8754b776022e64eca7e1b97a2c62efde.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 International Conference on Engineering Education - ICEE 2008 CLOSING CEREMONY Welcome Address Prof. Gyula SALLAI, DSc Budapest University of Technology and Economics (BME) BME, Budapest, 31 st July, 2008 http: //icee 2008 hungary. net/ www. bme. hu
International Conference on Engineering Education - ICEE 2008 CLOSING CEREMONY Welcome Address Prof. Gyula SALLAI, DSc Budapest University of Technology and Economics (BME) BME, Budapest, 31 st July, 2008 http: //icee 2008 hungary. net/ www. bme. hu
 Facts and Strategies, 2008 Budapest University of Technology and Economics, BME Prof. Dr. Gyula SALLAI
Facts and Strategies, 2008 Budapest University of Technology and Economics, BME Prof. Dr. Gyula SALLAI
 1782 BME in Figures Institutum Geometricum – Hydrotechnicum 1783 - - - - - 17841949 -2000 Technical University of Budapest 2000 - Budapest University of Technology and Economics v 8 Faculties, 77 Departments v v Faculties: v Civil Engineering v Mechanical Engineering v Architecture v Chemical and Bioengineering v Electrical Engineering and Informatics v Transportation Engineering v Natural Sciences v Economic and Social Sciences (1782) (1871) (1873) (1949) (1951) (1998) 24 000 Students Academic Staff: 1300, with scientific qualification: 700 Golden Quality Prize in HE – (in Hungary, 2007) Web Popularity Ranking: 81 st in Europe (2007) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 3 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
1782 BME in Figures Institutum Geometricum – Hydrotechnicum 1783 - - - - - 17841949 -2000 Technical University of Budapest 2000 - Budapest University of Technology and Economics v 8 Faculties, 77 Departments v v Faculties: v Civil Engineering v Mechanical Engineering v Architecture v Chemical and Bioengineering v Electrical Engineering and Informatics v Transportation Engineering v Natural Sciences v Economic and Social Sciences (1782) (1871) (1873) (1949) (1951) (1998) 24 000 Students Academic Staff: 1300, with scientific qualification: 700 Golden Quality Prize in HE – (in Hungary, 2007) Web Popularity Ranking: 81 st in Europe (2007) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 3 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
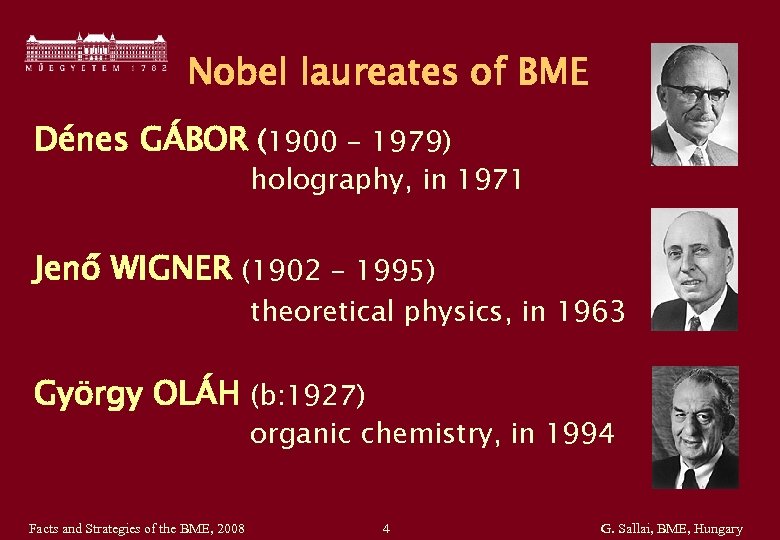 Nobel laureates of BME Dénes GÁBOR (1900 - 1979) holography, in 1971 Jenő WIGNER (1902 - 1995) theoretical physics, in 1963 György OLÁH (b: 1927) organic chemistry, in 1994 Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 4 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Nobel laureates of BME Dénes GÁBOR (1900 - 1979) holography, in 1971 Jenő WIGNER (1902 - 1995) theoretical physics, in 1963 György OLÁH (b: 1927) organic chemistry, in 1994 Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 4 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 Former students of BME Tódor (Theodore) von KÁRMÁN Aeronautical Engineer & Mathematician (1881 -1963) Leo SZILÁRD Physicist (1898 -1964) Ede TELLER Physicist (1908 - 2004) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 5 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Former students of BME Tódor (Theodore) von KÁRMÁN Aeronautical Engineer & Mathematician (1881 -1963) Leo SZILÁRD Physicist (1898 -1964) Ede TELLER Physicist (1908 - 2004) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 5 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 Former graduates of BME Donát BÁNKI inventor of carburator (1859 - 1922) Károly ZIPERNOWSKY inventor of transformer (1853 -1942) Ernő RUBIK inventor of Rubik’s cube (1944 -) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 6 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Former graduates of BME Donát BÁNKI inventor of carburator (1859 - 1922) Károly ZIPERNOWSKY inventor of transformer (1853 -1942) Ernő RUBIK inventor of Rubik’s cube (1944 -) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 6 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 Education at the BME v Traditional Dipl. Eng. Programs (MSc, 5 years) – in Hungarian v From 2005/2006 two-cycle linear higher education system in Hungary (Bologna process). Engineering education in general: 7 semester BSc programs (210 credits) 4 semester MSc programs (120 credits) v Ph. D Programs (3 years) v BSc, MSc and Ph. D curricula in English, partly in German, French, Russian v Since 1994 European Credit Transfer Scheme v Programs are qualified by the Hungarian Accreditation Body (MAB) v Continuing Engineering Education, postgraduate courses, MBA, etc. Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 7 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Education at the BME v Traditional Dipl. Eng. Programs (MSc, 5 years) – in Hungarian v From 2005/2006 two-cycle linear higher education system in Hungary (Bologna process). Engineering education in general: 7 semester BSc programs (210 credits) 4 semester MSc programs (120 credits) v Ph. D Programs (3 years) v BSc, MSc and Ph. D curricula in English, partly in German, French, Russian v Since 1994 European Credit Transfer Scheme v Programs are qualified by the Hungarian Accreditation Body (MAB) v Continuing Engineering Education, postgraduate courses, MBA, etc. Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 7 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 Students attending the BME (2007) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 8 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Students attending the BME (2007) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 8 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
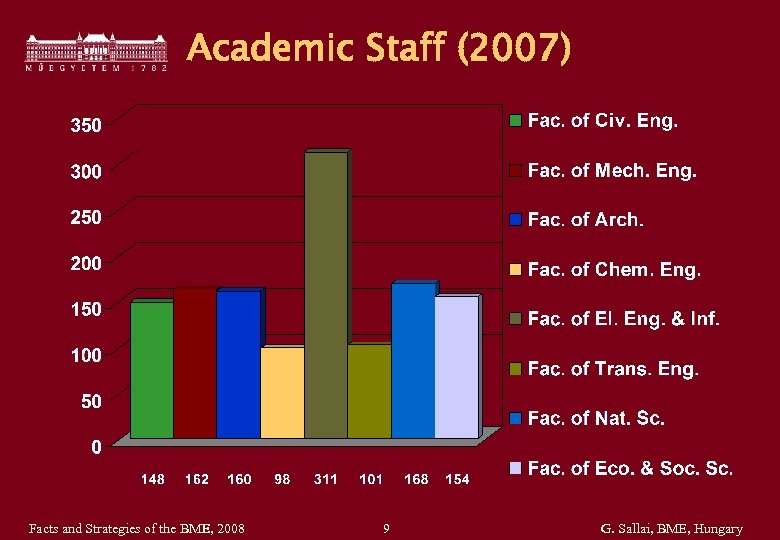 Academic Staff (2007) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 9 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Academic Staff (2007) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 9 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 Traditional MSc (5 year) Programmes Faculty of Civil Engineering Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Faculty of Architecture Faculty of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Informatics Faculty of Transportation Engineering Faculty of Natural Sciences Faculty of Economic and Social Sciences Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 • • • • • Civil Engineering Land Surveying and Geoinformatics Mechanical Engineering Production Engineering Power Engineering Architectural Engineering Chemical Engineering Bioengineering Environmental Engineering Electrical Engineering Technical Informatics Transportation Engineering Mechanical Engineering Engineer-Physics Mathematics Engineering Manager Business Manager 10 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Traditional MSc (5 year) Programmes Faculty of Civil Engineering Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Faculty of Architecture Faculty of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Informatics Faculty of Transportation Engineering Faculty of Natural Sciences Faculty of Economic and Social Sciences Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 • • • • • Civil Engineering Land Surveying and Geoinformatics Mechanical Engineering Production Engineering Power Engineering Architectural Engineering Chemical Engineering Bioengineering Environmental Engineering Electrical Engineering Technical Informatics Transportation Engineering Mechanical Engineering Engineer-Physics Mathematics Engineering Manager Business Manager 10 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 BSc/BA Programmes at the BME Faculty of Civil Engineering (EMK) • Civil Engineering (8 semesters) Faculty of Mechanical Engineering • Mechanical Engineering (7) (GPK) • Energy Engineering (7) • Industrial Design Engineering (7) • Mechatronics (7) Faculty of Architecture (EPK) • Architecture (8) Faculty of Chemical Engineering and • Chemical Engineering (7) Bioengineering (VBK) • Bioengineering (7) • Environmental Engineering (7) Faculty of Electrical Engineering • Electrical Engineering (7) and Informatics (VIK) • Computer Science and Engineering (7) Faculty of Transportation Eng. (KSK) • Transportation Engineering (7) Faculty of Natural Sciences (TTK) • Mathematics (6) • Physics (6+1) Faculty of Economic and • Management in Engineering (7) Social Sciences (GTK) • Business and Management BA (6+1) • International Business BA (6+1) • Applied Economics BA (6) • Communication and Media Sciences BA (6) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 11 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
BSc/BA Programmes at the BME Faculty of Civil Engineering (EMK) • Civil Engineering (8 semesters) Faculty of Mechanical Engineering • Mechanical Engineering (7) (GPK) • Energy Engineering (7) • Industrial Design Engineering (7) • Mechatronics (7) Faculty of Architecture (EPK) • Architecture (8) Faculty of Chemical Engineering and • Chemical Engineering (7) Bioengineering (VBK) • Bioengineering (7) • Environmental Engineering (7) Faculty of Electrical Engineering • Electrical Engineering (7) and Informatics (VIK) • Computer Science and Engineering (7) Faculty of Transportation Eng. (KSK) • Transportation Engineering (7) Faculty of Natural Sciences (TTK) • Mathematics (6) • Physics (6+1) Faculty of Economic and • Management in Engineering (7) Social Sciences (GTK) • Business and Management BA (6+1) • International Business BA (6+1) • Applied Economics BA (6) • Communication and Media Sciences BA (6) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 11 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 2 year MSc/MA Programmes at the BME from 2008 ENGINEERING MASTER PROGRAMMES EMK Structure civil engineer (1, 5 years, 2009) EMK Infrastructure civil engineer (1, 5 y, 2009) EMK Geodesy & geoinformatics (1, 5 y, 2009) G P K M e c h a n i c a l e n g i n e e r OTH G P K M e c h a t r o n i c s e n g i n e e r. E R M A S T E R P R O G R A M M E S T n G P K M e c h a n i c a l m o d e l i. T Kg A p p l i e d M a t h e m a t i c s P h y s i c s E P K A r c h i t e c t u r e ( 5 y e. T r s ) K a T E c o n o m i c s V B K C h e m i c a l e n g i n e e r ( 2 G 0 T ) K 0 9 V B K B i o e n g i n e e r ( 2 0 G T 9 ) I n t e r n a t i o n a l e c o n o m y 0 K GTK r V B K E n v i r o n m e n t a l e n g i n e e. Regional and environmental economy T M a r k e t i n g V I K E l e c t r i c a l e n g i n. Ge e r K V I K C o m p u t e r e n g i n. GTK Master of Business Administration e e r F i n a n c i a l V I K B i o m e d i c a l e n g i n e e r ( 2 G 0 T ) K 0 9 T A c c o u n t i n g K S K T r a n s p o r t e n g i n. Ge e r K Te M K S K L o g i s t i c s e n g i n. Ge K r a n a g e m e n t a n d O r g a n i s a t i o n K S K V e h i c l e e n g i n G T Kr C o g n i t i v e s c i e n c e s e e GTK Technical manager (2009) G T K E n g i n e e r - t e a c h e r Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 12 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
2 year MSc/MA Programmes at the BME from 2008 ENGINEERING MASTER PROGRAMMES EMK Structure civil engineer (1, 5 years, 2009) EMK Infrastructure civil engineer (1, 5 y, 2009) EMK Geodesy & geoinformatics (1, 5 y, 2009) G P K M e c h a n i c a l e n g i n e e r OTH G P K M e c h a t r o n i c s e n g i n e e r. E R M A S T E R P R O G R A M M E S T n G P K M e c h a n i c a l m o d e l i. T Kg A p p l i e d M a t h e m a t i c s P h y s i c s E P K A r c h i t e c t u r e ( 5 y e. T r s ) K a T E c o n o m i c s V B K C h e m i c a l e n g i n e e r ( 2 G 0 T ) K 0 9 V B K B i o e n g i n e e r ( 2 0 G T 9 ) I n t e r n a t i o n a l e c o n o m y 0 K GTK r V B K E n v i r o n m e n t a l e n g i n e e. Regional and environmental economy T M a r k e t i n g V I K E l e c t r i c a l e n g i n. Ge e r K V I K C o m p u t e r e n g i n. GTK Master of Business Administration e e r F i n a n c i a l V I K B i o m e d i c a l e n g i n e e r ( 2 G 0 T ) K 0 9 T A c c o u n t i n g K S K T r a n s p o r t e n g i n. Ge e r K Te M K S K L o g i s t i c s e n g i n. Ge K r a n a g e m e n t a n d O r g a n i s a t i o n K S K V e h i c l e e n g i n G T Kr C o g n i t i v e s c i e n c e s e e GTK Technical manager (2009) G T K E n g i n e e r - t e a c h e r Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 12 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 Doctorate Schools (Ph. D/DLA) ~900 Ph. D students/candidates Faculty of Civil Engineering • • Faculty of Mechanical Engineering • Faculty of Architecture • • Fac. of Chemical and Bioengineering • Faculty of Electrical Engineering • and Informatics • Faculty of Transportation Engineering • • Faculty of Natural Sciences • • Faculty of Economic and • Social Sciences • • Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 Civil Engineering Sciences Earth Sciences Mechanical Engineering Sciences Architectural Art (DLA) Building Sciences Chemistry and Chemical Engineering Electrical Engineering Information Technology Transport Science Vehicle, Mobile Machines Engineering Mathematics and Computer Science Physics Economy, Management and Organizations Psychological Sciences History of Technology and Science 13 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Doctorate Schools (Ph. D/DLA) ~900 Ph. D students/candidates Faculty of Civil Engineering • • Faculty of Mechanical Engineering • Faculty of Architecture • • Fac. of Chemical and Bioengineering • Faculty of Electrical Engineering • and Informatics • Faculty of Transportation Engineering • • Faculty of Natural Sciences • • Faculty of Economic and • Social Sciences • • Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 Civil Engineering Sciences Earth Sciences Mechanical Engineering Sciences Architectural Art (DLA) Building Sciences Chemistry and Chemical Engineering Electrical Engineering Information Technology Transport Science Vehicle, Mobile Machines Engineering Mathematics and Computer Science Physics Economy, Management and Organizations Psychological Sciences History of Technology and Science 13 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 Continuing/Adult Education at the BME • Institute for Continuing Engineering Education (MTI) Idea of life long learning of engineers in 1924 Established in 1939 (1 st in Europe) Qualified by MAB in 2001 (EN ISO 9001: 2001) „UNESCO Chair” Award in 2000 Member of SEFI, IACEE, FEANI… Qualification for the „Eur-Ing” in FEANI register (633 Eur-Ing at Dec. 2007) Aim: full CEE program, fitting to the market demand incl. : Postgraduate engineering courses, Economic, management and IT studies, Courses for special qualification / certificate (e. g. building surveyor, quality manager) Special EU topics (legal, economic, R&D…. ) Annually in average: 80 courses, 1750 participants Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 14 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Continuing/Adult Education at the BME • Institute for Continuing Engineering Education (MTI) Idea of life long learning of engineers in 1924 Established in 1939 (1 st in Europe) Qualified by MAB in 2001 (EN ISO 9001: 2001) „UNESCO Chair” Award in 2000 Member of SEFI, IACEE, FEANI… Qualification for the „Eur-Ing” in FEANI register (633 Eur-Ing at Dec. 2007) Aim: full CEE program, fitting to the market demand incl. : Postgraduate engineering courses, Economic, management and IT studies, Courses for special qualification / certificate (e. g. building surveyor, quality manager) Special EU topics (legal, economic, R&D…. ) Annually in average: 80 courses, 1750 participants Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 14 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 Other forms of Continuing Education at the BME • Postgraduate education in eng. specialization Organized by the Faculties for engineers 4 semesters with exams, diploma-work, certificate 63 curricula, e. g. : welding, pharmacochemistry, R&D in EE, manager in energetics, city-planning, color-dynamics, reactor-technology, financial IT • Master in Business Administration (MBA) Since 1992 with Heriot-Watt University, since 1996 gradually redesigned with the assistance of American institutions by Fac. Economic Sciences MBA executive, professional Annually in average: 500 MBA diplomas • Further education courses: with certificate by Fac. Econ. Sci. E. g. : teachers of secondary schools, techn. experts in justice, educational manager, media designer, taxation expert, regional developer, environmental manager, etc. Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 15 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Other forms of Continuing Education at the BME • Postgraduate education in eng. specialization Organized by the Faculties for engineers 4 semesters with exams, diploma-work, certificate 63 curricula, e. g. : welding, pharmacochemistry, R&D in EE, manager in energetics, city-planning, color-dynamics, reactor-technology, financial IT • Master in Business Administration (MBA) Since 1992 with Heriot-Watt University, since 1996 gradually redesigned with the assistance of American institutions by Fac. Economic Sciences MBA executive, professional Annually in average: 500 MBA diplomas • Further education courses: with certificate by Fac. Econ. Sci. E. g. : teachers of secondary schools, techn. experts in justice, educational manager, media designer, taxation expert, regional developer, environmental manager, etc. Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 15 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
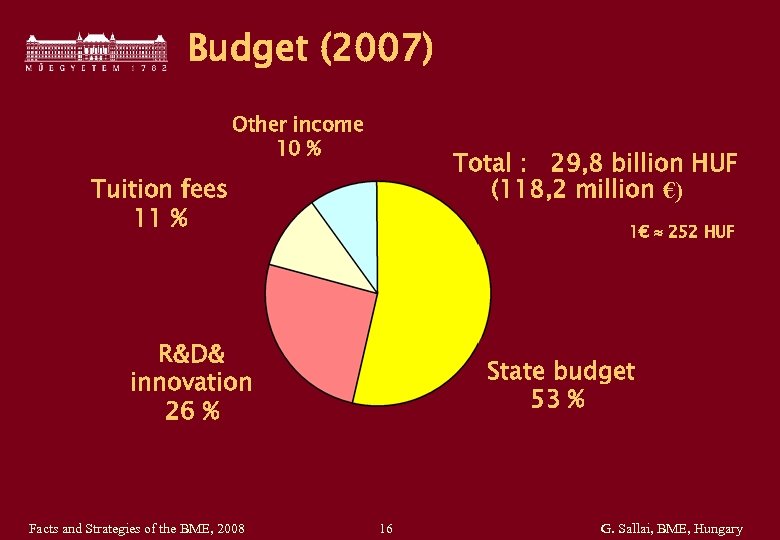 Budget (2007) Other income 10 % Total : 29, 8 billion HUF (118, 2 million €) Tuition fees 11 % 1€ 252 HUF R&D& innovation 26 % Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 State budget 53 % 16 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Budget (2007) Other income 10 % Total : 29, 8 billion HUF (118, 2 million €) Tuition fees 11 % 1€ 252 HUF R&D& innovation 26 % Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 State budget 53 % 16 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 BME as Research University v Competition and grants for basic and applied research § National (National Office for Research and Technology) § International (EU’s RTD Framework Programmes) v R&D for the industry and government § Bilateral strategic agreements, incl. e. g. : • collaborative and sponsored research • • • support of Ph. D education courses for updating knowledge of co’s engineers, managers involvement of co’s experts in the eng & mgmt education § Bilateral specification-based contracts, partly based on Contribution for Innovation by Act v Activity of the Scientific Workshops § Doctorate Schools (15), departmental research groups § Research groups (12) of Hungarian Academy of Sciences at the BME Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 17 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
BME as Research University v Competition and grants for basic and applied research § National (National Office for Research and Technology) § International (EU’s RTD Framework Programmes) v R&D for the industry and government § Bilateral strategic agreements, incl. e. g. : • collaborative and sponsored research • • • support of Ph. D education courses for updating knowledge of co’s engineers, managers involvement of co’s experts in the eng & mgmt education § Bilateral specification-based contracts, partly based on Contribution for Innovation by Act v Activity of the Scientific Workshops § Doctorate Schools (15), departmental research groups § Research groups (12) of Hungarian Academy of Sciences at the BME Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 17 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
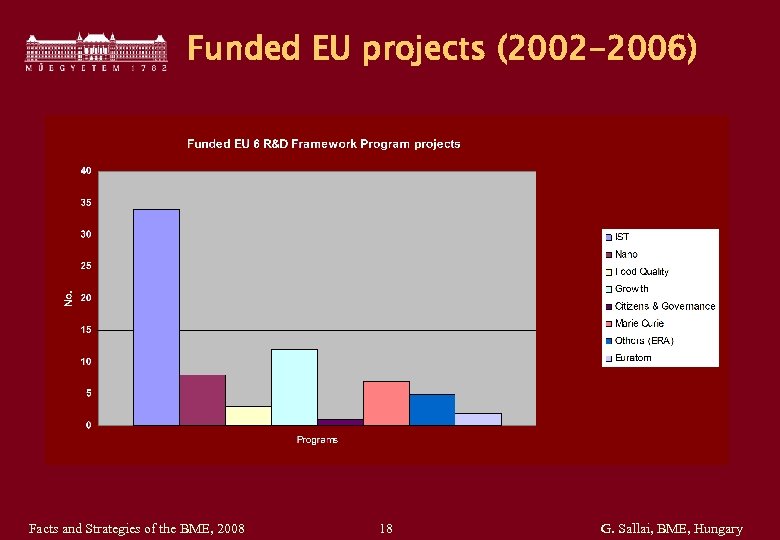 Funded EU projects (2002 -2006) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 18 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Funded EU projects (2002 -2006) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 18 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
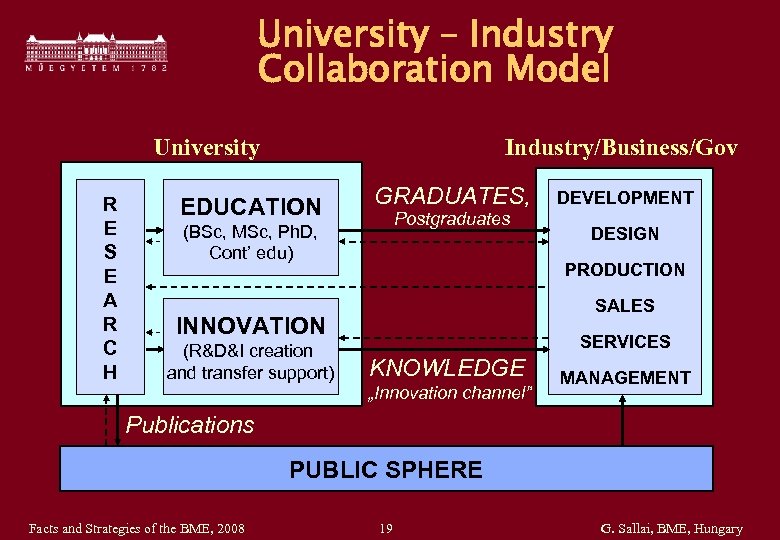 University – Industry Collaboration Model Industry/Business/Gov University R E S E A R C H EDUCATION GRADUATES, Postgraduates (BSc, MSc, Ph. D, Cont’ edu) DESIGN PRODUCTION SALES INNOVATION (R&D&I creation and transfer support) DEVELOPMENT SERVICES KNOWLEDGE „Innovation channel” MANAGEMENT Publications PUBLIC SPHERE Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 19 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
University – Industry Collaboration Model Industry/Business/Gov University R E S E A R C H EDUCATION GRADUATES, Postgraduates (BSc, MSc, Ph. D, Cont’ edu) DESIGN PRODUCTION SALES INNOVATION (R&D&I creation and transfer support) DEVELOPMENT SERVICES KNOWLEDGE „Innovation channel” MANAGEMENT Publications PUBLIC SPHERE Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 19 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 BME University Research Centers Consortia with industrial and academic partners • 3 G/4 G Mobile Communications R&D&I Centre • Information Technology Innovation and Knowledge Centre • Inter-University Cooperative Research Centre for ICT • Advanced Vehicle Control Knowledge Centre • Biomedical Engineering Knowledge Centre • Biomechanical Cooperative Research Centre • Cooperative Research Centre for Intelligent Materials Infopark: Innovation and Technology Park (1 st in CE Europe) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 20 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
BME University Research Centers Consortia with industrial and academic partners • 3 G/4 G Mobile Communications R&D&I Centre • Information Technology Innovation and Knowledge Centre • Inter-University Cooperative Research Centre for ICT • Advanced Vehicle Control Knowledge Centre • Biomedical Engineering Knowledge Centre • Biomechanical Cooperative Research Centre • Cooperative Research Centre for Intelligent Materials Infopark: Innovation and Technology Park (1 st in CE Europe) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 20 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 Strategic relations – Multinational and national companies • • • • Alcoa Audi Bosch Budapest Gas Works Continental Temic E. ON Ericsson Flextronics General Electric Hewlett-Packard Hungarian Electric Works Hungarian Oil Co. (MOL) Hungarian Posts Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 • • • • 21 Hungarian Telekom IBM Intel Knorr-Bremse Mentor Graphics Microsoft Nokia Oracle Paks Nuclear Power Plant Pannon Mobile SAP Siemens Visteon G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Strategic relations – Multinational and national companies • • • • Alcoa Audi Bosch Budapest Gas Works Continental Temic E. ON Ericsson Flextronics General Electric Hewlett-Packard Hungarian Electric Works Hungarian Oil Co. (MOL) Hungarian Posts Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 • • • • 21 Hungarian Telekom IBM Intel Knorr-Bremse Mentor Graphics Microsoft Nokia Oracle Paks Nuclear Power Plant Pannon Mobile SAP Siemens Visteon G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 • • • • • Memberships in international organisations and networks EUA (European University Association) CESAEER (Conf. of European Schools of Advanced Eng. Education and Research) SEFI (European Society for Engineering Education) Conference of Rectors and Presidents of European Universities of Technology 4 TU League: Regional cooperation of BME, CTU in Prague, SUT in Bratislava, TU Wien INU (International Network of Universities) AUF (Agence Universitaire de la Francophonie) ATHENS Network (Advanced Technology Higher Education Networks/Socrates) OECD-IMHE (OECD - Institutional Management in Higher Education) DEAN (Deans European Academics Network) WITEC (European Association for Women in Science Engineering and Technology) ENEN (European Nuclear Education Network) EDEN (European Distance Learning and E-Learning Network) ACA (Academic Cooperation Association) EU-ASEAN (Association of South East Asian Nations) University Network Program EAIE (European Association for International Education) IAUP ( International Association of University Presidents) EUNICE (European Universities Network for ICT) T. I. M. E. Association (Top Industrial Managers for Europe) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 22 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
• • • • • Memberships in international organisations and networks EUA (European University Association) CESAEER (Conf. of European Schools of Advanced Eng. Education and Research) SEFI (European Society for Engineering Education) Conference of Rectors and Presidents of European Universities of Technology 4 TU League: Regional cooperation of BME, CTU in Prague, SUT in Bratislava, TU Wien INU (International Network of Universities) AUF (Agence Universitaire de la Francophonie) ATHENS Network (Advanced Technology Higher Education Networks/Socrates) OECD-IMHE (OECD - Institutional Management in Higher Education) DEAN (Deans European Academics Network) WITEC (European Association for Women in Science Engineering and Technology) ENEN (European Nuclear Education Network) EDEN (European Distance Learning and E-Learning Network) ACA (Academic Cooperation Association) EU-ASEAN (Association of South East Asian Nations) University Network Program EAIE (European Association for International Education) IAUP ( International Association of University Presidents) EUNICE (European Universities Network for ICT) T. I. M. E. Association (Top Industrial Managers for Europe) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 22 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 • • • • • Some of the major University Bilateral Agreements Technical University of Vienna, Technical University of Graz, Austria Technical University of Helsinki, Finland INSA de Rennes, ENSAM, Paris. Tech, France KUL Leuven, Belgium NTNU Trondheim, Norway Zhejiang University (Hangzhou), Northeastern University (Shenyang), China TU Delft, The Netherlands RWTH Aachen, University of Karlsruhe, TU Berlin, TU Munich, Germany Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic Technical University of Cracow, TU Warsaw, Poland Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava, Technical University of Košice University of New Hampshire, of Virginia, Florida Tech, USA Hanoi Open University, Vietnam National University of Singapore, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel Indian Institute of Technology, Mumbay, Delhi, India University of Tokyo, Hokkaido University, Waseda University, Japan Seoul National University, Korea University, Republic of Korea Technical University of Tallinn, Estonia Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 23 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
• • • • • Some of the major University Bilateral Agreements Technical University of Vienna, Technical University of Graz, Austria Technical University of Helsinki, Finland INSA de Rennes, ENSAM, Paris. Tech, France KUL Leuven, Belgium NTNU Trondheim, Norway Zhejiang University (Hangzhou), Northeastern University (Shenyang), China TU Delft, The Netherlands RWTH Aachen, University of Karlsruhe, TU Berlin, TU Munich, Germany Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic Technical University of Cracow, TU Warsaw, Poland Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava, Technical University of Košice University of New Hampshire, of Virginia, Florida Tech, USA Hanoi Open University, Vietnam National University of Singapore, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel Indian Institute of Technology, Mumbay, Delhi, India University of Tokyo, Hokkaido University, Waseda University, Japan Seoul National University, Korea University, Republic of Korea Technical University of Tallinn, Estonia Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 23 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
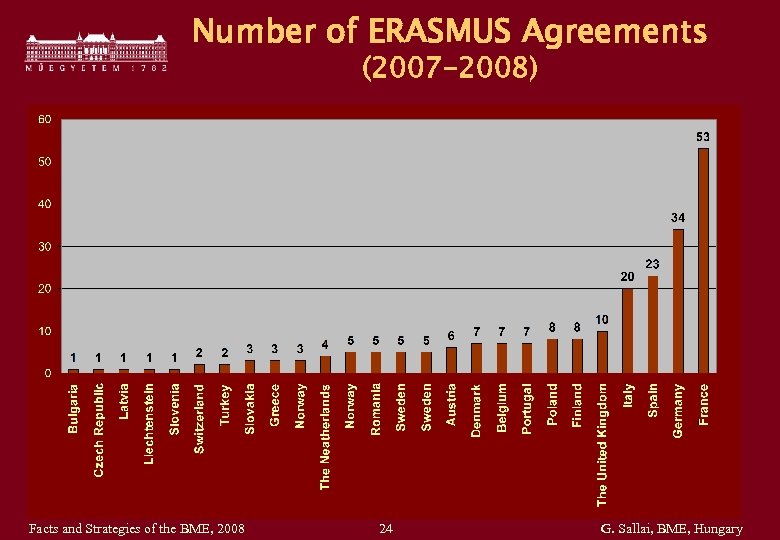 Number of ERASMUS Agreements (2007 -2008) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 24 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Number of ERASMUS Agreements (2007 -2008) Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 24 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 The BME Strategic Objectives A EUROPEAN CENTRE OF EXCELLENCE IN THE CREATION AND TRANSFER OF ENGINEERING AND BUSINESS KNOWLEDGE • Strong basic education and differentiated, high quality master education, aiming at prestigious BSc/BA and MSc /BA degrees, resp. • Ph. D/DLA education and scientific qualification in technical and natural sciences, partly in economic sciences • High-level research, development and innovation in cooperation with academic and business partners, by contracts, agreements and participation in national and European projects; • Training flexibility corresponding to changing social and professional needs, the extension of curricula in English • Perceptible contribution to the technical development of Hungary • To be a valuable member of the European Research and Higher Education Area, harmonising theory and practice. Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 25 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
The BME Strategic Objectives A EUROPEAN CENTRE OF EXCELLENCE IN THE CREATION AND TRANSFER OF ENGINEERING AND BUSINESS KNOWLEDGE • Strong basic education and differentiated, high quality master education, aiming at prestigious BSc/BA and MSc /BA degrees, resp. • Ph. D/DLA education and scientific qualification in technical and natural sciences, partly in economic sciences • High-level research, development and innovation in cooperation with academic and business partners, by contracts, agreements and participation in national and European projects; • Training flexibility corresponding to changing social and professional needs, the extension of curricula in English • Perceptible contribution to the technical development of Hungary • To be a valuable member of the European Research and Higher Education Area, harmonising theory and practice. Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 25 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 26 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 26 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 27 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
Facts and Strategies of the BME, 2008 27 G. Sallai, BME, Hungary
 Thanks for your kind attention! Budapest University of Technology and Economics, BME www. bme. hu
Thanks for your kind attention! Budapest University of Technology and Economics, BME www. bme. hu


