23120841a381e813c3669591087221fd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

International Business Environments & Operations 15 e, Global Edition Daniels ● Radebaugh ● Sullivan HSE International Business Some contents copyright © 2015 Pearson Education Ltd. 8 -1

Chapter 8 Markets for Foreign Exchange 8 -2

Learning Objectives p p p Learn the fundamentals of foreign exchange Identify the major characteristics of the foreignexchange market and how governments control the flow of currencies across national borders Describe how the foreign-exchange market works Examine the different institutions that deal in foreign exchange Understand why companies deal in foreign exchange 8 -3

Introduction Learning Objective: Learn the fundamentals of foreign exchange p Video: What is foreign exchange: 1: 47 min. https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=4 ca. Lz. G _Br 5 E p Video: How exchange rates work: 5 min. https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=u. WIm 4 -i. F 7 W 4 8 -4

What Is Foreign Exchange? p Foreign n money denominated in the currency of another nation or group of nations p Foreign n exchange market where foreign exchange transactions take place p Exchange n rate the price of a currency in another currency 8 -5
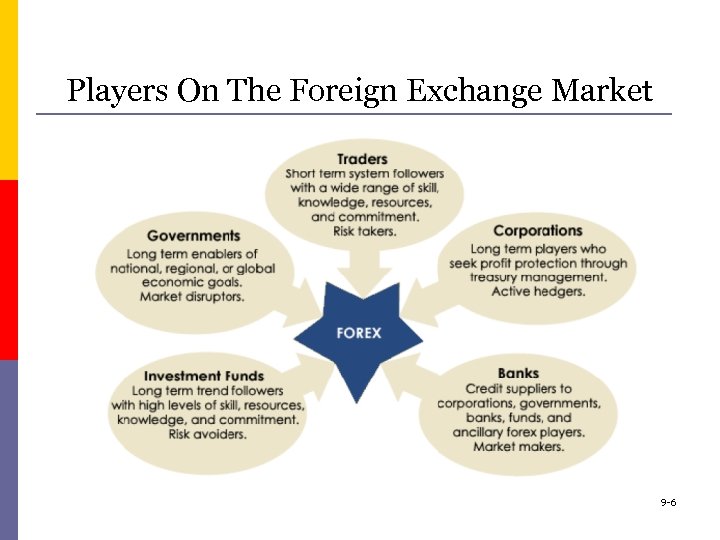
Players On The Foreign Exchange Market 9 -6

Players On The Foreign Exchange Market Learning Objective: Identify the major characteristics of the foreign-exchange market and how governments control the flow of currencies across national borders The foreign-exchange market: 2: 52 min. https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=qvr. RRTBYAk 8 -7

Players On The Foreign Exchange Market https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=G 4 KGp 2 a. Ht. GE p The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) divides the market into n Reporting dealers n Financial institutions n Nonfinancial institutions 8 -8
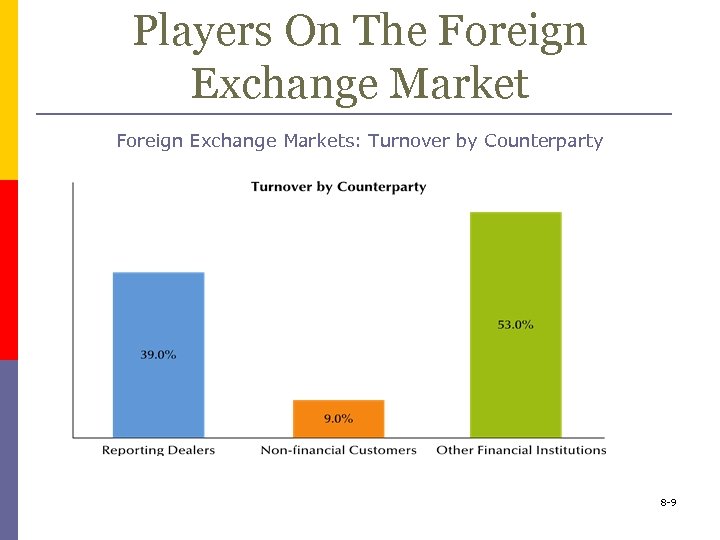
Players On The Foreign Exchange Markets: Turnover by Counterparty 8 -9

How To Trade Foreign Exchange Learning Objective: Describe how the foreign-exchange market works 8 -10

How To Trade Foreign Exchange p Dealers can trade foreign exchange n n Using electronic methods (41. 3%) Directly with customers (24. 3%) Through the interbank market (18. 5%) Through voice brokers (15. 9%) 8 -11

Some Aspects Of The Foreign Exchange Market p The foreign exchange market has two segments n n OTC commercial and investment banks Securities exchanges 8 -12

Global OTC Foreign Exchange Instruments p Global OTC foreign exchange instruments include n n n Spot transactions Outright forward transactions FX swap Currency swaps Options Futures contracts 8 -13
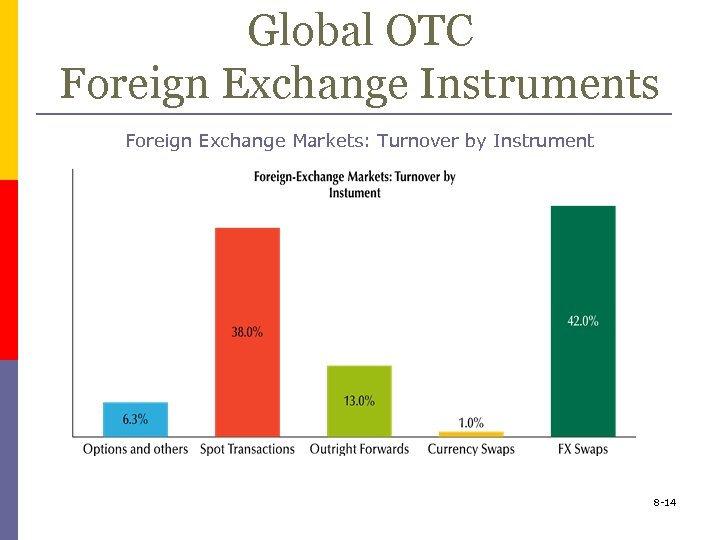
Global OTC Foreign Exchange Instruments Foreign Exchange Markets: Turnover by Instrument 8 -14

Size, Composition, and Location of the Foreign Exchange Market p Market size is $4 trillion daily n n p the U. S. dollar is the most important currency on the foreign-exchange market London is the main foreign exchange market in the world The most commonly traded currency pairs are EUR/USD and USD/JPY 8 -15
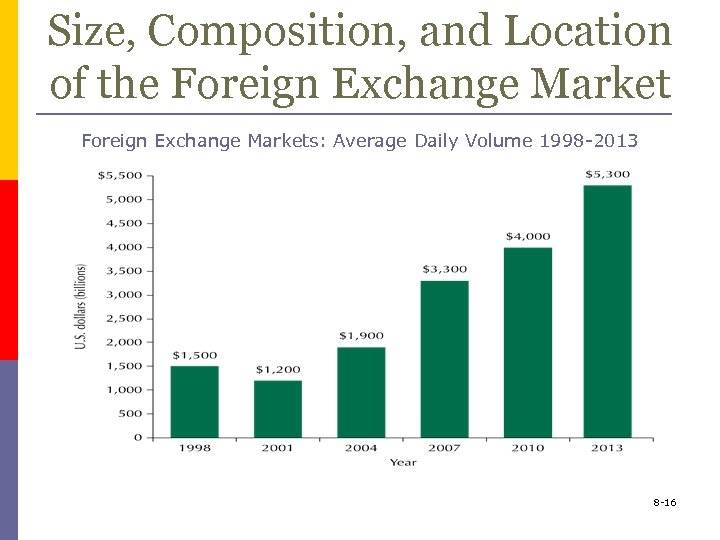
Size, Composition, and Location of the Foreign Exchange Markets: Average Daily Volume 1998 -2013 8 -16
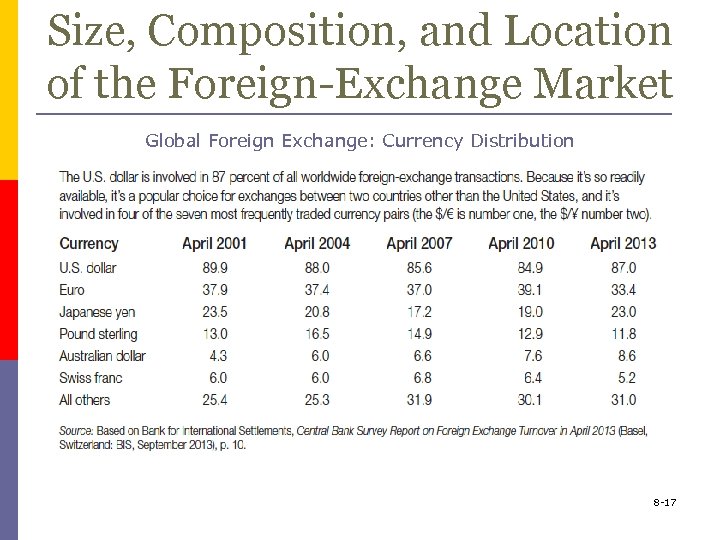
Size, Composition, and Location of the Foreign-Exchange Market Global Foreign Exchange: Currency Distribution 8 -17
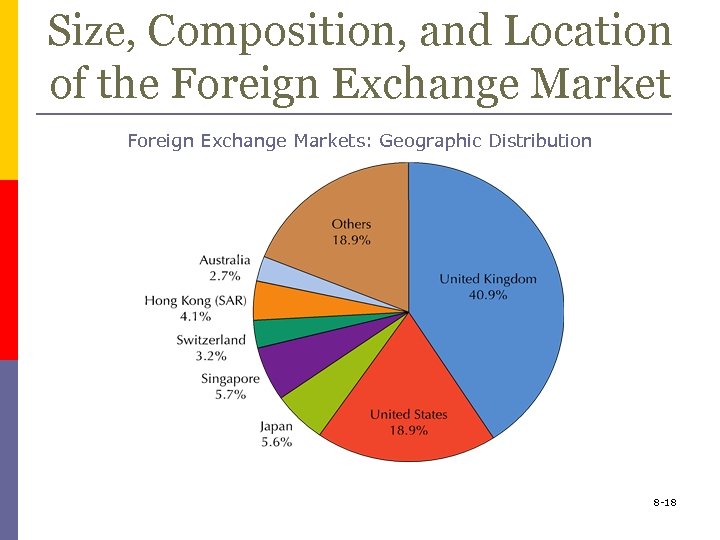
Size, Composition, and Location of the Foreign Exchange Markets: Geographic Distribution 8 -18

Major Foreign Exchange Markets p Foreign exchange dealers quote rates n n n Bid (buy) rate p the rate at which traders buy foreign exchange Offer (sell) rate p the rate at which traders sell foreign exchange Spread p the difference between bid and offer rates 8 -19

Major Foreign Exchange Markets p American terms (direct quote) n p the number of dollars per unit of foreign currency European terms (indirect quote) n the number of units of foreign currency per dollar Base currency p Terms currency p 8 -20

What is a 'Forward Market' • A forward market is an over-the-counter marketplace that sets the price of a financial instrument or asset for future delivery. • Forward markets are used for trading a range of instruments, but the term is primarily used with reference to the foreign exchange market. • It can also it can also apply to markets for securities and interest rates as well as commodities. 9 -21

Forward Market Details p p While forward contracts, like futures contracts, may be used for both hedging and speculation, there are some notable differences between the two. Forward contracts can be customized to fit a customer's requirements, while futures contracts have standardized features in terms of their contract size and maturity. Forwards are executed between banks or between a bank and a customer; futures are done on an exchange, which is a party to the transaction. The flexibility of forwards contributes to their attractiveness in the foreign exchange market. 9 -22

Details: 'Forward Market' p Pricing: Prices in the forward market are interestrate based. In the foreign exchange market, the forward price is derived from the interest rate differential between the two currencies, which is applied over the period from the transaction date to the settlement date of the contract. In interest rate forwards, the price is based on the yield curve to maturity. 9 -23

Details: 'Forward Market' p Foreign Exchange Forwards: Interbank forward foreign exchange markets are priced and executed as swaps. This means that currency A is purchased vs. currency B for delivery on the spot date at the spot rate in the market at the time the transaction is executed. At maturity, currency A is sold vs. currency B at the original spot rate plus or minus the forward points; this price is set when the swap is initiated. p The interbank market usually trades for straight dates, such as a week or a month from the spot date. Three- and six-month maturities are among the most common, while the market is less liquid beyond 12 months. Amounts are commonly $25 million or more and can range into the billions. 9 -24

Details: 'Forward Market' p p p Customers, both corporations and financial institutions such as hedge funds and mutual funds, can execute forwards with a bank counter-party either as a swap or an outright transaction. In an outright forward, currency A is bought vs. currency B for delivery on the maturity date, which can be any business day beyond the spot date. The price is again the spot rate plus or minus the forward points, but no money changes hands until the maturity date. Outright forwards are often for odd dates and amounts; they can be for any size. 9 -25

Details: 'Forward Market' p The most commonly traded currencies in the forward market are the same as on the spot market: EUR/USD, USD/JPY and GBP/USD. 9 -26

The Forward Market p Forward discounts n p Forward premiums n p when the forward rate is greater than the spot rate Option n p when the forward rate is less than the spot rate the right, but not the obligation, to trade a foreign currency at a specific exchange rate Futures n n specifies an exchange rate in advance of the actual exchange of currency not as flexible as a forward contract 8 -27
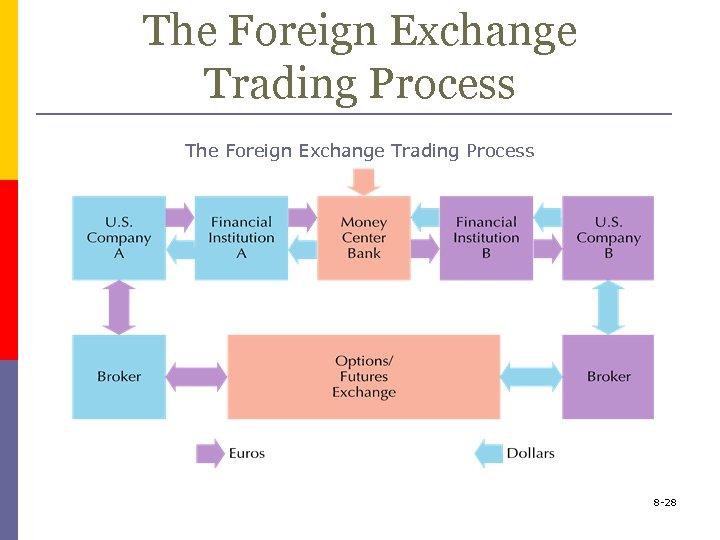
The Foreign Exchange Trading Process 8 -28

Banks And Exchanges p The top banks in the inter-bank market in foreign exchange can n n trade in specific market locations engage in major currencies and cross-trades deal in specific currencies handle derivatives p forwards, options, futures, swaps conduct key market research 8 -29
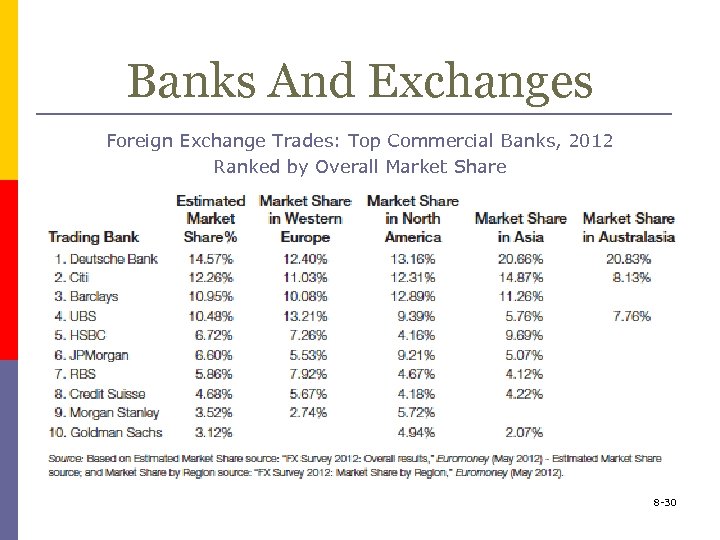
Banks And Exchanges Foreign Exchange Trades: Top Commercial Banks, 2012 Ranked by Overall Market Share 8 -30

Top Exchanges For Trading Foreign Exchange p Three of the best-known exchanges are n n n the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) Group the NASDAQ OMX the NYSE Liffe 8 -31

How Companies Use Foreign Exchange Learning Objective: Understand why companies deal in foreign exchange 8 -32

How Companies Use Foreign Exchange p Import and export cash flow options n n Commercial bills of exchange p sight draft p time draft Letters of credit p confirmed letter of credit 8 -33

How Companies Use Foreign Exchange p Other financial flows for business n n Speculation p buying or selling of a foreign currency that has an element of risk and a chance of great profits Arbitrage p the buying and selling of foreign currencies at a profit due to price discrepancies § interest arbitrage 8 -34
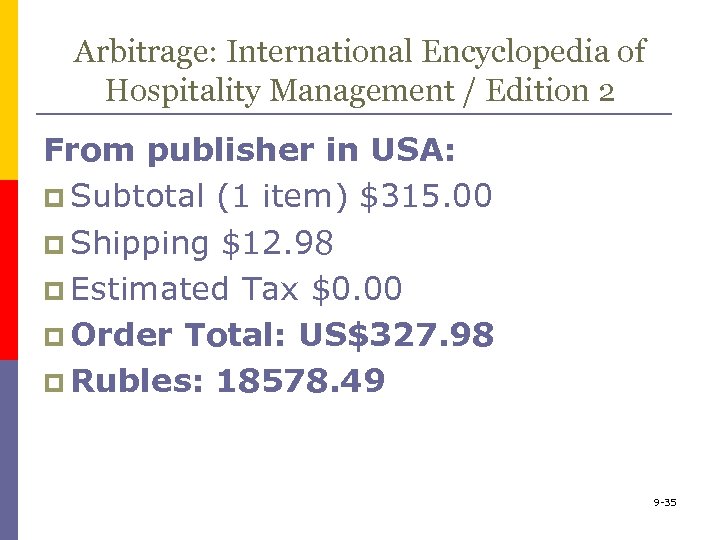
Arbitrage: International Encyclopedia of Hospitality Management / Edition 2 From publisher in USA: p Subtotal (1 item) $315. 00 p Shipping $12. 98 p Estimated Tax $0. 00 p Order Total: US$327. 98 p Rubles: 18578. 49 9 -35
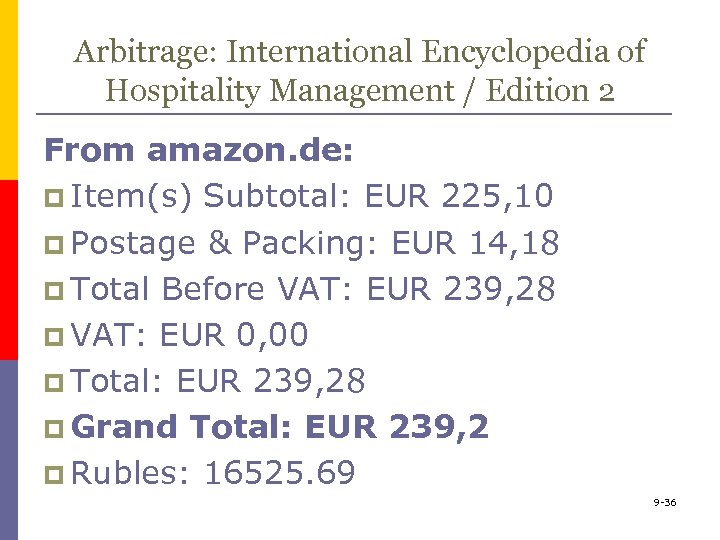
Arbitrage: International Encyclopedia of Hospitality Management / Edition 2 From amazon. de: p Item(s) Subtotal: EUR 225, 10 p Postage & Packing: EUR 14, 18 p Total Before VAT: EUR 239, 28 p VAT: EUR 0, 00 p Total: EUR 239, 28 p Grand Total: EUR 239, 2 p Rubles: 16525. 69 9 -36
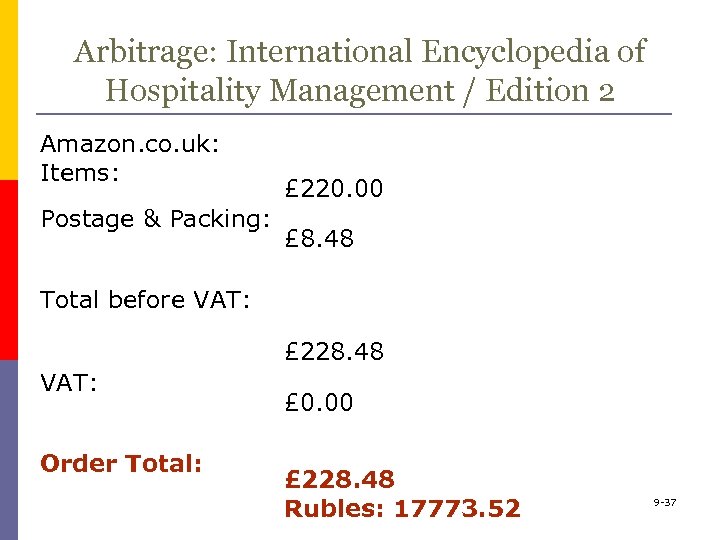
Arbitrage: International Encyclopedia of Hospitality Management / Edition 2 Amazon. co. uk: Items: Postage & Packing: £ 220. 00 £ 8. 48 Total before VAT: £ 228. 48 VAT: Order Total: £ 0. 00 £ 228. 48 Rubles: 17773. 52 9 -37

Arbitraging purchase price: U. S. PUBLISHER: p US$327. 98 p Rubles: 18578. 49 AMAZON. DE p EUR 239, 2 p Rubles: 16525. 69 AMAZON. CO. UK: p £ 228. 48 p Rubles: 17773. 52 9 -38

BMW foreign exchange management p FT case study. 9 -39

Where Are Foreign Exchange Markets Headed? p p More efficient markets n create more opportunities foreign exchange trading n lower costs Frequent financial crises in Europe n future of the euro Rise of the Chinese yuan and Brazilian real Technology developments n more electronic trades 8 -40
23120841a381e813c3669591087221fd.ppt