35831e325a5ec0901e514562d6fbc7d8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

International Business Environments & Operations 15 e Daniels ● Radebaugh ● Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Sullivan 3 -1

Chapter 3 The Political and Legal Environments Facing Business Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -2

Learning Objectives p p p Discuss the philosophy and practices of the political environment Profile trends in contemporary political systems Describe current trends in political ideologies and their implications to MNE’s choices Explain political risk management Compare the relative benefits and drawbacks of proactive versus passive political risk management Discuss the principles and practices of the legal system Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -3

The Political Environment p p Every country has its own political and legal environment Companies must determine where, when, and how to adjust their business practices to succeed Managers evaluate, monitor, and forecast political environments A country’s political system refers to the structural dimensions and power dynamics of its government that specify institutions, organizations, and interest groups, and define the norms that govern political activities Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -4

Individualism vs. Collectivism p Our political system emanates from our philosophical belief or orientation, our thought process, how we want to govern ourselves Individualism: primacy of the rights and role of the individual p Collectivism: primacy of the rights and role of the community p Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -5

Political Ideology p p p Why should we study the political system or the political ideology of the ruling parties of a country? What are the implications for business? A political ideology stipulates how society ought to function and outlines the methods by which it will do so. It affects government spending, trade, and investment. Most modern societies are pluralistic n different groups champion competing political ideologies, examples: Democrats vs. Republicans in the United States Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -6

Spectrum Analysis A political spectrum outlines the various forms of political ideology p Political freedom measures p n n the degree to which fair and competitive elections occur the extent to which individual and group freedoms are guaranteed the legitimacy ascribed to the general rule of law the freedom expression Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -7
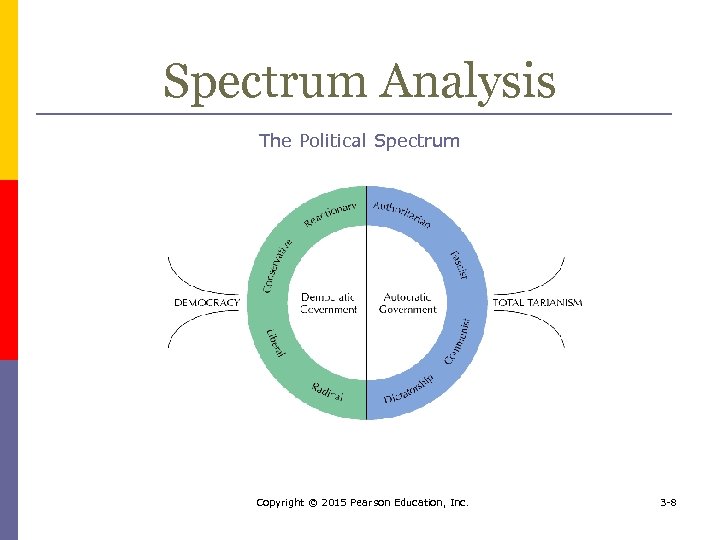
Spectrum Analysis The Political Spectrum Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -8

Democracy p In a democracy(a government “of the people, by the people and for the people”) n n n p all citizens are politically and legally equal all are equally entitled to freedom of thought, opinion, belief, speech, and association all equally command sovereign power over public officials Prominent types of democracy include n n Representative Multiparty Parliamentary Social Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -9

Modern History of Democracy p p p Before World War I After World War II n A decline in colonial empires n Rise of democratic nation states n Cold War Fall of Berlin Wall, 1989 -democratic governments/institutions are on the rise 1990 -2012 n Democracy in Latin America, Asia, Africa n Arab Spring Is democracy universal-Western vs. Eastern Models 10
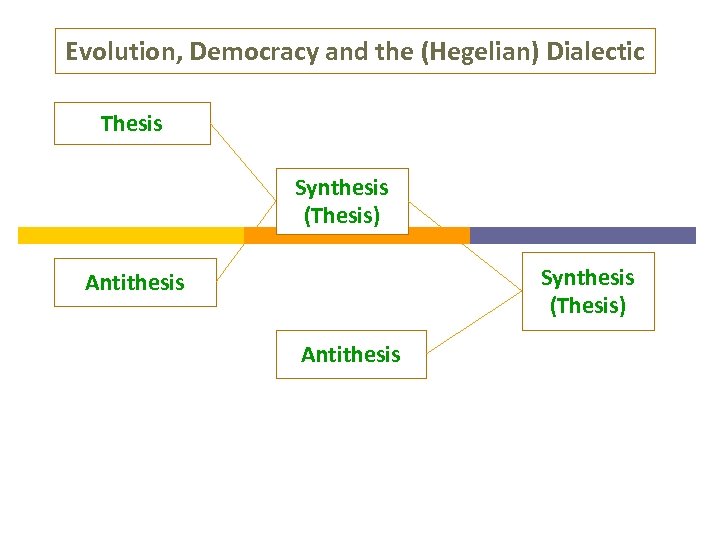
Evolution, Democracy and the (Hegelian) Dialectic Thesis Synthesis (Thesis) Antithesis
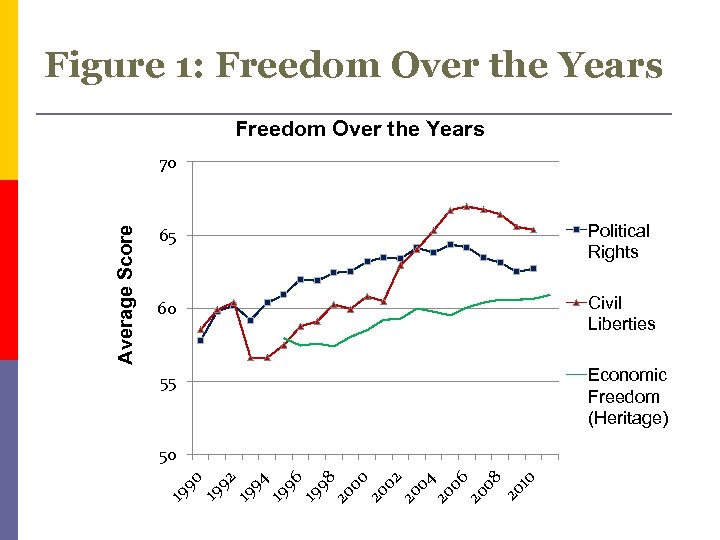
Figure 1: Freedom Over the Years 65 Political Rights 60 Civil Liberties 55 Economic Freedom (Heritage) 50 19 92 19 94 19 96 19 98 20 00 20 02 20 04 20 06 20 08 20 10 Average Score 70
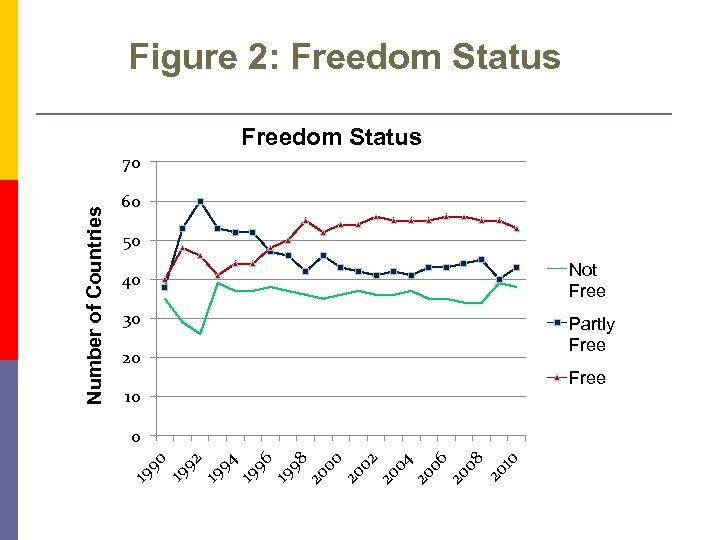
Figure 2: Freedom Status 60 50 40 Not Free 30 Partly Free 20 10 0 19 92 19 94 19 96 19 98 20 00 20 02 20 04 20 06 20 08 20 10 Number of Countries 70 Free
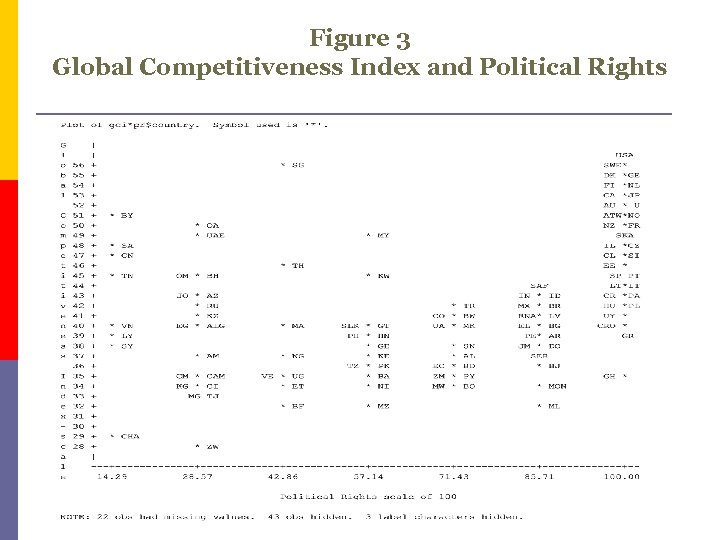
Figure 3 Global Competitiveness Index and Political Rights

Totalitarianism p p A totalitarian system subordinates the individual to the interests of the collective n monopolization of power by a single agent-opposition is neither recognized nor tolerated. n dissent is eliminated through indoctrination, persecution, surveillance, propaganda, censorship, and violence Prominent types of totalitarianism include n Authoritarianism n Fascism n Secular n Theocratic Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -15

The Standard of Freedom House, and independent watchdog organization, assesses political and civil freedom around the world p Freedom House recognizes three types of political systems p n n n Free Partly free Not free Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -16
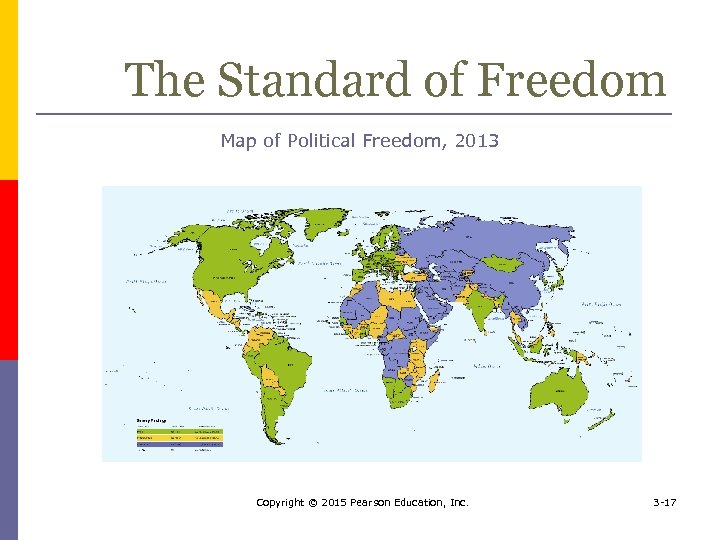
The Standard of Freedom Map of Political Freedom, 2013 Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -17

Third Wave of Democratization p Third Wave of Democratization n p number of democracies doubled in two decades Engines of Democracy 1. 2. 3. The failure of totalitarian regimes to deliver economic progress Improved communications technology Economic dividends of increasing political freedom Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -18

Democracy: Recession and Retreat p Democracy’s retreat n p just 26 of the world’s democracies are full democracies Engines of Authoritarianism n n Political economy of growth Rhetoric vs. Reality - Inconsistencies Economic problems Who defines Democracy? Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -19
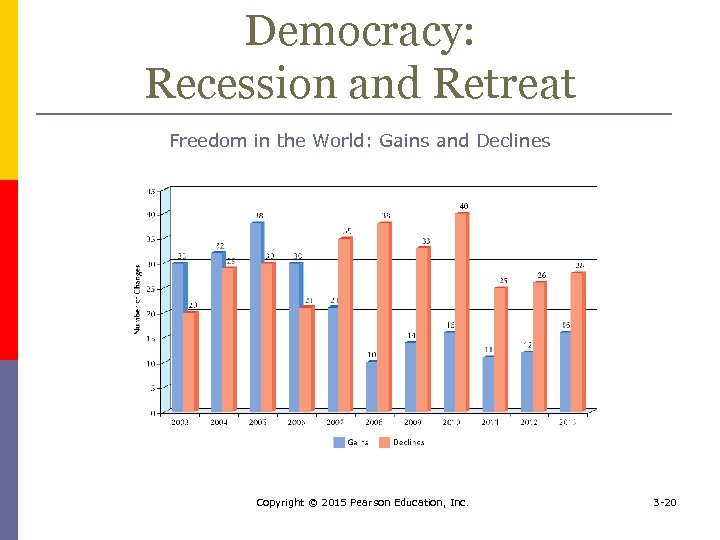
Democracy: Recession and Retreat Freedom in the World: Gains and Declines Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -20

Political Ideology and the MNE adapts to the political ideology of the country p What will the political map look like in the future? p n n n The Washington Consensus The Beijing Consensus The Clash of Civilizations Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -21

Political Risk Political risk refers to the risk that political decisions or events in a country negatively affect the profitability or sustainability of an investment p Types of Political Risk: Systemic, Procedural, Distributive, Catastrophic p Political Risk may involve Nationalization by the State (Confiscation, Expropriation, and Domestication) p Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -22
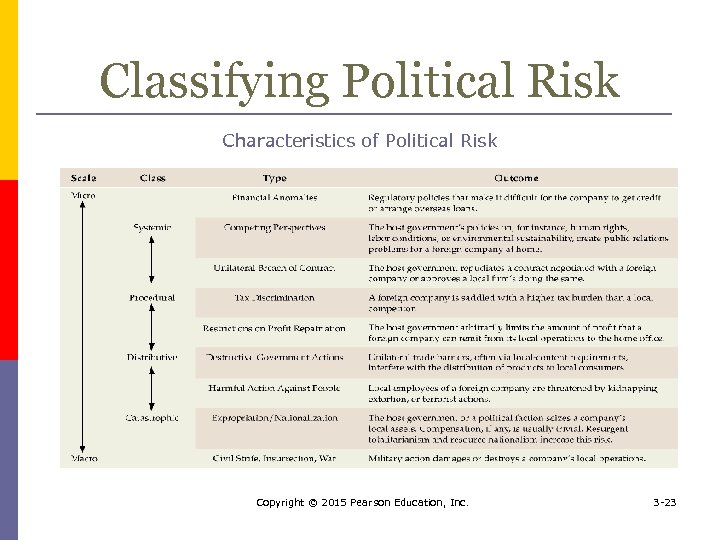
Classifying Political Risk Characteristics of Political Risk Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -23

Managing Political Risks Be a good corporate citizen (example: participate in development projects, literacy etc. ) p Expand power bases through business relationships (example: joint venture, licensing, political payoffs etc. ) p Study government attitude and participate government incentive programs p Maintain good relationship with political allies, other embassies in the country p 24

The Legal Environment The legal system is the mechanism for creating, interpreting, and enforcing the laws in a specified jurisdiction. p Types: p n n n Common law [based on precedent, traditions] Civil law [based upon a set of laws that comprise a code] Theocratic law [based upon religious precepts] Customary law [local customs and practices, example- indigenous societies] Mixed systems Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -25

The Legal Environment The Wide World of Legal Systems Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -26

Trends in Legal Systems p What is the basis of rule in a country? n n The rule of man p legal rights derive from the individual who commands the power to impose them p associated with a totalitarian system The rule of law p systematic and objective laws applied by public officials who are held accountable for their administration p associated with a democratic system Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -27

Trends in Legal Systems The Worldwide Practice of the Rule of Law Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -28

Implication for Managers p Operational concerns/issues n n n Starting a business Making and enforcing contracts Hiring and firing local workers Closing down the business Strategic concerns/issues n n Country Characteristics Product safety and liability Legal jurisdiction Intellectual property Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -29

Intellectual Property: Rights and Protection Intellectual property refers to creative ideas, expertise, or intangible insights that grant its owner a competitive advantage p Intellectual property rights refer to the right to control and derive the benefits from writing, inventions, processes, and identifiers p n no “global” patent, trademark or copyright exists Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -30

Intellectual Property: Rights and Protection p Attitudes towards intellectual property n n n Historical legacies p rule of man versus rule of law Economic circumstances p levels of economic development Cultural orientation p individualism versus collectivism Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -31

Chapter 3: Discussion Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Define political system and explain why a business manager should study the political system of a country. How does democracy differ from totalitarianism? Will the conduct of business be different in the two systems? How? Describe how the political ideologies are changing in the world. How a manager can adapt to such changes? What is political risk? How can we manage political risk? Define the Types Legal Systems and their implications in international business. 32

All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher. Printed in the United States of America. Copyright © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 -33
35831e325a5ec0901e514562d6fbc7d8.ppt