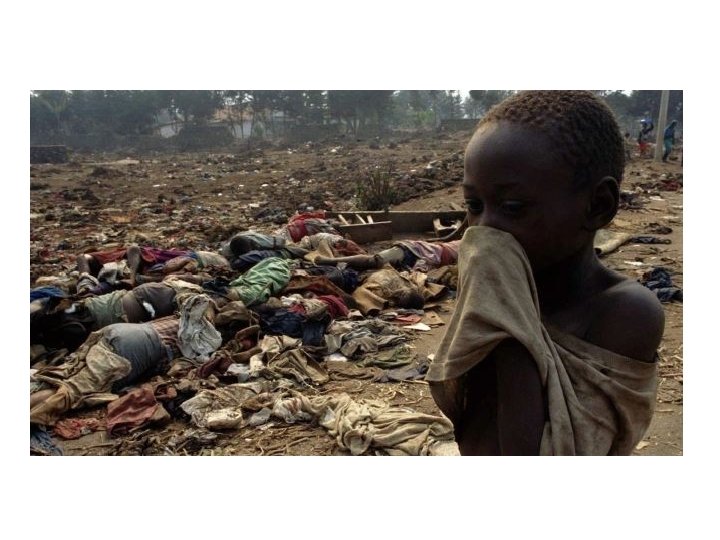
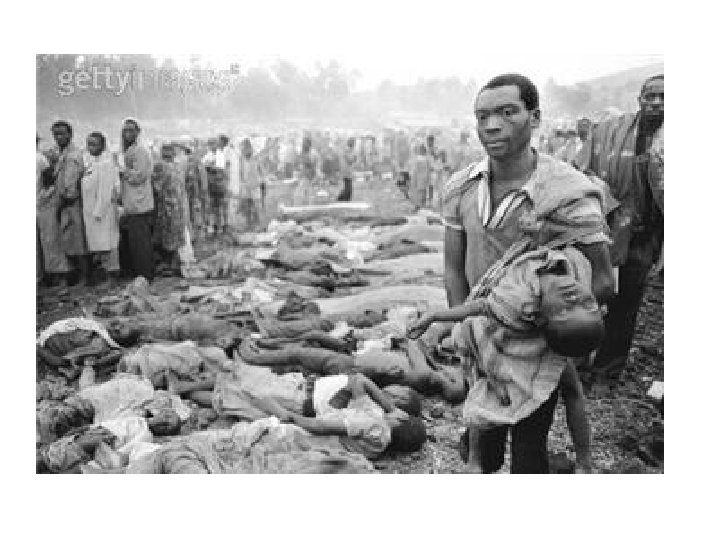
 Genocide in Rwanda 1994
Genocide in Rwanda 1994
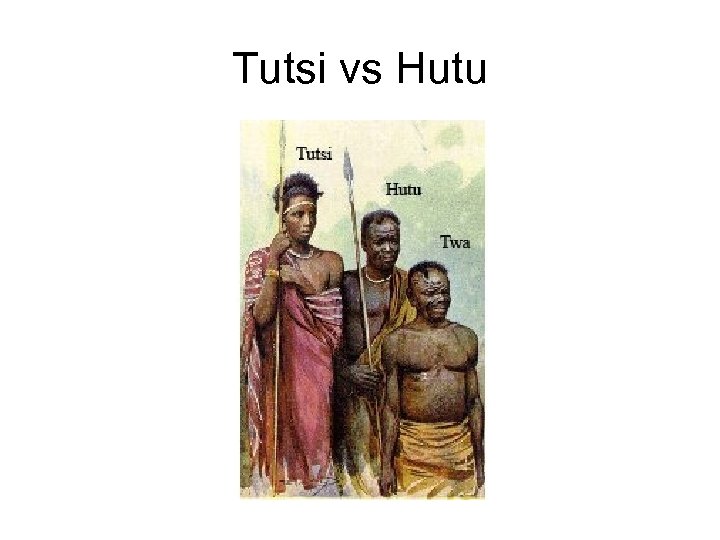 Tutsi vs Hutu
Tutsi vs Hutu
 Belgians in the Congo
Belgians in the Congo
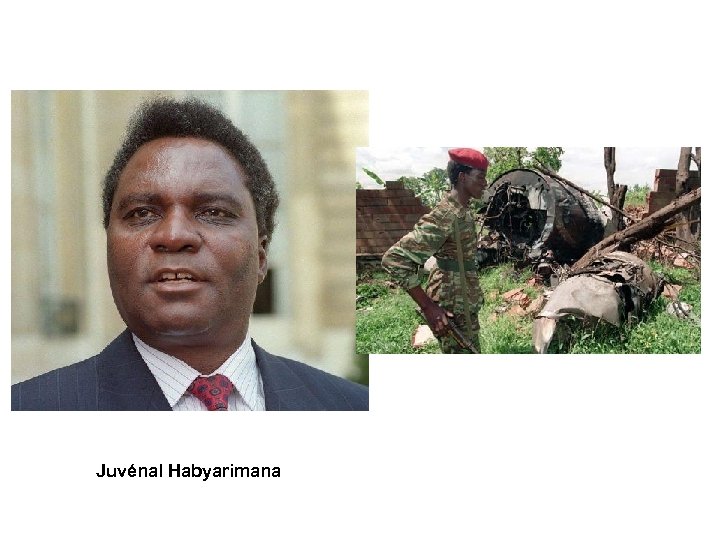 Juvénal Habyarimana
Juvénal Habyarimana
 Hutu Power movement
Hutu Power movement

 Romeo Dallaire and UNAMIR
Romeo Dallaire and UNAMIR

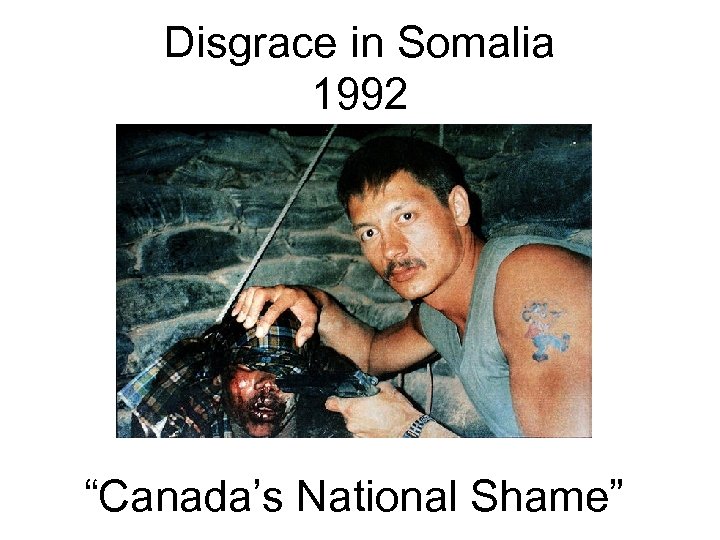 Disgrace in Somalia 1992 “Canada’s National Shame”
Disgrace in Somalia 1992 “Canada’s National Shame”
 Canadian Airborne Regiment
Canadian Airborne Regiment
 UN Operation “Restore Hope”
UN Operation “Restore Hope”
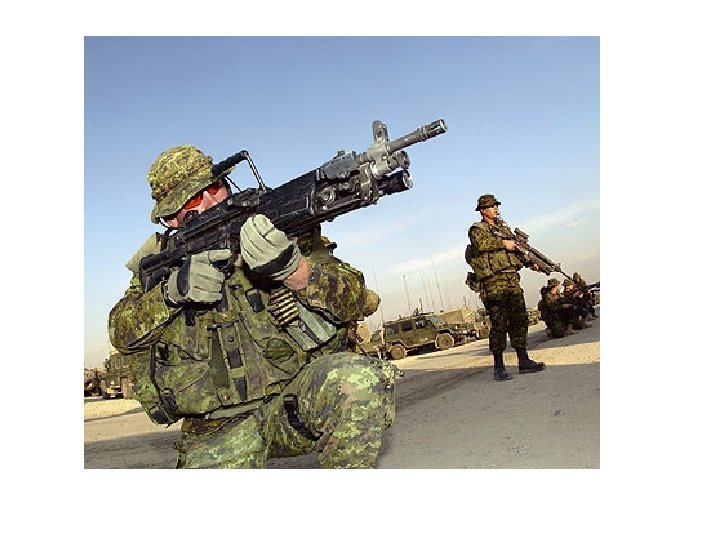

 Death of Shidane Arone
Death of Shidane Arone
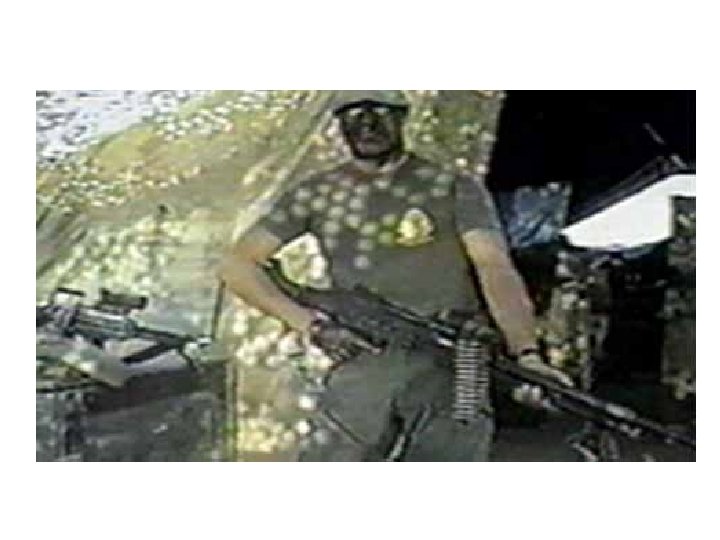


 Civil War in Yugoslavia
Civil War in Yugoslavia
 Srebrenica Genocide
Srebrenica Genocide
 NATO in Yugoslavia
NATO in Yugoslavia

 9/11
9/11
 War in Afghanistan
War in Afghanistan
 Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Laden
 Iraq War
Iraq War
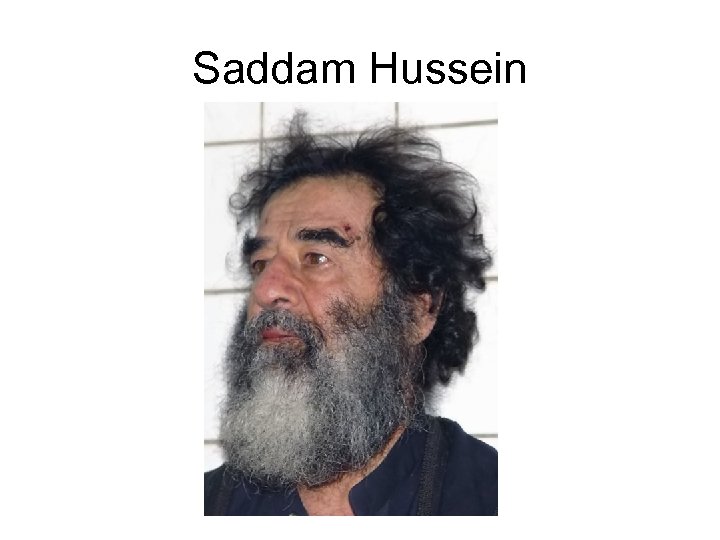 Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein
 WMDs?
WMDs?