c12dc3f05906f5f8fe24b2c965808889.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

International Business Environments & Operations 15 e Daniels ● Radebaugh ● Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Sullivan 14 -1

Chapter 14 Export and Import Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -2

Learning Objectives p p p Understand the role of export/import in the strategy of the multinationals Learn about export/import process and the documentation involved Explain the idea of exporting/importing and evaluate their relative benefits/drawbacks Describe the intermediaries in export/importresources and assistance for international traders Identify and discuss the platforms that support expanding international trade Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -3
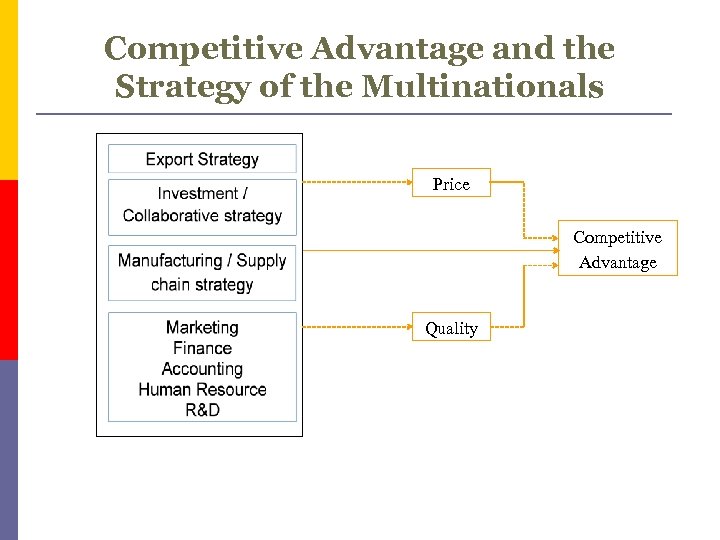
Competitive Advantage and the Strategy of the Multinationals Price Competitive Advantage Quality

Export Strategy of the Firm-1 p p Exporting and importing are the most common modes of international business; and, one of the fastest growing activities in the world Why Export…. n Profitability-increase revenues n Productivity-achieve economies of scale, alleviate excess capacity n Diversification-minimize risk and diversify markets 5

Export Strategy of the Firm-2 Firms’ “entry strategy/mode” is influenced by p p p Ownership advantages n the firm’s core competencies Location advantages n the combination of sales opportunity and investment risk that creates favorable locations in foreign markets Internalization advantages n reflect companies’ response to market imperfections that often create uncertainties Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -6

Exporters: Initiation and Development p Two approaches n Incremental internationalization p exporting is a learning process n Born global p instant internationalization p global focus Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -7
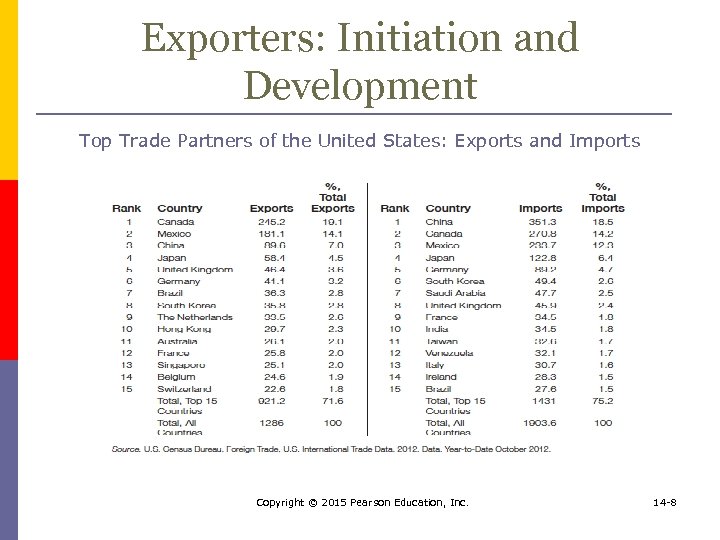
Exporters: Initiation and Development Top Trade Partners of the United States: Exports and Imports Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -8

Approaches to Exporting p Export approaches include n n Direct exporting p involves independent representatives, distributors, or retailers outside of the exporter’s home country Indirect exporting p products are sold to an intermediary in the domestic market, which then exports them Passively filling orders from domestic buyers who then export the product Selling to domestic buyers who represent foreign end users or customers Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -9
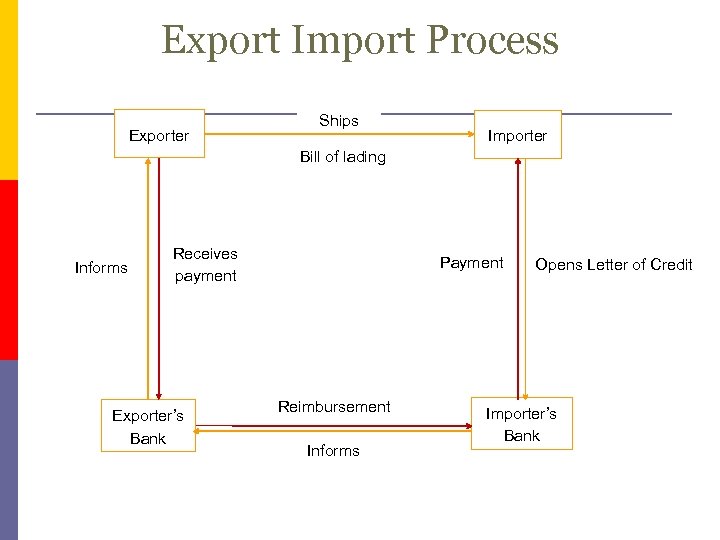
Export Import Process Exporter Ships Importer Bill of lading Receives payment Exporter’s Bank Payment Reimbursement Informs Opens Letter of Credit Informs Importer’s Bank

Types of Exports Documents p p p p Pro Forma Invoice: outlines the terms of sale, price, and delivery details, it is the basis for Commercial Invoice Shipper’s Export Declaration: used to monitor exports and compile trade statistics Bill of Lading: a detailed receipt from the carrier transporting the cargo Consular Invoice: required to monitor imports Certificate of Origin: determines the tariff Export Packing List: lists the cargo details Commercial Invoice: details of sale according to Pro Forma Invoice, it is legal document 11

Types of Exports Documents 12

Import Strategy of the Firm p Why import? Strategic advantages of import…. n n Specialization of labor Global rivalry Local unavailability Diversification of operation risks 13

Issues in Exporting/Importing Financial risks p Customer management p Lack of international business experience p Marketing challenges p Top management commitment p Government regulation p Trade documentation p Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -14

Support, Resources and Assistance p Companies can get support, resources and assistance from n Government agencies n The U. S. Department of Commerce International Trade Administration n The Small Business Administration Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -15

Support, Resources and Assistance Trade Assistance by Type and Source Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -16

Export/Import Intermediaries Export intermediaries: third party firms that market products and services abroad on behalf of manufacturers, farm groups, and distributors p Export management company (EMC) p Export trade companies (ETC) p Customs agents: enforce the rules of trade for a particular country p Customs brokers: help importers navigate the regulations imposed by customs agencies p Freight forwarders: the largest export/import intermediary in terms of value and weight of products shipped internationally p Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -17

An Export Plan Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -18

Countertrade p p Countertrade n different arrangements that parties use to trade products via transactions that use limited or no currency or credit n Examples of countertrade transactions…. p barter [based on clearing arrangements used to avoid money-based exchange] p buybacks, offsets, and counter purchase [all of which are used to impose reciprocal commitments] Costs and Benefits of Countertrade p Costs: inefficient, risky, cumbersome p Benefits: build mutually beneficial relationships Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -19

Types of Countertrade Common Types of Countertrade Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -20

Chapter 14: Discussion Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Explain why firms export or import. What are their competitive advantages for export or import? Describe the export-import process and explain the role of various “export documentation” involved in the process. Who are the export/import intermediaries? Explain their role and functions in the export-import process. What are the common issues in exporting/importing? Explain. What is countertrade? What are the different types of countertrade? Why firms or governments engage in countertrade? Explain. 21

All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher. Printed in the United States of America. Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 14 -22
c12dc3f05906f5f8fe24b2c965808889.ppt