85ed991b39e1c75aa40268b846b91adf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

International Business 9 e By Charles W. L. Hill Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.

Chapter 12 The Global Capital Market

Why Do We Have Capital Markets? Ø Capital markets bring together investors and borrowers Ø investors - corporations with surplus cash, individuals, and non-bank financial institutions Ø borrowers - individuals, companies, and governments Ø markets makers - the financial service companies that connect investors and borrowers, either directly (investment banks) or indirectly (commercial banks) Ø capital market loans can be equity or debt 12 -3
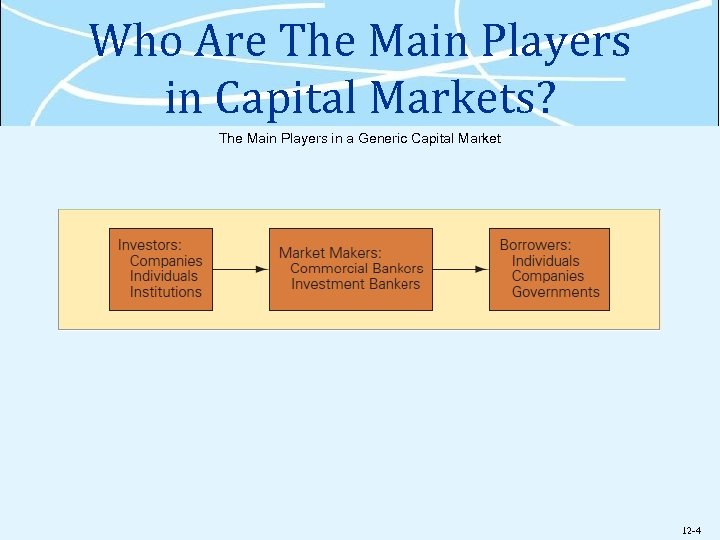
Who Are The Main Players in Capital Markets? The Main Players in a Generic Capital Market 12 -4

What Makes The Global Capital Market Attractive? Ø Today’s capital markets are highly interconnected and facilitate the free flow of money around the world Ø Borrowers benefit from the additional supply of funds global capital markets provide Ølowers the cost of capital Øthe price of borrowing money or the rate of return that borrowers pay investors 12 -5
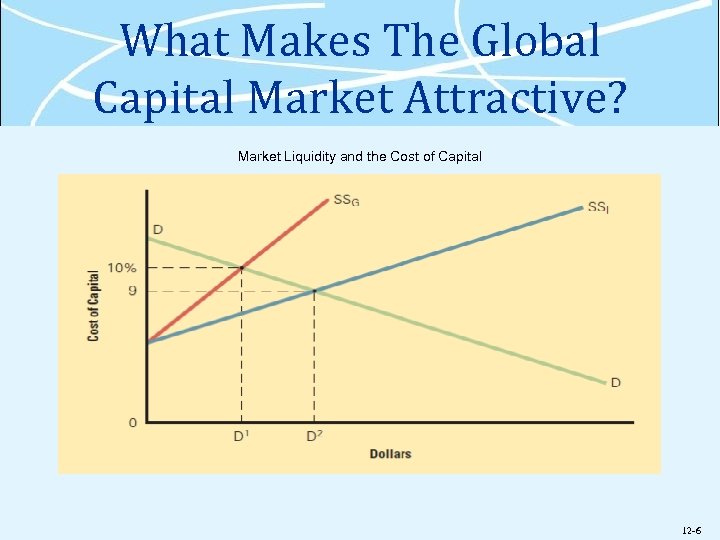
What Makes The Global Capital Market Attractive? Market Liquidity and the Cost of Capital 12 -6

What Makes The Global Capital Market Attractive? Ø Investors benefit from the wider range of investment opportunities Ødiversify portfolios and lower risk Ø But, volatile exchange rates can make what would otherwise be profitable investments, unprofitable 12 -7
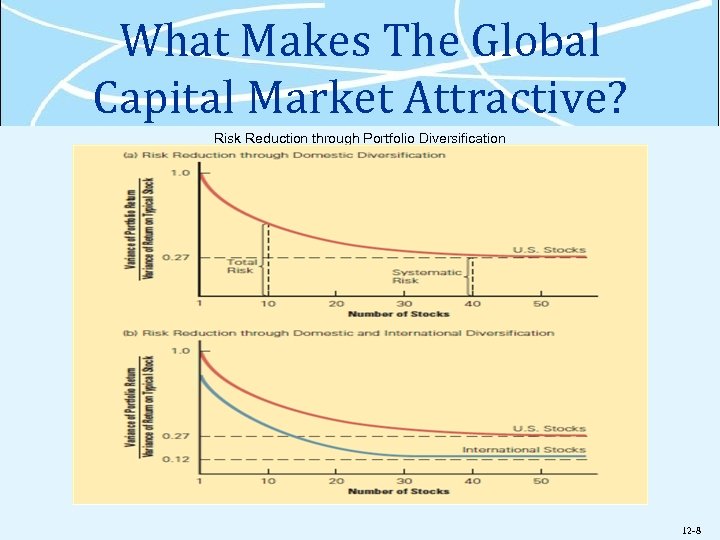
What Makes The Global Capital Market Attractive? Risk Reduction through Portfolio Diversification 12 -8

How Have Global Capital Markets Changed Since 1990? Ø Global capital markets have grown rapidly Øthe stock of cross-border bank loans was just $3, 600 billion in 1990, but $32, 430 in 2010 Øthe international bond market has grown from $3, 515 billion in 1997 to $26, 613 in 2010 Øinternational equity offerings were just $18 billion in 1990, but grew to $750 billion in 2009 12 -9

Why Is The Global Capital Market Growing? Ø Two factors are responsible for the growth of capital markets 1. Advances in information technology Ø the growth of international communications technology and advances in data processing capabilities Ø 24 -hour-day trading Ø so, shocks that occur in one financial market spread around the globe very quickly 12 -10

Why Is The Global Capital Market Growing? 2. Deregulation by governments Ø has facilitated growth in international capital markets Ø governments have traditionally limited foreign investment in domestic companies, and the amount of foreign investment citizens could make Ø since the 1980 s, these restrictions have been falling 12 -11

Why Is The Global Capital Market Growing? Ø deregulation began in the U. S. , then moved to Great Britain, Japan, and France Ø many countries have dismantled capital controls making it easier for both inward and outward investment to occur Ø The 2008 -2009 global financial crisis raised questions as to whether deregulation had gone too far Ø Question: Are new regulations for the financial services industry needed? 12 -12

What Are The Risks Of The Global Capital Markets? Ø Question: Could deregulation of capital markets and fewer controls on cross-border capital flows make nations more vulnerable to the effects of speculative capital flows? Ø can have a destabilizing effect on economies Ø Speculative capital flows may be the result of inaccurate information about investment opportunities Ø if global capital markets continue to grow, better quality information is likely to be available from financial intermediaries 12 -13

What Is A Eurocurrency? Ø A eurocurrency is any currency banked outside its country of origin Ø About two-thirds of all eurocurrencies are Eurodollars Ø dollars banked outside the U. S. Ø Other important eurocurrencies are the euro-yen, the euro-pound, and the euro-euro Ø The eurocurrency market is an important source of low-cost funds for international companies 12 -14

Why Has The Eurocurrency Market Grown? Ø The eurocurrency market began in the 1950 s when the Eastern bloc countries feared that the United States might seize their dollars Øso, they deposited them in Europe Øadditional dollar deposits came from Western European central banks and companies that exported to the U. S. Øcould earn a higher rate of interest in London 12 -15

Why Has The Eurocurrency Market Grown? Ø In 1957, the market surged again after changes in British laws Øunder the new laws, British banks had to attract dollar deposits and loan dollars rather pounds to finance non-British trade Ø London became the leading center of the eurocurrency market Øcontinues to hold this position today 12 -16

Why Has The Eurocurrency Market Grown? Ø In the 1960 s, the market grew once again Ø Changes in U. S. regulations discouraged U. S. banks from lending to non-U. S. residents Øwould-be borrowers of dollars outside the U. S. turned to the euromarket as a source of dollars 12 -17

Why Has The Eurocurrency Market Grown? Ø The next big increase came after the 197374 and 1979 -80 oil price increases Ø Arab members of OPEC accumulated huge amounts of dollars Øavoided potential confiscation of their dollars by the U. S. by depositing them in banks in London 12 -18

What Makes The Eurocurrency Market Attractive? Ø The eurocurrency market is attractive because it is not regulated by the government Øbanks can offer higher interest rates on eurocurrency deposits than on deposits made in the home currency Øbanks can charge lower interest rates to eurocurrency borrowers than to those who borrow the home currency 12 -19

What Makes The Eurocurrency Market Attractive? Ø The spread between the eurocurrency deposit and lending rates is less than the spread between the domestic deposit and lending rates Øgives eurocurrency banks a competitive edge over domestic banks 12 -20

What Makes The Eurocurrency Market Attractive? Interest Rate Spreads in Domestic and Eurocurrency Markets 12 -21

What Makes The Eurocurrency Market Unattractive? Ø The eurocurrency market has two significant drawbacks: 1. Because the eurocurrency market is unregulated, there is a higher risk that bank failure could cause depositors to lose funds Ø can avoid this risk by accepting a lower return on a home-country deposit 2. Companies borrowing eurocurrencies can be exposed to foreign exchange risk Ø can minimize this risk through forward market hedges 12 -22

What Is The Global Bond Market? Ø Bonds are an important means of financing for many companies Ø the most common bond is a fixed rate which gives investors fixed cash payoffs Ø The global bond market grew rapidly during the 1980 s and 1990 s and continues to grow today 12 -23

What Is The Global Bond Market? Ø There are two types of international bonds 1. Foreign bonds are sold outside the borrower’s country and are denominated in the currency of the country in which they are issued Ø used by companies when they think it will reduce the cost of capital 2. Eurobonds are underwritten by a syndicate of banks and placed in countries other than the one in whose currency the bond is denominated 12 -24

What Makes The Eurobond Market Attractive? Ø The eurobond market is attractive because 1. It lacks regulatory interference Ø since companies do not have to adhere to strict regulations, the cost of issuing bonds is lower 2. It has less stringent disclosure requirements than domestic bond markets Ø it can be cheaper and less time consuming to offer eurobonds than dollar-denominated bonds 3. It is more favorable from a tax perspective Ø eurobonds can be sold directly to foreign investors 12 -25

What Is The Global Equity Market? Ø The global equity market allows firms to 1. Attract capital from international investors Ø many investors buy foreign equities to diversify their portfolios 2. List their stock on multiple exchanges Ø this type of trend may result in an internationalization of corporate ownership 12 -26

What Is The Global Equity Market? 3. Raise funds by issuing debt or equity around the world Ø by issuing stock in other countries, firms open the door to raising capital in the foreign market Ø gives the firm the option of compensating local managers and employees with stock Ø provides for local ownership Ø increases visibility with local stakeholders 12 -27

How Do Exchange Rates Affect The Cost Of Capital? Ø Adverse exchange rates can increase the cost of foreign currency loans Ø While it may initially seem attractive to borrow foreign currencies, when exchange rate risk is factored in, that can change Ø firms can hedge their risk by entering into forward contracts Ø but this will also raise costs Ø Firms must weigh the benefits of a lower interest rate against the risk of an increase in the real cost of capital 12 -28

What Do Global Capital Markets Mean For Managers? Ø Growth in global capital markets has created opportunities for firms to borrow or invest internationally Øfirms can often borrow at a lower cost than in the domestic capital market Øfirms must balance the foreign exchange risk associated with borrowing in foreign currencies against the costs savings 12 -29

What Do Global Capital Markets Mean For Managers? Ø Growth in capital markets offers opportunities for firms, institutions, and individuals to diversify their investments and reduce risk Øagain though, investors must consider foreign exchange rate risk Ø Capital markets are likely to continue to integrate providing more opportunities for business 12 -30
85ed991b39e1c75aa40268b846b91adf.ppt