fa9010b31a5f692d5aaebce4b765868a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 International Civil Aviation Organization SAFETY MANAGEMENT An introduction to safety management systems (SMS) SEARAST/SARAST 10 January 2007
International Civil Aviation Organization SAFETY MANAGEMENT An introduction to safety management systems (SMS) SEARAST/SARAST 10 January 2007
 OVERVIEW COSCAP Ø Safety Management · An inside look · Systems Ø Management responsibilities · Culture and organizations Ø Safety and Objectives Ø One way forward · · Different perception Systems approach SMS framework ICAO contribution -2
OVERVIEW COSCAP Ø Safety Management · An inside look · Systems Ø Management responsibilities · Culture and organizations Ø Safety and Objectives Ø One way forward · · Different perception Systems approach SMS framework ICAO contribution -2
 Concept of safety (ICAO) COSCAP Ø Safety is the state in which the risk of harm to persons or property damage is reduced to, and maintained at or below, an acceptable level through a continuing process of hazard identification and risk management. -3
Concept of safety (ICAO) COSCAP Ø Safety is the state in which the risk of harm to persons or property damage is reduced to, and maintained at or below, an acceptable level through a continuing process of hazard identification and risk management. -3
 Safety Traditional approach – Accident prevention COSCAP · · · Focus on outcomes (causes) Unsafe acts by operational personnel Attach blame/punish for failures to “perform safely” Address identified safety concern exclusively Identifies: WHEN? WHAT? WHO? ä But not always discloses: WHY? HOW? -4
Safety Traditional approach – Accident prevention COSCAP · · · Focus on outcomes (causes) Unsafe acts by operational personnel Attach blame/punish for failures to “perform safely” Address identified safety concern exclusively Identifies: WHEN? WHAT? WHO? ä But not always discloses: WHY? HOW? -4
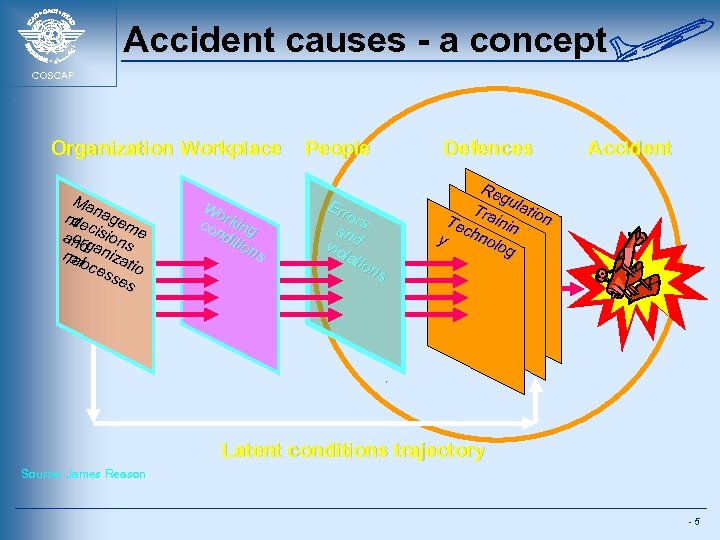 Accident causes - a concept COSCAP Organization Workplace Ma nde nage t c m or andg isions e nal aniza pro ces tio ses Wo co rking nd itio ns People Err ors an vio d lat ion s Defences Accident Re gu s Tra latio n Te g inin chn y olo g Latent conditions trajectory Source: James Reason -5
Accident causes - a concept COSCAP Organization Workplace Ma nde nage t c m or andg isions e nal aniza pro ces tio ses Wo co rking nd itio ns People Err ors an vio d lat ion s Defences Accident Re gu s Tra latio n Te g inin chn y olo g Latent conditions trajectory Source: James Reason -5
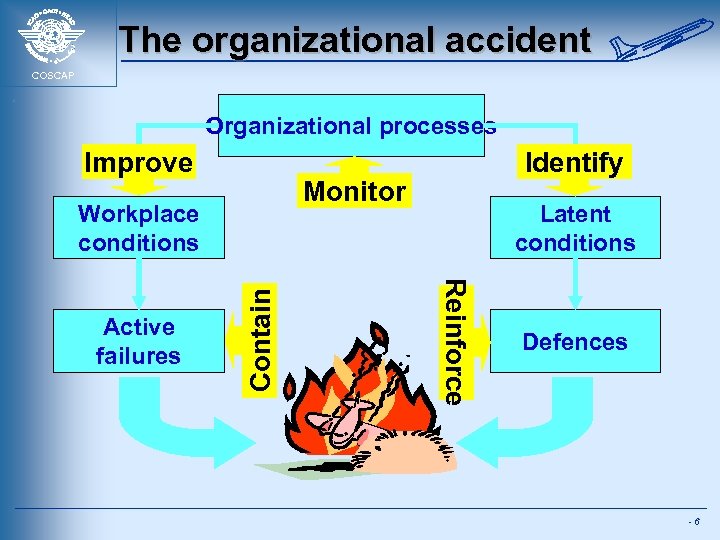 The organizational accident COSCAP Organizational processes Improve Monitor Latent conditions Reinforce Contain Workplace conditions Active failures Identify Defences -6
The organizational accident COSCAP Organizational processes Improve Monitor Latent conditions Reinforce Contain Workplace conditions Active failures Identify Defences -6
 Management responsibilities COSCAP Management commitment and responsibility Ø Senior management must: · Develop the safety policy, signed by the accountable executive, in accordance to national and international standards and organizational priorities. · Communicate, with visible endorsement, the safety policy to all staff. § Provide necessary human and financial resources. -9
Management responsibilities COSCAP Management commitment and responsibility Ø Senior management must: · Develop the safety policy, signed by the accountable executive, in accordance to national and international standards and organizational priorities. · Communicate, with visible endorsement, the safety policy to all staff. § Provide necessary human and financial resources. -9
 Head of organization COSCAP Management commitment and responsibility Ø Accountable executive must have: · Full authority for human resources issues. · Authority for major financial issues. · Direct responsibility for the conduct of the organization’s affairs. · Final authority over operations under certificate. · Final responsibility for all safety issues. - 10
Head of organization COSCAP Management commitment and responsibility Ø Accountable executive must have: · Full authority for human resources issues. · Authority for major financial issues. · Direct responsibility for the conduct of the organization’s affairs. · Final authority over operations under certificate. · Final responsibility for all safety issues. - 10
 The safety stereotype COSCAP - 15
The safety stereotype COSCAP - 15
 Is it? COSCAP - 16
Is it? COSCAP - 16
 Really? COSCAP - 17
Really? COSCAP - 17
 Objective of an organization? COSCAP - 18
Objective of an organization? COSCAP - 18
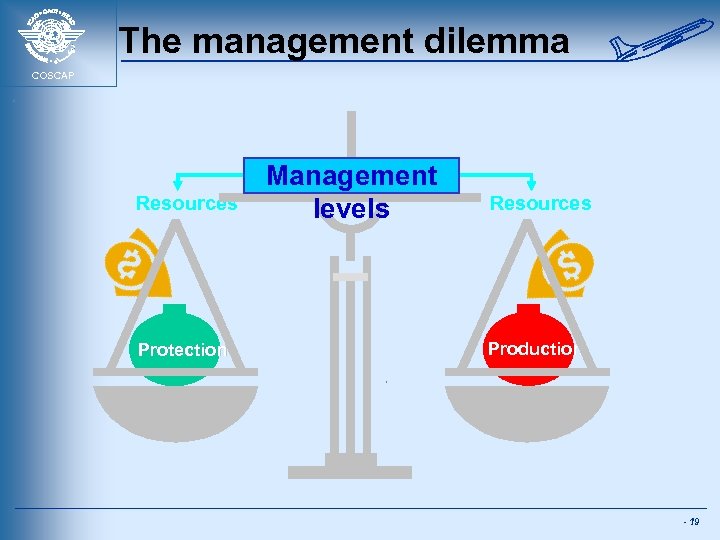 The management dilemma COSCAP Resources Protection Management levels Resources Production - 19
The management dilemma COSCAP Resources Protection Management levels Resources Production - 19
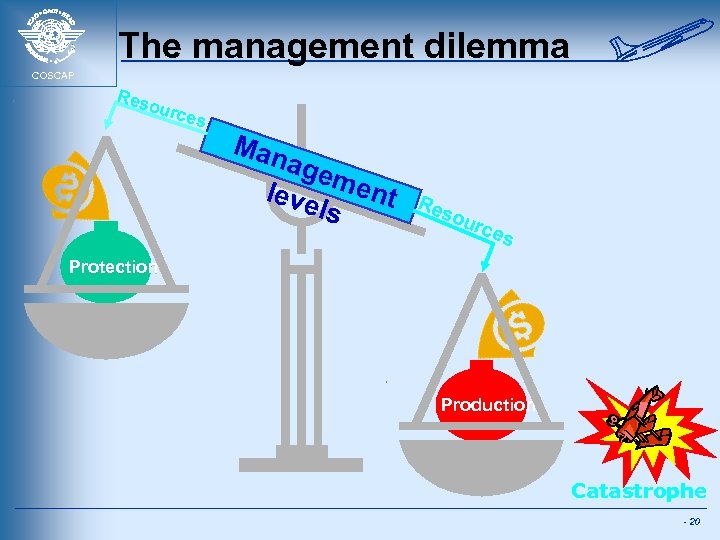 The management dilemma COSCAP Res ourc es Man age leve ment ls Res our c es Protection Production Catastrophe - 20
The management dilemma COSCAP Res ourc es Man age leve ment ls Res our c es Protection Production Catastrophe - 20
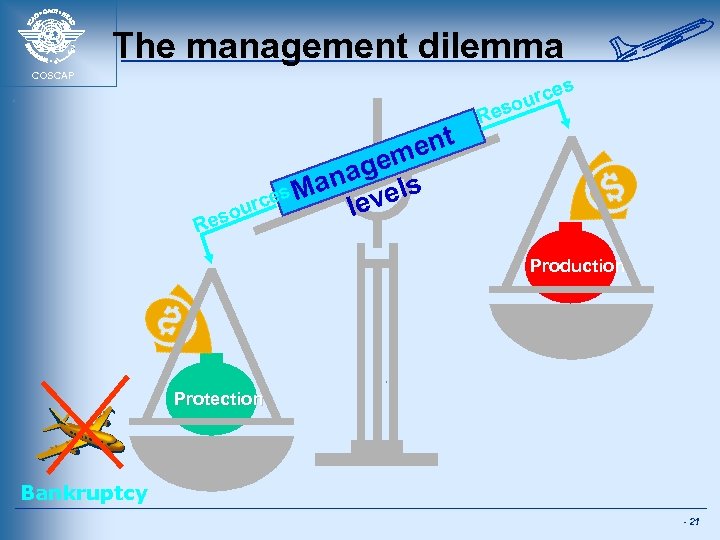 The management dilemma COSCAP es rc sou R ent gem ana els es M urc lev so e Re Production Protection Bankruptcy - 21
The management dilemma COSCAP es rc sou R ent gem ana els es M urc lev so e Re Production Protection Bankruptcy - 21
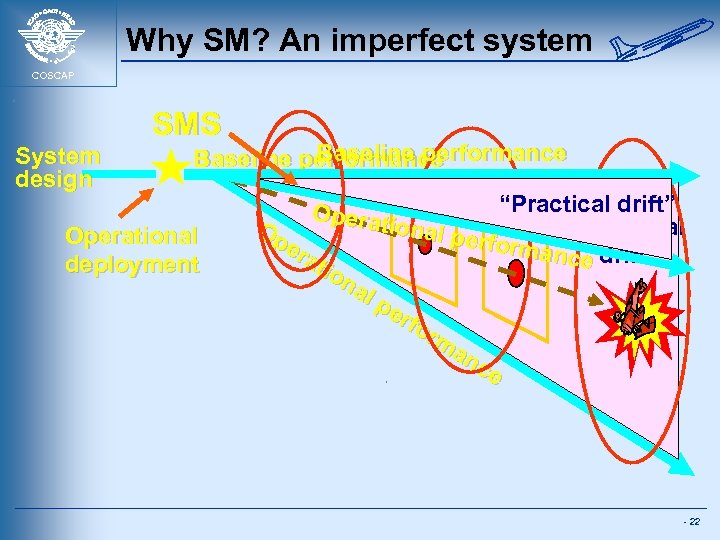 Why SM? An imperfect system COSCAP SMS System design Baseline performance Operational deployment “Practical drift” Opera tional “Practical Op perfor er mance drift” ati on al pe rfo rm an ce - 22
Why SM? An imperfect system COSCAP SMS System design Baseline performance Operational deployment “Practical drift” Opera tional “Practical Op perfor er mance drift” ati on al pe rfo rm an ce - 22
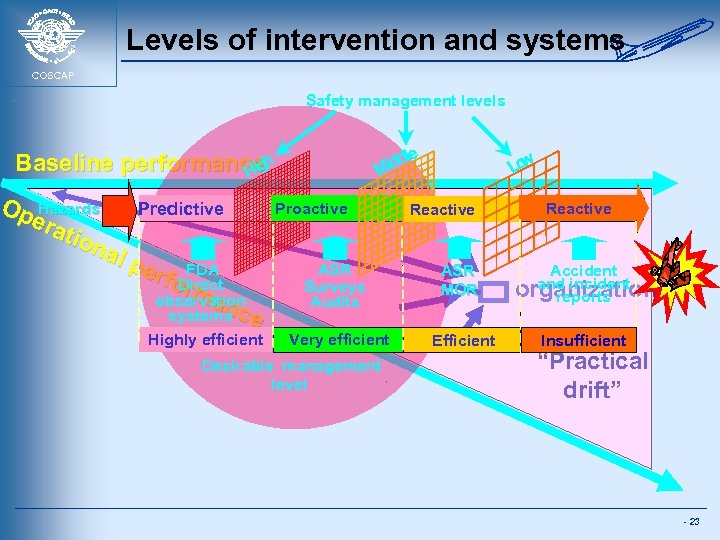 Levels of intervention and systems COSCAP Safety management levels e iddl M Baseline performanceh Hig Op Hazards Predictive era tion al p erf FDA o. Direct rm observation anc systems e Highly efficient Proactive ASR Surveys Audits Very efficient Desirable management level w Lo Reactive ASR MOR Accident and incident organization reports Efficient Insufficient “Practical drift” - 23
Levels of intervention and systems COSCAP Safety management levels e iddl M Baseline performanceh Hig Op Hazards Predictive era tion al p erf FDA o. Direct rm observation anc systems e Highly efficient Proactive ASR Surveys Audits Very efficient Desirable management level w Lo Reactive ASR MOR Accident and incident organization reports Efficient Insufficient “Practical drift” - 23
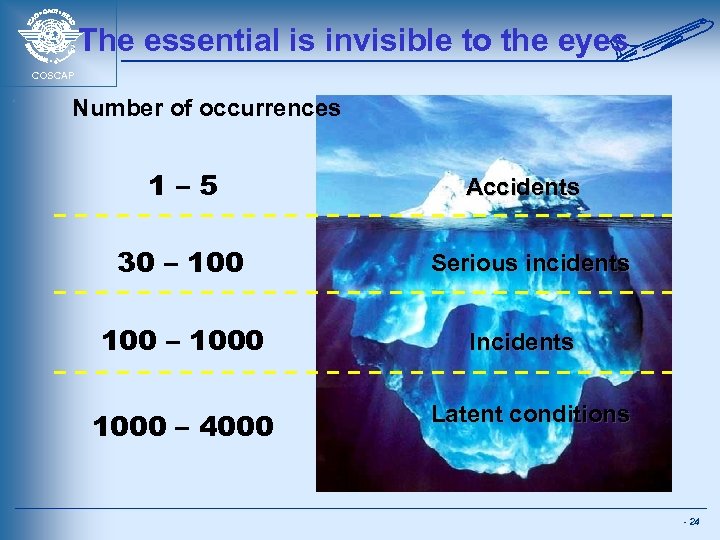 The essential is invisible to the eyes COSCAP Number of occurrences 1– 5 30 – 1000 – 4000 Accidents Serious incidents Incidents Latent conditions - 24
The essential is invisible to the eyes COSCAP Number of occurrences 1– 5 30 – 1000 – 4000 Accidents Serious incidents Incidents Latent conditions - 24
 One way forward COSCAP Ø Different perception · Safety management Ø A system approach · ICAO SMS framework Ø Building the system · Training · Responsibilities Ø Management process Ø Training - 25
One way forward COSCAP Ø Different perception · Safety management Ø A system approach · ICAO SMS framework Ø Building the system · Training · Responsibilities Ø Management process Ø Training - 25
 The changing of the guard COSCAP Ø Traditional – Accident/serious incident investigation · Aviation system – as pre-specified – is perfect. · Compliance based. · Outcome oriented. Ø Evolving – Safety management · Aviation system – as pre-specified – is imperfect. · Performance based. · Process oriented. - 26
The changing of the guard COSCAP Ø Traditional – Accident/serious incident investigation · Aviation system – as pre-specified – is perfect. · Compliance based. · Outcome oriented. Ø Evolving – Safety management · Aviation system – as pre-specified – is imperfect. · Performance based. · Process oriented. - 26
 ICAO SMS FRAMEWORK COSCAP Safety policy and objectives 1. 1 – Management commitment and responsibility 1. 2 – Safety accountabilities of managers 1. 3 – Appointment of key safety personnel 1. 4 – SMS implementation plan 1. 5 – Coordination of the emergency response plan 1. 6 – Documentation Safety risk management 2. 1 – Hazard identification processes 2. 2 – Risk assessment and mitigation processes 2. 3 – Internal safety investigations Safety assurance 3. 1 – Safety performance monitoring and measurement 3. 2 – The management of change 3. 3 – Continuous improvement of the safety system Safety promotion 4. 1 – Training and education 4. 2 – Safety communication - 27
ICAO SMS FRAMEWORK COSCAP Safety policy and objectives 1. 1 – Management commitment and responsibility 1. 2 – Safety accountabilities of managers 1. 3 – Appointment of key safety personnel 1. 4 – SMS implementation plan 1. 5 – Coordination of the emergency response plan 1. 6 – Documentation Safety risk management 2. 1 – Hazard identification processes 2. 2 – Risk assessment and mitigation processes 2. 3 – Internal safety investigations Safety assurance 3. 1 – Safety performance monitoring and measurement 3. 2 – The management of change 3. 3 – Continuous improvement of the safety system Safety promotion 4. 1 – Training and education 4. 2 – Safety communication - 27
 Responsibilities for managing safety COSCAP These responsibilities fall into four basic areas: Definition of policies and procedures regarding safety. Allocation of resources for safety management activities. Adoption of best industry practices. Incorporating regulations governing civil aviation safety. - 28
Responsibilities for managing safety COSCAP These responsibilities fall into four basic areas: Definition of policies and procedures regarding safety. Allocation of resources for safety management activities. Adoption of best industry practices. Incorporating regulations governing civil aviation safety. - 28
 State safety programme COSCAP Ø An integrated set of regulations and activities aimed at improving safety. Ø States are responsible for establishing a safety programme: · · · Safety regulation Safety oversight Accident/incident investigation Mandatory/voluntary reporting systems Safety data analysis Safety promotion - 29
State safety programme COSCAP Ø An integrated set of regulations and activities aimed at improving safety. Ø States are responsible for establishing a safety programme: · · · Safety regulation Safety oversight Accident/incident investigation Mandatory/voluntary reporting systems Safety data analysis Safety promotion - 29
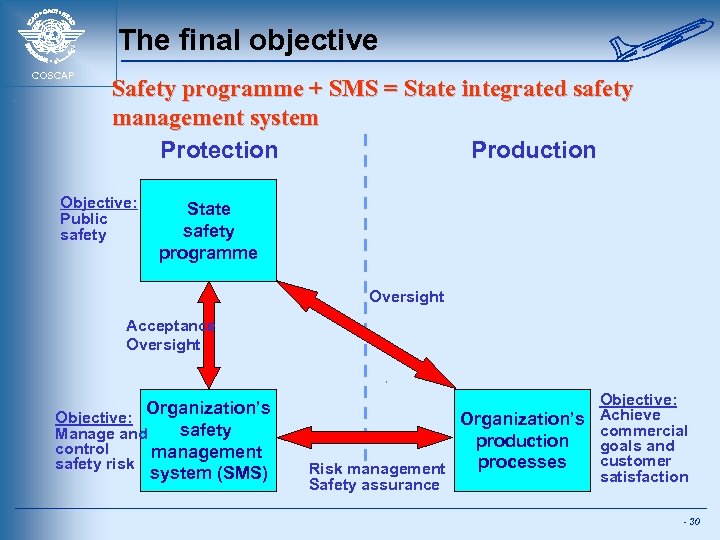 The final objective COSCAP Safety programme + SMS = State integrated safety management system Protection Production Objective: Public safety State safety programme Oversight Acceptance Oversight Organization’s Objective: safety Manage and control management safety risk system (SMS) Objective: Organization’s Achieve commercial production goals and customer processes Risk management satisfaction Safety assurance - 30
The final objective COSCAP Safety programme + SMS = State integrated safety management system Protection Production Objective: Public safety State safety programme Oversight Acceptance Oversight Organization’s Objective: safety Manage and control management safety risk system (SMS) Objective: Organization’s Achieve commercial production goals and customer processes Risk management satisfaction Safety assurance - 30
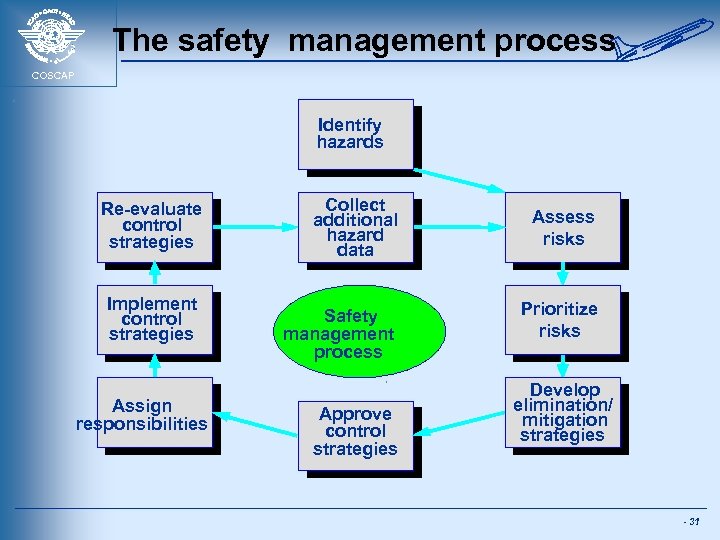 The safety management process COSCAP Identify hazards Re-evaluate control strategies Implement control strategies Assign responsibilities Collect additional hazard data Safety management process Approve control strategies Assess risks Prioritize risks Develop elimination/ mitigation strategies - 31
The safety management process COSCAP Identify hazards Re-evaluate control strategies Implement control strategies Assign responsibilities Collect additional hazard data Safety management process Approve control strategies Assess risks Prioritize risks Develop elimination/ mitigation strategies - 31
 ICAO contribution COSCAP Ø SMS SARPS Ø SMS Guidance Material · Safety Management Manual (SMM) § (DOC. 9859) Ø SMS training · Authorities · Lead SMS implementation · National training organizations § Train-the-trainers - 32
ICAO contribution COSCAP Ø SMS SARPS Ø SMS Guidance Material · Safety Management Manual (SMM) § (DOC. 9859) Ø SMS training · Authorities · Lead SMS implementation · National training organizations § Train-the-trainers - 32
 Course goals COSCAP Ø The goals of the ICAO Safety Management Systems (SMS) Course are to: · provide participants knowledge of safety management concepts and ICAO Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) on safety management in Annexes 6, 11 and 14, and related guidance material; and · develop participants’ knowledge to certify and oversee the implementation of key components of an SMS, in compliance with relevant ICAO SARPs. - 33
Course goals COSCAP Ø The goals of the ICAO Safety Management Systems (SMS) Course are to: · provide participants knowledge of safety management concepts and ICAO Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) on safety management in Annexes 6, 11 and 14, and related guidance material; and · develop participants’ knowledge to certify and oversee the implementation of key components of an SMS, in compliance with relevant ICAO SARPs. - 33
 Course contents COSCAP Ø Module 1 – SMS course introduction Ø Module 2 – Basic safety concepts Ø Module 3 – Introduction to safety management Ø Module 4 – Hazards Ø Module 5 – Risks Ø Module 6 – SMS regulation Ø Module 7 – Introduction to SMS Ø Module 8 – SMS planning Ø Module 9 – SMS operation Ø Module 10 – Phased approach to SMS Implementation - 34
Course contents COSCAP Ø Module 1 – SMS course introduction Ø Module 2 – Basic safety concepts Ø Module 3 – Introduction to safety management Ø Module 4 – Hazards Ø Module 5 – Risks Ø Module 6 – SMS regulation Ø Module 7 – Introduction to SMS Ø Module 8 – SMS planning Ø Module 9 – SMS operation Ø Module 10 – Phased approach to SMS Implementation - 34
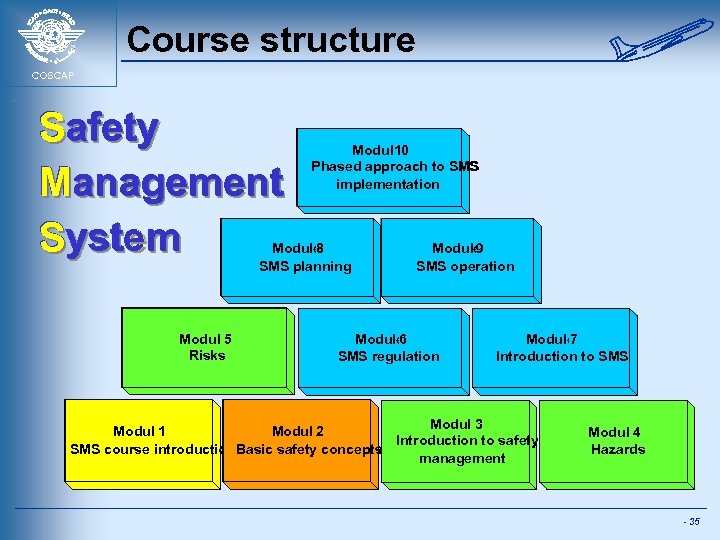 Course structure COSCAP Safety Management System Module 0 1 Phased approach to SMS implementation Module 8 SMS planning Module 5 Risks Module 9 SMS operation Module 6 SMS regulation Module 7 Introduction to SMS Module 3 Module 2 Module 1 Introduction to safety SMS course introduction. Basic safety concepts management Module 4 Hazards - 35
Course structure COSCAP Safety Management System Module 0 1 Phased approach to SMS implementation Module 8 SMS planning Module 5 Risks Module 9 SMS operation Module 6 SMS regulation Module 7 Introduction to SMS Module 3 Module 2 Module 1 Introduction to safety SMS course introduction. Basic safety concepts management Module 4 Hazards - 35
 Evaluation of participants COSCAP Ø Daily progress evaluation Ø A final evaluation test of one hour duration will be administered on the last day of the course. Ø The evaluation test includes twenty (20) questions of multiple choice answers. Ø Minimum pass mark: 70% - 36
Evaluation of participants COSCAP Ø Daily progress evaluation Ø A final evaluation test of one hour duration will be administered on the last day of the course. Ø The evaluation test includes twenty (20) questions of multiple choice answers. Ø Minimum pass mark: 70% - 36
 Why evaluation? COSCAP Ø The objective of the final evaluation test is to verify that participants have understood the basic principles of the planning, implementation and operation of safety management systems in order to be able to certify and oversee operators and service providers’ SMS according to ICAO requirements. - 37
Why evaluation? COSCAP Ø The objective of the final evaluation test is to verify that participants have understood the basic principles of the planning, implementation and operation of safety management systems in order to be able to certify and oversee operators and service providers’ SMS according to ICAO requirements. - 37
 If you are, ICAO is… COSCAP Ø Are you ready? Ø ICAO can assist · Guidance material · Training · Other support § § Direct indirect - 38
If you are, ICAO is… COSCAP Ø Are you ready? Ø ICAO can assist · Guidance material · Training · Other support § § Direct indirect - 38
 International Civil Aviation Organization SAFETY MANAGEMENT An introduction to safety management systems (SMS) St-Petersburg 12 – 13 December 2006
International Civil Aviation Organization SAFETY MANAGEMENT An introduction to safety management systems (SMS) St-Petersburg 12 – 13 December 2006


